New Theories on Dark Matter: Dr Basabendu Proposes New Insights in Q1 Journal
 In a significant advancement in the field of astrophysics, Dr Basabendu Barman, Assistant Professor in the Department of Physics, has published a groundbreaking paper titled “Dark matter-electron scattering and freeze-in scenarios in the light of \textit{Z’} mediation” in the prestigious Q1 journal, Physical Review D, known for its impact factor of 5.0 within the Nature Index.
In a significant advancement in the field of astrophysics, Dr Basabendu Barman, Assistant Professor in the Department of Physics, has published a groundbreaking paper titled “Dark matter-electron scattering and freeze-in scenarios in the light of \textit{Z’} mediation” in the prestigious Q1 journal, Physical Review D, known for its impact factor of 5.0 within the Nature Index.
Dr Barman’s research delves into the enigmatic realm of dark matter, proposing a novel mechanism through which dark matter might interact with the visible universe via a hypothesised fifth force. This interaction could provide vital insights into the nature of dark matter and its elusive characteristics. The study suggests that if this interaction is confirmed, experiments exploring the existence of a fifth force could concurrently unravel the mysteries surrounding dark matter, leading to a deeper understanding of the universe.
This publication not only highlights the potential for new discoveries in particle physics but also positions SRM University-AP at the forefront of cutting-edge research in dark matter studies. Dr. Barman’s findings could pave the way for further exploration and experimental validation, ultimately contributing to the ongoing quest to decode one of the universe’s greatest mysteries.
Abstract:
We investigate dark matter (DM-)electron scattering in a minimal U〖(1)〗_X extension of the Standard Model (SM), where the DM can appear as a Majorana fermion, a complex singlet scalar, or a Dirac fermion. To study bounds on the new gauge coupling and new gauge boson mass, from DM-electron scattering, we consider several direct search experiments like CDMS, DAMIC, SENSEI, PandaX-II, DarkSide-50, and XENON1T-S2 for different U〖(1)〗_X charges. In this setup, we consider DM production via freeze-in in both radiation-dominated and modified cosmological backgrounds to project sensitivities onto coupling vs mass plane satisfying observed relic abundance. DM-electron scattering could provide comparable, or even stronger, bounds compared to those obtained from the electron/muon (g-2), low-energy scattering, and intensity frontier experiments within mass range of 0.01-0.1 GeV. Constrains from freeze-in could provide stronger sensitivities for new gauge boson masses above about 1 GeV ; however, these limits are comparable to those obtained from LHCb and LEP experiments for mass between 10-150 GeV. In the future, electron-muon scattering (MUonE), proton (FASER and DUNE), and electron/positron (ILC) beam-dump experiments could probe these parameters.
From Layperson’s perspective:
We know there are four fundamental forces in nature: strong, weak, electromagnetic, and gravitational. But what if there’s a hidden, fifth force we haven’t discovered yet? The Standard Model of particle physics, which organizes all known particles, doesn’t include this fifth force (and doesn’t include gravity either, unfortunately). So, how can we theoretically create a particle physics model for this possible fifth force? That’s what we explore in this paper. Interestingly, there are already experiments (for example, the Large Hadron Collider or LHC at CERN, Geneva) searching for signs of fifth forces. If this force exists, our model could be tested by these experiments. But there’s more! We also wanted to tackle a big mystery in cosmology: dark matter. Dark matter makes up about 24% of the universe, but we’ve never directly detected it because it doesn’t reflect light—it’s “dark.” However, there are smart ways to try to find it. In this paper, we propose how the same dark matter might interact with the visible universe through this fifth force and thereby leave their footprints. If true, therefore, the experiments looking for the fifth force could also give us clues about the nature of dark matter.
Title:
Dark matter-electron scattering and freeze-in scenarios in the light of Z’ mediation.
In BibTeX (citation) format:
@article{PhysRevD.110.055029,
title = {Dark matter-electron scattering and freeze-in scenarios in the light of ${Z}^{\ensuremath{‘}}$ mediation},
author = {Barman, Basabendu and Das, Arindam and Mandal, Sanjoy},
journal = {Phys. Rev. D},
volume = {110},
issue = {5},
pages = {055029},
numpages = {20},
year = {2024},
month = {Sep},
publisher = {American Physical Society},
doi = {10.1103/PhysRevD.110.055029},
url = {https://link.aps.org/doi/10.1103/PhysRevD.110.055029}
}
Practical Implementations & Social Impact:
The primary goal of this study is to explore what lies beyond the known, visible universe. This curiosity has driven humanity for centuries—to build rockets and explore outer space and to smash particles in colliders, searching for the mysteries hidden within the atom. The desire to uncover the unknown, to shed light on the darkness, is a fundamental part of what it means to be human. In this sense, the work contributes to the realm of pure intellectual pursuit. Science speaks the language of data, and data is born from experiments. The validation of any well-constructed theory ultimately depends on experimental evidence. For this reason, it is essential for society to cultivate a culture that values fundamental scientific discussion and increases funding for basic research.
Collaborations:
This work was done in collaboration with Prof. Arindam Das from the Department of Physics, Hokkaido University, Sapporo, Japan, and Dr. Sanjoy Mandal from the Korea Institute for Advanced Study (KIAS), Seoul, Korea.
Future plans:
- A closer look into early universe dynamics by performing more involved simulations.
- Connection between particle physics models and early Universe cosmology.
- Complementary searches from different experiments in unravelling new physics beyond the Standard Model.
- Searching new physics at energy and intensity frontier.
- Published in Departmental News, News, Physics News, Research News
Language Lab to Boost Student Communication Skills
 The Department of Literature and Languages at SRM University-AP celebrated the launch of its Language Lab, a state-of-the-art, 70-seater facility designed to enhance the Listening, Speaking, Reading, and Writing (LSRW) skills of its students.
The Department of Literature and Languages at SRM University-AP celebrated the launch of its Language Lab, a state-of-the-art, 70-seater facility designed to enhance the Listening, Speaking, Reading, and Writing (LSRW) skills of its students.
The inauguration was witnessed and officiated by the honourable Vice Chancellor, Prof. Manoj K Arora, along with Prof. Vishnupad, Dean- ESLA; Prof. C V Tomy, Dean-SEAS, Dr Vinayak Kalluri, Dean-Academic Affairs, Ms Suma N, CFAO; Dr Sayantan Thakur, Assistant Professor and Head; Dr Karthik Rajendran; Dr Srabani Basu, other faculty members, research scholars and students.
The laboratory, valued at 10 million rupees, is equipped with Sanako and Lanquill software, providing students with access to advanced resources. During the event, Vice Chancellor Prof. Manoj K Arora emphasised the value of communication he stated “Communication is an essential skill. With this lab, our students have a real opportunity to build those skills and contribute meaningfully to society.” he also voiced that, In future, the varsity will also be looking forward to opening this facility to the wider community so that more people can benefit from this resource.
Dr Thakur and Dr Amlan Baisya, Assistant Professors at the university, provided insights into the laboratory’s cutting-edge software and technology. They explained how these tools can significantly enhance the learning experience, making language acquisition more interactive and engaging. The faculty expressed their excitement about the opportunities this facility will create for both students and instructors alike.
Prof. Arora took a moment to commend the Department of Literature and Languages and the Directorate of Information Technology and Knowledge Management (ITKM) for their commitment to advancing education through innovative resources. He underscored the bright future ahead, not only for students but for the entire university community, as they leverage this new laboratory to improve communication skills that are vital in both academic and professional settings.
- Published in Departmental News, English Current Happenings, English news, News
Dr Sayantan’s Research Paper on Overcoming the Digital Divide

In the context of online English education in India, the “digital divide” has emerged as a significant obstacle, especially for students from rural or underprivileged areas. Dr Sayantan Thakur, Assistant Professor at the Department of Literature and Languages in his article introduces a research study titled “Navigating the Digital Divide: Challenges and Strategies in Teaching Communicative English Online in Indian Classrooms,” which aims to address the unequal access to online learning tools.
Abstract
The advent of online learning platforms is providing new opportunities for English language learning (ELL) in India. However, there is a significant challenge posed by the digital divide – the gap in accessing technology. This study investigates what causes the digital divide in internet ELL classrooms such as infrastructure limitations, device ownership and usage, and digital literacy skills; and how they affect student engagement, development of communication skills, and overall learning experiences. It suggests ways to bridge this gap which include government policies on infrastructure development; affordable tech solutions like mobile apps; teaching programs that enhance digital literacy among learners; support for teachers involved in web-based pedagogy. Through these recommendations, education stakeholders can create an inclusive cyberspace for all students where their communication abilities will be nurtured throughout different parts of India.
The Practical Implementation
The practical implementation of your research on “Navigating the Digital Divide: Challenges and Strategies in Teaching Communicative English Online in Indian Classrooms” has far-reaching social implications. By addressing the digital divide, your work can help level the playing field in education, especially for students from underprivileged backgrounds.
Improved Access to Education: Implementing strategies like infrastructure development, affordable mobile-based learning tools, and digital literacy programmes can provide more students, especially in rural and low-income areas, access to online English learning resources. This improves their chances of acquiring essential communication skills, opening doors to better job opportunities.
Empowering Teachers: Equipping teachers with digital tools and training enables them to deliver more effective online lessons, increasing student engagement and success rates.
Reducing Inequality: Bridging the technology gap can reduce educational disparities between urban and rural areas, promoting social mobility and reducing the long-term impacts of inequality.
Building a Digitally Literate Society: Enhancing digital literacy among students and teachers fosters a society better prepared for the demands of the modern workforce, ultimately contributing to economic growth and social inclusion.
Future Research Plans
- Regional Literature in Translation
- Tantric Tradition and Eastern Indian Literature
- Folk Music of Bengal
- Indian Philosophy, Aesthetics & Literature
- Published in Departmental News, English Current Happenings, English news, News, Research News
A Sustainable Greywater Treatment Method

Addressing the ever-demanding crisis of water scarcity, Dr Mohit Aggarwal, Assistant Professor from the Department of Civil Engineering, has published a paper titled “Polyculture Microalgae and Zno/GAC-nanocomposite System for Greywater Treatment” in the Q1 journal Biomass and Bioenergy with an impact factor of 5.8. In his research, Dr Aggarwal explores sustainable methods to treat wastewater with algae and nanoparticles, providing an efficient method to reuse greywater and reduce water consumption.
Abstract
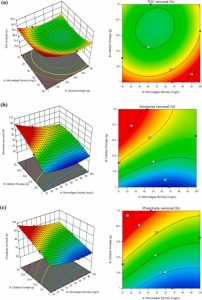
This study explores sustainable greywater treatment using microalgae and a ZnO/GAC nanocomposite in a 15-day batch photobioreactor. The system achieved significant nutrient removal, with 80% TOC, 94.2% PO43−, and 99.6% NH4+ efficiencies. Microalgal growth was enhanced by the nanocomposite, reaching a density of 1.8 g/L. The resulting biomass had a high heating value of 18.32 MJ/kg. The ZnO/GAC nanocomposite maintained effective removal over four cycles. The treated greywater met reuse standards for toilet flushing, with pH 8.5, turbidity <4 NTU, and COD, NH4+, and PO43− of 34, 0.032, and 0.48 mg/L, respectively.
Explanation of the research in layperson’s terms
Water scarcity and pollution are serious problems, and our research aims to find an environmentally friendly way to treat greywater (wastewater from sinks, showers, etc.). We explored the use of algae combined with special nanoparticles (zinc oxide) to clean the water more effectively. The algae grow in the water and help remove harmful substances like carbon, phosphorus, and nitrogen. The nanoparticles make this process even more efficient.
After treatment, the water is clean enough to be reused, for example, in toilet flushing. This method not only helps clean wastewater but also provides a sustainable way to reuse it, which can reduce water consumption and help the environment.
Practical implementation/ Social implications of the research
Practical implementation
The system developed in this research can be implemented in decentralised greywater treatment units, especially in water-scarce areas. It provides a cost-effective, eco-friendly solution for treating household or industrial greywater. The treated water meets the quality standards for reuse in applications like toilet flushing or landscape irrigation, reducing freshwater demand.
Social implications
This research promotes water recycling, contributing to sustainable water management practices and helping to address water scarcity issues. This can improve access to water in communities with limited resources, reduce the pressure on freshwater supplies, and lower the environmental impact of wastewater discharge, leading to healthier ecosystems and communities. Additionally, adopting such systems on a larger scale can foster greater awareness of water conservation and responsible resource usage.
- Published in CIVIL NEWS, Departmental News, News, Research News