Revisiting Clément Baloup’s Comics through Dr Gusain’s Research

SRM University-AP is proud to announce that Dr Abhilasha Gusain, Assistant Professor in the Department of Literature and Languages has made an outstanding contribution to the academic world with her recent publication. Her research paper, “Illustrating Memory: Clément Baloup’s Vietnamese Memories and the Visual Representation of the Past,” featured in 3L: The Southeast Asian Journal of English Language Studies, a Q1-ranked journal known for its high impact in the field.
Abstract
The present study aims to highlight the role that Clément Baloup’s comics, Vietnamese Memories: Leaving Saigon (Volume 1) and Vietnamese Memories: Little Saigon (Volume 2), play in the creation of an alternate archive that validates the forgotten tales and the memories of a neglected past. These texts provide an alternate form of remembrance by materialising the past in the form of images. The two volumes present the unheard experiences of the Vietnamese diaspora that Baloup recorded during his travels to the different parts of France and the U.S. Such experiences bring to the forefront memories that are otherwise kept at the margins or suppressed by the dominant discourse. If not recorded, they will be lost forever. The counter-memory, thus, calls for a reassessment of the idea of a singular past that denies the marginalised memories. It claims representation and restoration in the cultural memory. As works of postmemory, these texts form a link between the past and the present through mediation and give memorability to unremembered accounts. The memories are illustrated, and hence, visual representation becomes important to the task of postmemory here.
Explanation of the Research:
This study emphasises the significance of visual representation in postmemory, showing how the two graphic narratives create a space for counter-memory and contribute to a reassessment of cultural memory by including marginalised experiences. Postmemory is a term used to describe how the memories of one generation are shaped by the stories and experiences of the previous generation. It often relates to events that people haven’t directly experienced, like wars or significant historical events, but feel a strong connection to through family stories, photographs, or cultural narratives. The paper illustrates how Baloup’s works serve as an alternate archival repository, creating a dynamic and inclusive cultural memory that reflects the complex, polyphonic nature of human experience; thus contributing significantly to the fields of comics studies and memory studies.
- Published in Departmental News, English Current Happenings, English news, News, Research News
B Tech Students Pave the Path for Future Entrepreneurs with Vascan Solutions
 SRM University-AP is honoured to recognise the impressive accomplishments of B Tech CSE third-year students Sai Tharun Nelluru and Mahendra Kumar Velicheti, co-founders of Vascan Solutions, a startup aiming to disrupt the retail space. This is especially so when one considers that the decision to venture into entrepreneurship entails taking risks that the norm would prescribe against – seeking employment graduates.
SRM University-AP is honoured to recognise the impressive accomplishments of B Tech CSE third-year students Sai Tharun Nelluru and Mahendra Kumar Velicheti, co-founders of Vascan Solutions, a startup aiming to disrupt the retail space. This is especially so when one considers that the decision to venture into entrepreneurship entails taking risks that the norm would prescribe against – seeking employment graduates.
Vascan Solutions, as a company, is a clear Shiff economics and architecture in Context business solving real problems in the business of retailing. Understanding the pain points that exist for both shoppers and retailers, Sai Tharun and Mahendra created a mobile app intending to improve retailing activity. Shoppers can search for items, navigate inside the store accurately and use their phones to pay for items. This improves the ease of shopping for customers. On the one hand, retailers get valuable information from consumers about what they choose and how often they come. With this information, it is easy for marketers to reorganise the store improve customer service and increase sales.
The creation of Vascan Solutions is a testament to the vision and commitment of SRM AP students. However, their success story also highlights the importance of mentorship, an integral aspect of SRM AP’s entrepreneurial ecosystem. Sai Tharun and Mahendra were guided by Dr Shobin CC and Dr Randhir Singh, who provided technical expertise that helped refine their product and strategy. Additionally, Mr Siddharth Shankar Tripathy, Director of Entrepreneurship & Innovation, SRM University-AP, played a pivotal role in mentoring the co-founders, offering them the support needed to navigate the complexities of launching a startup.
SRM University-AP’s commitment to fostering entrepreneurship is evident in the success of Vascan Solutions. The university takes pride in cultivating an environment where students are encouraged to think creatively, innovate, and challenge the status quo. Sai Tharun and Mahendra’s decision to build their own business demonstrates the transformative potential of this environment. Their entrepreneurial journey serves as an inspiration not only to their peers but also to future generations of students who wish to explore non-traditional career paths and make a meaningful impact on society.
The establishment of Vascan Solutions aligns with SRM AP’s vision of empowering students to become leaders and innovators. The university strongly believes that entrepreneurship is not only a viable career option but also a path that can contribute to societal and economic development. Sai Tharun and Mahendra have proven that with determination, innovation, and the right mentorship, young entrepreneurs can turn challenges into opportunities.
Looking ahead, SRM University-AP is excited to see the continued growth of Vascan Solutions. With a solid foundation and a clear vision, the startup has the potential to scale and expand beyond the retail sector, further solidifying the impact of Sai Tharun and Mahendra’s contributions. As Vascan Solutions evolves, SRM AP remains committed to supporting entrepreneurial initiatives that empower students to become changemakers in their respective fields.
- Published in CSE NEWS, Departmental News, IDEA NEWS, News
Dr Jaidev Advances Green Chemistry with New Acetic Acid Production Technique
 In a remarkable contribution to the field of green chemistry, Dr Jaidev Kaushik, Assistant Professor in the Department of Chemistry, has published a significant research paper titled “Green Light Promoted Photoreduction of Carbonate to Acetic Acid by Zinc Ash-Derived ZCu@ZnO” in the prestigious Q1 journal, ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, with an impressive impact factor of 7.1.
In a remarkable contribution to the field of green chemistry, Dr Jaidev Kaushik, Assistant Professor in the Department of Chemistry, has published a significant research paper titled “Green Light Promoted Photoreduction of Carbonate to Acetic Acid by Zinc Ash-Derived ZCu@ZnO” in the prestigious Q1 journal, ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, with an impressive impact factor of 7.1.
Dr Kaushik’s research addresses the pressing need for sustainable methods of producing acetic acid, a widely used chemical in various industrial applications. The study explores an innovative photoreduction process that utilises green light to convert carbonate compounds into acetic acid using a novel catalyst derived from zinc ash. This approach not only showcases the potential for an eco-friendly production method but also emphasises the recycling of zinc waste, turning a byproduct into a valuable resource.

The paper highlights the efficiency of Zinc Ash-Derived ZCu@ZnO as a catalyst in the photoreduction process, demonstrating its effectiveness under green light conditions. The findings could pave the way for more sustainable practices in chemical manufacturing, aligning with global efforts to reduce carbon emissions and promote environmentally friendly technologies.
This publication underscores the commitment of SRM University – AP to fostering innovative research that addresses contemporary environmental challenges. Dr. Kaushik’s work exemplifies the university’s focus on sustainability and its aspiration to lead in the field of scientific research.
As the demand for sustainable chemical processes grows, Dr Kaushik’s research will likely inspire further investigations and developments in green chemistry, contributing to a more sustainable future.
Abstract of the Research
Mineralized carbon (carbonate) is the readily available carbon dioxide (CO2) source in acidic aqueous conditions. The photoreduction of carbonate to value-added hydrocarbons could be a novel finding performed in the presence of monochromatic visible light and waste-derived photo-active nanomaterials. In this report, we have synthesized ZnO particles from the zinc ash generated as waste in the galvanization process in the steel industry; ZnO particles were decorated with CuO nanoparticles and then further activated by reducing them to get a heterojunction photocatalyst (ZCu@ZnO). After that, ZCu@ZnO is utilized to photoreduce carbonate to acetic acid (AcOH) in a peroxy-rich solvent as a hydrogen-rich solvent under various monochromatic light sources and sunlight. Additionally, different physical and chemical parameters, such as solvent mixture, light sources, photocatalysts, time, etc., were optimized to get the maximum yield of AcOH under monochromatic light of 525 nm wavelength (Green light).
Explanation of the Research in Layperson’s Terms
This report is proposing the solution of two problem statements; first, utilization of zinc ash generated as a by-product after galvanization process; and second, cost-effective and energy efficient process for conversion of carbonates to value-added C2 hydrocarbon.
Practical Implementation and the Social Implications associated with the Research
The process adds value by converting low-value waste into high-value nanomaterials, potentially offering new revenue streams for recycling and waste management industries. It supports the principles of a circular carbon economy and green chemistry focusing on synthesis of hydrocarbons from carbonates.
Collaboration
Dr Sumit Kumar Sonkar (MNIT Jaipur, India)
Future Research Plans
1. The adsorption/photodegradation-assisted quick and efficient removal of next generation advanced pollutants such as microplastic, pesticides, pharmaceutical waste, etc. by hydrophobic carbon aerogel and their doped and functionalized versions.
2. Utilizing waste derived heterogeneous catalysts in organic transformation reactions.
3. Selective sensing of toxic metal ions/biomarkers/biomolecules using fluorescent nanomaterials.
4. Upcycling of carbonates/CO2 via photo/thermal assisted catalyzed reactions to get C1 and C2 hydrocarbons (green fuel).
- Published in Chemistry-news, Departmental News, News, Research News
From Lab to Land: One-Day Workshop Hosted on Road Maintenance & Rehabilitation (M&R)
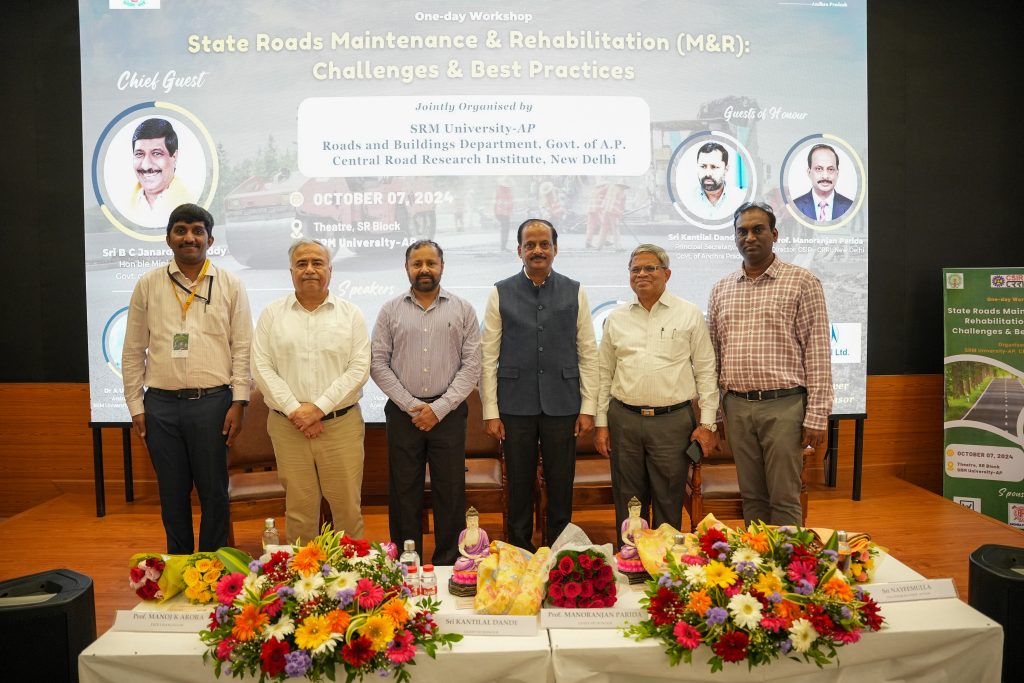

“Road is the index of a developed society” commented Sri Kantilal Dande IAS, Guest of Honour for the one-day workshop.
SRM University-AP, in association with the Andhra Pradesh Roads and Buildings (R&B) department and the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research-Central Road Research Institute (CSIR-CRRI), hosted a one-day workshop on exploring the Challenges and Best Practices for State Roads Maintenance and Rehabilitation (M&R). The ceremonious event welcomed the Honourable Minister of Roads & Buildings (R&B), Government of Andhra Pradesh, Sri B C Janardhan Reddy, as the Chief Guest along with Sri Kantilal Dande IAS, Principal Secretary, (R&B), Government of Andhra Pradesh and Prof. Manoranjan Parida, Director of CSIR-CRRI as the Guests of Honour. Distinguished dignitaries from the Government of Andhra Pradesh, the R&B Department, industries, universities, and research institutes participated in the workshop to address the critical challenges associated with the maintenance and rehabilitation of state roads.
In his virtual address to the participants, Honourable Minister Sri B C Janardhan Reddy explained that the Government had received proposals of Rs. 290 crores to convert 1393 damaged roads, covering 7071 kilometres, into pothole-free roads across the state. He said that with the latest technology and technical support from SRM University-AP, a complete restoration of the road network would be possible.
The event facilitated a constructive platform that assembled policymakers, academicians, researchers and young minds from various sectors to discuss the pressing challenges faced in the maintenance and rehabilitation of roads and exploring cost-effective and sustainable methods to achieve the same. “To tackle the key factors leading to road damage and rehabilitation, we require technical support and cutting-edge research from reputed institutes like CSIR-CRRI and new-age universities like SRM University-AP”, stated Guest of Honour Sri Kantilal Dande IAS.
Prof. Manoranjan Parida, Director of CSIR-CRRI, delivered a keynote session elucidating the immense significance of technology on road development. “A methodical approach to Road Asset Management is pivotal to ensure successful road maintenance and rehabilitation in the state of Andhra Pradesh. Sustainable technologies such as recycling technology can be utilised for rehabilitation projects, which will be cost-effective and economical”, advised Prof. Parida.
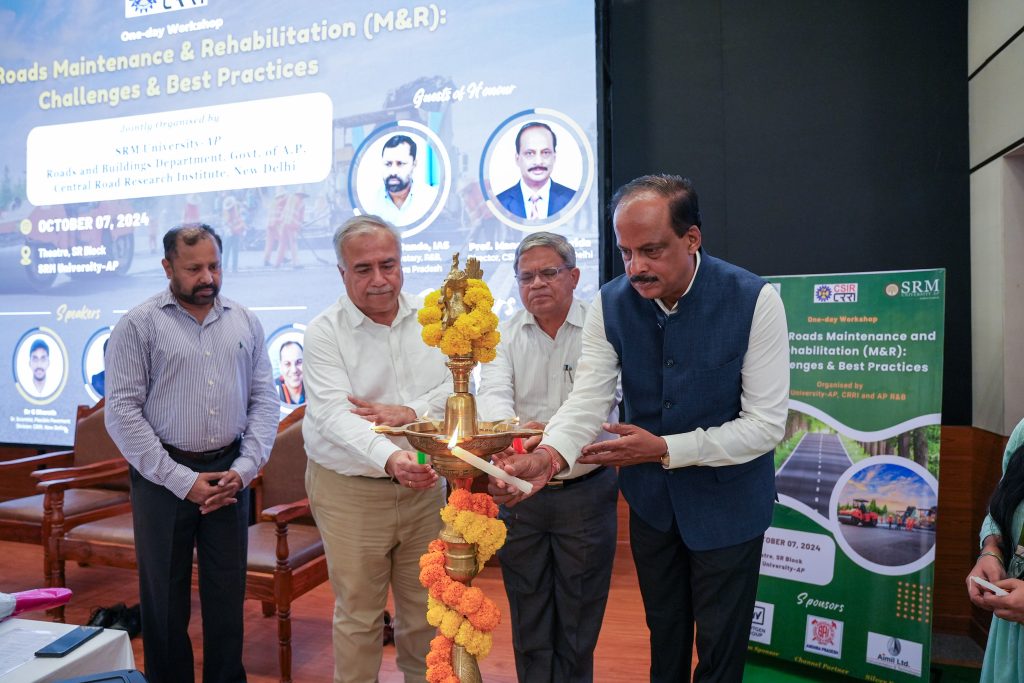

The workshop also encompassed insightful sessions on leading issues featuring esteemed speakers including Mr Nayeemulla, Engineer-in-Chief, R&B Department, Government of AP; Dr G Bharath, Sr. Scientist, Flexible Pavement Division, CRRI, New Delhi; Dr P S Prasad, Chief Scientist, Geotechnical Engg. Division, CRRI; and many more. A panel discussion on the way forward for AP State Roads M&R moderated by Mr Sitaramanjaneyulu, Visiting Professor of SRM University-AP & Former Chief Scientist, CRRI, was a highlight of the workshop.
Vice Chancellor of SRM University-AP, Prof. Manoj K Arora, praised the assemblage of government, industry, academia, research and the builders’ association at the workshop for a consulted approach towards the development of state roads. Dr Uma Maheswar, the organising secretary from SRM University-AP, stated that “Maintenance and rehabilitation of roads are key for any kind of success and development. In the next 5 to 10 years, SRM University-AP, the Government of AP and the industry will foster an ecosystem to rehabilitate the damaged roads through sustainable methods.”
The one-day workshop was a grand success in identifying a roadmap for sustainable programs tailored for AP state roads and formatting potential solutions for the challenges. The event also witnessed the presence of Mr Venkateswara Rao, Former President of the Builders’ Association of India AP Chapter, Mr Nagamalleswara Rao, President of Builders’ Association of India AP Chapter, Dr R Premkumar, Registrar of SRM University-AP, Dr Raviteja KVNS, HOD, Department of Civil Engineering, SRM University-AP, participants from neighbouring universities, industry professionals and faculty and students of SRM University-AP.
- Published in CIVIL NEWS, Departmental News, News
New Theories on Dark Matter: Dr Basabendu Proposes New Insights in Q1 Journal
 In a significant advancement in the field of astrophysics, Dr Basabendu Barman, Assistant Professor in the Department of Physics, has published a groundbreaking paper titled “Dark matter-electron scattering and freeze-in scenarios in the light of \textit{Z’} mediation” in the prestigious Q1 journal, Physical Review D, known for its impact factor of 5.0 within the Nature Index.
In a significant advancement in the field of astrophysics, Dr Basabendu Barman, Assistant Professor in the Department of Physics, has published a groundbreaking paper titled “Dark matter-electron scattering and freeze-in scenarios in the light of \textit{Z’} mediation” in the prestigious Q1 journal, Physical Review D, known for its impact factor of 5.0 within the Nature Index.
Dr Barman’s research delves into the enigmatic realm of dark matter, proposing a novel mechanism through which dark matter might interact with the visible universe via a hypothesised fifth force. This interaction could provide vital insights into the nature of dark matter and its elusive characteristics. The study suggests that if this interaction is confirmed, experiments exploring the existence of a fifth force could concurrently unravel the mysteries surrounding dark matter, leading to a deeper understanding of the universe.
This publication not only highlights the potential for new discoveries in particle physics but also positions SRM University-AP at the forefront of cutting-edge research in dark matter studies. Dr. Barman’s findings could pave the way for further exploration and experimental validation, ultimately contributing to the ongoing quest to decode one of the universe’s greatest mysteries.
Abstract:
We investigate dark matter (DM-)electron scattering in a minimal U〖(1)〗_X extension of the Standard Model (SM), where the DM can appear as a Majorana fermion, a complex singlet scalar, or a Dirac fermion. To study bounds on the new gauge coupling and new gauge boson mass, from DM-electron scattering, we consider several direct search experiments like CDMS, DAMIC, SENSEI, PandaX-II, DarkSide-50, and XENON1T-S2 for different U〖(1)〗_X charges. In this setup, we consider DM production via freeze-in in both radiation-dominated and modified cosmological backgrounds to project sensitivities onto coupling vs mass plane satisfying observed relic abundance. DM-electron scattering could provide comparable, or even stronger, bounds compared to those obtained from the electron/muon (g-2), low-energy scattering, and intensity frontier experiments within mass range of 0.01-0.1 GeV. Constrains from freeze-in could provide stronger sensitivities for new gauge boson masses above about 1 GeV ; however, these limits are comparable to those obtained from LHCb and LEP experiments for mass between 10-150 GeV. In the future, electron-muon scattering (MUonE), proton (FASER and DUNE), and electron/positron (ILC) beam-dump experiments could probe these parameters.
From Layperson’s perspective:
We know there are four fundamental forces in nature: strong, weak, electromagnetic, and gravitational. But what if there’s a hidden, fifth force we haven’t discovered yet? The Standard Model of particle physics, which organizes all known particles, doesn’t include this fifth force (and doesn’t include gravity either, unfortunately). So, how can we theoretically create a particle physics model for this possible fifth force? That’s what we explore in this paper. Interestingly, there are already experiments (for example, the Large Hadron Collider or LHC at CERN, Geneva) searching for signs of fifth forces. If this force exists, our model could be tested by these experiments. But there’s more! We also wanted to tackle a big mystery in cosmology: dark matter. Dark matter makes up about 24% of the universe, but we’ve never directly detected it because it doesn’t reflect light—it’s “dark.” However, there are smart ways to try to find it. In this paper, we propose how the same dark matter might interact with the visible universe through this fifth force and thereby leave their footprints. If true, therefore, the experiments looking for the fifth force could also give us clues about the nature of dark matter.
Title:
Dark matter-electron scattering and freeze-in scenarios in the light of Z’ mediation.
In BibTeX (citation) format:
@article{PhysRevD.110.055029,
title = {Dark matter-electron scattering and freeze-in scenarios in the light of ${Z}^{\ensuremath{‘}}$ mediation},
author = {Barman, Basabendu and Das, Arindam and Mandal, Sanjoy},
journal = {Phys. Rev. D},
volume = {110},
issue = {5},
pages = {055029},
numpages = {20},
year = {2024},
month = {Sep},
publisher = {American Physical Society},
doi = {10.1103/PhysRevD.110.055029},
url = {https://link.aps.org/doi/10.1103/PhysRevD.110.055029}
}
Practical Implementations & Social Impact:
The primary goal of this study is to explore what lies beyond the known, visible universe. This curiosity has driven humanity for centuries—to build rockets and explore outer space and to smash particles in colliders, searching for the mysteries hidden within the atom. The desire to uncover the unknown, to shed light on the darkness, is a fundamental part of what it means to be human. In this sense, the work contributes to the realm of pure intellectual pursuit. Science speaks the language of data, and data is born from experiments. The validation of any well-constructed theory ultimately depends on experimental evidence. For this reason, it is essential for society to cultivate a culture that values fundamental scientific discussion and increases funding for basic research.
Collaborations:
This work was done in collaboration with Prof. Arindam Das from the Department of Physics, Hokkaido University, Sapporo, Japan, and Dr. Sanjoy Mandal from the Korea Institute for Advanced Study (KIAS), Seoul, Korea.
Future plans:
- A closer look into early universe dynamics by performing more involved simulations.
- Connection between particle physics models and early Universe cosmology.
- Complementary searches from different experiments in unravelling new physics beyond the Standard Model.
- Searching new physics at energy and intensity frontier.
- Published in Departmental News, News, Physics News, Research News
Language Lab to Boost Student Communication Skills
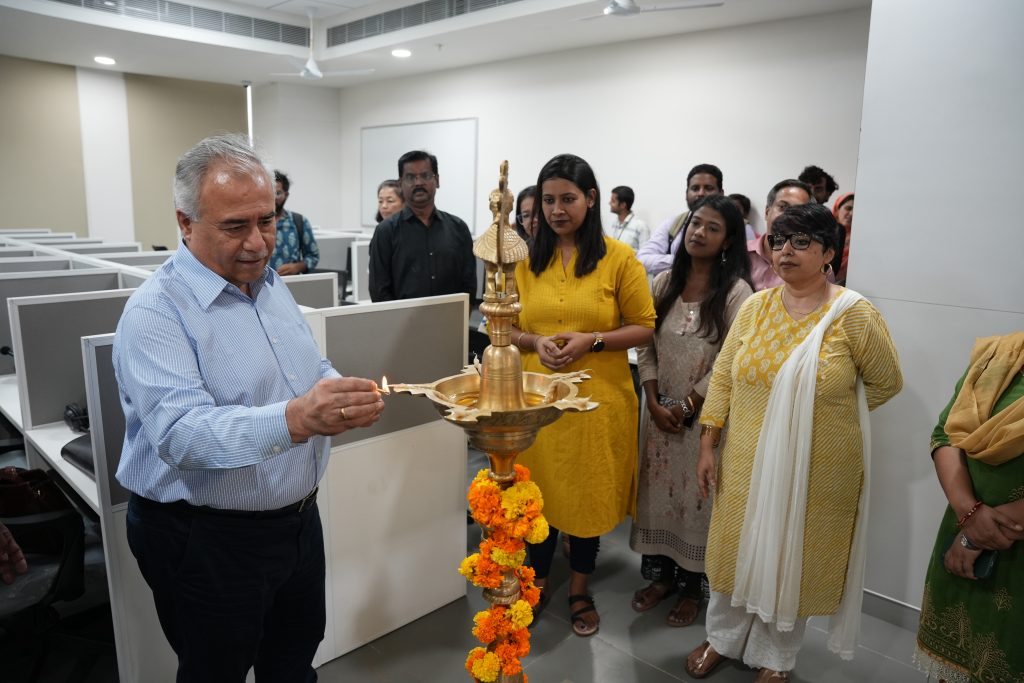 The Department of Literature and Languages at SRM University-AP celebrated the launch of its Language Lab, a state-of-the-art, 70-seater facility designed to enhance the Listening, Speaking, Reading, and Writing (LSRW) skills of its students.
The Department of Literature and Languages at SRM University-AP celebrated the launch of its Language Lab, a state-of-the-art, 70-seater facility designed to enhance the Listening, Speaking, Reading, and Writing (LSRW) skills of its students.
The inauguration was witnessed and officiated by the honourable Vice Chancellor, Prof. Manoj K Arora, along with Prof. Vishnupad, Dean- ESLA; Prof. C V Tomy, Dean-SEAS, Dr Vinayak Kalluri, Dean-Academic Affairs, Ms Suma N, CFAO; Dr Sayantan Thakur, Assistant Professor and Head; Dr Karthik Rajendran; Dr Srabani Basu, other faculty members, research scholars and students.
The laboratory, valued at 10 million rupees, is equipped with Sanako and Lanquill software, providing students with access to advanced resources. During the event, Vice Chancellor Prof. Manoj K Arora emphasised the value of communication he stated “Communication is an essential skill. With this lab, our students have a real opportunity to build those skills and contribute meaningfully to society.” he also voiced that, In future, the varsity will also be looking forward to opening this facility to the wider community so that more people can benefit from this resource.
Dr Thakur and Dr Amlan Baisya, Assistant Professors at the university, provided insights into the laboratory’s cutting-edge software and technology. They explained how these tools can significantly enhance the learning experience, making language acquisition more interactive and engaging. The faculty expressed their excitement about the opportunities this facility will create for both students and instructors alike.
Prof. Arora took a moment to commend the Department of Literature and Languages and the Directorate of Information Technology and Knowledge Management (ITKM) for their commitment to advancing education through innovative resources. He underscored the bright future ahead, not only for students but for the entire university community, as they leverage this new laboratory to improve communication skills that are vital in both academic and professional settings.
- Published in Departmental News, English Current Happenings, English news, News
Dr Sayantan’s Research Paper on Overcoming the Digital Divide

In the context of online English education in India, the “digital divide” has emerged as a significant obstacle, especially for students from rural or underprivileged areas. Dr Sayantan Thakur, Assistant Professor at the Department of Literature and Languages in his article introduces a research study titled “Navigating the Digital Divide: Challenges and Strategies in Teaching Communicative English Online in Indian Classrooms,” which aims to address the unequal access to online learning tools.
Abstract
The advent of online learning platforms is providing new opportunities for English language learning (ELL) in India. However, there is a significant challenge posed by the digital divide – the gap in accessing technology. This study investigates what causes the digital divide in internet ELL classrooms such as infrastructure limitations, device ownership and usage, and digital literacy skills; and how they affect student engagement, development of communication skills, and overall learning experiences. It suggests ways to bridge this gap which include government policies on infrastructure development; affordable tech solutions like mobile apps; teaching programs that enhance digital literacy among learners; support for teachers involved in web-based pedagogy. Through these recommendations, education stakeholders can create an inclusive cyberspace for all students where their communication abilities will be nurtured throughout different parts of India.
The Practical Implementation
The practical implementation of your research on “Navigating the Digital Divide: Challenges and Strategies in Teaching Communicative English Online in Indian Classrooms” has far-reaching social implications. By addressing the digital divide, your work can help level the playing field in education, especially for students from underprivileged backgrounds.
Improved Access to Education: Implementing strategies like infrastructure development, affordable mobile-based learning tools, and digital literacy programmes can provide more students, especially in rural and low-income areas, access to online English learning resources. This improves their chances of acquiring essential communication skills, opening doors to better job opportunities.
Empowering Teachers: Equipping teachers with digital tools and training enables them to deliver more effective online lessons, increasing student engagement and success rates.
Reducing Inequality: Bridging the technology gap can reduce educational disparities between urban and rural areas, promoting social mobility and reducing the long-term impacts of inequality.
Building a Digitally Literate Society: Enhancing digital literacy among students and teachers fosters a society better prepared for the demands of the modern workforce, ultimately contributing to economic growth and social inclusion.
Future Research Plans
- Regional Literature in Translation
- Tantric Tradition and Eastern Indian Literature
- Folk Music of Bengal
- Indian Philosophy, Aesthetics & Literature
- Published in Departmental News, English Current Happenings, English news, News, Research News
A Sustainable Greywater Treatment Method

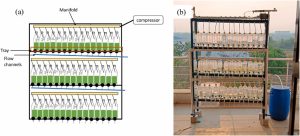
Addressing the ever-demanding crisis of water scarcity, Dr Mohit Aggarwal, Assistant Professor from the Department of Civil Engineering, has published a paper titled “Polyculture Microalgae and Zno/GAC-nanocomposite System for Greywater Treatment” in the Q1 journal Biomass and Bioenergy with an impact factor of 5.8. In his research, Dr Aggarwal explores sustainable methods to treat wastewater with algae and nanoparticles, providing an efficient method to reuse greywater and reduce water consumption.
Abstract
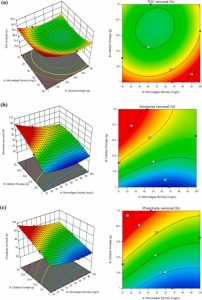
This study explores sustainable greywater treatment using microalgae and a ZnO/GAC nanocomposite in a 15-day batch photobioreactor. The system achieved significant nutrient removal, with 80% TOC, 94.2% PO43−, and 99.6% NH4+ efficiencies. Microalgal growth was enhanced by the nanocomposite, reaching a density of 1.8 g/L. The resulting biomass had a high heating value of 18.32 MJ/kg. The ZnO/GAC nanocomposite maintained effective removal over four cycles. The treated greywater met reuse standards for toilet flushing, with pH 8.5, turbidity <4 NTU, and COD, NH4+, and PO43− of 34, 0.032, and 0.48 mg/L, respectively.
Explanation of the research in layperson’s terms
Water scarcity and pollution are serious problems, and our research aims to find an environmentally friendly way to treat greywater (wastewater from sinks, showers, etc.). We explored the use of algae combined with special nanoparticles (zinc oxide) to clean the water more effectively. The algae grow in the water and help remove harmful substances like carbon, phosphorus, and nitrogen. The nanoparticles make this process even more efficient.
After treatment, the water is clean enough to be reused, for example, in toilet flushing. This method not only helps clean wastewater but also provides a sustainable way to reuse it, which can reduce water consumption and help the environment.
Practical implementation/ Social implications of the research
Practical implementation
The system developed in this research can be implemented in decentralised greywater treatment units, especially in water-scarce areas. It provides a cost-effective, eco-friendly solution for treating household or industrial greywater. The treated water meets the quality standards for reuse in applications like toilet flushing or landscape irrigation, reducing freshwater demand.
Social implications
This research promotes water recycling, contributing to sustainable water management practices and helping to address water scarcity issues. This can improve access to water in communities with limited resources, reduce the pressure on freshwater supplies, and lower the environmental impact of wastewater discharge, leading to healthier ecosystems and communities. Additionally, adopting such systems on a larger scale can foster greater awareness of water conservation and responsible resource usage.
- Published in CIVIL NEWS, Departmental News, News, Research News
Marketing Wizard Delivers Lecture on D2C Marketing
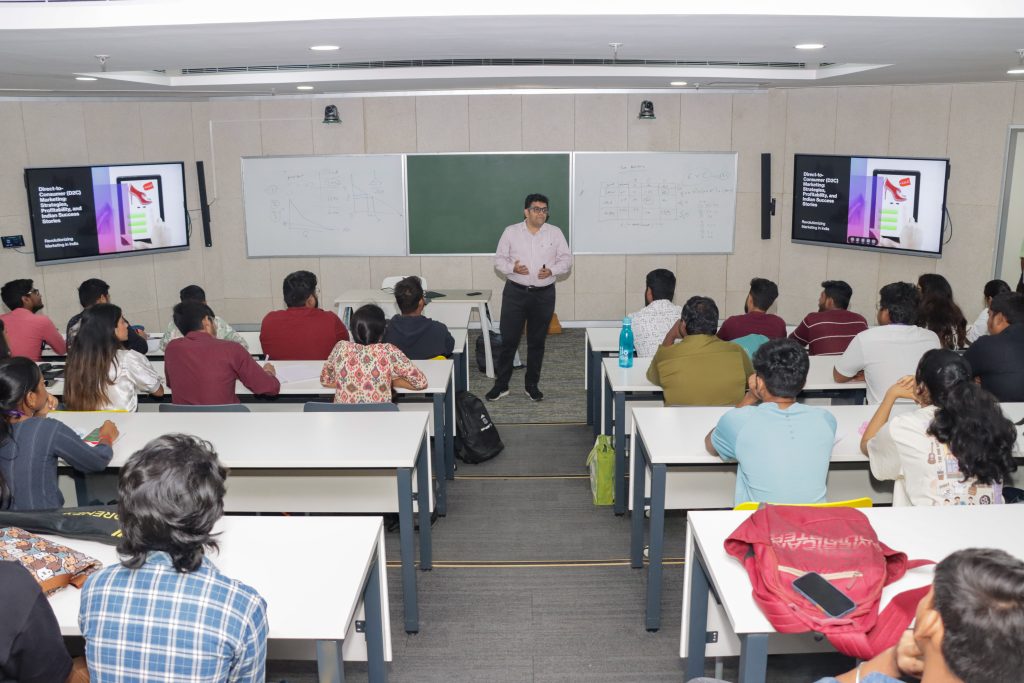 The students of Paari School of Business (PSB) had a memorable experience when Mr Siddesh Joglekar joined as a guest lecturer at SRM University-AP. The CRCS team’s dedicated efforts and the unwavering support of Prof. Bharadwaj Sivakumaran, Dean of PSB, made this unique opportunity possible. Students had the privilege of engaging in a personal interaction with the esteemed guest on September 18, 2024.
The students of Paari School of Business (PSB) had a memorable experience when Mr Siddesh Joglekar joined as a guest lecturer at SRM University-AP. The CRCS team’s dedicated efforts and the unwavering support of Prof. Bharadwaj Sivakumaran, Dean of PSB, made this unique opportunity possible. Students had the privilege of engaging in a personal interaction with the esteemed guest on September 18, 2024.
During the lecture Mr Joglekar shed light on various aspects of professional growth and marketing strategies. He placed significant emphasis on the need to foster a collaborative environment and recognising the contributions of peers.The lecture also delved into the imporatance of networking for career advancement, especially through ones’ Alumni Associations
Mr Joglekar delved into the expansive potential of Direct to Consumer (D2C) marketing, using examples from renowned companies like Twitter, Walmart, Instagram, Zomato, Amazon, Tesla, and Google to illustrate the evolution of brand images. A poignant quote from Mr Joglekar, “Companies are transformed into brands by people who dare to dream,” encapsulated the essence of the discussion, emphasising the role of visionary individuals in shaping successful brands.
Interactive elements were woven into the session, including an activity where students were tasked with creating logos that branded themselves, thus reflecting a unique aspect of their identity. This hands-on approach not only made the learning process engaging but also provided practical insights into branding.
A comparative analysis between traditional retail and D2C highlighted key differences such as distribution channels, pricing strategies, and brand control, offering a deeper understanding of the contemporary marketing landscape. The concepts of Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) and Life-Time Value (LTV) were also explored, underscoring their importance in building a strong brand identity.
As the session neared its conclusion, Mr Joglekar introduced an innovative activity that involved reverse engineering an advertisement concept, inspired by the 2022 ad campaign featuring Mr Neeraj Chopra for Cred. This exercise prompted students to think creatively and apply the concepts discussed in a practical context.
The session wrapped up with a Q&A segment, where discussions ranged from market profitability to the advantages of D2C marketing, allowing for a comprehensive review of the topics covered. Ms Andrea Benedict extended a vote of thanks on behalf of the student fraternity of PSB, culminating in a group photo session that captured the essence of the enriching experience.
- Published in Departmental News, News, Paari Current Happenings, paari-guest-lectures
Dr Kousik Das Receives Project Sanctioned by the Ministry of Earth Science

Dr Kousik Das, Assistant Professor from the Department of Environmental Science and Engineering has been sanctioned the project titled “Present Day and predicted physico-chemical and climate change influence on solute influx to Northern Bay of Bengal and its impact on biotic system”. sanctioned by the Deep Ocean Mission (DOM) of the Ministry of Earth Science, Govt. of India. Dr Kousik Das has been granted Rs. 42,42,000 as CO-PI for Rs. 1,89,19,100/- worth project, which will be undertaken in collaboration with researchers from esteemed institutes such as IIT Kharagpur and IISc Bangalore.
Explanation of the research in layperson’s terms
The proposed research work consists of a quantitative and qualitative study of seasonal solute geochemistry of ocean water and biotic diversity in marine ecosystems, along with scenarios of predicted oceanic circulation pathways at present times and futuristic cases expected in a changing climate. The study will be done by coupling physical and chemical hydrogeological techniques, which include the installation of marine observation stations and field equipment after the generation of the conceptual framework. The project will work towards making the scientific community more acquainted with the hydrodynamics and chemodynamics of the Bay of Bengal ocean water.
Practical implementation/ Social implications of your research
Seawater characteristics in the head of the Bay of Bengal are rapidly evolving due to changing influx from terrestrial sources. In particular, the head Bay region has undergone rapid variations in water quality due to extreme climate conditions, sea level rise, tidal impact, and effects of ocean acidification. Our aim is to hypothesise the climatic and hydrological processes involved in altering the ocean water nutrient and trace element cycling and their subsequent impact on the marine biohabitat.
Future research plans
- Nutrient cycle of northern Bay of Bengal
- Trace element cycle of the Bay of Bengal
- Impact of climate change on biogeochemical cycle
- Impact of hydrological drivers on marine ecosystems
- Published in Departmental News, ENVS News, News, Research News