Dr Sanjay Kumar and Team Publish Digital Image Security Invention in the Patent Office Journal
 In a recent development, Dr Sanjay Kumar, Assistant Professor in the Department of Computer Science and Engineering, along with a team comprising N Ujwala, J Yashwanth Sri Ram, J Lakshmi Prasanna Kumar, and K Heman Rai Choudhary, have successfully filed and published an innovative invention in the Patent Office Journal titled “SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR DISCRETE WAVELET TRANSFORM (DWT)-BASED SECURE IMAGE WATERMARKING” with the application number “202441045387”.
In a recent development, Dr Sanjay Kumar, Assistant Professor in the Department of Computer Science and Engineering, along with a team comprising N Ujwala, J Yashwanth Sri Ram, J Lakshmi Prasanna Kumar, and K Heman Rai Choudhary, have successfully filed and published an innovative invention in the Patent Office Journal titled “SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR DISCRETE WAVELET TRANSFORM (DWT)-BASED SECURE IMAGE WATERMARKING” with the application number “202441045387”.
This invention holds great promise in the field of digital image security and watermarking. The patented system and method are based on the discrete wavelet transform (DWT), a widely used signal processing technique, to embed secure watermarks into digital images. The application of DWT ensures that the watermarking process is robust and secure, making it suitable for a wide range of applications where image integrity and authenticity need to be ensured.
Dr Sanjay Kumar’s expertise as an Assistant Professor, coupled with the team’s skills and dedication, has resulted in the successful development and patenting of this cutting-edge technology. The “SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR DISCRETE WAVELET TRANSFORM (DWT)-BASED SECURE IMAGE WATERMARKING” promises to be a significant addition to the field of digital image security and watermarking, offering enhanced protection against unauthorised tampering and misuse of digital images. It is expected that this invention will garner attention from industry professionals, researchers, and policymakers, paving the way for its integration into diverse digital imaging systems.
Abstract
Our research introduces a robust image watermarking technique that combines Discrete Wavelet Transform (DWT) and chaotic map-based encryption. The method analyzes high-frequency sub-bands derived from DWT applied to the blue channel of an RGB image, selecting the block with the highest energy for embedding a grayscale watermark encrypted with the Henon Map. The alpha blending technique is used to integrate the encrypted watermark, ensuring both imperceptibility and robustness. The method achieves an average PSNR of 43.7211 dB and SSIM of 0.9950. The watermark can be extracted by analyzing patterns in the high-frequency component, even after various attacks, using inverse DWT and Henon Map for decryption.
Explanation of the Patent in Layperson’s Terms
Our research focuses on protecting digital images by embedding a hidden watermark that is hard to remove. We use a mathematical method called the Discrete Wavelet Transform (DWT) to break down an image into different parts and find the best place to hide the watermark. The watermark is further secured by encrypting it with a technique called the Henon Map. Our method ensures that the watermark remains invisible to the naked eye while being resistant to tampering. This means the watermark can be detected and recovered even if the image is altered.
Practical Implementation and the Social Implications
The primary application of our research is in protecting the ownership and integrity of digital images. This technique can be used by photographers, artists, and digital content creators to ensure their work is not copied or altered without permission. By embedding a secure, invisible watermark, they can prove ownership and detect unauthorised use. Additionally, this method can be applied in sensitive fields such as medical imaging and legal documents where tamper detection is crucial.
Collaborations
This research was conducted by the Visual Information Processing Lab at the Department of Computer Science and Engineering, SRM University AP, Guntur, India. The team comprised Nadella Ujwala, Sanjay Kumar, Jayyavarapu Yaswanth Sri Ram, Jetti Lakshmi Prasanna Kumar, and Katragadda Heman Rai Choudhary.
Future Research Plans
Our future research will focus on enhancing the watermarking technique’s robustness against more sophisticated attacks, exploring real-time applications in video watermarking, and developing methods to embed multiple watermarks in a single image. We also aim to reduce the computational complexity to make the algorithm more efficient for practical applications.
- Published in CSE NEWS, Departmental News, News, Research News
Research to Revenue: 3-day Workshop Concludes
 The Office of the Dean-Research and IPR Cell at SRM University-AP hosted a highly impactful 3-day Workshop on “Research Commercialisation.” The workshop was graced by industry expert Mr Rakesh Sharma, a leading figure in business restructuring and global marketing. Mr Sharma with his notable experience of 38 years at Philips, imparted valuable insights on innovation, venture development, and commercialisation.
The Office of the Dean-Research and IPR Cell at SRM University-AP hosted a highly impactful 3-day Workshop on “Research Commercialisation.” The workshop was graced by industry expert Mr Rakesh Sharma, a leading figure in business restructuring and global marketing. Mr Sharma with his notable experience of 38 years at Philips, imparted valuable insights on innovation, venture development, and commercialisation.
The workshop was attended by faculty and research scholars, all keen on understanding the intricacies of research commercialisation. The inaugural ceremony of the workshop was highlighted by the felicitation of Mr Sharma by the Vice Chancellor, Prof. Manoj K Arora, along with Prof. Ranjit Thapa, Dean—Research; Deans of the three schools; Prof. G S Vinodkumar, Coordinator—IPR Cell & Convenor of this workshop; and other senior faculty members.
In his address, Prof. Manoj K Arora underscored the critical role of research, he urged the attendees to “think differently and change your mindset to unlock the boundless potential of your research and innovation.” He engaged with faculty and research scholars, seeking their perspectives. Prof. Ranjith Thapa, the Dean of Research, presented an overview of the varsity’s research capabilities, spotlighting its achievements in Q1 publications and patents across different departments.
Day 1– The workshop kicked off with Mr Sharma encouraging participants to voice their queries and concerns about commercialisation. Key discussion points covered included linking university research with practical applications, the transformation of patents and research into industry-ready products, understanding market needs, fundraising for research projects, and leveraging humanities and liberal arts in patent implementation. Mr Sharma engaged with each of the queries and closely explained to the students with simple and easy-to-understand examples, thereby making the session worthwhile and interesting.
Day 2—Scholars had the opportunity to present their published and granted patents. They received constructive feedback from faculty and Mr Sharma and understood how these patents could be further developed for commercialisation, thereby leading to fruitful discussions on improving and materialising these ideas.
Day 3– A significant outcome of the workshop was the proposal to establish a new centre for research commercialisation designed to offer students an in-house pathway to commercialise their patents. This initiative received widespread acclaim from all participants and sparked engaging discussions about transforming research into viable business ventures, facilitated by the session by the Director of Entrepreneurship and Innovation, Mr Sidharth Shankar Tripathy.
The workshop offered a crucial platform for students, offering both inspiration and guidance in their pursuit of entrepreneurship. The event was specifically designed for all PhD Scholars who are currently working on their research papers and looking for ways to commercialise their innovative ideas, projects, or inventions.
Through a series of expert-led sessions, interactive discussions, and networking opportunities, students were encouraged to think critically about their project’s potential impact, market readiness, and the pathways to achieving sustainable business growth.
- Published in News, Research, Research News, Research Workshop, Workshop
MOU with ASPIRE BioNEST, UoH for Augmenting Innovation and Incubation

SRM University-AP signs an MOU with the Association for Scientific Pursuits in Innovative Research BioNEST (ASPIRE BioNEST) of the University of Hyderabad, facilitating a dynamic transformation in the innovation and entrepreneurial ecosystem of the institute. Prof. S Rajagopal, Director ASPIRE BioNEST and Dr R Premkumar, Registrar, SRM University-AP signed the MOU in the presence of Dr Anil Kondreddy, COO, ASPIRE BioNEST, Prof. Jayaseelan Murugaiyan, Associate Dean-Sciences, SRM University-AP and Dr Pitchaiah Cherukuri, Assistant Professor, SRM University-AP.
The agreement will ensure guidance and support from ASPIRE BioNEST in establishing, operating and maintaining the best innovation and incubation practices at the SRM AP incubation centres. ASPIRE BioNEST will also provide support in selection of incubates/start-ups, finalising facilities/designs, procurement of instruments and help in formulating guidelines and policies for operating incubation centres at the university.
The MOU is a significant milestone for the young innovators and venturers at SRM AP as ASPIRE BioNEST will furnish internship opportunities with incubatees and startups at ASPIRE, mentor support for startups, collaboration in applying for grant proposals and raising funds, and training and skill development programmes.
Vice Chancellor, Prof. Manoj K Arora expressed his ardour on the collaboration. He stated that “ASPIRE BioNEST is one of the Best Bio-incubator where most of the innovative research is translated into technologies. As an institute that prioritise innovation and entrepreneurship, this MOU will stimulate and enrich SRM University-AP’s entrepreneurial culture, helping us to become one of the preferred incubation and innovation centres in Andhra Pradesh.”
ASPIRE BioNEST of the University of Hyderabad is a deep-tech life sciences incubator established in 2018 with the support of BIRAC, Government of India and ASPIRE, a section 8 non-profit company established by University of Hyderabad. One of the key objectives of ASPIRE BioNEST is to provide support and guidance, including technological, professional and collaborative inputs to help other incubation centres raise their entrepreneurial culture. With the agreement, both SRM University-AP and ASPIRE BioNEST have undertaken to synergistically support each other in the larger interest of innovation and entrepreneurship.
CSE Academic Innovators File Patent for AI-Powered Refrigeration System
 In a significant development for the field of artificial intelligence and sustainable technologies, Dr Subhankar Ghatak, Dr Aurobindo Behera, Assistant Professor, and Ms Samah Maaheen Sayyad, an undergraduate student from the Department of Computer Science and Engineering, have collectively filed a patent for an “Artificial Intelligence (AI) Enabled Refrigeration System.” The patent, bearing the Application Number 202441036548, has been officially published in the Patent Office Journal, marking a milestone in their academic and research careers.
In a significant development for the field of artificial intelligence and sustainable technologies, Dr Subhankar Ghatak, Dr Aurobindo Behera, Assistant Professor, and Ms Samah Maaheen Sayyad, an undergraduate student from the Department of Computer Science and Engineering, have collectively filed a patent for an “Artificial Intelligence (AI) Enabled Refrigeration System.” The patent, bearing the Application Number 202441036548, has been officially published in the Patent Office Journal, marking a milestone in their academic and research careers.
This innovative refrigeration system promises to enhance efficiency and reduce energy consumption, potentially revolutionising the way we preserve food and other perishables. The team’s dedication to integrating AI into practical applications is a testament to their commitment to advancing technology for the betterment of society. The academic community and industry experts alike are eagerly anticipating further details on the implementation and impact of this patented technology.
Abstract
The invention is an advanced smart and AI-enabled refrigerator that seamlessly integrates device and software components. Key features include automatic quantity detection, a reminder system, a spoiler alert system, an inbuilt voice system, an inbuilt barcode scanner, an emotion detection system, and a personalised recipe recommendation system based on user preferences, weather conditions, season, location, and precise quantity measurements.
Research in Layperson’s Terms
The invention represents a groundbreaking improvement in traditional refrigerators, providing a new and enriched user experience through AI integration. It addresses food management, user interaction, and personalised recipe recommendations, incorporating user preferences, weather considerations, seasonal variations, location-specific nuances, and accurate quantity measurements.
Practical implementation and the social implications associated with it
The practical implementation of the “AN ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE (AI) ENABLED REFRIGERATION SYSTEM ” involves the seamless integration of advanced hardware and sophisticated AI algorithms to create an intelligent and user-friendly refrigerator. The following steps outline the practical implementation:
Hardware Integration:
Sensors: Install advanced sensors, including thermistors for temperature, humidity sensors, barcode scanners, ultrasonic quantity measurement sensors, cameras, spoilage identification sensors, level sensors, defrost sensors, and weight sensors within the refrigerator compartments.
Voice and Emotion Detection Modules: Incorporate a microphone and speaker system for voice interaction and integrate cameras and emotion analysis algorithms for facial recognition and emotion detection.
Connectivity Components: Equip the refrigerator with Wi-Fi or Bluetooth modules to enable seamless data transfer and communication with other smart devices.
Processor and Memory: Utilize a powerful processor and ample memory to support AI algorithms, data processing, and smooth operation.
Display Panel: Implement an LED or touchscreen display for user interaction, providing real-time information and control over the refrigerator’s functionalities.
Software Development:
AI Algorithms: Develop and integrate AI algorithms for automatic quantity detection using computer vision, sentiment analysis for emotion detection, and collaborative filtering for personalised recipe recommendations.
Natural Language Processing (NLP): Implement NLP algorithms to enable the inbuilt voice system to understand and respond to user commands effectively.
Image Recognition Software: Utilize image recognition software to accurately read barcodes and analyse visual data from the integrated cameras.
Connectivity Software: Develop software protocols to ensure reliable wireless communication between the refrigerator and other devices or cloud services.
User Interface Software: Design a user-friendly interface for the display panel, allowing users to interact with and manage refrigerator contents easily.
Social Implications:
The “AI Enabled Refrigeration System” invention has several profound social implications:
1. Reduction in Food Wastage: The automatic quantity detection, reminder system, and spoilage alert system significantly reduce food wastage by ensuring that users are alerted about unused items and potential spoilage. This contributes to more efficient food management and a reduction in household food waste, addressing a critical global issue.
2. Enhanced Food Safety and Health: By providing real-time alerts about food spoilage and precise quantity measurements, the invention ensures that users consume fresh and safe food. This minimizes health risks associated with consuming spoiled food and promotes overall well-being.
3. Personalized Dietary Support: The personalized recipe recommendation system caters to individual dietary preferences and requirements, promoting healthier eating habits. By suggesting recipes based on user preferences, weather conditions, seasonality, and location, the system encourages balanced and nutritious meal planning.
4. Convenience and Efficiency: The inbuilt voice system, emotion detection, and intuitive user interface enhance the convenience and efficiency of managing refrigerator contents. Users can easily access information, receive reminders, and interact with the refrigerator, making food storage and preparation more streamlined.
5. Technological Advancements: The integration of advanced AI technologies in everyday appliances like refrigerators represents a significant step forward in smart home innovation. This can drive further advancements in the field, encouraging the development of more intelligent and interconnected household devices.
6. Environmental Impact: By promoting efficient food management and reducing wastage, the invention indirectly contributes to environmental sustainability. Less food waste translates to lower carbon footprints and reduced strain on food production resources, aligning with global efforts to combat climate change.
Overall, the “AI Enabled Refrigeration System” invention not only offers practical benefits in terms of food management and user convenience but also holds significant social implications by promoting health, reducing waste, and advancing technological innovation in household appliances.
Future Research Plans
Building on the innovative foundation of the “AN ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE (AI) ENABLED REFRIGERATION SYSTEM, ” future research plans involve enhancing the AI algorithms for even greater accuracy in food quantity detection, spoilage prediction and personalised recipe recommendations. This includes exploring more advanced machine learning techniques and incorporating real-time feedback mechanisms to continuously refine the system’s performance. Additionally, research will focus on integrating the refrigerator with broader smart home ecosystems, allowing for seamless interaction with other smart appliances and IoT devices to create a fully connected kitchen experience. Investigations into more sustainable and energy-efficient sensor technologies will also be pursued to further reduce the environmental footprint of the device. Finally, extensive user studies will be conducted to gather feedback and insights, ensuring that the next iterations of the refrigerator are even more aligned with consumer needs and preferences, ultimately driving widespread adoption and maximising the social benefits of this technology.
Pictures Related to the Research
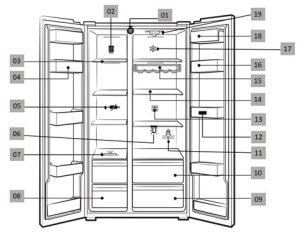
Fig 1: Schematic Arrangement of various Components for adequate operation of the proposed scheme
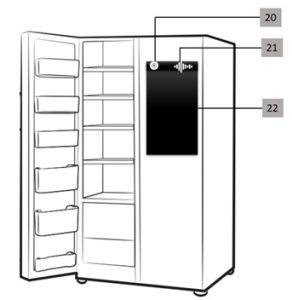
Fig 2: Schematic Arrangement of various Components for user interaction
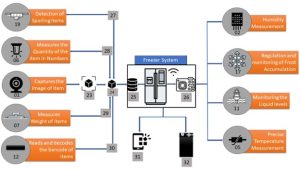
Fig 3: Schematic representation of working of various components in the freezer system
• Pointer Number-27: Spoilage Detection Sensor (19) detects the item that is being spoiled and maps to particular item for alerting the user with the help of the capturing Device (01) and the info associated with that particular item like Expiry date etc.
• Pointer Number-28: The Ultra Sonic Quantity Measurement Sensor (06) senses the quantity of the ITEM “x” (24), and the camera (01) is used to identify what is ITEM “x” through (23).
• Pointer Number-29: Weight Sensor (07), using newly captured item ITEM “x” (24) by capturing device (01), identifies the weight of that item by subtracting the weight obtained after the addition of that item with the initial holding by the cabinet and attaching the value with corresponding ITEM “x” (24).
• Pointer Number-30: Barcode Scanner (12) scans the Barcode associated with the item and maps the corresponding information with that particular item with the help of the capturing device (01).
• Port Number-31: Mobile Application.
- Published in CSE NEWS, Departmental News, News, Research News











