Paaridhan: Weaving a Tapestry of Culture and Ethnicity!
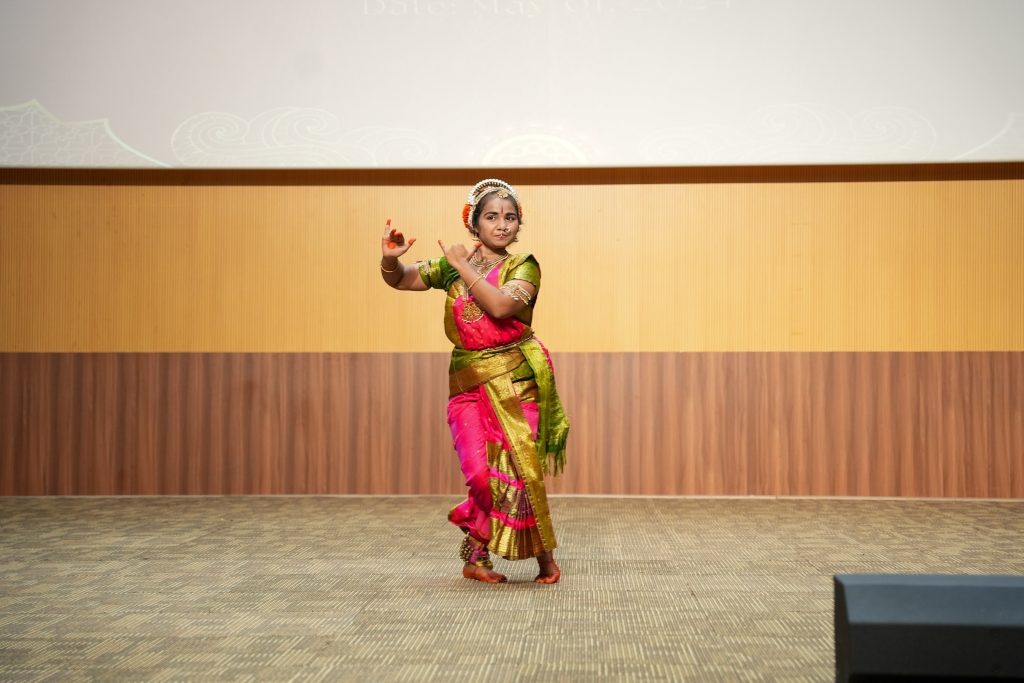

“India is a place where colour is doubly bright. Pinks that scald your eyes, blues you could drown in.” – Kiran Millwood Hargrave
This was a reality at SRM University-AP on May 01, 2024, as the university transformed into a vibrant hub of cultural pride and unity as it celebrated “Paaridhaan”. Students dazzled the campus with an array of performances, fashion walks, and activities, each showcasing the rich tapestry of our diverse backgrounds. The campus was engulfed in a colourful hue as students attended the celebration adorned in traditional ethnic wear.
This remarkable event, organised under the aegis of the Directorate of Student Affairs, included breathtaking dance acts, soulful musical performances, and a fashion show that captivated all in attendance. This celebration brought the university together and left lasting memories of a community united in its diversity.
- Published in Departmental News, News, student affairs news
Groundbreaking Research on Advanced Technology Nodes

Dr M Durga Prakash, Assistant Professor in the Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, and his PhD scholar, Ms U Gowthami, have published a research paper titled “Performance Improvement of Spacer-engineered N-type Tree Shaped NSFET towards Advanced Technology nodes” in the Q1 journal, IEEE Access. The paper has an impact factor of 3.9 and will pave the way for significant advancements in the field.
Here’s an abstract of their research paper
Abstract:
Scaling gate lengths deep is most reliable with tree-shaped Nanosheet FETS (NSFET). This paper uses TCAD simulations to study the 12nm gate length (LG) n-type Tree-shaped NSFET with a stack of high-k dielectric (HfO2) and (SiO2) spacers. The Tree-shaped NFET device features high on-current (ION) and low off-current (IOFF) with T(NS) = 5 nm, W(NS) = 25 nm, WIB=5nm, and HIB = 25 nm. Comparison of single- and dual-k spacer 3D devices and DC properties are shown. Because fringing fields with spacer dielectric prolong the effective gate length, the dual-k device has the highest ION / IOFF ratio, 109, compared to 107. This research also examines where work function, inter bridge height, breadth, gate lengths, temperature, and analog/RF and DC metrics affect the device. The suggested device has good electrical properties at 12 nm LG, with DIBL = 23 mV/V, SS = 62 mV/dec, and switching ratio (ION / IOFF) = 109. The device’s performance proves Moore’s law applies to lower technological nodes, enabling scalability.
The link to the article- https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10499264 DOI: 10.1109/ACCESS.2024.3388504
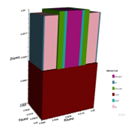
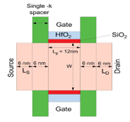
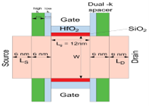
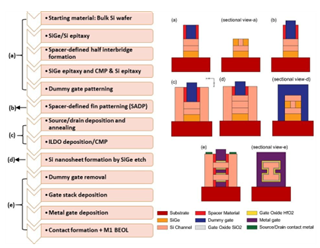
- Published in Departmental News, ECE NEWS, News, Research News
Enhancing International Placements with Simandhar Education
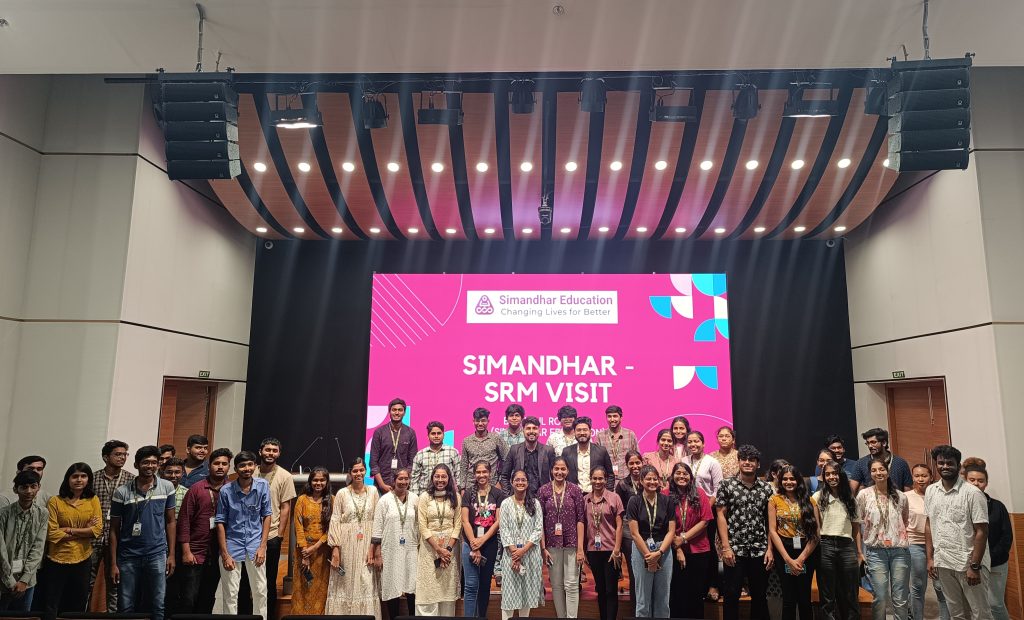

The Paari School of Business has networked with various industry, academia, and social sector partners to ensure that the management and commerce students are placed at national and international firms with lucrative packages. Recently, the school had a visit from Simandhar Education, one of India’s leading institutes providing certified US finance courses in India on April 29, 2024. Mr Rahul Roy and Mr Anupam Biswas, SME from Simandhar Education, shared a comprehensive insight into a potential collaboration between Paari School of Business and Simandhar Education.
Simandhar Education is one of the renowned Indian institutes that provide US CPA/CMA/EA courses. They have 100+ Corporate Tie-ups for training and placement, including with Big 4s and Top 10 global accounting firms. They are the best channel partner of Becker in India, an approved channel partner of AICPA and a Silver approved partner of IMA.
Mr Roy explained the extensive services offered by Simandhar Education in providing quality training and placements for the students of Paari. These include live interactive classes, recorded classes, unlimited practice tests, mock tests, revision lectures, etc. This partnership could be a silver lining for the students of Paari as it enhances their chances of placement in multinational firms in the US.
- Published in Departmental News, News, Paari Current Happenings
Critical Analysis of the Influence of Hydroclimatic Variability and Anthropocene on the Groundwater of the Sundarbans

The water crisis in India, especially in the coastal regions, has worsened alarmingly, coercing environmentalists and researchers to critically study the reason behind this phenomenon. The Sundarbans region faces a scarcity of drinking water in terms of quality and quantity due to various reasons. Dr Kousik Das, Asst. Professor, Department of Environmental Science and Engineering, Dr Harish Puppala, Asst Professor, Department of Civil Engineering and Mr Mijanur Mondal, Research Scholar from the Department of Environmental Science and Engineering has conducted a groundbreaking study on the increased salinization of water due to human activities. The research trio has published a paper titled “Understanding the susceptibility of groundwater of Sundarbans with hydroclimatic variability and anthropogenic influences” in the prestigious Q1 journal Groundwater for Sustainable Development, which has an impact factor of 5.9, critically analysing the numerous factors that affect the quality of drinking water in the Sundarbans region.
Abstract
Coastal aquifers worldwide are experiencing increased salinisation due to climate change and human activities. Sundarbans, in India, is one such area where this phenomenon is noticed at an unprecedented rate, making drinking water unpotable for consumption. Existing studies lack a comprehensive analysis of the underlying causes. This study conducts a systematic literature review to identify drivers of groundwater salinisation, examining climate change parameters such as rainfall patterns, sea level rise, El Niño-Southern Oscillation, and tropical cyclones. Significant groundwater level declines from 1996 to 2017 are primarily attributed to variations in the Indian Ocean Dipole and El Niño Southern Oscillation, affecting rainfall and recharge rates. During tropical cyclones, groundwater levels rise rapidly, and quality is sensitive to El Niño Southern Oscillation. Rising sea levels, changing rainfall, and increasing population density worsen salinisation. Shallow aquifers have high salinity, whereas deep aquifers exceed permissible limits. This underscores the urgent need to address drinking water scarcity and potential migration resulting from complex interactions between climate, population, and groundwater management.
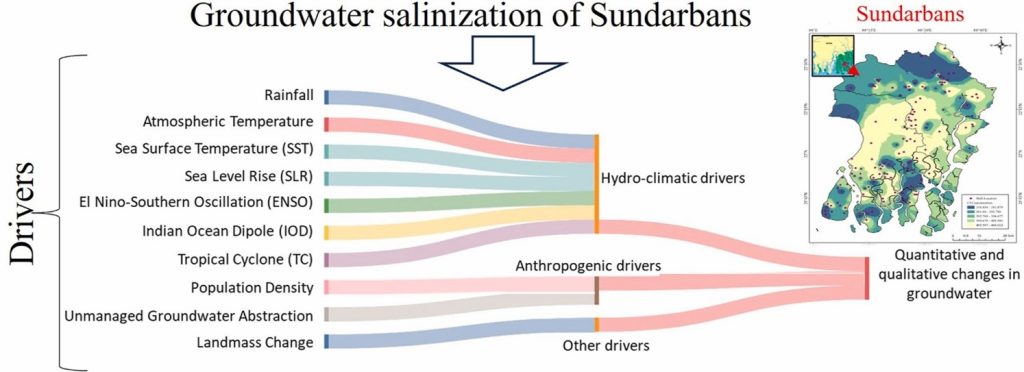
Social Implications of the Research
- Water Quality Monitoring: Implementing regular monitoring of salinity levels in groundwater to ensure compliance with safety standards.
- Community Awareness Programmes: Conducting educational campaigns to inform local communities about the risks of high salinity levels in drinking water and promoting the judicious use of water sources so that unscientific abstraction can be reduced.
- Policy Development: Formulating policies at the local and national levels to regulate salinity levels in drinking water and ensure public health protection.
- Infrastructure Improvement: Investing in water treatment facilities or technologies to remove high salt levels from groundwater sources. Alternative sources and rainwater harvesting can be taken into consideration.
Collaborations – IIT Kharagpur, India
The research team plans to work on Groundwater vulnerability modelling using AI/ML in Sundarbans, India next. The team has begun collecting primary data using questionnaire surveys and interviews to throw light on socio-economic conditions and to understand the core reasons for the water crisis and health and psychological issues due to water unavailability, especially during extreme events like cyclones.
Link to the article
- Published in CIVIL NEWS, Departmental News, ENVS News, News, Research News
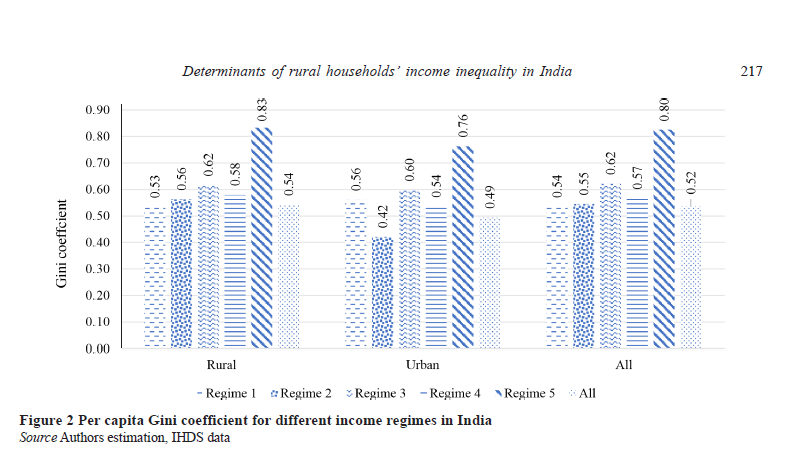
Uncovering the Factors Influencing Income Inequality in Rural Indian Households: A Comprehensive Study

The Department of Economics takes immense pride in announcing the publication of the research paper, “Determinants of Rural Households’ Income Inequality in India” authored by Dr Ghanshyam Pandey, Assistant Professor. The paper has been published in the Journal of Agricultural Economics Research Review (ABDC-C), and has an impact factor of 0.19. Dr Pandey’s paper examines the factors that determine income inequality among rural farm households in India and discusses the implications of the findings for policymakers, practitioners, and researchers. The study highlights how addressing the identified factors could potentially reduce income inequality among rural farm households and improve the overall well-being of the rural population.
Abstract
This study has identified the drivers of income inequality in rural India using IHDS 2011–12 national-level survey. The inequality decomposition methodology developed by Fields (2003) based on a two-way regression methodology has been used. The study has modified the previous regression based inequality decomposition technique by accounting for diverse income sources and regimes as well as by effectively correcting for selectivity in the various income regimes. The CLAD model has been used to distinguish the determinants of income inequality in rural India. The study has indicated that income inequality in farm households can be attributed to the level of education, family size, caste/social group composition, and composition in land ownership and that family size and land ownership are instrumental primarily due to off-farm labour income. The study has shown that education is a significant factor in income inequality due to its impact on off-farm work income. The study has suggested that a continued increase in variability in land distribution may exacerbate income inequality in households in rural India.
Link to the Article
Pandey G and Devi B (2023). Determinants of rural households’ income inequality in India. (2024). Agricultural Economics Research Review, 36(2), 213-225. https://epubs.icar.org.in/index.php/AERR/article/view/150669
- Published in Departmental News, Economics Current Happenings, Economics News, News, Research News
Dr Chimoy Das’ Research Makes Latest Breakthrough in Material Science

The Department of Chemistry is thrilled to announce the paper “Mechanochemically-induced glass formation from two-dimensional hybrid organic-inorganic perovskites”, published by Dr Chinmoy Das, Assistant Professor in the reputed Q1 Journal Chemical Science with an 8.4 Impact Factor. This groundbreaking research introduces a novel method for transforming crystalline phases into glasses through mechanochemical processes. This environmentally friendly and efficient method opens new doors for manufacturing glasses, revolutionising traditional processes. This remarkable research celebrates this extraordinary blend of chemistry, physics, and innovation!
Abstract
The first mechanochemically-induced hybrid organic-inorganic perovskites (HOIPs) crystal-to-glass transformation was reported as a quick, environmentally friendly, and productive method of making glasses. Within ten minutes of mechanical ball milling, the crystalline phase transformed into the amorphous phase, demonstrating glass transition behaviour as shown by thermal analysis methods. The microstructural evolution of amorphization was studied using time-resolved in situ ball-milling with synchrotron powder diffraction. The results indicated that energy may accumulate as crystal defects because the crystallite size reaches a comminution limit before the amorphization process is finished. The limited short-range order of amorphous HOIPs was discovered through total scattering experiments, and photoluminescence (PL) and ultraviolet-visible (UV-vis) spectroscopy were used to examine their optical characteristics.
Explanation of the research in layperson’s terms
Crystalline inorganic perovskites (general chemical formula is ABX3, where A and B are cations, and X is anion) are generally known for their unique optoelectronic applications, such as solar cells, photodetectors, and LEDs (light emitting diodes). In this research, Dr Das revealed hybrid materials comprised of organic linkers and inorganic nodes, which constitute hybrid organic-inorganic perovskites (HOIPs). The research demonstrated a rapid and environment-friendly (mechanochemically ball milling assisted) synthetic approach to transform the crystalline phase to its non-crystalline/amorphous phase. Interestingly, the amorphous phase of HOIPs showed temperature-dependent glass transition temperature (Tg) at very low temperatures, ~50 C. The structure of the HOIP glasses has been characterised through total-X-ray diffraction studies and pair-distribution functions. The crystalline and glassy HOIPs showed optical properties, which were studied by photoluminescence (PL) and ultraviolet-visible (UV-vis) spectroscopy.
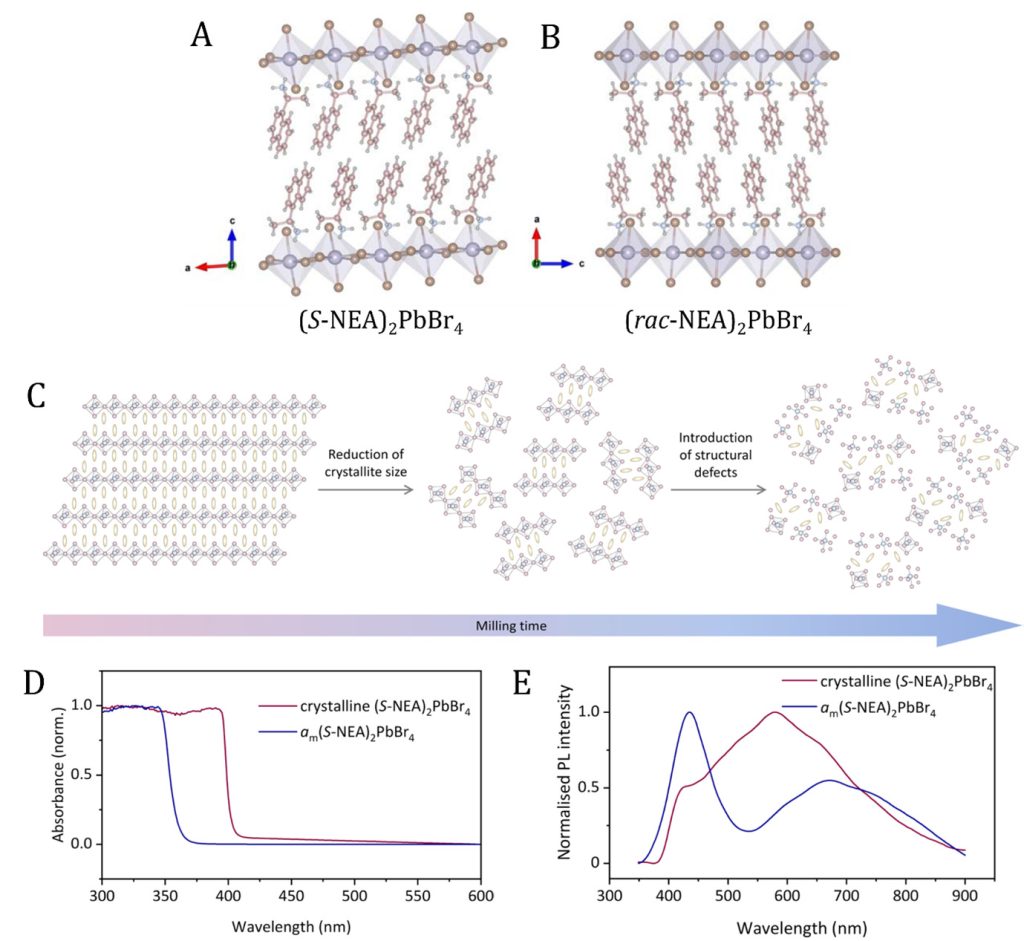
Figure 1. Single crystal structures of (A) (S-NEA)2PbBr4 and (B) (rac-NEA)2PbBr4. Pb, Br, C, N and H atoms are represented by purple, brown, pink, blue, and grey colours, respectively. (C) Schematic illustration of the microstructural evolution on 2D HOIPs upon ball-milling. (D) UV-Vis and (E) photoluminescent properties of crystalline (S-NEA)2PbBr4 (purple) and glassy (S-NEA)2PbBr4 (blue) HOIPs.
Practical implementation/ social implications of your research
Through the mechanochemical approach, we prepared novel hybrid organic-inorganic perovskite (HOIP) glasses within ten minutes, showing the greater feasibility of processing the glass material for industrial implication. On the other hand, we also demonstrated that the HOIP glasses showed photoluminescence properties, which would enable us to fabricate the device for solar cells, photodetectors, LEDs and many more.
Collaborations
- Department of Materials Science and Metallurgy, University of Cambridge, United Kingdom.
The Department of Chemistry has established a research group at SRM University-AP, and the group has started to explore an emergent research area of crystal-glass composite materials towards the applications of atmospheric water harvesting, solid-state electrolytes, photovoltaics, and conversion of gaseous Carbon-dioxide molecules to industrially relevant liquids, such as methanol or ethanol.
Any interested candidate can reach out to Dr Chinmoy for exciting projects.
- Published in Chemistry-news, Departmental News, News, Research News
GPEMC Sanctions Consultancy Project Worth 48.9 Lakhs
 Green Pearl Education and Management Corporation (GPEMC) has recently sanctioned a significant consultancy project to SRM University-AP, titled “Multilingual Minutes of the Meeting Generation.” This project aims to develop innovative solutions for generating multilingual minutes of meetings, ensuring effective communication, and understanding across language barriers.
Green Pearl Education and Management Corporation (GPEMC) has recently sanctioned a significant consultancy project to SRM University-AP, titled “Multilingual Minutes of the Meeting Generation.” This project aims to develop innovative solutions for generating multilingual minutes of meetings, ensuring effective communication, and understanding across language barriers.
The Consultancy Project has been assigned to Dr. Ashu Abdul and Dr. Dinesh Reddy Vemula, Assistant Professors for a period of 7 months from the Department of Computer Science and Engineering (CSE). Their expertise in language processing and computational linguistics will play a crucial role in the successful execution of this project.
Joining them in this endeavour is Mr Phanindra Kumar, a dedicated PhD scholar, and a team of talented B.Tech. students, including Mr Shivansh Goel, Mr Md Ahmad Raza Khan, Ms Subrabala Dash, Mr Nithish Sri Ram, Mr Hadi Mahmood, and Mr Phanidra Kumar. Their combined skills and enthusiasm will contribute to the development of innovative solutions for multilingual meeting documentation.
The Consultancy Project has been sanctioned with an outlay of Rs 48,91,786/- as consultancy charges for a period of 7 months. This funding will support the research and development efforts required to deliver efficient and accurate multilingual minutes of meetings.
The objective of this project is to create an automated system that can generate minutes of meetings in multiple languages, ensuring accurate and comprehensive documentation. By overcoming language barriers, this project aims to facilitate effective communication and collaboration in diverse organizational settings.
The collaboration between SRM University-AP and GPEMC highlights the commitment of both institutions to research and innovation. This consultancy project presents an exciting opportunity for the faculty members and students to contribute to real-world problem-solving and make a substantial impact in the field of language processing.
Abstract
The project ‘Multilingual Minutes of the Meeting Generation’ aims to develop an innovative application that automates the creation of meeting minutes, action plans, and summaries in multiple languages. Leveraging advanced research in natural language processing and speech recognition technologies, our application seeks to streamline the tedious and time-consuming task of minute-taking. It will do so by accurately identifying, associating, and documenting statements with their respective speakers during meetings using speech diarization techniques.
The primary objective is to enhance the efficiency and accuracy of meeting minutes while supporting diverse linguistic needs and eliminating human error, thereby catering to global business environments. The system will improve the meeting outcomes for all participants by identifying the action items from the meeting. This project intends to deliver an effective solution for enterprises by combining the latest technological advances with a user-centric design.
Explanation of the Research in Layperson’s Terms
The project called “Multilingual Minutes of the Meeting Generation” is about creating a new tool that automatically writes down what happens in meetings—like the minutes, action items, and summaries—and can do this in several languages. This tool uses the latest technology in understanding and processing human speech, which helps make the task of recording meeting details much faster and easier.
The special feature of this tool is its ability to figure out who is speaking and accurately attach their words to them in the meeting notes. This makes sure the meeting records are both correct and detailed. The main goal here is to make creating and keeping track of meeting records more efficient and accurate, help people who speak different languages, and reduce mistakes that can happen when humans take down notes.
This system is especially useful in today’s global business setting, where people from different parts of the world need to work together smoothly. It aims to lessen the work involved in manually writing meeting notes and make the results easier for everyone to use and understand. Overall, the project promises to blend cutting-edge technology with designs that focus on the needs of the users to provide a practical tool for businesses.
Practical Implementation or the Social Implications Associated with the Research
The practical implementation of this project is particularly beneficial for enterprises, institutions, and professional settings where meetings are frequent. By automating minute-taking, it allows participants to focus more on discussion and decision-making, rather than note-taking. This leads to more productive meetings and ensures that important details are not lost or misinterpreted. Ultimately, this technology enhances communication and documentation accuracy across diverse linguistic and cultural landscapes in business and professional environments.
Collaborations
This project is being developed in collaboration with the members of the Next Tech Lab AP at SRM University-AP
Future Research Plans
The future plans for this project involve integrating the application with widely used platforms such as Zoom, Google Meet, and others that support video/audio conferencing. This integration aims to seamlessly incorporate the automated minute-taking functionality into these platforms, enhancing accessibility and usability for users across various companies and institutions. By expanding compatibility with popular conferencing tools, the project seeks to further streamline meeting documentation processes and cater to a broader user base in diverse professional settings.
- Published in Computer Science News, Departmental News, News, Research News
Field Visit: Biological Sciences Students at AIIMS Mangalagiri
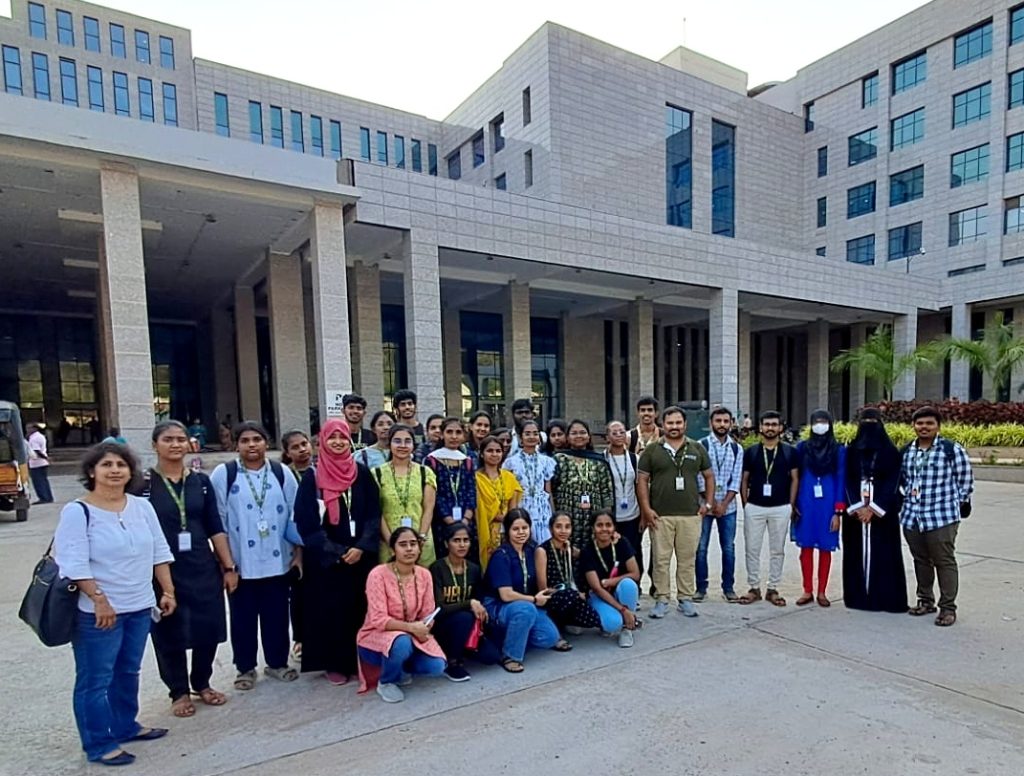

In a significant stride towards enriching their academic experience, students from the Department of Biological Sciences embarked on a captivating field trip to AIIMS Mangalagiri. This excursion served as an integral component of their Active Learning Process, fostering a deeper understanding of real-world applications in the realm of biology. The cohort comprised students from diverse academic backgrounds, including those pursuing 1st year B.Sc in Integrative Biology and M.Sc in Molecular Biology & Biotechnology. Their visit to AIIMS Mangalagiri provided them with a unique opportunity to gain firsthand insights into cutting-edge practices in the field of biomedicine.
During their visit, the students were granted exclusive access to the Integrated Stewardship and OPD Labs, where they were immersed in a world of advanced diagnostics and research methodologies. Expert lectures and demonstrations on state-of-the-art diagnostic techniques such as MALDI-TOF, CBNAAT, CLIA, Vitek, and BactAlert offered invaluable insights into the intricacies of disease detection and monitoring.
This excursion underscored the department’s commitment to fostering a culture of active learning and practical exposure among its students. By exposing them to prominent institutions and industries, such as AIIMS Mangalagiri, students were provided with hands-on training and the opportunity to engage with leading experts in the field.
Accompanying the students were esteemed faculty members of the department, including Dr Sutharsan Govindarajan, Dr Sudeshna Saha, and Dr Prateek Gupta, whose guidance and mentorship further enriched the learning experience.
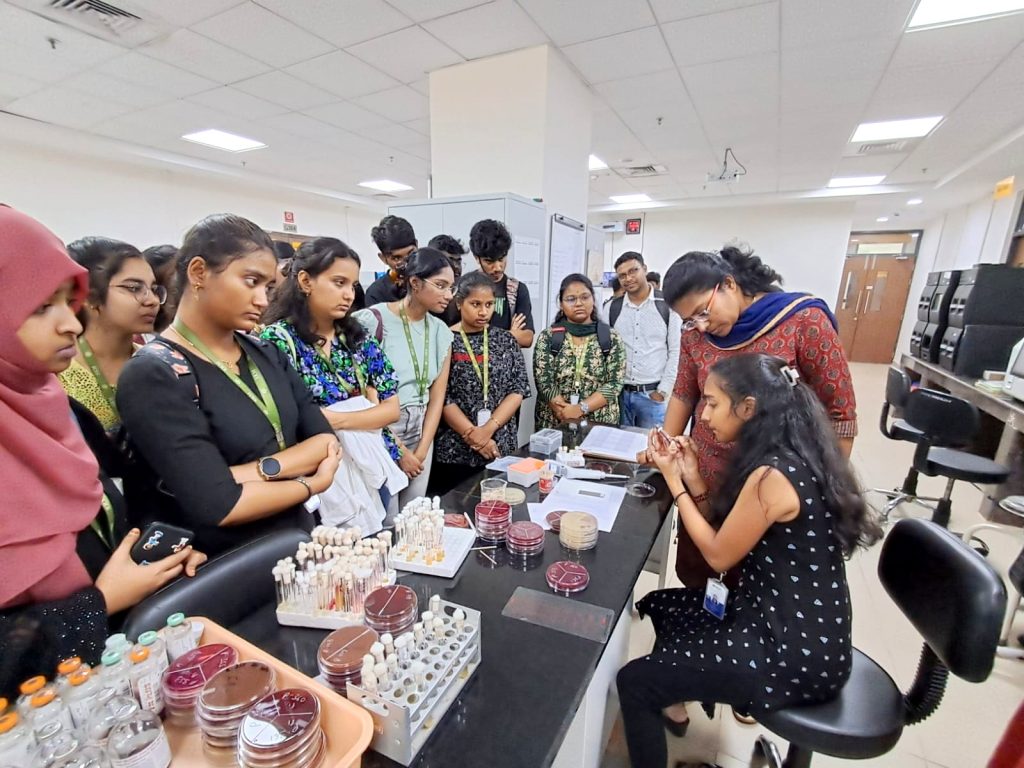

Furthermore, the collaborative efforts between the faculty of SRM University-AP and researchers at AIIMS Mangalagiri were highlighted during the visit. These collaborations span various domains, from developing biomedical devices for disease diagnosis to research endeavours in antimicrobial resistance (AMR), early cancer detection, and drug targeting. Such synergies between academia and research institutions present students with unparalleled opportunities to engage in impactful research initiatives and contribute meaningfully to the advancement of scientific knowledge
Overall, the field visit to AIIMS Mangalagiri served as a catalyst for academic excellence and professional growth, empowering students with the skills, knowledge, and networks necessary to thrive in the dynamic field of biological sciences.
- Published in Biology News, Departmental News, News
Unlocking Branding Insights with Mr Harish Bhardwaj
 On March 20, 2024, MBA students at Paari School of Business had the privilege of attending an enlightening discourse on communication strategies for branding, delivered by the distinguished speaker, Mr Harish Bhardwaj. Throughout the session, Mr Harish emphasised the pivotal role of problem identification in effecting meaningful change.
On March 20, 2024, MBA students at Paari School of Business had the privilege of attending an enlightening discourse on communication strategies for branding, delivered by the distinguished speaker, Mr Harish Bhardwaj. Throughout the session, Mr Harish emphasised the pivotal role of problem identification in effecting meaningful change.
Mr Harish urged the students to adopt fresh perspectives and delve deep into issues, highlighting the importance of uncovering root causes. He asserted that solutions to complex problems often stem from simplicity. By encouraging students to think critically and analyse situations from different angles, he empowered them to approach branding challenges with innovative and effective strategies.
Furthermore, Mr Harish underscored the necessity of comprehending audience needs, stating, “It is not about what you have, but what they want.” He emphasised the power of active listening and genuine connections. By understanding the desires and preferences of the target audience, businesses can tailor their communication strategies to effectively engage and resonate with their customers.
Engaging the students in stimulating discussions, Mr Harish explored various topics related to branding. He delved into personal branding, emphasizing the importance of cultivating a strong and authentic personal brand that aligns with one’s values and goals. He also discussed the concepts of the ‘moment of truth’ and the ‘zero moment of truth,’ highlighting the significance of making positive impressions during customer interactions and the influence of online research on consumer decision-making.
He challenged the attendees to dissociate physical attributes from personality traits, emphasizing that serving others transcends mere personality. By focusing on providing value and meeting customer needs, businesses can build long-lasting relationships and establish a strong brand presence.
The session culminated in the exploration of the transformative potential of storytelling. He exemplified how stories can catalyse change, foster connections, and leave indelible impressions on audiences. Through captivating narratives, he illustrated the power of storytelling in creating emotional connections and engaging customers on a deeper level.
The discourse left the students at Paari School of Business enlightened and inspired, equipped with valuable insights into effective communication strategies for driving branding change. Mr Harish’s expertise and engaging delivery style ensured an enriching experience that will undoubtedly resonate with attendees for years to come.
Paari School of Business is committed to providing its students with opportunities to learn from industry experts and gain practical knowledge. Such insightful sessions contribute to the holistic development of students and prepare them to excel in their future careers.
- Published in Departmental News, News, Paari Current Happenings, paari-guest-lectures
Creating History: A Chase to Mt. Everest!

SRM University-AP is gearing up for the ultimate thrill-seeking escapade, which will have hearts racing and adrenaline pumping like never before! The Directorate of Entrepreneurship & Innovation and the Directorate of Student Affairs jointly organise the “Everest Base Camp Expedition”, the mother of all adventures – a daring conquest of the Earth’s highest mountain above sea level – Mount Everest!
The 15-day exhilarating journey will take flight with a maiden batch of 20 young adventurers selected through a rigorous physical and mental ability test on October 11, 2024 (tentative). 4 months of extensive training will commence in full swing, with the selected students pushing their limits and testing their endurance, moulding them into a complete voyager. Various training and practice trips have been scheduled to Arakku Valley to test their strength, Mangalagiri temple for elevation trekking training and much more.
This is a first-of-its-kind initiative by a university in India, presenting a unique opportunity for every enthusiastic explorer to witness the magnificence of the cold, icy peaks of the Himalayas. In addition to providing students with exemplary academic, research and entrepreneurial resources, SRM AP also emphasises the significance of 21st-century skills in nurturing them into socially aware and ethical citizens of tomorrow. This one-of-a-kind trip will ensure that students imbibe the value of belief and courage to instil purpose or a greater aim for anything that they might pursue in life, the importance of not losing faith during hard times and overcoming the obstacles that hinder your aim, the significance of camaraderie and teamwork, to develop essential leadership skills etc.

Students and their mentors have already begun their footsteps on a journey that will transform their lives! Embracing the thrill, embracing the adventure!
This journey will undoubtedly etch unforgettable memories into the fabric of their existence!
- Published in Departmental News, IDEA NEWS, News, student affairs news
















