Recent News
- Patent on Controlling DC-DC Buck Power Converters January 30, 2025
 The patent titled “A System to Control Dc-Dc Buck Power Converter And A Method Thereof” by research scholar K Mounika Nagabushanam, and Assistant Professors, Dr Somesh Vinayak Tewari, and Dr Tarkeshwar Mahto with application no: 202441098288 presents an innovative approach to managing power conversion in renewable energy systems extending its applications in electric vehicles and microgrids, highlighting the importance of robust power control in advancing sustainable energy technologies.
The patent titled “A System to Control Dc-Dc Buck Power Converter And A Method Thereof” by research scholar K Mounika Nagabushanam, and Assistant Professors, Dr Somesh Vinayak Tewari, and Dr Tarkeshwar Mahto with application no: 202441098288 presents an innovative approach to managing power conversion in renewable energy systems extending its applications in electric vehicles and microgrids, highlighting the importance of robust power control in advancing sustainable energy technologies.Abstract
The work disclosed a system to control DC-DC buck power converter and a method thereof. The system comprises a photovoltaic (PV) panel, a first DC-DC buck converter for voltage step-down, and a battery for energy storage. A bidirectional DC-DC converter manages power flow between the battery and the source bus, while a second bidirectional converter exchanges power with the AC grid. The load bus integrates a second DC-DC buck converter to regulate power for constant power loads and resistive loads. Switching components like IGBTs controlled through PWM signals, ensure precise power control. Inductive and capacitive elements stabilize voltage, filter ripples, and reduce noise. The system supports adaptive power distribution and robust load handling, ensuring efficient energy management.
Explanation in layperson’s terms
Passivity-based control (PBC) is a control technique applied to buck converters within renewable energy systems to maintain stability and efficiency despite varying input conditions. Buck converters are essential for stepping down fluctuating voltage outputs from renewable sources, such as solar panels, to a consistent level suitable for storage or direct use. In solar power systems, PBC is used to manage the voltage conversion from solar panels to batteries or the grid. It stabilizes the voltage output, ensuring efficient battery charging and smooth integration with the electrical grid. PBC’s application in renewable energy systems demonstrates its critical role in advancing sustainable energy technologies, providing a reliable and efficient power supply.
Practical and Social Implications
The proposed control can be used in Electric Vehicle, Microgrid applications to stabilize voltage under load variations.
Future research plans
Future research plan is to work on the testing of proposed control with high level DC-DC converters
Continue reading →

- Establishing an Innovative Technology for Intelligent Management of Battery Systems January 28, 2025

Dr Satyavir Singh, Assistant Professor from the Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering and his PhD scholar, Mr Tasadeek Hassan Dar, have published a groundbreaking research paper titled “Advanced integration of bidirectional long short-term memory neural networks and innovative extended Kalman filter for state of charge estimation of lithium-ion battery.” The research that revolves around establishing technology for intelligent management of battery systems and their sustainability for longer life has been published in the Q1 journal, Journal of Power Sources, having an impact factor of 8.1.
Further to their research, the team will continue to work on robust techniques to BMS in the future.
Abstract
The state of charge (SoC) of a battery is a crucial monitoring indicator for battery management systems and it helps to assess how much further an electric vehicle can travel. This work proposes a novel approach for predicting battery SoC by developing a closed-loop system that integrates a bidirectional long short-term memory neural network with an innovative algorithm- extended Kalman filter. A second-order equivalent circuit model is selected, and its parameters are computed using the variational and logistic map cuckoo search approach.

Further, an Extended Kalman filter is combined with an innovation algorithm to update process noise in real-time, and a bidirectional long short-term memory neural network takes the input from the Extended Kalman filter and gives the compensated error value for the final SoC estimation. 75% of dynamic stress test data from the Extended Kalman filter is used for training purposes, remaining data sets are used for testing purposes. The addressed algorithm is validated by evaluating its performance in comparison to individual algorithms and various combined approaches. Empirical analysis demonstrates that the proposed model achieves a root mean square error of 0.11% and mean absolute error of 0.1% positioning it as a valuable tool for battery management systems.
Continue reading → - SRM AP Partners with Uniglobus Electrical and Electronics Pvt. Ltd. for EC-less LED Lighting Research January 24, 2025

In a significant stride towards advancing sustainable energy technologies, SRM University-AP has signed an Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with Uniglobus Electrical and Electronics Pvt. Ltd. The collaboration aims to develop cutting-edge EC-less LED lighting systems through a joint research initiative. The partnership was formalised following an exploratory visit by Uniglobus representatives, Mr Gajanan Inamdar and Mr Saurabh Maheta, to SRM AP. During their visit, they engaged in extensive discussions with the university faculty, identifying EC-less LED drivers as a promising area for impactful research.
Dr Ramanjaneya Reddy Udumula, Assistant Professor from the Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, will lead this innovative project as the Principal Investigator. Highlighting the significance of the collaboration, he noted, “This research initiative will address critical challenges in energy-efficient lighting while fostering a bridge between academic insights and industrial expertise.”
Uniglobus has also invited Dr Udumula to visit its state-of-the-art facilities to gain an in-depth understanding of their advanced product line. This visit underscores the mutual commitment to fostering a symbiotic relationship between academia and industry, paving the way for groundbreaking technological advancements.
Key figures instrumental in making this collaboration a reality include Vice Chancellor Prof. Manoj K. Arora, Prof. Ranjit Thapa, Dean of Research; Prof. Vinod Kumar G S, Associate Dean of the Technology Transfer Cell; and Prof. C.V. Tomy, Dean of the School of Engineering and Applied Sciences (SEAS). Their collective efforts, alongside the support of Mr BS Praveen from Uniglobus, have laid the foundation for this transformative partnership.
The project focuses on addressing critical global challenges associated with energy sustainability and efficiency. With the rapid industrial growth and increasing global population driving energy demand, the limitations of conventional energy sources have become a pressing concern. Governments and industry leaders worldwide are calling for innovative solutions to promote energy-saving and sustainable technologies.

A Game-Changing Innovation
The research aims to develop an Electrolytic Capacitor (EC)-less, ripple-free LED driver system. Unlike conventional LED drivers, this system employs a DC-DC converter as a power factor correction (PFC) unit and a bi-directional buck-boost converter (BDC) to eliminate second harmonic ripples. This configuration simplifies control mechanisms while ensuring high power factor and reduced total harmonic distortion, delivering a steady DC current to the LED load.
Towards a Sustainable Future
This collaboration marks a significant milestone in addressing sustainability challenges through innovation. By merging the academic expertise of SRM University-AP with the industrial insights of Uniglobus Electrical and Electronics Pvt. Ltd., the partnership seeks to deliver impactful solutions for a greener, more sustainable future.
The MoU underscores SRM University-AP’s commitment to fostering innovation through strategic collaborations, positioning the institution at the forefront of research and technological development in energy efficiency. Both partners look forward to a fruitful and enduring collaboration that promises to benefit society at large.
Continue reading → - Developing a High Gain Bi-directional Converter to Improve Efficacy in EV Applications December 23, 2024

Electronic Vehicles (EVs) are a key element of carbon emission reduction strategies and pivotal to contributing to sustainable development. Operating solely on electrical energy, eliminating the need for petrol or diesel, EVs leave a significantly reduced carbon footprint compared to fossil fuel-powered vehicles. Underscoring the impact of EVs on the environment, advanced research is conducted to improve the efficacy and reliability of EVs.
On this note, a research team from the Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering – Dr Tarkeshwar Mahto, Dr Somesh Vinayak Tewari, Dr Ramanjaneya Reddy and PhD scholar Ms K Mounika Nagabushanam has published a paper titled “High Gain Bi-directional KY converter for low power EV Applications” in the Q1 journal Energy having an Impact Factor of 9. Their research work focuses on the development of a bi-directional DC-DC converter that can be used in EVs for integration of battery to traction motor.
Abstract
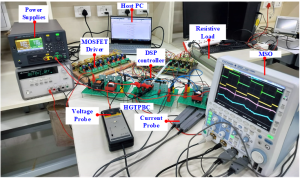
In electric vehicles (EVs), the type of electric motor and converter technology have a significant impact on regulating the operational characteristics of the vehicle. Therefore, in this work, the modified bi-directional KY converter (BKYC) is proposed for EV applications. The main contributions of the proposed converter are high step-up/step-down conversion gain, bi-directional power flow, simplified control structure, continuous current, common ground, low volume, and high efficiency. An inductor on either side of the converter ensures continuous current flow and passive components are arranged to operate in series to offer high step-up/step-down conversion. The charging and discharging operations, steady-state analysis, and design process of the proposed converter are discussed in detail and compared with similar bi-directional converter topologies. Further, the efficiency analysis of the proposed converter is presented, and it was found that the efficacy is 95.51% in the charging operation and 96.52% in the discharging operation. The simulations are carried out using MATLAB/Simulink environment. Further, a prototype of a modified bi-directional KY converter is implemented with a TMS320F28335 processor and validated with theoretical and simulation counterparts.
Explanation of the Research in Layperson’s Terms
Electric vehicles (EVs) are built with traction motors, charging circuits, energy storage devices, and lighting systems. Each runs at a different voltage and has a different power level. Various power electronic converters are used to integrate the individual components of an electric vehicle. An electric vehicle (EV) runs primarily on battery power, which can be obtained from on-board charging or charging stations. The battery has a voltage range of 24 to 48 volts. The traction motor, coupled to a DC link bus with a voltage range of 400V to 600V, needs to receive this energy. Consequently, it is necessary to integrate a power converter to raise the voltage from lower voltage batteries to a higher voltage DC link. Additionally, energy lost during motor running can be used to charge batteries to improve the efficiency of the electric vehicle. Therefore, a separate power electronic converter is required for the power flow from the motor to the battery. The primary output of our study is the development of a bi-directional DC-DC converter that facilitates power flow from the battery to the motor and motor to the battery with the necessary voltage gains while maintaining improved efficiency and low cost.
The main challenges in EV technology are battery deterioration due to frequent charging and discharging and the volume of the power converter. The research team plans –
- To work on the noise reduction methods that are brought on by regeneration action
- To work on various control techniques to keep the DC link voltage of the propulsion system constant
- Student-Teacher Collaboration Culminates in IEEE Transactions December 10, 2024
 The increasing demand for sustainable energy solutions has led to the development of hybrid energy systems that integrate renewable sources like solar photovoltaic (PV) systems and fuel cells (FC). The practical applications of the research in sectors such as electric vehicles and residential power systems, contribute to a more reliable and sustainable energy future contributing to a more reliable and sustainable future.
The increasing demand for sustainable energy solutions has led to the development of hybrid energy systems that integrate renewable sources like solar photovoltaic (PV) systems and fuel cells (FC). The practical applications of the research in sectors such as electric vehicles and residential power systems, contribute to a more reliable and sustainable energy future contributing to a more reliable and sustainable future.Abstract of the research.
This paper introduces novel high-gain tertiary port boost converter (HGTPBC) designed for hybrid energy sources such as solar photovoltaic (PV) and fuel cells (FC). The converter is employed with dual input sources by facilitating modular converters and accomplishes a high step-up voltage gain by virtue of a voltage multiplier in a DC microgrid, where the prosumers can have an islanded operation. The proposed topology allows home appliances to be powered by multiple energy source without the need for a large storage unit. Key features include continuous input current, reduced normalized voltage stress on switches, expandability for multiple input sources and independent source control. The independent control facilitates the standalone operation with single source during source failure or absence. To evaluate the converter performance, a thorough steady-state analysis, both with and without consideration of nonidealities is carried out. Detailed comparisons with existing converter topologies highlight the advantages of the proposed converter. Moreover, the loss distribution and efficiency analysis of proposed converter are presented and found to be 91.59% efficiency at rated power. Theoretical aspects are validated through hardware testing on a 100W laboratory prototype.
Explanation of the Research in layperson’s terms.
The proposed converter is a 100W DC-DC converter topology used in hybrid energy systems applications and electric vehicular applications in DC microgrid. The converter can accept two sources like fuel cell and solar PV system to supply the load and even can be extended for a greater number of sources. Thus, it is suitable for various applications of traction vehicles, household electrifications etc. It exhibits a lower switch stress and higher step-up conversion gain.
Practical Implementation and Social implications
The features include high step-up conversion gain, independent control possible, reduced normalised switch voltage stress. And flexible operation based on PV availability. It is most suitable for electric vehicles, Unmanned ariel vehicles, and hybrid energy systems etc. It improves the reliability of the renewable energy source by the incorporation of the second fixed source, fuel cell. It can be used in various on-grid and off-grid applications like home, hospitals, offices, and educational institutions, especially where source reliability is necessary. The major advantage is the reduction in the size of the source due to higher step-up gain and ease of control between the sources.
Future Research Plans
We are working towards the development of efficient and ultra-high gain bidirectional converters for various applications on DC microgrids. That should be able of reducing the source ratings and to integrate multiple sources to improve the grid reliability. Design and implementation of bidirectional multi-port converters for various applications of DC microgrids, such as renewable and hybrid storage integration are the scope of our research.
The link to the article- https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10772206
Continue reading →