SRM-AP All News
ALL News
- PhD scholars attended the INUP-i2i Familiarisation Workshop at IIT Kharagpur August 18, 2022
 The Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) established the Indian Nanoelectronics User’s Programme (INUP) about a decade ago with the intention of improving skilled manpower in the areas of micro and nanoelectronics. This has laid the necessary foundation for the next step of the programme, INUP-i2i. It is a matter of pride that four PhD students from the Department of Chemistry attended the INUP-i2i Familiarisation Workshop on Nanofabrication and characterisations held from August 10 to 12, 2022, at IIT Kharagpur. Mr Syed Akhil, Mr Rahul SIngh, Mr Manoj Palabathuni, and Mr Subarna Biswas are the scholars who have grabbed this incredible opportunity.
The Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) established the Indian Nanoelectronics User’s Programme (INUP) about a decade ago with the intention of improving skilled manpower in the areas of micro and nanoelectronics. This has laid the necessary foundation for the next step of the programme, INUP-i2i. It is a matter of pride that four PhD students from the Department of Chemistry attended the INUP-i2i Familiarisation Workshop on Nanofabrication and characterisations held from August 10 to 12, 2022, at IIT Kharagpur. Mr Syed Akhil, Mr Rahul SIngh, Mr Manoj Palabathuni, and Mr Subarna Biswas are the scholars who have grabbed this incredible opportunity.Indian Nanoelectronics User’s Programme- Idea to Innovation (INUP-i2i) is developed to facilitate and support the generation of expertise in Nanoelectronics through participation and utilisation of the facilities at Nano-centres at IISc Bangalore, IIT Bombay, IIT Delhi, IIT Kharagpur, IIT Madras, and IIT Guwahati.
INUP will provide easy access to state-of-the-art nanofabrication and characterisation facilities to researchers, thereby creating a critical mass of hands-on experimental researchers across the country. This workshop is being organised both for familiarisation and interaction of the participants with faculty members of IITKGP. INUP has provided the accommodation and food for these shortlisted students. At the end of the workshop, they presented a poster as well.
Continue reading → - SRM University-AP celebrated 75 years of India’s Independence August 16, 2022

SRM University-AP celebrated the 75th Independence Anniversary of the nation in all its pomp and glory. As India has surpassed 75 years of independence and is propelling towards a glorious future of many more accomplishments, the nation was painted with the colours of courage, peace, and prosperity as part of the Har Ghar Tiranga campaign launched by the Prime Minister. In keeping with the vibe and vigour of freedom celebrations resonating all over the nation, the SRMAP NSS unit and the Department of Student Affairs visited houses in the nearby villages to promote the campaign.
The celebrations started off with the hoisting of the National Flag ceremony by the honourable Vice-Chancellor Prof VS Rao. He conveyed his Independence Day greetings to all and paid homage to all the brave warriors of our nation including Mahatma Gandhi, Subash Chandra Bose, Chandra Shekhar Azad, and all other known and unknown heroes of the land who lived, fought, and died for the nation.
Prof V S Rao also highlighted the role of Science & Technology in taking the country forward along the paths of sustainable and inclusive development. ”From green revolution and nuclear technology to our space missions, entrepreneurial evolution, and contribution to covid abatement, Science & Technology has effectively spread to every possible sector”, he remarked. He urged the student community to mould themselves up to be active collaborators in the process of nation-making. He also accentuated that SRM-AP is replete with opportunities for students to navigate their skills in all possible ways.
Students staged a colourful array of cultural programmes including songs and dance performances expressing their patriotic spirits. Prof VS Rao felicitated students who have brought laurels to the institute for their outstanding skills in various curricular and extra-curricular activities. Certificates were distributed to the participants of the Blood Donation camp. And the celebration came to a closure with the prize distribution ceremony to the winners of various games and sports events conducted on campus as part of the Azadi ka Amrit Mahotsav celebrations.
Continue reading → - Tummala Bhuvitha bags 3 gold in state-level rifle shooting August 12, 2022
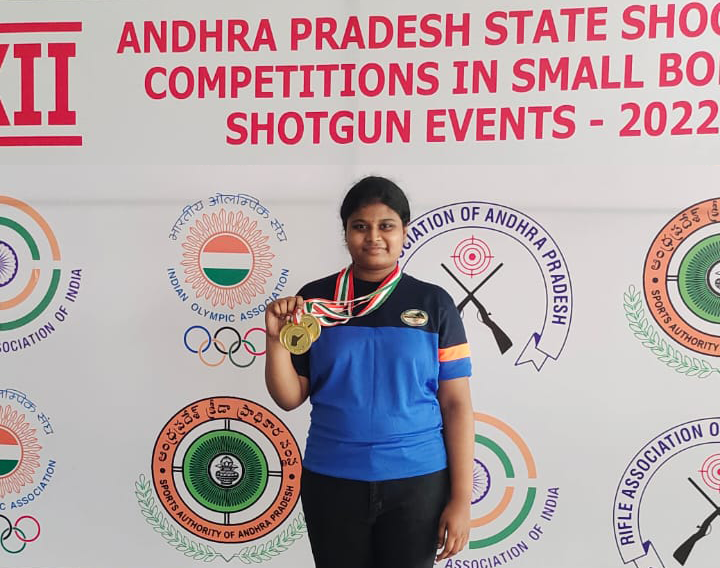

Tummala Bhuvitha, Computer Science Engineering student at SRM University-AP showed exceptional talent in the 22nd state-level rifle shooting competition organised at Hyderabad Central University under the aegis of the National Rifle Association of India. She won the first position and 3 gold medals in the 10m air rifle shooting competitions held in senior, junior and youth categories, respectively.
More than 100 shooters from Andhra Pradesh took part in the competition held from the 4th to 7th of this month. Participating in the competition from SRM AP, Bhuvitha stunned the organisers by winning three gold medals in a row. Bhuvitha had won gold medals twice in the past in state and national level rifle shooting competitions held in different places. According to her father, Bhuvitha learned shooting techniques from Subrahmanyeshwar Rao, the coach at the Indian Academy of Shooting Sports in Vijayawada.
“I grew passionate about rifle shooting because it is an individual sport that requires so much concentration and focus”, says Ms Bhuvitha while sharing the joy of her success. University President Dr P Satyanarayanan, Vice-Chancellor Prof V S Rao and Registrar Dr R Premkumar praised Bhuvitha for winning three gold medals consecutively in state-level competitions.
Continue reading → - Prediction of breakdown in disordered solids August 11, 2022
The Department of Physics is glad to announce that Assistant Professor Dr Soumyajyoti Biswas and his PhD scholar Ms Diksha have published their article “Prediction of imminent failure using supervised learning in a fiber bundle model” in the Q1 journal, Physical Review E. Prediction of breakdown in disordered solids under external loading is a question of paramount importance to the stability of buildings and bridges to earthquakes. The researchers used numerical simulations of a model of disordered solids and recorded the time series of the avalanche sizes and energy bursts. They propose that a systematic analysis of these time series using supervised machine learning can predict the time of failure. Interestingly, the most important feature for such predictions turns out to be the measures of how unequal the avalanche sizes are.
Applying external stress on disordered materials beyond their mechanical limits results in their fracture. Hence it is important to know the limit or how the material behaves as it approaches the limit and the factors that influence it. The failure properties of materials are very distinct from other properties such as elasticity, in the sense that their predictions are not always straightforward. Predicting the failure in driven disordered systems is a long-standing problem in physics, engineering, and earth sciences. So, for understanding the fracture process and predicting the failure properties of the materials, a mathematical model (fibre bundle model) has been used.
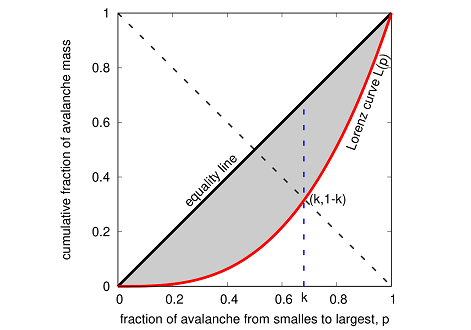
They introduced the disorder to the system and generated the time series of avalanche size and energy bursts. Some inequality indices i.e., Hirsch index (h), Gini index (g) and recently introduced Kolkata index (k) were measured for the response statistics of the driven systems. These social inequalities are usually represented by the Lorenz function L(p), where p fraction of the population (events) possesses L(p) fraction of total wealth (avalanche mass) when the population (avalanche events) are arranged in the ascending order of their wealth (size). Based on these time series, the machine learning algorithm can predict the prior failure time of the system. So, they have used a supervised machine learning algorithm (with the above-mentioned indices as some of the features) to predict the failure time of the model. They observed that these inequality measures play an important role in making predictions.
Prediction of imminent fracture has its implications in a wide range of disciplines, including stability of mechanical structures (buildings, aircraft, bridges etc.), extraction of oil (fracking) to the largest scale of mechanical failure i.e., earthquakes. Here a supervised machine learning approach is used to make such predictions in numerical models. However, with the important features identified here for such predictions, such research can carry out similar predictions for experimental data. A follow-up of this work is being carried out by Ms Diksha with a group in Spain regarding the experimental verification. Their future research plans include applications of the methods developed here to be applied to real-life physical structures for their stability analysis and predictions of impending catastrophes.
Illustration 1: A schematic diagram of the Lorenz function L(p)is shown, where L(p) denotes the cumulative fraction of the avalanche mass contained in the smallest p fraction of avalanches. If all avalanches were equal in size, this would be a diagonal straight line, called the equality line. The area between the equality line and the Lorenz curve (shaded area),therefore, is a measure of the inequality in the avalanche sizes. Two quantitative measures of such inequality are extracted from here, the ratio of the shaded area and that under the equality line (Gini index, g) and the crossing point of the opposite diagonal – from (0,1) to (1,0), shown in dashed line,and the Lorenz curve, giving the Kolkata index, k. 1 − k fraction of avalanches contain k fraction of the cumulative avalanche mass.
Continue reading → - Energy efficient MIMO-NOMA aided IoT network in B5G communications August 8, 2022

The Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering is glad to announce that Assistant Professor Dr Sunil Chinnadurai and his research scholar Mr Shaik Rajak have published a paper titled “Energy Efficient MIMO-NOMA aided IoT Network in B5G Communications” in the Q1 journal Computer Networks having an Impact Factor of 5.5. With an intent to accelerate the development of future intelligence wireless systems, the paper proposes an energy-efficient massive multiple-input-multiple-output (MIMO)- non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) aided internet of things (IoT) network to support the massive number of distributed users and IoT devices with seamless data transfer and connectivity.
Abstract of the research
Massive MIMO has been identified as a suitable technology to implement the energy efficient IoT network beyond 5G (B5G) communications due to its distinct characteristics with a large number of antennas. However, providing fast data transfer and maintaining hyperconnectivity between the IoT devices in B5G communications will bring the challenge of energy deficiency. Hence, they considered a massive MIMO-NOMA aided IoT network considering imperfect channel state information and practical power consumption at the transmitter. The far users of the base stations are selected to investigate the power consumption and quality of service. Then, they calculated the power consumption which is a non-convex function and non-deterministic polynomial problem. To solve the above problem, fractional programming properties are applied which converted the polynomial problem into the difference of convex function. And then they employed the successive convex approximation technique to represent the non-convex to convex function. Effective iterative-based branches and the reduced bound process are utilized to solve the problem. Numerical results observed that their implemented approach surpasses previous standard algorithms on the basis of convergence, energy efficiency, and user fairness.
Explanation of the research in layman’s terms
- A cost-effective (i.e., energy efficient) maximization problem for the multiple cells NOMA heterogeneous network scheme is explored when meeting the transmission power and data necessity of far users. The singular value uncertainty model (SVUM) is deliberated to add the errors with the transmitted signal. Since it’s a non-convex problem and challenging to solve, they used the properties of fractional programming to convert it into its corresponding mathematical terms. ITS needs higher data rate and seamless connectivity to operate with maximum speed and safety.
- SCA methods are then applied to change the optimisation problem. After that, an effective iterative scheme is employed based on Branch and Reduced Bound (BRB) that resolves the energy-efficient SVUM problem and satisfies the convergence criteria.
- The proposed iterative BRB method enhances user fairness and decreases inter-tier interference (ITI). IRS has been recognised as the key enabling technology to provide the data required by the ITS with less power consumption.
- Energy efficiency achieved by the proposed BRB method is examined with the help of numerical results and found that the proposed algorithm provides better efficacy than the majorisation minimisation (MM) method and the well-known OMA scheme.
Practical implementations of the research
- To provide high data rates to wireless sensors and the internet of things (IoT), future communication systems can ultimately be advanced by implementing NOMA, small cell, and heterogeneous networks (HetNets) along with MIMO.
- An energy-efficient massive MIMO-NOMA aided IoT network to support the massive number of distributed users and IoT devices with seamless data transfer and connectivity between them in B5G communications.
Future research plans
- To explore the energy efficiency of AI-driven IoT networks for applications such as intelligent health care and intelligent vehicular communications.
- MIMO-NOMA with IRS elements to reduce power consumption and improve the connectivity between the users.
- Indian Bank inks MoU with SRM University-AP to lend up to 50 Cr for start-ups August 8, 2022

Indian Bank has collaborated with Hatchlab Research Centre, TBI of SRM University-AP to launch ‘IND Spring Board’, an initiative for financing start-ups and MSMEs. The bank will extend loans of up to Rs. 50 crore to start-ups incubated at SRM Hatchlab for their working capital requirements or purchase of machinery and equipment. This collaboration is one of its kind in the state of Andhra Pradesh.
Introducing the ventures at Hatchlab Research Centre, which will be availing of the Ind Spring Board scheme, Mr Udayan Bakshi, Associate Director – Entrepreneurship, Department of Entrepreneurship and Innovation, highlighted the successful student ventures from SRM University-AP that has crossed 1Cr turnover. “SRM AP actively engage in business through the local community. This collaboration will further strengthen the MSME sector,” stated University Registrar Dr R Premkumar, signing the MoU.
Speaking on the occasion, Sri N K Sharma GM – MSME Indian Bank expressed his delight in collaborating with SRM University-AP along with other premier institutes like IITs and IIMs across the country. Sri C D Ramarao – Zonal Manager, Indian Bank, Guntur, described the genesis of the Ind Spring Board project and said Andhra Pradesh has a start-up-friendly ecosystem to nurture innovations.
Hatchlab Research Centre – the technology and livelihood business incubator of SRM University-AP facilitates the incubation of student startups. 10,000+ sq. ft., state-of-the-art incubator space and Seed Funding are provided to eligible student ventures. 40+ student startups, 200+ industry mentors, and $120,000 angel investment are peculiar to the conducive entrepreneurial environment of SRM University-AP. The alum entrepreneurial venture Oureye.ai received an additional investment of $50,0000. Integrating global vision and grassroots connect, the entrepreneurship-based clubs and activities like Socio Impacto, Explorer Hive, Saurvi, Research Clan, etc., are vital elements of SRM E-cell. The university further promotes student-run labs such as Next-Tech Lab and Ennovab, where students share their ideas to curate those into applications that benefit society.
Sri C Jagan Mohan Rao – Deputy Zonal Manager, Sri Raghavendra – Senior Manager, Sri Satya Dev-Branch Manager, Sri M S Sagar – Chief Manager and Jaya Prakash Narayana – Head of International Collaboration & PR – Hatchlab Research Centre were also present on the occasion.
Continue reading → - Charge transfer in photoexcited cesium lead halide perovskite nanocrystals August 8, 2022
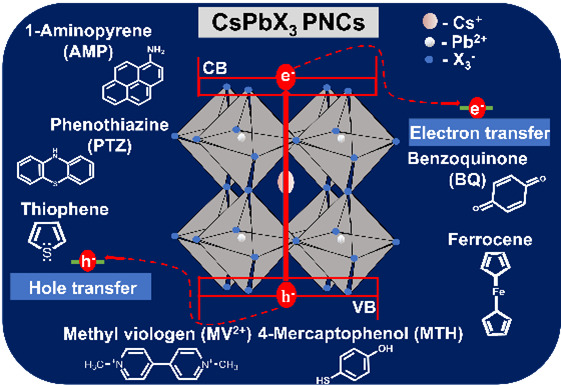
The Department of Chemistry is glad to announce that Assistant Professor Dr Nimai Mishra and his research group Manoj Palabathuni, Syed Akhil, and Rahul Singh have published an article titled “Charge Transfer in Photoexcited Cesium Lead Halide Perovskite Nanocrystals: Review of Materials and Applications” in the Q1 journal “ACS Applied Nano Materials ” published by The American Chemical Society. The journal has an Impact Factor of 6.14.
Cesium Lead Halide (CsPbX3) perovskite nanocrystals (PNCs) have attracted significant views from researchers due to their essential optoelectronic properties, especially long charge carrier transfer, high efficiency in visible light absorption, and long excited states lifetime, etc. Because of these properties, these materials exhibit outstanding charge transfer and charge separation, which enables them for solar cell applications. Recently, cesium lead halide perovskites have emerged as photocatalysts. In photovoltaics or photocatalysis, upon photoexcitation, the exciton dissociates, and the electron/hole is transmitted from the conduction/valance bands to the electron/hole acceptors. Therefore, it is essential to understand how the charge transfer occurs at the PNCs interface, which can help the researcher maximize the output in solar cells and photocatalytic efficiency.
In this article, Dr Mishra’s research group has outlined different charge transfer dynamics based on critical factors and discussed their optoelectronic properties. Electron/hole transfer dynamics are the most concerning characteristic; thus, they reviewed the relevant literature that reported efficient electron/hole transfer performance. In the end, they highlighted the recent development of the use of perovskite nanocrystal as photocatalyst in organic synthesis.
Continue reading → - Sustainable strategies for solid waste management August 5, 2022
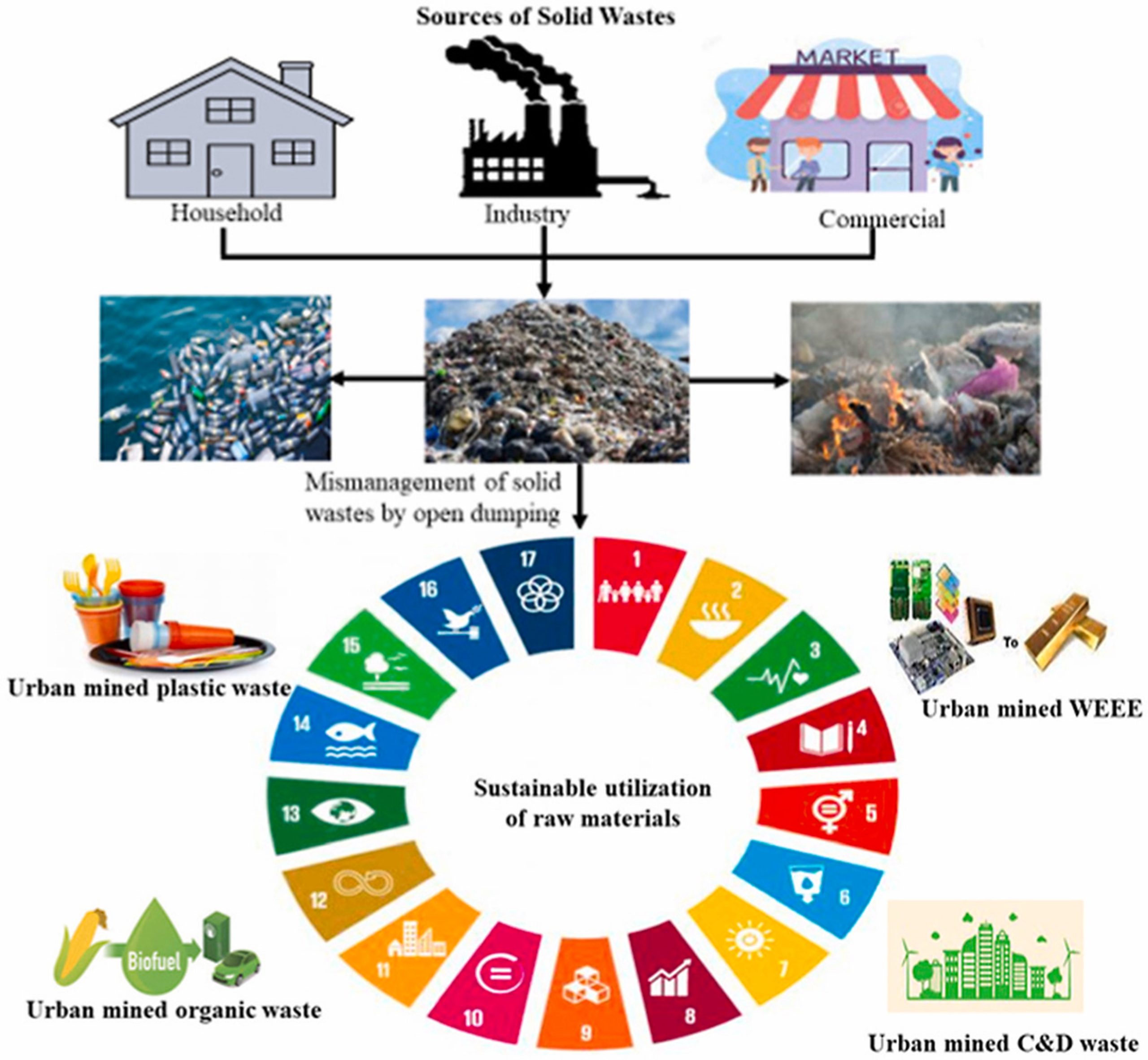 Dr Pankaj Pathak from the Department of Environmental Science has been keenly involved in research studies involving solid waste management and the effective conversion of wastes to energy. Her latest research publication Sustainable approach for valorization of solid wastes as a secondary resource through urban mining proposes an enhanced solution for the sustainable management of different types of solid wastes. It was published in the Journal of Environmental Management with an impact factor 8.98.
Dr Pankaj Pathak from the Department of Environmental Science has been keenly involved in research studies involving solid waste management and the effective conversion of wastes to energy. Her latest research publication Sustainable approach for valorization of solid wastes as a secondary resource through urban mining proposes an enhanced solution for the sustainable management of different types of solid wastes. It was published in the Journal of Environmental Management with an impact factor 8.98.In this paper, sustainable alternative valorisation techniques that aid in maximum recovery from waste materials, and associated challenges and limitations have been highlighted. These solid wastes mainly include construction and demolition wastes, organic food wastes, plastic, and WEEE (Waste electrical and electronic equipment) from various sources. In order to overcome these challenges, a sustainable circular model is recommended in this paper that will help minimise the negative environmental impacts, maximise the life cycle of material, reduce the consumption of fossil fuels, and thereby sustainably manage waste. Implementation of this recommendation can help in achieving the target of sustainable development goals (SDGs).
The article was published in collaboration with her PhD Scholar MSSR Tejaswini, and D.K. Gupta, Member Secretary in the Hazardous Substance Management Division in the Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change, New Delhi.
Abstract
The incessant population has increased the production and consumption of plastics, paper, metals, and organic materials, which are discarded as solid waste after their end of life. The accumulation of these wastes has created growing concerns all over the world. However, conventional methods of solid waste management i.e., direct combustion and landfilling have caused several negative impacts on the environment (releasing toxic chemicals and greenhouse gases, huge land use) besides affecting human health. Therefore, it is requisite to determine sustainable alternative technologies that not only help in mitigating environmental issues but also increase the economic value of the discarded solid wastes. This process is known as urban mining where waste is converted into secondary resources and thereby conserves the natural primary resources. Thus, this review highlights the technological advancements in the valorisation process of discarded wastes and their sustainable utilization. We also discussed several limitations of the existing urban mining processes and further the feasibility of valorisation techniques was critically analysed from a techno-economical perspective. This paper recommends a novel sustainable model based on the circular economy concept, where waste is urban mined and recovered as a secondary resource to support the united nations sustainable development goals (SDGs). The implementation of this model will ultimately help the developing countries to achieve the target of SDGs 11, 12, and 14.
- Dr Divya Chaturvedi to join as a special issue guest editor at Hindawi August 5, 2022

It is a matter of incredible honour to SRM University-AP, for Dr Divya Chaturvedi, Assistant Professor, Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering has been chosen as a special issue guest editor at Hindawi, one of the world’s largest publishers of peer-reviewed, fully open access journals of scientific, technical, and medical literature. Dr Divya has been keenly pursuing the umpteen possibilities of substrate integrated waveguide based cavity backed antennas, leaky wave antennas, wearable antennas for medical applications, and Multi-Input Multi-Output (MIMO) for 5G communication since the beginning of her career. And her research genius has bestowed her with numerous awards and recognitions over these years.
As a guest editor for Hindawi, Dr Divya would be responsible for the special issues “Substrate Integrated Waveguide (SIW) Based Circuits and Systems” and “The Future of Wireless Communications Systems: 5G and beyond” from the journals: International Journal of Antennas and Propagation and Journal of Computer Networks and Communications respectively. While the former aims to publish outstanding papers presenting cutting-edge advances in the field of microwave and millimetre-wave circuits and systems, the recent technological advancements in wireless communication systems will be focused in the latter.
Having served as the reviewer and member of various editorial boards and conferences, Dr Divya comes with a wealth of experience to put her expertise for the advancement of the publication. At Hindawi, she gets to work with a strong team of editors and network with like-minded colleagues around the world. ”It is truly fascinating to be a part of the Hindawi editorial board. The influential network that we build here could provide leads on professional opportunities or introduce us to new contacts in our discipline”, she remarked. This would also give her the liberty to handle manuscripts close to her professional interests and exert her creativity in the inception and development of a topic. The tenure of her role as an editor is expected to last for twelve months.
Continue reading → - A happy conclusion to the UTP Familiarisation Programme August 5, 2022
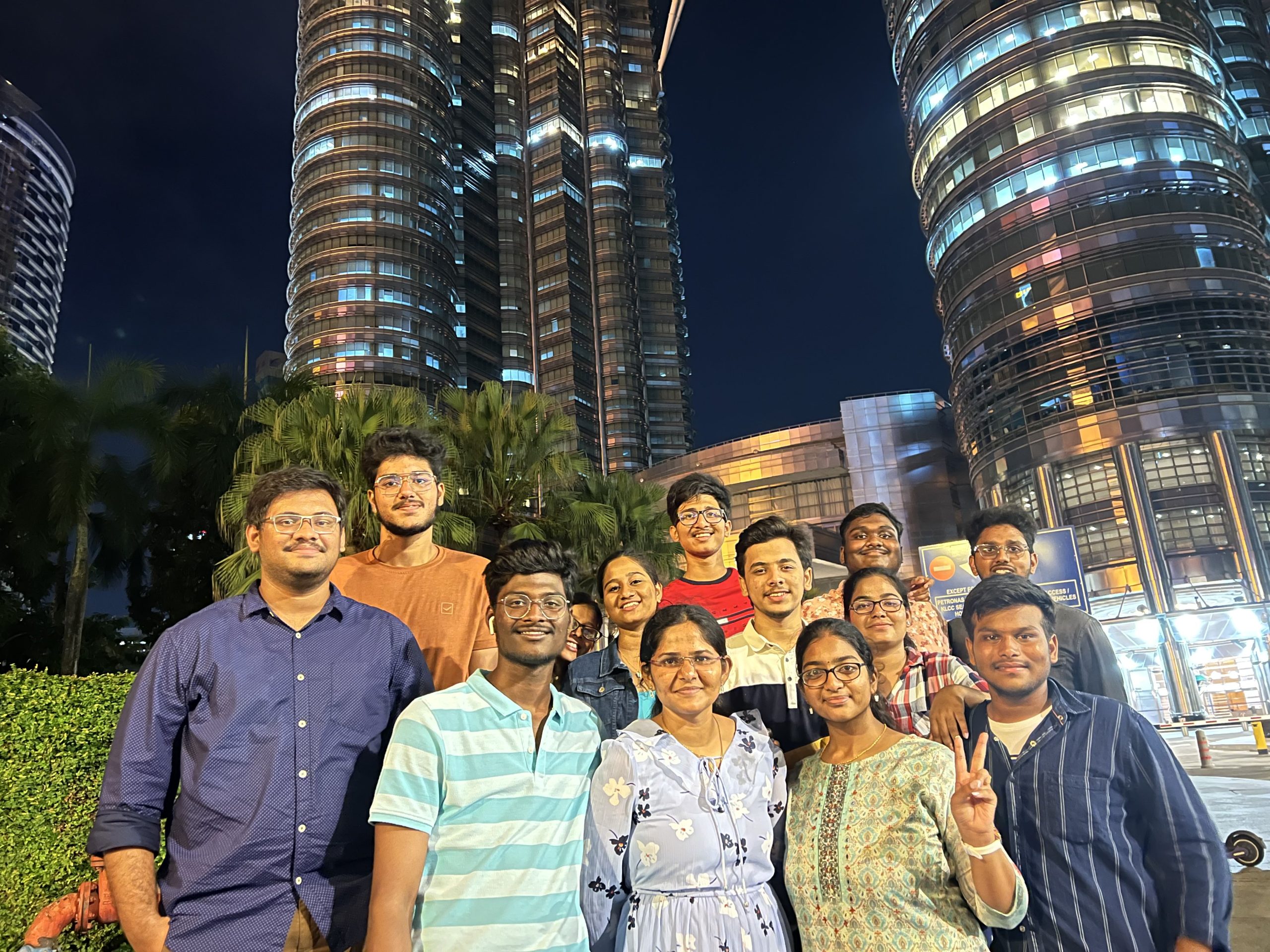

The UTP Familiarisation Programme was brought to a successful closure with the last batch of SRM University-AP students landing back from Malaysia. The familiarisation programme at Universiti Teknologi PETRONAS (UTP) Malaysia, was organised as part of Global Immersion facilitated by the Office of International Relations and Higher Studies at SRM AP. Students and faculty have participated in various on and off-campus programmes such as campus tours, training sessions, and cultural exchanges, organised as part of the programme that commenced in June 2022. The last batch of students was accompanied by Dr Uma Maheswar Arepalli on their educational trip to Kuala Lumpur and PETRONAS Twin Towers.
Several short courses centred on Data Analysis, Latex presentations, Finance and Economics for engineers were organised to acquaint students with the emerging engineering technologies. Students were also introduced to UTP’s facilities, programmes, research capabilities, and campus life. In the words of Shravani Vedantham, “The UTP Campus and its students were so welcoming that they made our journey an unforgettable experience”. While as far as Vishnu is concerned, the exposure to international teaching methodologies was the best part of the trip.
Students were also taken on study visits to cities such as Ipo and Penang to render them a brief cultural impression of the country. “The trip to Penang was my personal favourite. It is one of the best memories I have ever made”, exclaimed Payaswini. Other major highlights of the visits were Petrosains, the discovery centre, Batu Caves Temple, and KL Sentral. “The local tourist destinations, their architecture, culture, and street art were so mesmerising, and I am looking forward to more such experiences”, remarked Shravani. The UTP Centre for Student Development expressed its gratitude to SRMAP for being part of this global collaboration programme.
Continue reading →















