Computing Influential nodes in complex networks
With its vast applications in the industry, computing influential nodes is becoming a popular research field in recent days. The Department of Computer Science and Engineering is delighted to inform you that the paper, Computing Influential Nodes Using Nearest Neighborhood Trust Value and Pagerank in Complex Networks have been published by Dr Murali Krishna Enduri, Assistant Professor, Dr Satish Anamalamudi, Associate Professor, and the PhD students; Koduru Hazarathaiah, Ms Srilatha Tokala in the Entropy Journal (Q2 Journal), with an impact factor 2.587.
Abstract
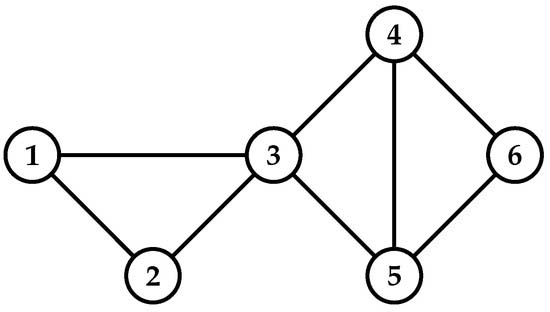 Computing influential nodes attract many researchers’ attention for spreading information in complex networks. It has vast applications such as viral marketing, social leaders, rumour control, and opinion monitoring. The information spreading ability of influential nodes is more compared with other nodes in the network. Several researchers proposed centrality measures to compute the influential nodes in the complex network, such as degree, betweenness, closeness, semi-local centralities, PageRank, etc. These centrality methods are defined based on the local and/or global information of nodes in the network. However, due to the high time complexity, centrality measures based on the global information of nodes have become unsuitable for large-scale networks. Very few centrality measures exist that are based on the attributes between nodes and the structure of the network. We propose the Nearest Neighbourhood Trust PageRank (NTPR) based on the structural attributes of neighbours and nearest neighbours of nodes. We define the measure based on the degree ratio, the similarity between nodes, the trust value of neighbours, and the nearest neighbours.
Computing influential nodes attract many researchers’ attention for spreading information in complex networks. It has vast applications such as viral marketing, social leaders, rumour control, and opinion monitoring. The information spreading ability of influential nodes is more compared with other nodes in the network. Several researchers proposed centrality measures to compute the influential nodes in the complex network, such as degree, betweenness, closeness, semi-local centralities, PageRank, etc. These centrality methods are defined based on the local and/or global information of nodes in the network. However, due to the high time complexity, centrality measures based on the global information of nodes have become unsuitable for large-scale networks. Very few centrality measures exist that are based on the attributes between nodes and the structure of the network. We propose the Nearest Neighbourhood Trust PageRank (NTPR) based on the structural attributes of neighbours and nearest neighbours of nodes. We define the measure based on the degree ratio, the similarity between nodes, the trust value of neighbours, and the nearest neighbours.
Explanation of the research
The research computes the influential nodes on the various real-world networks by using the proposed centrality method NTPR. The researchers find the maximum influence by using influential nodes with SIR and independent cascade methods. They also compare the maximum influence of our centrality measure with the existing basic centrality measures.
Social implications
Viral Marketing is a business strategy that uses existing social networks to promote products. The influential nodes in complex networks can be found using the centrality measure and can be used as the seed nodes for promoting products in the social networks. A rumour is a statement being said without knowing if it is true or not. The rumours can be easily controlled by discovering influential nodes. The researchers look forward to finding a centrality measure to detect the influential nodes efficiently.
- Published in CSE NEWS, Departmental News, News, Research News
Classical concert on Annamacharya Sankeertanas

Tallapaka Annamacharya, popularly known as ‘Anamayya’, was a 15th-century saint and the earliest known Indian musician to compose songs called sankeertanas in praise of Lord Venkateswara. His compositions have strongly influenced the structure of Carnatic Music and are still making rounds in various music concerts and performances the world over.
Having composed countless odes to Sri Tirumala Venkateswara Swamy, Annamacharya is widely regarded as the Pada Kavitaa Pitamaha of Telugu poetry. He was a reputed singer and an eminent poet who gave life to the Telugu song and lyricism by blending the Telugu ‘Andhra Vedam’ for the easy understanding of the common man, with the summary of ‘Sanskrit Vedas’.
Tirumala Tirupati Devasthanams, also known as TTD, are on an endeavour to preserve the rich heritage of his compositions. They have set music to over 800 compositions of Annamacharya that have amassed wide popularity among the devotees. We are delighted to announce that the following TTD musicians will be offering a beautiful rendition of Annamacharya’s compositions at our university campus:
Mr M B Loganatha Reddy (Singer)
Mr Srinivasulu (Keyboard)
Mr Bujji (Tabla)
Mr Ramachandraiyya (Shruthi)
Lend your ears to their soothing and heart-warming performance.
Date: June 8, 2022
Time: 4.00 pm to 5.00 pm
Venue: Auditorium
- Published in Events, Students Affairs Events
Ameliorated Follow the Leader: Algorithm and Application to Truss Design Problem
Q1 journal publications of our faculty members always bring honour to SRM University-AP. Dr Priyanka Singh, Assistant Professor from the Department of Computer Science and Engineering has published a paper titled “Ameliorated Follow the Leader: Algorithm and Application to Truss Design Problem” in the journal Structures (Q1 journal) having an impact factor of 2.983.
Abstract
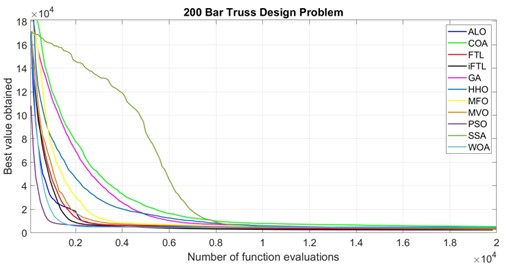 In the real world, resources, time, and money are always limited, necessitating the need for well-balanced algorithms. According to the “No-free-lunch” theorem, no single algorithm exists that works well in all applications. Hence, an optimisation algorithm with improved performance is always needed. The paper presents an improved follow the leader (iFTL) algorithm that imitates the behavioural movement of a sheep within the flock. The algorithm has been utilised to solve eight complex 10, 37, 52, 72, 120, 200, 224, and 942 bar truss design problems.
In the real world, resources, time, and money are always limited, necessitating the need for well-balanced algorithms. According to the “No-free-lunch” theorem, no single algorithm exists that works well in all applications. Hence, an optimisation algorithm with improved performance is always needed. The paper presents an improved follow the leader (iFTL) algorithm that imitates the behavioural movement of a sheep within the flock. The algorithm has been utilised to solve eight complex 10, 37, 52, 72, 120, 200, 224, and 942 bar truss design problems.
Practical implications
The algorithm can be utilised to solve several structural and mechanical design problems such as bride design, antenna design, welded beam design, speed reducer, and many more. The algorithm is well suited for all types of real-life engineering problems where optimisation is required, from travel cost optimisation to optimisation of resources in the organisation under the given constraints and objective function.
Collaborators
1. Rahul Kottath (Computer Vision Engineer, Digital Tower, Bentley Systems India Private Limited, Pune, India)
2. Ghanshyam G. Tejani (Assistant Professor, Department of Mechanical Engineering, School of Technology, GSFC University, Vadodara, Gujarat, India)
Future Research Plan
Currently, Dr Priyanka is exploring new engineering applications where optimisation techniques can be used. She is working on optimisation methods that can be utilised to classify microarray data, energy optimisation, and mechanical and structural design problems. In future, she plans to propose her work to the industrial level for the greater good and better solutions.
- Published in CSE NEWS, Departmental News, News, Research News
Recasting high-entropy alloys for enhanced performance

High-entropy alloys (HEAs) are gaining research significance in recent times as they propose novel alloy designs and concepts demonstrating better performance. HEAs constitute multiple principal elements in varying concentrations and combinations to produce new materials with excellent physical properties and superior performance at extreme temperature conditions. Recent studies have brought out a few high-entropy alloys possessing exceptional properties, even capable of challenging the existing theories and models for conventional alloys. However only very little has been explored within this multidimensional space leaving limitless possibilities to be explored and materialized.
Dr Sheela Singh, from the Department of Mechanical Engineering, has been conducting rigorous research in this domain and she has published research articles proposing novel ideas to tweak the properties of HEAs. In one of the articles co-authored by Dr Sheela, “Effect of minute element addition on the oxidation resistance of FeCoCrNiAl and FeCoCrNi2Al high entropy alloy”, published in the journal Advanced Powder Technology, she investigates the effect of Ti0.1 and Ti0.1Si0.1 addition on the high-temperature isothermal oxidation behaviour of dense FeCoCrNiAl and FeCoCrNi2Al high entropy alloys.
Mechanical properties such as hardness & young’s modulus, thermal properties such as melting temperature, specific heat capacity and coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) were investigated by Nano hardness tester (NHT), differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and dilatometer, respectively. The phases present in the HEAs produced by hot vacuum pressing and after isothermal oxidation were characterized by X-ray diffraction, Scanning Electron Microscopy and Raman Spectroscopy.
The weight gain recorded after isothermal oxidation for 5,25,50 and 100 hours at 1050°C was found to be parabolic in nature. X-ray diffraction analysis (XRD), as well as Raman spectroscopy analysis of HEA’s oxidized at 1050°C for 100 hours, shows the formation of the Al2O3 phase. A homogeneous thin oxide scale without any discontinuity was observed throughout the cross-section. It has been confirmed that Ti & Si addition in minute amount (0.1 at. % each) improves the mechanical properties and oxidation resistance as well as reduces the waviness of the oxide scale.
Another article co-published by her, “Enhanced Magnetization with Increased Chromium Concentration in FeCoCrxNi2Al High-Entropy Alloy”, in Materials and Science Technology, reports the effect of increasing the concentration of antiferromagnetic element Cr in FeCoCrxNi2Al (x = 0.5, 1.5) High Entropy Alloy (HEA) on their magnetic properties. It was found that the structure and composition of different phases, and the likely degree of spinodal decomposition in the Cr-Fe rich BCC phase significantly affects the magnetic properties.
Interestingly, the sample with Cr concentration x=1.5 showed two times larger saturation magnetization as compared to x=0.5. Furthermore, the magnetization versus temperature response shows a multi-phase character and exhibits distinct behaviour in low temperature and high-temperature regimes in both samples. The obtained soft ferromagnetic behaviour of these HEAs is crucial for the development of a new class of HEA for various applications.
The considerable structural and functional potential, as well as the richness of design, make HEAs promising candidates for new applications prompting further studies in the field. There remains a vast compositional space that is yet to be discovered. New studies have to be initiated finding out effective ways to recognise regions within this space where high-entropy alloys with potentially interesting properties may be lurking. Dr Sheela’s research is a right step in this direction to pave the way for fruitful developments in the future.
- Published in Departmental News, Mechanical Engineering NEWS, News, Research News
An oil stove burning the waste oil: Innovation of the month

Innovation is seeing what everybody has seen and thinking what nobody has thought.
-Dr Albert Szent-Gyorgyi
The uncompromising vision to mould the students to be the leaders of tomorrow and to gear them up to think beyond the possible has been the propelling factor that drives each student of SRM University-AP to tread the unexplored paths and embrace the unseen challenges. They come out as transformed individuals, outgrown with enriching experiences, capable of introducing new changes into the world. Students are offered ample space and time to ideate, innovate, and build themselves into coming-of-age professionals.
Innovator Square is one such platform set up by the Entrepreneurship-cell to nurture innovative ideas and thoughts having the potential to be converted into a meaningful product or service. Each month, it brings out young talents who have expanded their limits to fashion out an unforeseen solution to the mundane troubles of society. The title winners of the ‘Innovator of the Month’ contest this time, are, Shaik Nagoor, Kalakoti Smaran, and Komirisetti Gopi, from the Department of Mechanical Engineering. They have designed a special stove that runs on used cooking oil.
Introducing innovations out of bits and pieces of the commonest of things adds value to our everyday lives. These budding masterminds deserve acknowledgement for their incredible solution to utilise the leftover oil. Cooking oil is a daily essential abundantly used in food processing industry, such as restaurants and fast food, as well as in households. Reusing the oil is found to have harmful effects as it contains carcinogenic substances, that may lead to cancer or other chronic health disorders. Hence the common practice followed is to dump it in open soil. However, this will affect soil fertility and a myriad of environmental concerns.
Their motive to offer a sustainable solution to this menace is what prompted them to devise a user-friendly stove that will consume the used cooking oil. This will also serve as a better alternative to LPG, saving up to 50% of the expenditure. The students expressed their happiness in having made their tiny share of contribution for the well-being of their society. They also thanked their faculty and the university for extending unswerving support to complete this project. “We can never thank enough Dr Venkata Nori sir for guiding and supporting us from the beginning of our project, he helped us achieve this innovation, we are also thankful to Mr Udayan Bakshi sir for helping us to build a start-up”, they remarked.
- Published in IDEA NEWS, News, Students Achievements
The pertinence of human activity recognition systems in the present era
In recent years, human activity recognition has gained significant attention inside the scientific community. The enhanced spotlight is on the ground of its direct application in multiple domains. The latest research at the Department of Computer Science validates this assumption. Assistant Professor Dr V M Manikandan, and the 4th year B Tech Student Chaitanya Krishna Pasula have published a chapter titled An analysis of human activity recognition systems and their importance in the current era in the book Computational Intelligence Based Solutions for Vision Systems. The book is published by IOP Publishing Ltd.
Explanation of the chapter
 Human activity recognition is one of the most interesting and active research areas in computer vision. More research efforts are being put towards automatically identifying and analysing human activities due to their emerging importance in everyday applications. It serves applications in various areas like security video surveillance, smart homes, healthcare, human-computer interaction, virtual reality, robotics, and digital entertainment. Numerous papers have been published in the domain of human activity recognition. This book chapter discusses the various applications of human activity recognition, different methods available for automatic activity detection from videos, and the advantages of the human activity recognition system. It also describes the challenges in designing and implementing human activity detection schemes. Researchers further explain the publicly available datasets used for training and evaluating the systems for human activity recognition. The efficiency parameters used to evaluate the human activity recognition systems are also briefed in this chapter. The chapter is concluded by comparing the methodologies and speculating the possibilities of future research in this field.
Human activity recognition is one of the most interesting and active research areas in computer vision. More research efforts are being put towards automatically identifying and analysing human activities due to their emerging importance in everyday applications. It serves applications in various areas like security video surveillance, smart homes, healthcare, human-computer interaction, virtual reality, robotics, and digital entertainment. Numerous papers have been published in the domain of human activity recognition. This book chapter discusses the various applications of human activity recognition, different methods available for automatic activity detection from videos, and the advantages of the human activity recognition system. It also describes the challenges in designing and implementing human activity detection schemes. Researchers further explain the publicly available datasets used for training and evaluating the systems for human activity recognition. The efficiency parameters used to evaluate the human activity recognition systems are also briefed in this chapter. The chapter is concluded by comparing the methodologies and speculating the possibilities of future research in this field.
In the future, the researchers are planning to design and implement an activity recognition system to identify abnormal activities in public places for safety purposes. This book chapter will be a helpful reference for UG/PG/Ph.D students who aspire to research in the domain of activity detection from video.
- Published in CSE NEWS, Departmental News, News, Research News
Food safety applications of surface-enhanced Raman Spectroscopy
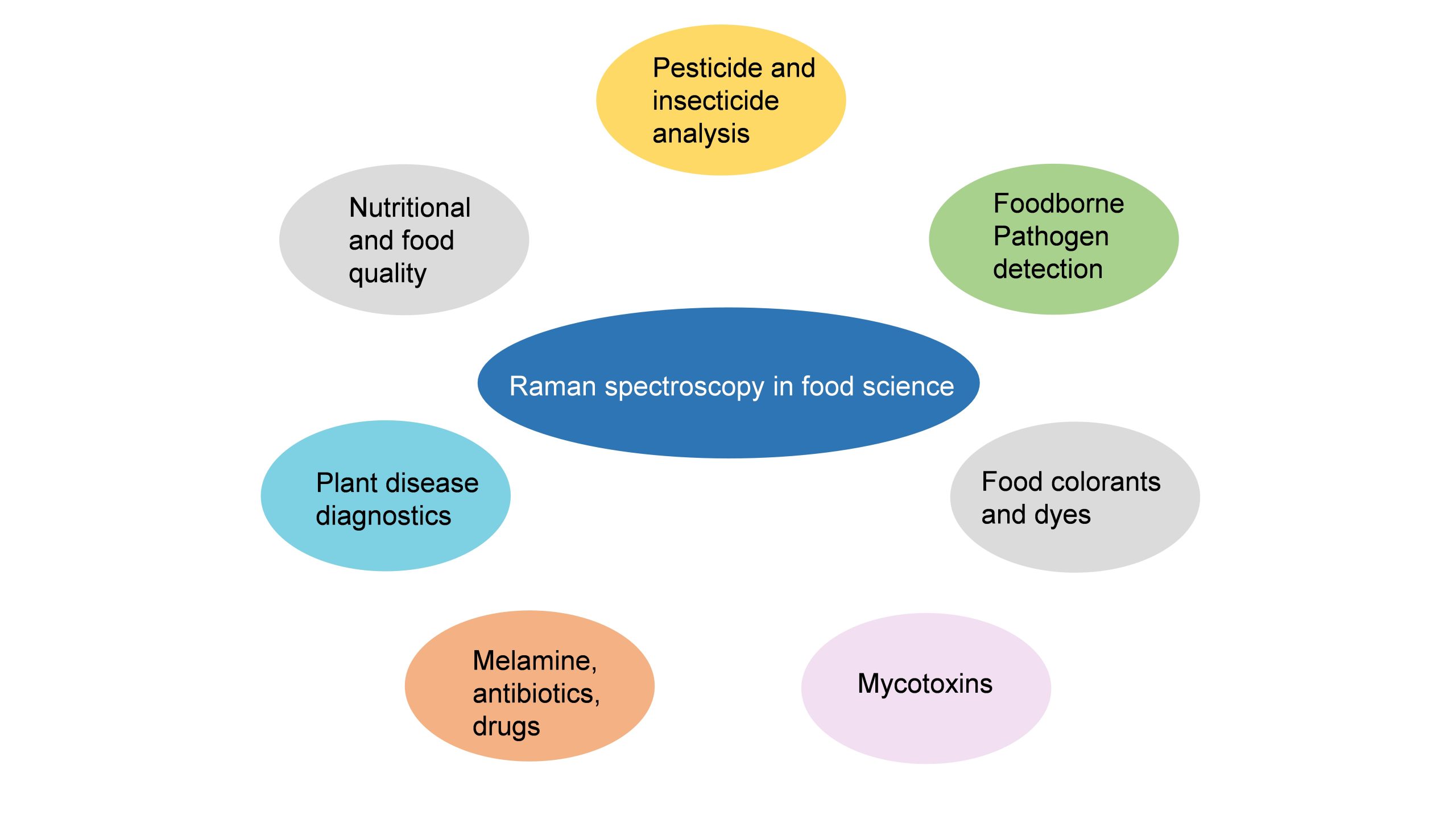
Surface-enhanced Raman Spectroscopy (SERS) is a nuanced chemical technique that amplifies the Raman scattering of molecules by utilising plasmonic nanostructured materials. SERS operates as a powerful detection tool that allows for the structural fingerprinting of a molecule. The ultra-high sensitivity and selectivity of the process offer it a vast array of applications in surface and interface chemistry, nanotechnology, biology, biomedicine, food science, environmental analysis and other areas.
Dr J P Raja Pandiyan and his PhD scholar, Ms Arunima Jinachandran from the Department of Chemistry have been keenly involved in exploring the possibilities of SERS technology in food science and other fields. The safety and quality concerns related to food were the primary reasons that impelled them to step into this domain. Their article “Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy for food quality and safety monitoring” was published in the book Nanotechnology Applications for Food Safety and Quality Monitoring, published by Elsevier. The article was published in collaboration with Dr Selvaraju Kanagarajan from the Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences.
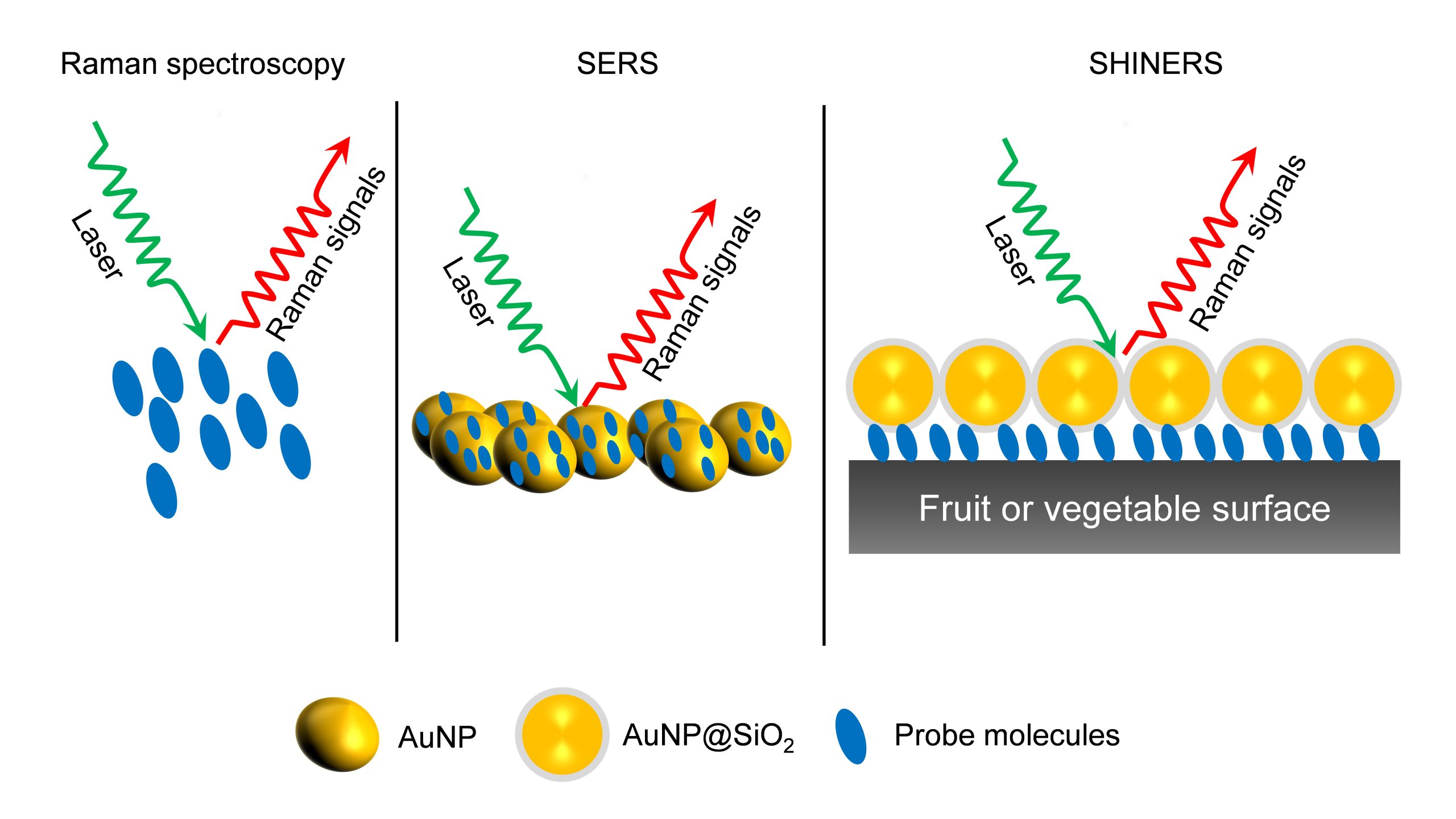 As an analytical technique, SERS possesses several advantages such as non-destructive, sensitive, and selective. In the chapter, the necessity, and applications of SERS in food science are elaborately discussed. They have also discussed all the possible food contaminants and how to identify them using SERS to ensure food quality. This book will serve as an enlightening read to research groups who are working on Raman, surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy, analytical chemistry, and food quality analysis.
As an analytical technique, SERS possesses several advantages such as non-destructive, sensitive, and selective. In the chapter, the necessity, and applications of SERS in food science are elaborately discussed. They have also discussed all the possible food contaminants and how to identify them using SERS to ensure food quality. This book will serve as an enlightening read to research groups who are working on Raman, surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy, analytical chemistry, and food quality analysis.
- Published in Chemistry-news, Departmental News, News, Research News
Comparing organic food preferences of American and Indian consumers

A paper titled “Organic food preferences: A comparison of American and Indian consumers” has been published by Prof Bharadhwaj Sivakumaran, Dean- SEAMS, SRM University-AP, Kirubaharan Boobalan (SSN College of Engineering), and Margaret Susairaj (Great Lakes Institute of Management, Chennai) in the journal Food Quality and Preference having an Impact Factor of 5.6.
This research tests a nomological model predicting organic food attitudes and purchase intentions in USA and India. Data were collected from India (n = 687) and the USA (n = 632) using Amazon M Turk and were analyzed using structural equation modelling and multi-group moderation technique. Results revealed that over and above attitude, subjective norm and perceived behavioural control, response efficacy and self-expressive benefits significantly affect consumers’ attitudes and purchase intentions toward organic food among American and Indian consumers. Findings reveal that response efficacy and attitude matter more in the USA while subjective norms and self-expressive benefits exert a greater influence in India. Therefore, marketers may reinforce belief-related elements while selling organic food products in the USA and societal-related elements while selling in India. Theoretically, this work adds to the Theory of Planned Behavior by adding self-expressive benefits and develops a common model for organic food across samples in USA and India.
- Published in Dean, Departmental News, News, Paari Current Happenings, Research News
Interview mastery for global study opportunities
 As you are aware, applying for international education can be daunting. Mastery of interview fundamentals is required to grab global study opportunities. Mr P Mahammad Farooq, Counselor- Student Services, Office of International Relations & Higher Studies, SRM University-AP, is conducting a session on the topic Interview Mastery For Global Study Opportunities on June 16, 2022, at 3.00 pm.
As you are aware, applying for international education can be daunting. Mastery of interview fundamentals is required to grab global study opportunities. Mr P Mahammad Farooq, Counselor- Student Services, Office of International Relations & Higher Studies, SRM University-AP, is conducting a session on the topic Interview Mastery For Global Study Opportunities on June 16, 2022, at 3.00 pm.
The session aims to train students to respond to the interview questions, understand difficult interviewer personalities and showcase confidence that differentiates them from other candidates.
Avail this opportunity to sketch your study abroad pathway with the Office of International Relations and Higher Studies at SRM University-AP! Join the session on June 16, 2022, at 3.00 pm.
About the speaker
P.Md. Farooq is a well-known academician with more than five years of teaching, training research in the educational industry, and administrative experience. Before joining SRM University-AP, he was a freelance trainer for soft skills, career guidance coaching, advanced spoken English and employability skills. He expanded his academic boundaries by working at training institutions like the “Global talent track Pvt Ltd-Mumbai”, seventh sense solutions-Bangalore, Pygmalion Skills solutions Pvt Ltd-Bangalore, Rubicon Skill Development Pvt Ltd-Pune etc.
- Published in Events, International Relations, IR-Events
Neodymium-doped bismuth ferrite thin films for random access memory applications
 A paper titled “Study on ferroelectric polarization induced resistive switching characteristics of neodymium-doped bismuth ferrite thin films for random access memory applications” has been published by Dr Pranab Mandal, Assistant Professor of Physics and his PhD student, Ms K N Malleswari in the journal ‘Current Applied Physics’ having an Impact Factor of 2.480.
A paper titled “Study on ferroelectric polarization induced resistive switching characteristics of neodymium-doped bismuth ferrite thin films for random access memory applications” has been published by Dr Pranab Mandal, Assistant Professor of Physics and his PhD student, Ms K N Malleswari in the journal ‘Current Applied Physics’ having an Impact Factor of 2.480.
Doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cap.2022.04.013
Abstract
Resistive random-access memory (ReRAM) devices are based on the resistance switching (RS) effect. Such RS devices have recently attracted significant attention due to their potential application in realizing the next-generation non-volatile memory (NVM) devices. The present work reports on resistive switching (RS) characteristics of Neodymium (Nd)-doped bismuth ferrite (BFO) layers. The Nd (2–10 at%) doped BFO thin film layers were deposited using a spray pyrolysis method. The structural analysis reveals that a higher Nd doping concentration in BFO leads to significant distortion of the prepared Nd: BFO thin films from rhombohedral to tetragonal characteristics. The morphological analysis shows that all the deposited Nd: BFO thin films have regularly arranged grains. The X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) analysis reveals that the prepared Nd: BFO thin films have a higher Fe3+/Fe2+ ratio and fewer oxygen vacancy (VO) defects which enrich the ferroelectric characteristics in Nd: BFO layers. The polarization-electric field (P-E) and RS characteristics of the fabricated Nd: BFO-based RS device were examined. It was observed that the Nd (7 at%) doped BFO RS device shows large remnant polarization (P r) of 0.21 μC/cm2 and stable RS characteristics.
Research in brief
Non-volatile resistive random access memory (RRAM) are future generation random access memory device with potential benefits such as high operational speed (nanoseconds read and write time), non-volatility, high endurance scalability and low power consumption [Namnoscale Research Lett., 15, 90, 2020]. Here in this work, we presented the resistive switching characteristics of a multiferroic material namely Nd-doped BiFeO3 material. The device shows stable resistive switching characteristics.
Practical implementation/social implications
Researchers in this field are focusing to overcome challenges of high operation current, lower resistance ratios, and reliability issues [Namnoscale Research Lett., 15, 90, 2020]. While several prototype RRAMs have been developed by other groups, future memory applications would require overcoming the challenges mentioned above.
Collaboration
The work has been conceptualized by Dr Amiruddin at Crescent Institute of Science and Technology, Chennai; and Dr Pranab Mandal and Ms Malleswari provided inputs on ferroelectric polarization – electric field (P – E) measurement and drafting.
- Published in Departmental News, Physics News, Research News

