SRM-AP All News
ALL News
- Inspiring the world with quality research facilities May 7, 2022
 SRM AP is known for its resources and facilities for pioneering research with the support of global leaders and SME’s while sticking to compliance and international regulations. Obtaining research excellence in every field of study has been a mission of the university. Recently, 50 MSc students from the Department of Chemistry, KBN College, Vijayawada, visited our university to explore the analytical and research facilities available here.
SRM AP is known for its resources and facilities for pioneering research with the support of global leaders and SME’s while sticking to compliance and international regulations. Obtaining research excellence in every field of study has been a mission of the university. Recently, 50 MSc students from the Department of Chemistry, KBN College, Vijayawada, visited our university to explore the analytical and research facilities available here. The research areas handled by the Department of Chemistry of SRM AP include the disciplines of chemical sciences, ranging from organic, inorganic, and physical, to theoretical or computational chemistry. The department’s highly disciplinary and collaborative environment is indeed inspiring, and it continues to grab attention. The strong interactions of the university with other premier institutions across India and around the world refine the quality of analytical and research facilities available here. The students from KBN college eagerly interacted with the faculty members and research scholars. Dr Mahesh Kumar Ravva and Dr Rajapandiyan, Faculty members, coordinated the visit.
Continue reading → - The network of mindfulness, leadership, and performing arts May 6, 2022
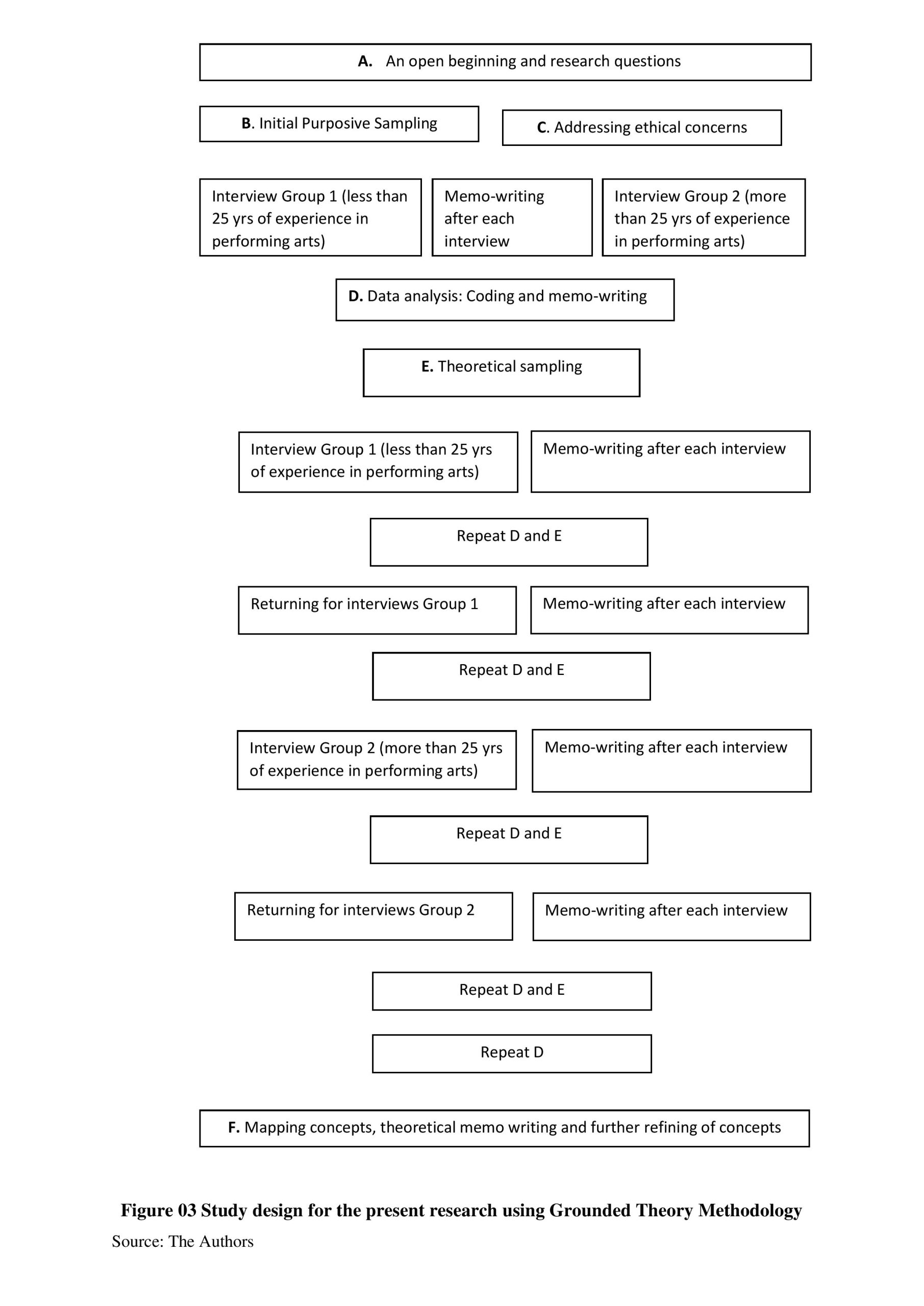 Mindfulness, leadership, and performing arts have deep interconnections that, if approached theoretically, can give productive outcomes to implement in workplaces and potential employees. The School of Entrepreneurship and Management Studies is delighted to inform you that the paper titled ‘Exploring mindfulness and leadership development: Lessons learned using grounded theory through the study of the performing arts’ by Dr Vimal Babu, Associate Professor, got published in the journal FIIB Business Review published by SAGE publication.
Mindfulness, leadership, and performing arts have deep interconnections that, if approached theoretically, can give productive outcomes to implement in workplaces and potential employees. The School of Entrepreneurship and Management Studies is delighted to inform you that the paper titled ‘Exploring mindfulness and leadership development: Lessons learned using grounded theory through the study of the performing arts’ by Dr Vimal Babu, Associate Professor, got published in the journal FIIB Business Review published by SAGE publication.Abstract of the research
The research looks at mindfulness mechanisms and leadership characteristics as they are expressed in performing art forms. This qualitative study examines major categories to create a theoretical framework for mindful leadership development using performing arts. The present study employs the research paradigm of interpretivism to investigate respondents’ experiences and unique phenomena. The Grounded theory (GT) methodology helps explore grounded data and the development of theories. The abstract core category ‘Immense Concentration and Self-Control’ captures the abstract and inclusive meaning as understood by the sample respondents. The qualitative coding analysis aided in the investigation of the data-driven abstract phenomena. According to the findings of this study, all performing artists require a higher level of attention and self-control to demonstrate fascinating performances like Koodiyattam. A higher level of attention and self-control can be ensured based on increased mindfulness, identified leadership attributes, motivation components, values and beliefs, and personality dispositions of the performing artists. In-depth theoretical reflections on the relationships between the relevant categories are presented. The relationships between the five major categories of mindfulness processes, leadership abilities, motivation components, values and beliefs, and personality dispositions are very significant.
Explanation of the research
In simple terms, the present research explores the dynamics of mindfulness, leadership, and other potential variables enabling mindful leadership through performing arts, helping the practicing managers learn the innovative approaches to inculcate mindful leadership in employees in the workplace. To attain the research purpose, researchers studied the Koodiyattam performing arts as an instrument of mindfulness and leadership based on in-depth interviews of Koodiyattam performing artists. Since the present work explores deeper meanings and experiences to unearth unique and insightful phenomena, the Grounded Theory was appropriately employed as a methodology.
Practical implementation of the research
Managers and executives can derive valuable insights based on the present study. They would be able to understand the interconnections of mindfulness, leadership, and performing arts. It would offer them a better grounding to argue and introduce arts-based initiatives at their workplaces to enhance mindful leadership amongst potential employees aiming for well-being and career development in the organization. Several organizations have been experimenting with arts and its impact on business. However, the studies are in the nascent stage. Hence, more like-minded researchers need to join hands for diverse, global, and intercultural studies, focusing on different variables, including arts. The findings of the present research exhibit firm conviction in enlightening the industry practitioners to consider performing arts based mindful leadership training to enhance mindfulness and leadership attributes of the employees, in turn, making them productive and engaged workforce in the long run.
For this research, Dr Vimal babu has collaborated with Dr Amresh Kumar, IIM, Bodh Gaya, India, and Vipin Kumar, PMP, BT India, Gurgaon, India. His future research plans are to work in strategic leadership, negotiation, and conflict management using innovative qualitative research methods. Entrepreneurship education and circular entrepreneurship are also an area of much interest.
Continue reading → - SRM AP Team Meets ARCI: Mutual Discussions on Research Projects May 6, 2022
Continue reading → The SRM University-AP team met Dr. Tata Narasinga Rao, Director, International Advanced Research Centre for Powder Metallurgy and New Materials (ARCI, Hyderabad) on 7 April 2022, Thursday. ARCI is an internationally acknowledged autonomous body under the Department of Science and Technology (DST), Government of India. Ten professors, led by SRM University Pro-Vice-Chancellor, Prof. D Narayana Rao, went to Hyderabad to meet the ARCI Director. Projects related to key advanced materials in the field of scientific research were discussed during the meeting. Discussions were held on research projects related to additive (3D) manufacturing, solar energy materials, automotive energy and nanomaterials. The SRM AP Professors; Prof. D Narayana Rao, Prof. G S Vinod Kumar and Prof. Ranjit Thapa explained the key points of the research to the ARCI Director. During the event, an understanding was reached on issues such as research partnership between the two organisations and the design of research facilities. Director Dr. Tata Narasinga Rao assured that ARCI would extend full cooperation in areas such as research assistance in the selected fields and provide other facilities. Prof. Narayana Rao affirmed that ARCI has agreed to provide necessary funds for the development of solid electrolytes used to manufacture Lithium Ion batteries.
The SRM University-AP team met Dr. Tata Narasinga Rao, Director, International Advanced Research Centre for Powder Metallurgy and New Materials (ARCI, Hyderabad) on 7 April 2022, Thursday. ARCI is an internationally acknowledged autonomous body under the Department of Science and Technology (DST), Government of India. Ten professors, led by SRM University Pro-Vice-Chancellor, Prof. D Narayana Rao, went to Hyderabad to meet the ARCI Director. Projects related to key advanced materials in the field of scientific research were discussed during the meeting. Discussions were held on research projects related to additive (3D) manufacturing, solar energy materials, automotive energy and nanomaterials. The SRM AP Professors; Prof. D Narayana Rao, Prof. G S Vinod Kumar and Prof. Ranjit Thapa explained the key points of the research to the ARCI Director. During the event, an understanding was reached on issues such as research partnership between the two organisations and the design of research facilities. Director Dr. Tata Narasinga Rao assured that ARCI would extend full cooperation in areas such as research assistance in the selected fields and provide other facilities. Prof. Narayana Rao affirmed that ARCI has agreed to provide necessary funds for the development of solid electrolytes used to manufacture Lithium Ion batteries. - Launching antenna-multiplexer for seamless IoMT connectivity May 2, 2022
Dr Divya Chaturvedi, Assistant Professor, Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, has come up with an exciting proposal for enhanced connectivity and high-speed data transmission across the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) devices. Her research paper titled “Design of Antenna-Multiplexer for Seamless On-Body Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) Connectivity” has been published in the journal ‘IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs’, having an impact factor of 3.71. It was published in collaboration with Dr Arvind Kumar from Vellore Institute of Technology and Dr Imaculate Rosaline from Ramaiah Institute of Technology, Bangalore.
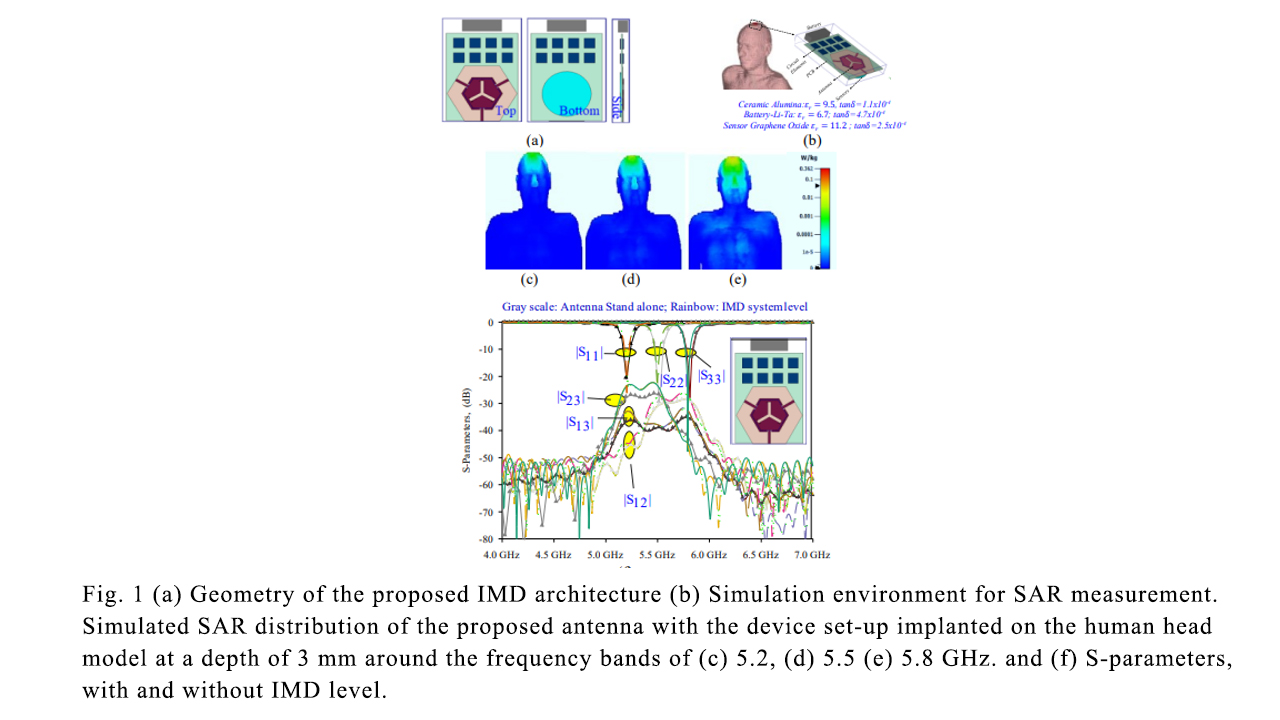
The research looks into the design and development of a multi-band self-triplexing antenna for Medical Things (IoMT) applications. The antenna is designed to operate at 5.2, 5.5 and 5.8 GHz and self-isolation is achieved below -23.9 dB. It also offers seamless communication links to other devices operating at the same frequencies. The designed antenna is cost-effective and compact in size, that can easily fit into any implantable medical device. To avoid the harmful effect of radiation, the SAR value should be <1.6 W/kg. The SAR for this antenna is achieved at 0.362 W/kg in a very simple profile. Due to its compact size, the antenna can be easily mounted in a wireless portable device. The self- triplexing property of the device also enables full-duplex communication between different devices in a single antenna. This design suggestively simplifies the density of the RF front-end subsystem and leads to a simple and efficient communication system.
Abstract of the Research
Here, a compact design of antenna-multiplexer is engineered specifically to meet the stringent requirement imposed by intricate subsystems operating at 5.2, 5.5, and 5.8 GHz frequency bands for Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) applications. The proposed design includes a hexagonal-shaped substrate integrated waveguide (HSIW) cavity, tripole-shaped radiating slot, tuning vias, and three inset microstrip feedlines. A tripole-shaped slot is imprinted on the top of the SIW. This slot subdivides the cavity into trio-radiating segments and each segment offers a single frequency band. Further, the frequency bands are tuned at 5.2/5.5/5.8 GHz. The design maintains mutual port isolation better than 23.9 dB. Compared with the conventional tri-frequency antennas, the proposed design is highly compact and doesn’t need any additional circuitry to improve the port isolations. The measured results confirm the expected performance of the design. Furthermore, the proposed antenna is optimized within an implantable medical device (IMD) and simulated inside a realistic Human Head model at a depth of 3 mm and the Specific Absorption Rate (SAR) value is estimated. The SAR values are well below 0.362 W/Kg at the functioning bands due to the unidirectional radiation pattern from the antenna.
Her future research plan includes designing and developing a cost-effective bra-like prototype of Antenna-Array Sensors for breast cancer detection.
- Paridhaan: Celebrating the myriad hues of India May 2, 2022

“India is the One land that all men desire to see and having seen once, by even a glimpse, would not give that glimpse for all the shows of all the rest of the globe combined” – Mark Twain
His words express the wonder of experiencing the myriad shades of culture thriving on the Indian landscape. Celebrations marking the beauty of our enriching tradition are indeed reminders of the boundless diversity of this country. An ethnic day is an occasion to look back and marvel at the greatness of Indian civilization. It endows us with an opportunity to embrace and rejoice in the shimmering diversity of our motherland. Such good times are meant to be cherished forever as it ties together the manifold differences our people foster.
The Department of Student Affairs proudly organised ‘Paridhaan’, an Ethnic-Cultural event for celebrating the rich Indian heritage. Students came decked up parading the exquisite fashion culture existing across different parts of the nation. The day was brimming with high-sprits and festivity as students from different parts of the country came attired in their traditional outfits flaunting their cultural legacy. An array of dance and musical performances was organised for students to put their talent and vigour on display.
There were programmes ranging from solo musical performances to dance medleys and fashion shows. The stage was set on fire with a live opera performance of Sanjana, who mesmerised the crowd with her mellifluous voice. Equally stunning was the musical entertainment of Amrit who weaved magic with his Santoor, playing the Hamsadhwani raga. Each performer enthralled the audience with different musical stylings, such as mashups, raps and so on. The crowd was also clamouring with joy at the rocking dance performances by the students of the dance club.
The major highlight of the day was the fashion show. The participants adorned the stage with ravishing ethnic outfits representing their cultural distinctiveness. There were portrayals of different dressing styles of India as well as countries like China and Africa. Donning the garbs of different regions from Assam to Gujarat and Kerala, even dating back to the times of the Mughal Era, the show dazzled the crowd with enchanting hues. The celebrations came to a closure with a few more delightful performances. All the SRM dignitaries including the Vice-Chancellor, Prof V S Rao, took part in the celebrations and congratulated the students for making the event a huge success.
Continue reading → - Unwinding the transgender travails April 26, 2022

Embracing one’s transgender identity is a tremendous act of courage in a world that refuses to acknowledge their very existence. The narrations of their trials and tribulations continue to prevail despite the measures taken by the state machinery to assert their rights or the transgender revolution that spilt over in recent times. So long as the society continues to deny them a conducive space to exert their existence, the transgender community will have to endure hardships in all walks of life. The present-day researchers have increasingly shifted their focus on the LGBTQIA+ community to unravel their survival tales and awaken the population to their basic human rights.
Dr Anu Kuriakose, Assistant Professor from the Department of English, has also been looking into transgender lives and the anomalies in their representation. Her research analyses the inclusion and representation of transgender people in Indian films with a specific focus on the shift in representational politics and inclusive strategies in films of late. She has recently published a paper titled “Deconstructing the Trans-Inclusivity Myth in Chandigarh Kare Aashiqui” in the Economic and Political Weekly.
The article offers a critical reading of the Hindi film Chandigarh Kare Aashiqui (2021), which appears to maintain an inclusive outlook towards the queer community. Through the article, Dr Anu draws attention to the glaring presence of transphobic and homophobic attributes even in such progressive films. Her research attempts to analyse whether there have been any significant shifts in trans representation and inclusion in contemporary cinema.
She has also published two chapters, “The Impact of COVID 19 Pandemic on Employment and Livelihood Opportunities of Transgender Community in Kerala” and “The Double Marginalization of Transgender People During the COVID 19 Pandemic”, in the books COVID-19 Pandemic and the New Normal and Keralam in the Path of Survival respectively. The works recount the unspoken sufferings underwent by the transgender community in Kerala during the pandemic times. The chapters were co-authored by her peer, Dr Vinshi P K.
Her upcoming research plans include addressing gender diversity and inclusion in academic discourses in the vernacular of Kerala and critically reviewing the representational politics of trans femininity in visual cultural texts. By researching the portrayals of transgender community, Dr Anu intends to enhance awareness on the deviant representation of queer community in the realms of literature.
Continue reading → - High gain boost converter fed inverter for better power supply April 26, 2022
The Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering is glad to announce that Dr Ramanjaneya Reddy, Assistant Professor; his students, Mr Rahul Kotana and Ms SK Hima Bindu have published a paper titled “High Gain Boost Converter Fed Single-Phase Sine Pulse Width Modulated Inverter” in the journal ‘International Journal of Renewable Energy Research’ having a Scopus site score of 4.2.
Abstract of the Research
A high gain boost converter fed single-phase voltage source inverter with its control for DC to AC power conversion in uninterrupted power supply and renewable energy applications is presented in this paper. The conventional DC-DC boost converter with a coupled inductor and switched capacitor is utilised to obtain high gain. Further, the output voltage of the inverter is controlled by the sinusoidal pulse width modulation technique. The detailed design and analysis of a high gain boost converter fed single-phase voltage source inverter is presented. The sine pulse width modulation control scheme for the voltage source inverter is also developed and presented. To validate the high gain boost converter fed single-phase voltage source inverter, the simulation model is developed in the LTspice software environment, and the results are validated. The results show high gain boost converter achieves a gain of about 10 and the single-phase voltage source inverter can provide an rms voltage of 228 V without using the step-up transformer. The total harmonic distortion of output current is found to be below 4.
About the Research
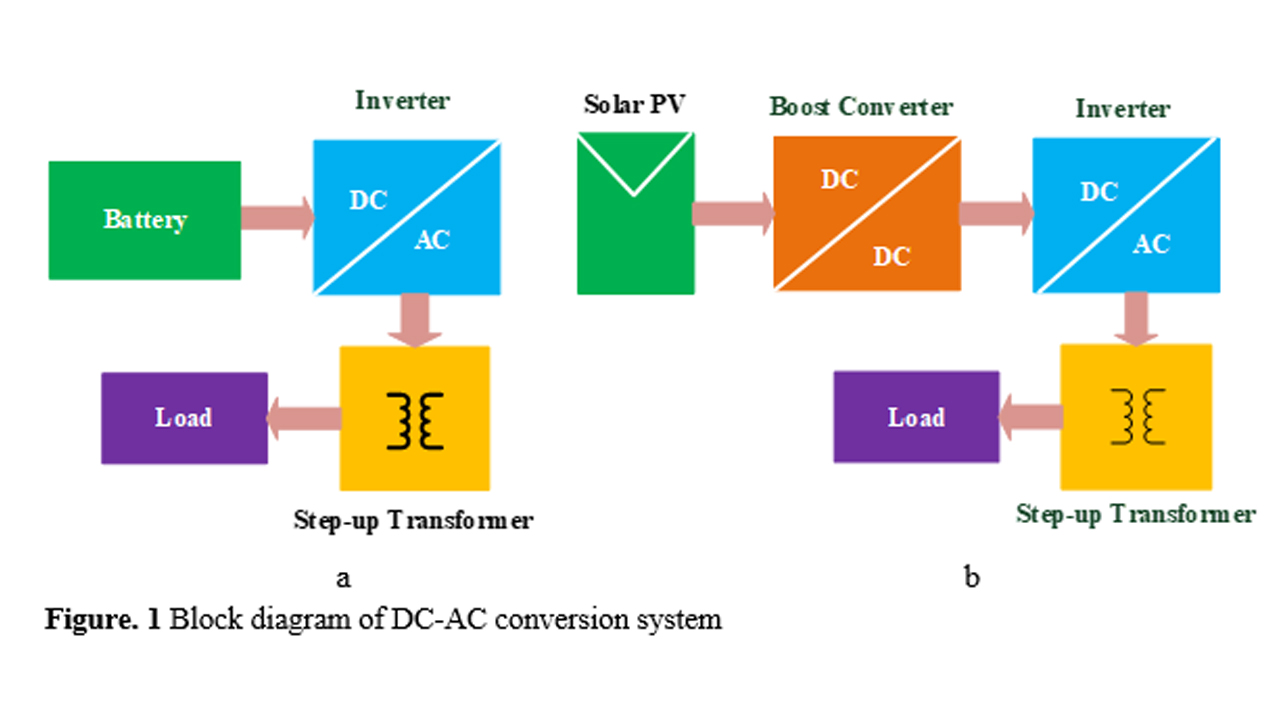
Energy is an essential factor for the functioning and economic development of the industrialized world. It plays a key role in our day-to-day life. On the other hand, energy management has become a critical factor for our successive economic prosperity. The energy consumption process frequently needs either DC-AC conversion or AC-DC conversion. The DC-AC conversion finds its major application in uninterrupted power supply (UPS) and renewable energy (RE). To supply during power outages, most UPS systems use batteries, usually lead-acid, as the storage mechanism. The battery is supposed to provide the backup in the absence of the grid supply. However, the voltage provided by the battery alone may not be enough to provide the backup. At first, the battery output power which is DC needs to be converted to AC with the help of an inverter. Apparently, the output of the inverter needs to be stepped up with the help of a step-up transformer to achieve an output of 220V 50Hz. An alternative approach to the same process is by using a power electronic converter called the DC-DC boost converter. The boosting of battery/PV voltage can be achieved with the help of a standard boost converter as shown in Fig. 1(b), or by using a battery capable of supplying higher voltage and a step-up transformer as shown in Fig. 1(a). High power batteries and step-up transformers can be eliminated if a high gain boost (HGB) converter is used instead of a standard boost converter. The HGB converter fed DC-AC conversion system is presented in this paper which eliminates the step-up transformer. The circuit configuration of the proposed work is depicted in Fig. 2.
Practical Implementations of the Research
The DC-AC conversion method proposed is based on the HGB converter fed single-phase SPWM inverter. The proposed model is best suited when a low voltage DC supply is available, and a standard 230V AC output is needed to deliver the load. The detailed design and analysis of the HGB converter are carried out, and the gain of the converter is achieved at around 10, which is very high compared with conventional boost converter topologies. A unipolar SPWM control scheme is developed in LTspice to control the single-phase VSI. The simulation results of the complete DC-AC conversion system are in close agreement with the design parameters. Further, the total harmonic distortion of the output current waveform is around 4% which is well below the international standards. In addition, the complete model consisting of both HGB converter and single-phase VSI are successfully simulated for an input of 36 V DC and produced an rms output voltage of 228 V.
In future, the DC-AC conversion method based on a high gain boost converter can be extended with the three-phase voltage source inverter with electric drive applications.
Continue reading →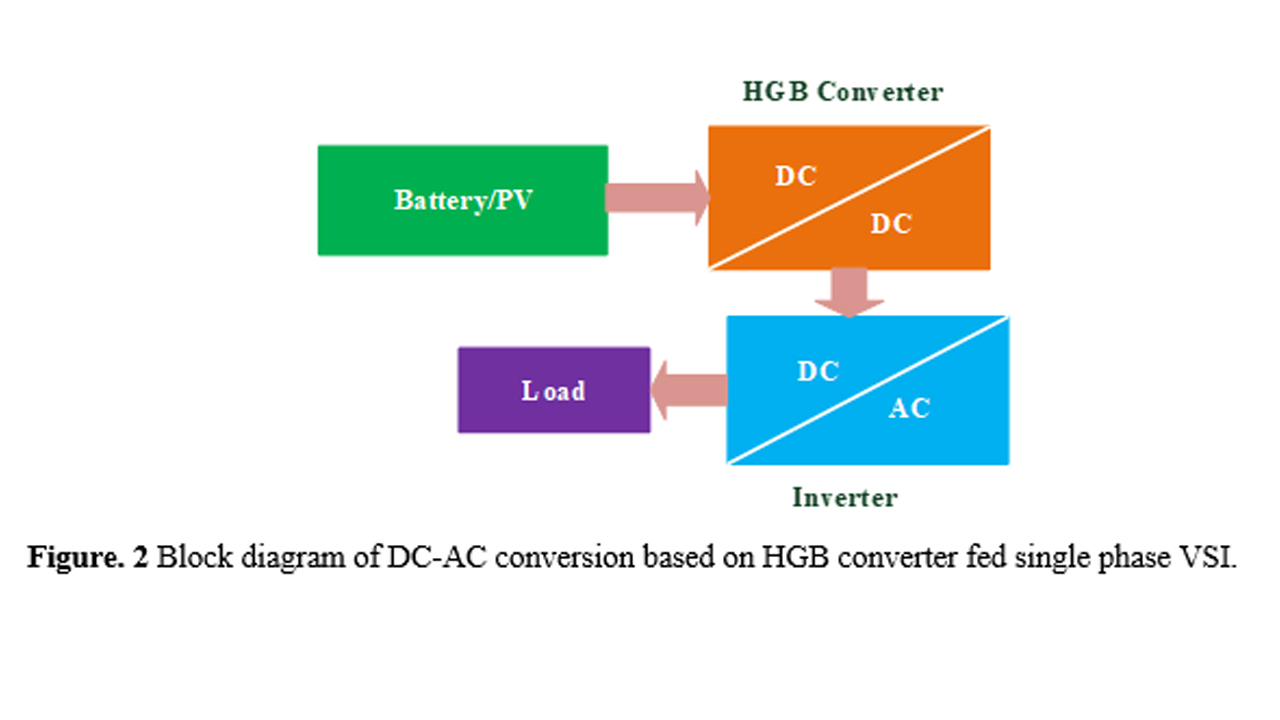
- C-SMILE: Pertinent feedbacks and effective learning April 21, 2022

“The correct analogy for the mind is not a vessel that needs filling, but wood that needs igniting” – Plutarch
Where would you go to get the most appropriate feedback to improve your learning? Whom would you approach? An active learner requires continuous assessment. Exposure to relevant remarks can make a significant impact in the learning output. Choosing the right source of feedback is important to locate your position in the learning ecosystem. This is where C-SMILE enters the frame.
The Department of Computer Science and Engineering is delighted to inform you that the patent application (202241010415) entitled ‘Classification of Student’s Misconceptions in Individualized Learning Environments (C-SMILE)’ got published. The patent application was submitted by Associate professor Dr Sobin C C and BTech final year student Meka Varsha as part of the Capstone Project.
C-SMILE is an innovative platform which allows students to take assessment and receive feedback based on their performance and misconceptions. This targets to refine their conceptual and individualised learning. The platform offers the benefits of automated identification of misconceptions and classification of their level of conceptual clarity. This eventually leads to pertinent feedbacks and ensures quality learning. It also helps engineering educators to classify their students into different categories based on their level of conceptual clarity. Short quizzes and multi-level assessments can utilise the objective of this platform.
Dr Sobin C C and Meka Varsha have collaborated with Mr Subheesh N P from IIT Madras and Mr Jahfar Ali from IIT Hyderabad as part of this work. The team has already published 2 conference papers. One of them is in the prestigious IEEE Global Engineering Education Conference (EDUCON 2022), which is the flagship conference of IEEE Education Society.
The researchers are now working on to extend this concept to incorporate Bloom’s taxonomy to formulate more specific questions based on their level in the cognitive domain.
Continue reading → - Presenting our first doctorate holder: Dr Vasavi Dutt April 21, 2022
 The university revels in its monumental achievement of bringing out the maiden doctorate degree holder, Dr Vasavi Dutt, within four years of its inception. Dr Vasavi Dutt enrolled as a PhD scholar in the Department of Chemistry, under the supervision of Dr Nimai Mishra, Assistant Professor, in 2018. She received the academic honour for her research thesis titled “Improvement of Photoluminescence and Achieving the Stabilization of Cesium Lead Halide Perovskite Nanocrystals for Light-emitting Applications”. Dr Vasavi has been an extremely diligent student and she mustered up immense courage to bring her research to closure even during the testing times of the pandemic.
The university revels in its monumental achievement of bringing out the maiden doctorate degree holder, Dr Vasavi Dutt, within four years of its inception. Dr Vasavi Dutt enrolled as a PhD scholar in the Department of Chemistry, under the supervision of Dr Nimai Mishra, Assistant Professor, in 2018. She received the academic honour for her research thesis titled “Improvement of Photoluminescence and Achieving the Stabilization of Cesium Lead Halide Perovskite Nanocrystals for Light-emitting Applications”. Dr Vasavi has been an extremely diligent student and she mustered up immense courage to bring her research to closure even during the testing times of the pandemic.In the words of Dr Nimai Mishra, “It was a great privilege for me to supervise Ms Vasavi, (correct me Dr Vasavi now) as my first PhD student. She joined my research lab in July 2018 when there was no lab at all, and we started our work at Chemistry BTech Lab”. Dr Mishra was gleaming with pride as he spoke more about his scholar, “During these three and a half years, I had relentless scientific discussions with Vasavi which enriched both of us. Her attitude towards research was remarkable, whenever I gave her a research problem, she used to come up with a detailed outline of how to go ahead with the project”. He also praised her for all her accomplishments which include the publication of 13 research papers, filing of 3 patents and winning the best poster in national & internal conferences.
Dr Vasavi also shared her happiness for having received the mentorship of Dr Mishra, “Working in Dr Nimai Mishra’s lab was a great experience. I had the opportunity to engage and initiate multiple research topics and collaborations. He has always encouraged me to explore new fields to broaden perspectives and bring together new ideas”. She also expressed her gratitude to him for being a welcoming and approachable mentor. “I’m eternally thankful to Dr Mishra for his friendship, empathy, and moreover, for his great sense of humour”. She currently resides in the US with her family. Now that she has successfully completed her PhD, soon she would start looking for a job or rather pursue a post-doctoral fellowship in America.
Dr Vasavi was out of words to thank the university for facilitating and bringing the best in technology and infrastructure for advanced research. “I can never thank my university enough for extending a hospitable environment and nutritious food for all the doctorate students”, she further mentioned. The university serves as a promised land for thousands of research aspirants like her to head towards their dream of making unfeigned contributions to academia.
- Do you think CSIR-JRF is a tough nut to crack? Persistence is the key April 21, 2022

“Believe you can and you’re halfway there.” – Theodore Roosevelt
Jesni M Jacob, currently doing research under Dr Mahesh Kumar Ravva narrates her journey to achieving CSIR-JRF All India Rank of 65 through persistent efforts.
I’m working in the field of computational chemistry on designing and developing organic molecules for OLED applications. Securing an AIR of 65 in the CSIR JRF in Chemical Science June 2021 exam is a dream come true moment for me.
In 2019, I completed my post-graduate studies at Madras Christian College, Chennai. The four-year-long journey from zero to JRF AIR 65 was of hard work, patience, sleepless nights, sacrifices and even frustrated moments. It was challenging to remain motivated after multiple unsuccessful attempts. But I wasn’t ready to give up hope. I believed in myself and dreamed big with faith in God Almighty.
My previous attempts didn’t provide me with any hope of continuing my preparation because my marks were consistently far below the cutoffs. That made me realise one thing: without coaching and ample guidance, qualifying for CSIR JRF is a toiling task for an average student. But I learned that with strong passion, proper dedication, and right strategies of do’s and don’ts, any aspiring student can pass the exam with flying colours.
After each attempt, I learned from my mistakes and tried to optimise my strategies. One should never try to cover the entire syllabus and be bothered about it. I analysed the unit-wise weightage and narrowed it down to a few important topics that I found exciting and comfortable.

- Choose topics carefully and focus solely on mastering them.
- Try to stick to and rely on reliable standard textbooks as much as possible.
- The SRMAP library provided me with excellent access to a wide range of standard texts.
The JRF aspirants should try to solve previous years’ questions from standard exams (CSIR, GATE, IISc, etc.) and note new concepts or approaches every day. Enjoy and prepare short notes with a lot of scribbling and highlighting in various colours. Notes should be concise and simple to revise later. But don’t spend too much time making notes.
I made time for exam preparation along with my work and research activities. I’m grateful to my family, teachers, and especially my guide- Dr Mahesh Kumar Ravva, for their constant support and encouragement. He gave me a safe space to express my desire to ace the exam and my anxieties about it. Dr Mahesh always listened to my concerns and helped me to gain clarity on my thoughts. He always encouraged me to dream big and shared his perspectives and lessons from his life experiences. He is a great mentor, motivator, and teacher to me.
Continue reading →












