Undergraduate gets placed in Danske IT, a fully owned subsidiary of Danske Bank
 Purab Agarwal from the Department of Computer Science and Engineering has been successfully placed at Danske IT, a fully owned subsidiary of Danske Bank with an exciting CTC of 10 LPA. The company is headquartered in Bengaluru.
Purab Agarwal from the Department of Computer Science and Engineering has been successfully placed at Danske IT, a fully owned subsidiary of Danske Bank with an exciting CTC of 10 LPA. The company is headquartered in Bengaluru.
Danske IT, which has been in operation since 2015, is a fully owned subsidiary of the Danske Bank Group, Denmark’s largest bank and a leading bank in Northern Europe with a global presence. Danske IT is dedicated to providing cutting-edge, end-to-end solutions to clients by providing value through high-performing teams. They are also committed to assisting Danske Bank in realising its goal of becoming the most trusted financial partner in the world.
Purab Agarwal with overwhelming joy narrates his experience at SRM University-AP. “I was good in academics from the beginning of my degree. I believe that the curriculum helped me in enhancing my knowledge of different domains. It showed me a direction to what I need to pursue. CCC training organised by the placement cell of the university helped me a lot in my preparation. I had earlier also been shortlisted for ABInbev, Sahaj, Nielsen, and Bajaj Finserv. My advice to juniors would be to always be curious and humble.
- Published in CR&CS, CR&CS NEWS, News, Students Achievements
Cost-effective electro-catalyst for oxygen reduction reaction
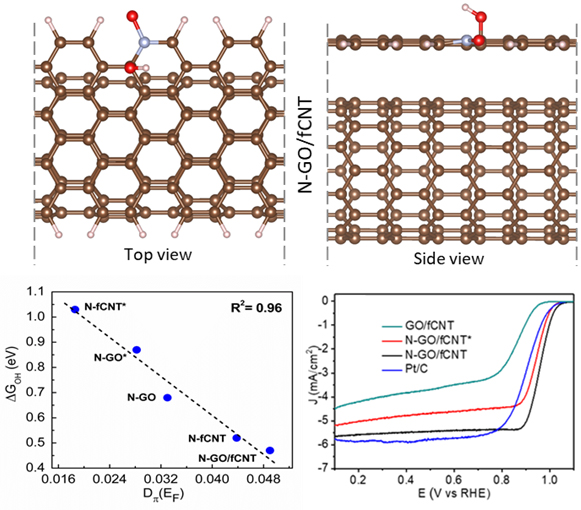 A research paper titled “Nitrogen doping derived bridging of Graphene and Carbon Nanotube composite for oxygen electroreduction” has been published by Prof Ranjit Thapa, Professor of Physics, SRM University – AP, as a co-author, in International Journal of Energy Research, having Impact Factor of 5.164.
A research paper titled “Nitrogen doping derived bridging of Graphene and Carbon Nanotube composite for oxygen electroreduction” has been published by Prof Ranjit Thapa, Professor of Physics, SRM University – AP, as a co-author, in International Journal of Energy Research, having Impact Factor of 5.164.
In this work, the research group investigated the origin of high catalytic activity of oxidic-N configuration in nitrogen-doped CNT and graphene heterostructure using density functional theory (DFT). We have plotted the free energy profile of the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) to estimate the thermodynamic overpotential and catalytic performance of the respective active sites. The overpotential is related to the quantifying parameter ∆GOH (with R2 = 0.98) and the π electron density at the Fermi level, defined as an electronic descriptor, which is highly correlated with the ∆GOH with R2 value 0.96. For various N doped configurations, we correlated the ∆GOH values with π electron density at the Fermi level and found that the carbon site adjacent to the oxide-N configuration is a more prominent site for ORR. Further, we show that the oxidic-N configuration in the heterostructure of graphene and CNT is the ideal configuration, which gives a lower overpotential of 0.54 eV for ORR on adjacent carbon sites. Therefore, the charge transfer occurs from underneath CNT to graphene and increases the value of π electron density at the Fermi level which leads to the higher catalytic performance of the active site.
In the early 20th century, fuel cells were invented and their global impact has not reached up to its regular commercialization when compared with battery technology. The fuel cell device could be a powerful technique to generate electricity for large energy demand without greenhouse gas emissions. However, other major hurdles in the commercialization of fuel cell devices are the cost of platinum (as a catalyst), its poisoning and stability. Recently, carbon-based materials such as graphene, carbon nanotubes and activated carbon have been evolved as metal-free low-cost catalysts due to their (i) high abundance/yield (ii) reactivity towards oxygen just by introducing impurities like heteroatoms or other metals. However, identifying an efficient design principle to search optimal doping configurations in various carbon systems is a grand challenge for researchers.
This work is done in collaboration with Research Institute, SRM Institute of Science & Technology, Kattankulathur-603203, Chennai (India).
In future, the study aims to propose the effective design principle for various doped carbon systems as a catalyst to identify the optimal active sites and configurations for ORR. The role of π orbital in carbon systems such as graphene, graphene nanoribbons, carbon nanotube, etc is very important and can be a general electronic descriptor to define catalytic activity. Also, π electron descriptors and machine learning algorithms based combined approach can boost the search for ideal carbon catalyst for ORR with low DFT cost.
Read the full paper here: https://doi.org/10.1002/er.7179
- Published in Departmental News, News, Physics News, Research News
Prof U Ramamurty, renowned researcher from NTU Singapore, visits SRM University-AP
 An interactive session between Prof U Ramamurty, President Chair Professor, School of Mechanical & Aerospace Engineering at Nanyang Technological University (NTU), Singapore, and the faculty members of SRM University – AP, Andhra-Pradesh was held on Monday.
An interactive session between Prof U Ramamurty, President Chair Professor, School of Mechanical & Aerospace Engineering at Nanyang Technological University (NTU), Singapore, and the faculty members of SRM University – AP, Andhra-Pradesh was held on Monday.
During the discussion, Prof Ramamurty emphasized the importance of research collaboration between faculty members from different research areas and about utilizing expertise to achieve significant scientific output.
Dr Pardhasaradhi Maram from the Department of Chemistry, Dr Sabyasachi Mukhopadhyay from the Department of Physics, and Prof G S Vinod Kumar from the Department of Mechanical Engineering presented their detailed research areas that focus on storage devices, catalysts for value-added products, energy and sensing devices, novel metallic materials, additive manufacturing of metals and Bio-implants, and industry collaborative research work.
Prof Ramamurty said that he is glad to see that productive science is being done at SRM University-AP. “Given that the University has started only 4 years ago and been functioning amidst a pandemic for more than one and a half years, the progress in research is significant and very impressive. Interdisciplinary efforts between various departments in the University will give effective results”, he added.
Prof D Narayana Rao, Pro-Vice-Chancellor, SRM University – AP expressed his interest in establishing NTU – SRM joint Centre for Advanced Research in functional and structural materials at SRM University campus to Prof Ramamurty. The centre that Prof Rao envisions will provide an opportunity to synergize the expertise and resources of NTU, Singapore, and SRM University – AP to carry out front-line research in the areas of novel materials, self-healing materials and also additive manufacturing (3D Printing of metals and bio-implants).
- Published in Chemistry-news, Departmental News, Mechanical Engineering NEWS, News, Physics News, Research News
Simple and portable spectrochemical probe for rapid detection of chlorides ions in water
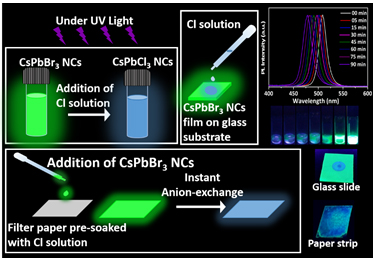 Dr Nimai Mishra, Assistant Professor, Department of Chemistry, SRM University-AP, Andhra Pradesh, along with his research group comprising of students pursuing PhD under him, Ms V.G.Vasavi Dutt and Mr Syed Akhil has published a research article titled Cesium Lead Bromide Perovskite Nanocrystals as a Simple and Portable Spectrochemical Probe for Rapid Detection of Chlorides in the Journal ChemistrySelect (Publisher: Wiley-VCH on behalf of Chemistry Europe, Impact Factor-2.2).
Dr Nimai Mishra, Assistant Professor, Department of Chemistry, SRM University-AP, Andhra Pradesh, along with his research group comprising of students pursuing PhD under him, Ms V.G.Vasavi Dutt and Mr Syed Akhil has published a research article titled Cesium Lead Bromide Perovskite Nanocrystals as a Simple and Portable Spectrochemical Probe for Rapid Detection of Chlorides in the Journal ChemistrySelect (Publisher: Wiley-VCH on behalf of Chemistry Europe, Impact Factor-2.2).
Chloride anions are widely abundant in water and when they combine with calcium, potassium, and magnesium, they form chloride salts. However, the higher concentrations badly affect the environment by causing severe dehydration and even plant death. High concentrations of sodium chloride exhibit the potential of corrosive damage thereby releasing toxic metals from plumbing fixtures. Hence, there is a need to monitor the concentration levels of chloride salts in water. Several techniques like titration, spectrophotometry, ion chromatography, electrochemistry, etc have been reported to date. Despite the high accuracy and precision of these techniques, they involve expensive instrumentation and is out of reach from on-site detection. Hence, it is necessary to look for simple, portable, and cost-effective strategies for the detection of chlorides in the water.
In this article, Dr Mishra’s research group demonstrated that the wide spectral tunability of CsPbBr3 perovskite nanocrystals (NCs) via instantaneous and facile anion exchange, make them a suitable candidate for chloride detection. Rapid anion-exchange processes between CsPbBr3 perovskite NCs and different chloride solutions were carried out in ambient conditions. The resultant anion-exchanged CsPbCl3-xBrx NCs preserved the structural properties and exhibited a remarkable blue shift in photoluminescence spectra. This forms a basis for the detection of chloride ions in water. This has been applied with the limit of detection up to 100 µM. The detection strategies were not only limited to the direct addition of chloride solutions to NCs, but they also showed a visual colour change under UV light when the chloride solution is drop-casted on CsPbBr3 films that are deposited on glass substrates. Furthermore, the detection strategy is established by drop-casting CsPbBr3 NCs onto paper strips that are pre-soaked in chloride solutions. A considerable blue shift in fluorimetry proves them to be an excellent sensing medium as practical spectrochemical probes for on-site detection of chlorides. Based on this, a colour chart and selectivity chart to access the presence of chlorides and their concentration is also demonstrated.
- Published in Chemistry-news, Departmental News, News, Research News











