Electric vehicles are the future of India: Daimler Buses India CEO
Karl-Alexander Seidel at Freshers Orientation 2021, SRM University-AP
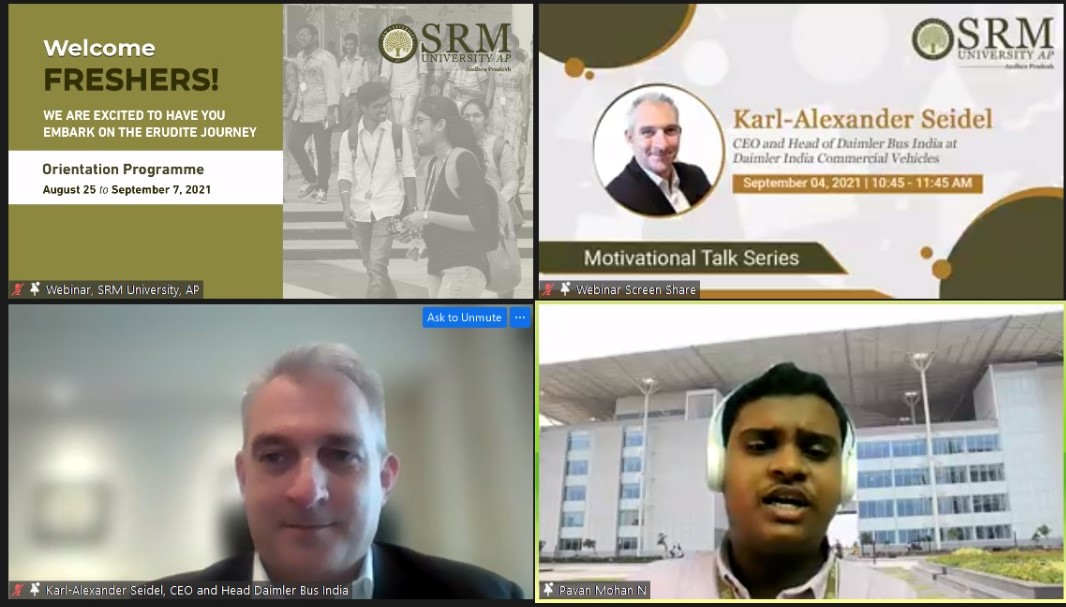
Mr Karl-Alexander Seidel, CEO and Head of Daimler Bus, India at Daimler India Commercial Vehicles interacted with the freshers of SRM University-AP in a session organised as part of the Orientation 2021. In his address to the students, Mr Seidel recollected his university days, love for automotive and the challenges he faced in contributing to Euro 6 emission standards.
While answering a question put forward by students, Mr Seidel said that strong theoretical knowledge along with interpersonal skills such as teamwork which lead to cocreation is what he appreciates in job seekers. As the CEO of a company that is a subsidiary of German multinational automotive corporation Daimler, he said he would recruit people who have a vision, creativity and pioneering spirit wanting to do something bigger and better. “I see electric vehicles as the future of India. The infrastructure required for driverless cars is currently a challenge in Indian cities” Mr Seidel said. “If you can come up with solutions to make autonomous driving happen in India, our company will be happy to have you on board”, he added, encouraging the inquisitive minds of SRM University-AP.
Vice-Chancellor Prof V S Rao recollected his industry visit to Daimler in Germany and how impressed he was about the perfection of the workers and the discipline that ensures quality. He expressed his interest in conducting online research internships with the best companies and facilities abroad in association with Daimler India Commercial Vehicles. Mr Vivekanandan, Associate Director, Department of Corporate Relations and Career Services expressed his sincere gratitude on behalf of the university. “We are extremely glad that Mr Seidel could inspire the freshers and incite dreams for an innovative future”, he added. Mr Laxmanan Angu Raju, Senior Manager from the Department of CR&CS was present during the occasion.
- Published in CR&CS, CR&CS NEWS, News
Mechanical Engineering students soar to Ather Energy
 Chirag Vinodkumar Menon and Mudireddy Raviteja Reddy, two vibrant students from the Department of Mechanical Engineering, have been placed in Ather Energy with a CTC of ₹10.00 LPA. The Ather 450Xur and Ather 450 Plus are two electric scooters that the company manufactures. Tarun Mehta and Swapnil Jain established Ather Energy Pvt. Ltd., an Indian electric car startup, in 2013. It has also founded the Ather Grid electric vehicle charging infrastructure across the country.
Chirag Vinodkumar Menon and Mudireddy Raviteja Reddy, two vibrant students from the Department of Mechanical Engineering, have been placed in Ather Energy with a CTC of ₹10.00 LPA. The Ather 450Xur and Ather 450 Plus are two electric scooters that the company manufactures. Tarun Mehta and Swapnil Jain established Ather Energy Pvt. Ltd., an Indian electric car startup, in 2013. It has also founded the Ather Grid electric vehicle charging infrastructure across the country.
Let’s look into what our students say about their placement experience!
Chirag Vinodkumar Menon
For me, this job offer from Ather Energy is a dream come true. This is everything I ever expected for my first job and I can’t be happier. As soon as I saw the job offer, I started to prepare for my logic and technical assessment. The coursework provided by CDC was very helpful and the domain training lessons provided by the college helped me cinch the assessments. After I received news that I am selected for the technical interview, I immediately started focusing on my projects, which are innovative and relevant, as a result of repeated consult with the esteemed faculty of SRM University-AP. Their guidance is a vital reason why my projects have been a success, despite remotely working due to the pandemic. I consulted with my teammates and friends as well and as a result of efforts and determination, I have been able to crack the final HR interview.
The mock interviews conducted by the CR&CS department helped me refine my answers and my personality as a suitable candidate. My mother also helped me immensely to prepare for my interviews. I thank the CR&CS department for choosing reputed companies and giving me a chance to apply for this job opening and for ensuring the process is as smooth as possible. I would like to wish the very best for all my peers and juniors, success in their professional and educational endeavours.
Raviteja Mudireddy
I’m very excited and happy in receiving the job offer from Ather Energy. From the beginning of my B Tech itself, I have had much interest and passion towards automobiles which actuated me to do many projects. This in turn helped me in gaining knowledge in Electric Vehicles and added extra weight to my resume. I extend my gratitude to SRM University-AP for supporting my projects by providing technical assistance and monetary help beyond measure. The Mechanical Engineering curriculum is diversified and helped me gain knowledge in fields like Manufacturing Technology, 3D printing, etc. Of course, my research in EV (Electric Vehicle) Tech has also helped me a lot.
I thank the Placement department for bringing Ather Energy to our campus and guiding me to the HR Round. My message to my juniors in Mechanical Engineering is that the projects and the research work in the undergraduate coursework will differentiate a student from the rest of the crowd. Projects are not just for the marks or grades, they will lead you to get your dream job or even help you to start your own company.
- Published in CR&CS, CR&CS NEWS, Departmental News, Mechanical Engineering NEWS, News
Research scholar gets prestigious scholarship from IRRI
 A Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) student of the Department of Biological Sciences at SRM University-AP, Andhra Pradesh, Faraz Azeem, has been awarded a prestigious scholarship by the International Rice Research Institute (IRRI), Manila, Philippines. The scholarship will enable Faraz to carry out a part of his PhD research under the supervision of Dr Jauhar Ali, Senior Scientist-II, Head – Hybrid Rice Development Consortium (HRDC), Leader – Hybrid Rice Breeding Cluster, Rice Breeding Platform, International Rice Research Institute, Los Banos, Philippines, for a period of one year and four months.
A Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) student of the Department of Biological Sciences at SRM University-AP, Andhra Pradesh, Faraz Azeem, has been awarded a prestigious scholarship by the International Rice Research Institute (IRRI), Manila, Philippines. The scholarship will enable Faraz to carry out a part of his PhD research under the supervision of Dr Jauhar Ali, Senior Scientist-II, Head – Hybrid Rice Development Consortium (HRDC), Leader – Hybrid Rice Breeding Cluster, Rice Breeding Platform, International Rice Research Institute, Los Banos, Philippines, for a period of one year and four months.
Faraz joined SRM University-AP, Andhra Pradesh, in January 2021 and is working on “Understanding the genetics and molecular biology of nitrogen-use efficiency in rice” under the guidance of Prof Jayaseelan Murugaiyan, HoD, Department of Biological Sciences, SRM University-AP. Dr P Sathyanarayanan, President; Prof V S Rao, Vice-Chancellor; Prof D Narayana Rao, Pro-Vice-Chancellor of SRM University-AP congratulated Faraz for this accomplishment.
The International Rice Research Institute (IRRI) is a global agricultural research and training organisation with offices in seventeen countries and headquarters in Los Banos, Laguna, Philippines. IRRI is well-known for its role in producing rice varieties that contributed to the 1960s Green Revolution, which helped Asia avoid famine. The CGIAR Consortium of International Agricultural Research Centres, a global alliance of institutions involved in food security research, includes 15 agricultural research centres worldwide. The International Rice Research Institute (IRRI) is one of the Asia’s largest non-profit agricultural research facility.
SRM University-AP provides a wide array of opportunities and benefits along with its PhD Programmes. The nascent university has more than 150 PhD students to date in various departments of Engineering, Science, Liberal Arts, Business Administration and Social Sciences. SRM University-AP university has a vibrant research environment with state-of-the-art facilities along with attractive fellowship and complimentary food and accommodation at the university campus. The faculty advisers have paramount knowledge and experience in research along with international exposure. The university also provides support for journal publications, patent filing, and attending national and international conferences.
SRM University-AP further has MoUs with reputed universities abroad for Student Exchange Programme. In addition, the university is conducting research projects funded by prominent organisations, industries and the Government of India. Research projects sponsored by DST, DST-NSM, DBT, DBT-Wellcome Trust, UGC-DAE, ARBL, Titan industries etc are a few of the current ongoing projects.
- Published in Biology News, News, Research News, Students Achievements
Third year CSE students innovate efficient plastic recycling technology
 Swikriti Khadke, Pragya Gupta, and Shanmukh Rachakunta from third-year Computer Science Engineering have published a research paper titled “Efficient Plastic Recycling and Remold Circular Economy using the Technology of Trust – Blockchain” along with their mentors from SRM University-AP Dr Jatindra Kumar Dash, Dr Goutam Kumar Dalapati and Dr Sabyasachi Chakrabortty in the peer-reviewed journal Sustainability.
Swikriti Khadke, Pragya Gupta, and Shanmukh Rachakunta from third-year Computer Science Engineering have published a research paper titled “Efficient Plastic Recycling and Remold Circular Economy using the Technology of Trust – Blockchain” along with their mentors from SRM University-AP Dr Jatindra Kumar Dash, Dr Goutam Kumar Dalapati and Dr Sabyasachi Chakrabortty in the peer-reviewed journal Sustainability.
Global plastic waste is increasing rapidly. The strategic management of plastic waste and recycling can preserve environmental species and associated costs. The utilization of plastic can be done by introducing Blockchain during plastic waste recycling. Automation for the segregation and collection of plastic waste can effectively establish a globally recognizable tool using Blockchain-based applications. Collection and sorting of plastic recycling are feasible by keeping track of plastic with unique codes or digital badges throughout the supply chain. Efficient recycling technology is essential to reduce plastic pollution. Many technologies have been employed to enhance plastic recycling. Among them, blockchain is promising for plastic recycling and circular economy (CE). Blockchain, a distributed ledger, consists of some ordered blocks which are unchangeable. This can be considered an exemplary way to push the transactions of their customers under the same blockchain technology. The research group used machine learning techniques to predict plastic generation globally so that they could see the impact it will make in the coming future. The students have used ARIMA – Auto-Regressive Integrated Moving Average for the study.
The potential idea is to utilize an approach wherein recyclers can keep track of generated waste as it moves through the various chains. A platform that works by tracking recycling activities across a local recycling supply chain on the Blockchain. When this will be publicly available, consumers can also use the ledger info to make more informed purchasing decisions. The Blockchain can be utilized to track individual items through the recycling supply chain by creating physical markers like QR codes.
The suggested Blockchain-based platform can be implemented in various nations with an autonomous waste collector and storage system. This process can be expanded to individual collectors and storage systems. The novel process will be created by incorporating a reward-based Blockchain scheme with the collaboration of global businesses and local waste collectors. The proposed model further allows the effective sharing of databases among various supply chains to create a CE.
Talking about the social implications of the research, the students firmly believe that the study will result in the introduction of new technology in the recycling industry and promote awareness about technology in rural areas. Developing a platform and implementing blockchain and other facilities will be the focus of these young innovative brains of SRM University-AP in the forthcoming days.
Read the full paper here: https://doi.org/10.3390/su13169142
- Published in Chemistry-news, Computer Science News, Departmental News, News, Physics News, Research News

