High-quality perovskite nanocrystals for light-emitting applications
 Dr Nimai Mishra, Assistant Professor, Department of Chemistry, SRM University-AP, Andhra Pradesh, along with his research group comprising of students pursuing PhD under his supervision, Ms VG Vasavi Dutt, Mr Syed Akhil, Mr Rahul Singh, and Mr Manoj Paalabathuni have published a research article titled “High-Quality CsPbX3 (X = Cl, Br, or I) Perovskite Nanocrystals Using Ascorbic Acid Post-Treatment: Implications for Light-Emitting Applications” in the Journal “ACS Applied Nano Materials” (published by The American Chemical Society) having an impact factor of ~5.1.
Dr Nimai Mishra, Assistant Professor, Department of Chemistry, SRM University-AP, Andhra Pradesh, along with his research group comprising of students pursuing PhD under his supervision, Ms VG Vasavi Dutt, Mr Syed Akhil, Mr Rahul Singh, and Mr Manoj Paalabathuni have published a research article titled “High-Quality CsPbX3 (X = Cl, Br, or I) Perovskite Nanocrystals Using Ascorbic Acid Post-Treatment: Implications for Light-Emitting Applications” in the Journal “ACS Applied Nano Materials” (published by The American Chemical Society) having an impact factor of ~5.1.
Abstract:
Cesium lead halide perovskite nanocrystals (CsPbX3 PNCs) have been the flourishing area of research in the field of photovoltaic and optoelectronic applications because of their excellent optical and electronic properties. However, they suffer from low stability and deterioration of photoluminescence (PL) properties post-synthesis. One of the ways to minimize the surface defects in the surface treatment with suitable ligands is to achieve the PNCs with superior PL properties for light-emitting applications.
In this article, Dr Mishra’s research group addressed the issue of stability in PNCs. We demonstrate to achieve high photoluminescence and stability of CsPbX3 PNCs by incorporating ascorbic acid via post-treatment as a new capping ligand that is abundantly available. Upon addition of ascorbic acid as surface passivation ligand into the oleic acid/oleylamine system to get near-unity photoluminescence quantum yield (PLQY) of CsPbBr3, CsPb(Br/I)3, and for CsPbI3 perovskite NCs. Maintaining stability has become the hotspot of research in this field. Hence, as-a-proof of concept, the stability studies of PNCs in ambient conditions, under continuous UV irradiation, and PL with temperature variations are put forth here. The stability enhancement with post-treatment of ascorbic acid is highly reproducible as we tested for four batches of samples.
Despite the significant advancements of PNCs, there is a challenge afflicting the stability of CsPbI3 PNCs. They are thermodynamically unstable and undergo a non-perovskite phase (δ-phase) transition at room temperature. Many efforts have been reported in the stabilization of iodide perovskite NCs by critically passivating PNCs and applying them for optoelectronics and photovoltaics. On the other hand, mixed halide perovskites like CsPbBrI2 which are relatively stable than CsPbI3 PNCs are a better choice for device applications. But, photo-induced halide segregation is unavoidable which in turn again limit their usage in practical applications. In this manuscript, we demonstrated that the ultra-stable iodide-based PNCs can be achieved by simple and facile surface treatment with ascorbic acid.
The PL intensity of untreated and ascorbic acid-treated PNCs is recorded for 42 days since the date of synthesis. The measurements are carried out for 4 different batches of samples to ensure reproducibility. It is found that the PL intensity is deteriorating rapidly for untreated PNCs while the PL intensity is largely maintained for ascorbic acid treated PNCs. Nearly ̴72% of the initial PL intensity is maintained even after 42 days for the ascorbic acid-treated CsPbBr3 PNCs while the PL intensity is dropped to 24% for untreated PNCs. Ascorbic acid treated CsPbBrI2 PNCs exhibited exceptional ambient stability where ̴69% of the initial PL intensity is maintained after 42 days while the PL of untreated CsPbBrI2 PNCs is degraded rapidly within 2 weeks from the date of synthesis. Moreover, the PL stability of CsPbI3 PNCs is high for ascorbic acid-treated samples even after 55 days while the PL has deteriorated within 4 days for untreated CsPbI3 PNCs. The PL of untreated CsPbI3 PNCs is completely lost in the first 4 hours of UV illumination while ̴ 76.7% remnant PL is observed for ascorbic acid-treated CsPbI3 PNCs. We believe the stabilization of CsPbX3 PNCs of different halide compositions via simple surface treatment with ascorbic acid could form a basis for futuristic light-emitting applications.
Read the full paper: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/full/10.1021/acsanm.1c04312
- Published in Chemistry-news, News, Research News
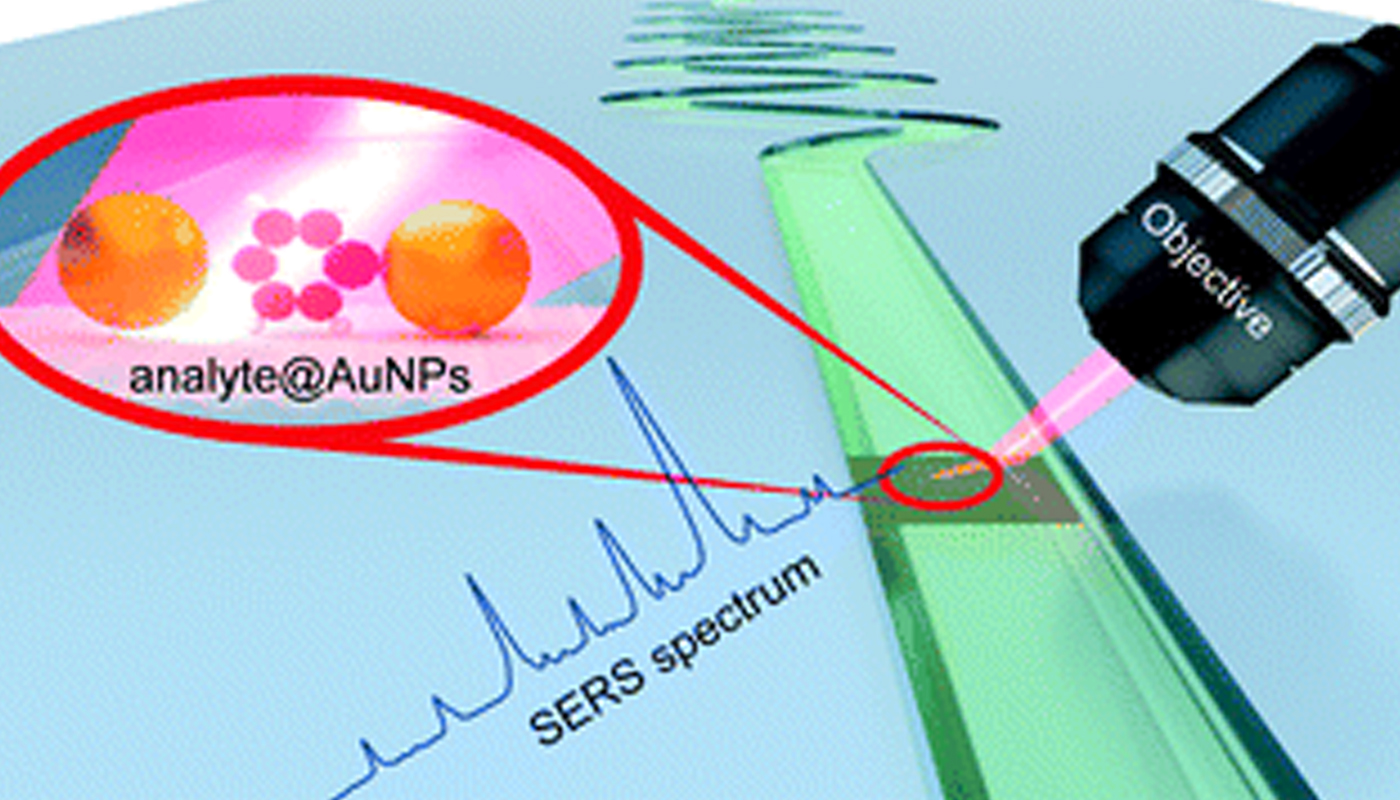
Microfluidic SERS as a powerful tool in Analytical Chemistry
The Department of Chemistry is glad to announce that Dr J P Raja Pandiyan has published a paper titled ” Microfluidics and surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy, a win-win combination?” in the journal ‘Lab on a Chip’ having an impact factor of 6.79 in collaboration with researchers from different universities across India, Germany, and Japan.
Abstract of the Research
With the continuous development in nanoscience and nanotechnology, analytical techniques like surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) render structural and chemical information of a variety of analyte molecules in ultra-low concentration. Although this technique is making significant progress in various fields, the reproducibility of SERS measurements and sensitivity towards small molecules are still daunting challenges. In this regard, microfluidic surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (MF-SERS) is well on its way to join the toolbox of analytical chemists. This review article explains how MF-SERS is becoming a powerful tool in analytical chemistry. We critically present the developments in SERS substrates for microfluidic devices and how these substrates in microfluidic channels can improve the SERS sensitivity, reproducibility, and detection limit. We then introduce the building materials for microfluidic platforms and their types such as droplet, centrifugal, and digital microfluidics. Finally, we enumerate some challenges and future directions in microfluidic SERS. Overall, this article showcases the potential and versatility of microfluidic SERS in overcoming the inherent issues in the SERS technique and also discusses the advantage of adding SERS to the arsenal of microfluidics.
About the Raman Research Group at SRM AP
Raman spectroscopy, invented by Sir CV Raman in 1928 and got Nobel Prize in 1930, is a vibrational spectroscopic technique that works based on the principle of inelastic scattering of light. Surface-Enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) is one of the modern analytical techniques which can detect chemical and biomolecules in an ultra-low concentration. The research group is working on the development of the SERS technique to address the issues in food, environmental, energy and biological science.
The newly developed SERS substrates are mainly used for the detection of biological samples for disease diagnosis, food samples to ensure food safety, water samples to study the contamination and pollution rate. These studies can make meaningful social changes and improvements.
- Published in Chemistry-news, Departmental News, News, Research News
Chanakya Karra admitted to PhD at Purdue University, USA
 Once you are a part of SRM University-AP, we ensure that your future is secured! With the guidance of Dr Sujith Kalluri, Assistant Professor, Electronics and Communication Engineering, Mr Chanakya wends his way to Purdue University, USA, a world-renowned research university, for doing his PhD. He secured admission with a full tuition fee waiver and teaching assistantship. Chanakya Karra spent his two years DST-SERB JRF position at SRM AP and has made remarkable contributions to SRM-Amararaja Centre for Energy Storage Devices.
Once you are a part of SRM University-AP, we ensure that your future is secured! With the guidance of Dr Sujith Kalluri, Assistant Professor, Electronics and Communication Engineering, Mr Chanakya wends his way to Purdue University, USA, a world-renowned research university, for doing his PhD. He secured admission with a full tuition fee waiver and teaching assistantship. Chanakya Karra spent his two years DST-SERB JRF position at SRM AP and has made remarkable contributions to SRM-Amararaja Centre for Energy Storage Devices.
DST-SERB JRF position helped Chanakya resume his research career, which had a pause for over a year. “It fills me with immense joy to see the SRM-Amararaja Centre for Energy Storage Devices shape up with every possible equipment to conduct research on batteries. Kudos to the management and the efforts of the faculty associated with the centre,” says Mr Chanakya. He further mentioned that the research work conducted at SRM-Amara Raja Centre enabled him to write over three papers that catapulted his chances of admission.
“I would urge the students to make the best use of the opportunities available at SRM-AP and discuss their plans with the faculty. I am sure new avenues will open with the mentoring of world-class faculty at SRM”, says Mr Chanakya to the junior batches of students aspiring for a research career.
Mr Chanakya expressed his gratitude to the faculty members associated with Amararaja Centre for Energy Storage Devices- Dr Pardha Saradhi Maram, Associate Professor, Chemistry, Dr Surfarazhussain S Halkarni, Assistant Professor, Mechanical Engineering, Dr Laxmi Narayana Patro, Assistant Professor, Physics, and others.
- Published in Chemistry-news, Departmental News, ECE NEWS, Mechanical Engineering NEWS, News, Physics News
Do you think CSIR-JRF is a tough nut to crack? Persistence is the key

“Believe you can and you’re halfway there.” – Theodore Roosevelt
Jesni M Jacob, currently doing research under Dr Mahesh Kumar Ravva narrates her journey to achieving CSIR-JRF All India Rank of 65 through persistent efforts.
I’m working in the field of computational chemistry on designing and developing organic molecules for OLED applications. Securing an AIR of 65 in the CSIR JRF in Chemical Science June 2021 exam is a dream come true moment for me.
In 2019, I completed my post-graduate studies at Madras Christian College, Chennai. The four-year-long journey from zero to JRF AIR 65 was of hard work, patience, sleepless nights, sacrifices and even frustrated moments. It was challenging to remain motivated after multiple unsuccessful attempts. But I wasn’t ready to give up hope. I believed in myself and dreamed big with faith in God Almighty.
My previous attempts didn’t provide me with any hope of continuing my preparation because my marks were consistently far below the cutoffs. That made me realise one thing: without coaching and ample guidance, qualifying for CSIR JRF is a toiling task for an average student. But I learned that with strong passion, proper dedication, and right strategies of do’s and don’ts, any aspiring student can pass the exam with flying colours.
After each attempt, I learned from my mistakes and tried to optimise my strategies. One should never try to cover the entire syllabus and be bothered about it. I analysed the unit-wise weightage and narrowed it down to a few important topics that I found exciting and comfortable.

- Choose topics carefully and focus solely on mastering them.
- Try to stick to and rely on reliable standard textbooks as much as possible.
- The SRMAP library provided me with excellent access to a wide range of standard texts.
The JRF aspirants should try to solve previous years’ questions from standard exams (CSIR, GATE, IISc, etc.) and note new concepts or approaches every day. Enjoy and prepare short notes with a lot of scribbling and highlighting in various colours. Notes should be concise and simple to revise later. But don’t spend too much time making notes.
I made time for exam preparation along with my work and research activities. I’m grateful to my family, teachers, and especially my guide- Dr Mahesh Kumar Ravva, for their constant support and encouragement. He gave me a safe space to express my desire to ace the exam and my anxieties about it. Dr Mahesh always listened to my concerns and helped me to gain clarity on my thoughts. He always encouraged me to dream big and shared his perspectives and lessons from his life experiences. He is a great mentor, motivator, and teacher to me.
- Published in Blog, Chemistry-news, Departmental News, News, Research, Students Achievements
Presenting our first doctorate holder: Dr Vasavi Dutt
 The university revels in its monumental achievement of bringing out the maiden doctorate degree holder, Dr Vasavi Dutt, within four years of its inception. Dr Vasavi Dutt enrolled as a PhD scholar in the Department of Chemistry, under the supervision of Dr Nimai Mishra, Assistant Professor, in 2018. She received the academic honour for her research thesis titled “Improvement of Photoluminescence and Achieving the Stabilization of Cesium Lead Halide Perovskite Nanocrystals for Light-emitting Applications”. Dr Vasavi has been an extremely diligent student and she mustered up immense courage to bring her research to closure even during the testing times of the pandemic.
The university revels in its monumental achievement of bringing out the maiden doctorate degree holder, Dr Vasavi Dutt, within four years of its inception. Dr Vasavi Dutt enrolled as a PhD scholar in the Department of Chemistry, under the supervision of Dr Nimai Mishra, Assistant Professor, in 2018. She received the academic honour for her research thesis titled “Improvement of Photoluminescence and Achieving the Stabilization of Cesium Lead Halide Perovskite Nanocrystals for Light-emitting Applications”. Dr Vasavi has been an extremely diligent student and she mustered up immense courage to bring her research to closure even during the testing times of the pandemic.
In the words of Dr Nimai Mishra, “It was a great privilege for me to supervise Ms Vasavi, (correct me Dr Vasavi now) as my first PhD student. She joined my research lab in July 2018 when there was no lab at all, and we started our work at Chemistry BTech Lab”. Dr Mishra was gleaming with pride as he spoke more about his scholar, “During these three and a half years, I had relentless scientific discussions with Vasavi which enriched both of us. Her attitude towards research was remarkable, whenever I gave her a research problem, she used to come up with a detailed outline of how to go ahead with the project”. He also praised her for all her accomplishments which include the publication of 13 research papers, filing of 3 patents and winning the best poster in national & internal conferences.
Dr Vasavi also shared her happiness for having received the mentorship of Dr Mishra, “Working in Dr Nimai Mishra’s lab was a great experience. I had the opportunity to engage and initiate multiple research topics and collaborations. He has always encouraged me to explore new fields to broaden perspectives and bring together new ideas”. She also expressed her gratitude to him for being a welcoming and approachable mentor. “I’m eternally thankful to Dr Mishra for his friendship, empathy, and moreover, for his great sense of humour”. She currently resides in the US with her family. Now that she has successfully completed her PhD, soon she would start looking for a job or rather pursue a post-doctoral fellowship in America.
Dr Vasavi was out of words to thank the university for facilitating and bringing the best in technology and infrastructure for advanced research. “I can never thank my university enough for extending a hospitable environment and nutritious food for all the doctorate students”, she further mentioned. The university serves as a promised land for thousands of research aspirants like her to head towards their dream of making unfeigned contributions to academia.
- Published in Chemistry-news, Departmental News, News, Students Achievements
Inspiring the world with quality research facilities
 SRM AP is known for its resources and facilities for pioneering research with the support of global leaders and SME’s while sticking to compliance and international regulations. Obtaining research excellence in every field of study has been a mission of the university. Recently, 50 MSc students from the Department of Chemistry, KBN College, Vijayawada, visited our university to explore the analytical and research facilities available here.
SRM AP is known for its resources and facilities for pioneering research with the support of global leaders and SME’s while sticking to compliance and international regulations. Obtaining research excellence in every field of study has been a mission of the university. Recently, 50 MSc students from the Department of Chemistry, KBN College, Vijayawada, visited our university to explore the analytical and research facilities available here.
The research areas handled by the Department of Chemistry of SRM AP include the disciplines of chemical sciences, ranging from organic, inorganic, and physical, to theoretical or computational chemistry. The department’s highly disciplinary and collaborative environment is indeed inspiring, and it continues to grab attention. The strong interactions of the university with other premier institutions across India and around the world refine the quality of analytical and research facilities available here. The students from KBN college eagerly interacted with the faculty members and research scholars. Dr Mahesh Kumar Ravva and Dr Rajapandiyan, Faculty members, coordinated the visit.
- Published in Chemistry Events, Chemistry-news, News
Green hydrogen to combat global warming
‘Energy Conversion & Management’ is a journal that belongs to the top 2% of the “Renewable Energy, Sustainability, and the Environment” subject category. Publishing a paper with an impact factor of 9.7 in such a journal is a considerable achievement. Assistant Professors Dr Sabyasachi Chakrabortty and Dr Mahesh Kumar Ravva and their PhD scholar Ms Mounika Sai Ambati from the Department of Chemistry have accomplished this by publishing a paper titled Photovoltaic/Photo-Electrocatalysis Integration for Green Hydrogen: A review in this Q1 journal.
Abstract of the research
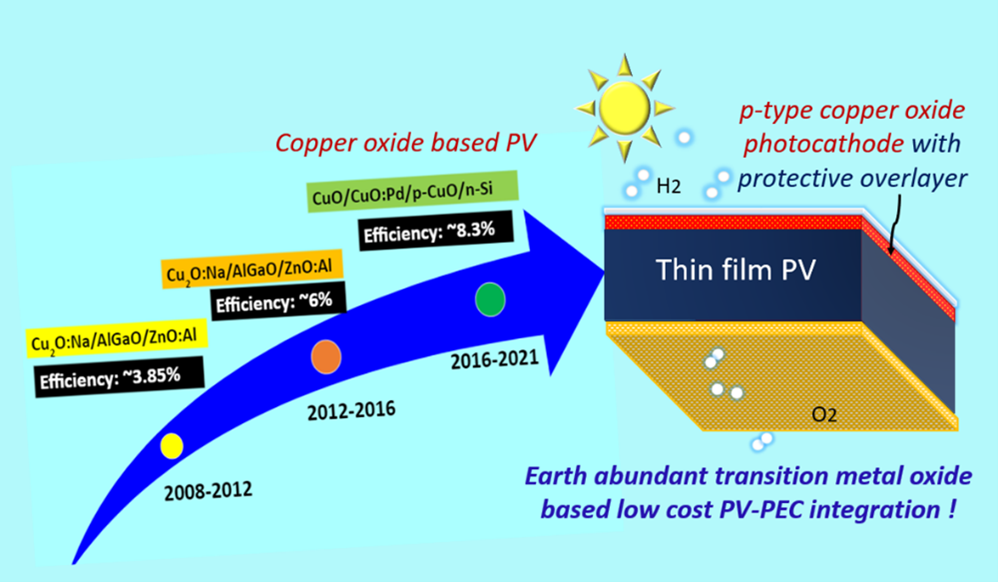 Solar light-driven hydrogen generation via water splitting is essential to combat global warming and CO2 emission. The production of hydrogen from fossil fuels produces massive amounts of CO2. Developing a sustainable and eco-friendly approach to hydrogen production is the need of the hour. Photoelectrochemical water splitting is a clean way to produce hydrogen by using water. The hydrogen generated through water splitting is referred to as Green Hydrogen. Photoelectrochemical water splitting uses metal oxides as photocathode/anode. The challenges that occur here are stability, low efficiency, and large-scale development (reusable electrodes are essential). Hence, the primary goal is to demonstrate photoelectrodes using different metal oxides by in-situ doping of different metals to detect the challenges.
Solar light-driven hydrogen generation via water splitting is essential to combat global warming and CO2 emission. The production of hydrogen from fossil fuels produces massive amounts of CO2. Developing a sustainable and eco-friendly approach to hydrogen production is the need of the hour. Photoelectrochemical water splitting is a clean way to produce hydrogen by using water. The hydrogen generated through water splitting is referred to as Green Hydrogen. Photoelectrochemical water splitting uses metal oxides as photocathode/anode. The challenges that occur here are stability, low efficiency, and large-scale development (reusable electrodes are essential). Hence, the primary goal is to demonstrate photoelectrodes using different metal oxides by in-situ doping of different metals to detect the challenges.
- Published in Chemistry-news, Departmental News, News, Research News
Ultra-stable perovskite nanocrystals for light-emitting applications
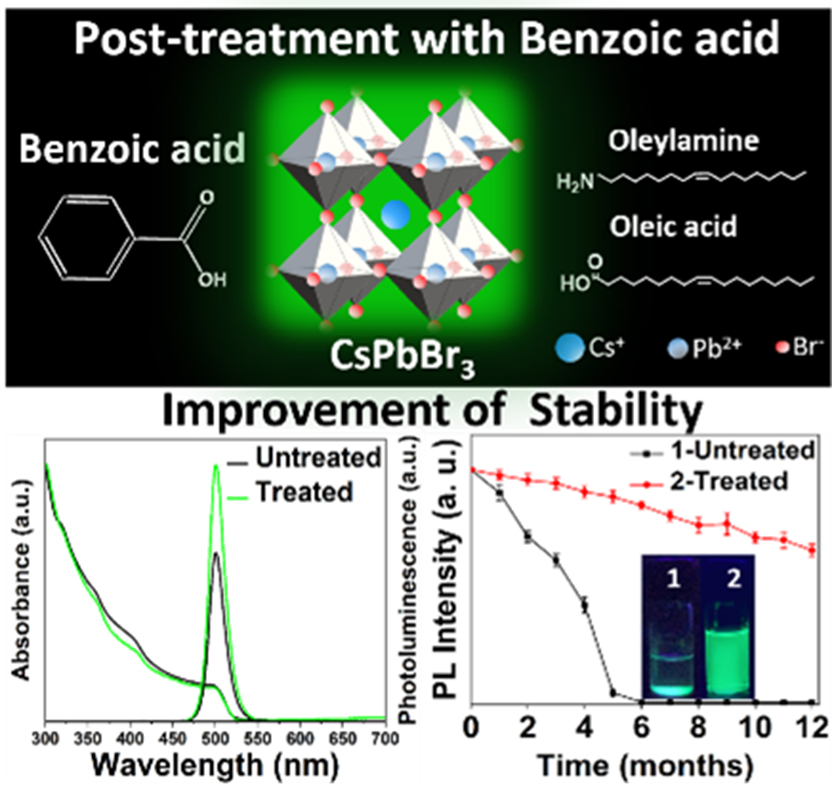
Cesium lead halide perovskite nanocrystals (PNCs) belong to the flourishing research area in the field of photovoltaic and optoelectronic applications because of their excellent optical and electronic properties. Mainly, Cesium lead bromide (CsPbBr3) NCs with bright green photoluminescence (PL) and narrow full-width at half-maximum (FWHM) of <25 nm are the most desirable for television displays and green-emitting LEDs. However, challenges with respect to CsPbBr3 PNCs‘ stability, limit their usage in practical applications. The recent findings of Dr Nimai Mishra and his research team assert that surface passivation with an additional ligand could be an excellent, easy, and facile approach to enhancing the photoluminescence and stability of PNCs.
Dr Nimai Mishra, Assistant Professor, Department of Chemistry, along with his research group comprising of students pursuing PhD under him, Dr V G Vasavi Dutt, Mr Syed Akhil, Mr Rahul Singh, and Mr Manoj Palabathuni have published their research article titled “Year-Long Stability and Near-Unity Photoluminescence Quantum Yield of CsPbBr3 Perovskite Nanocrystals by Benzoic Acid Post-treatment“ in The Journal of Physical Chemistry C (A Q1 journal published by ‘The American Chemical Society’) having an impact factor of ~4.2.
In this article, the research group addresses the stability issues of green-emitting CsPbBr3 PNCs with simple post-treatment using benzoic acid (BA). A remarkable improvement in PLQY from 69.8% to 97% (near unity) was observed in benzoic acid-treated CsPbBr3 PNCs. The effective surface passivation by benzoic acid is also apparent from PL decay profiles of BA-CsPbBr3 PNCs. The long-term ambient stability and stability against ethanol of BA-CsPbBr3 PNCs are also well presented in the research. The PL intensity of untreated CsPbBr3 PNCs is completely lost within five months since the synthesis date, while ̴ 65% of initial PL intensity is preserved for BA-CsPbBr3 PNCs even after one year.
Furthermore, BA-CsPbBr3 PNCs exhibits excellent photo-stability where 36% of PL is retained while PL is completely quenched when the PNCs are exposed to 24 hours of continuous UV irradiation. Importantly, BA-CsPbBr3 PNCs show excellent stability against ethanol treatment as well. Finally, green, emitting diodes using BA-CsPbBr3 PNCs are fabricated by drop-casting NCs onto blue-emitting LED lights. Thus a simple benzoic acid posttreatment further presents the scope of use of these materials display technologies.
- Published in Chemistry-news, Departmental News, News, Research News
Food safety applications of surface-enhanced Raman Spectroscopy
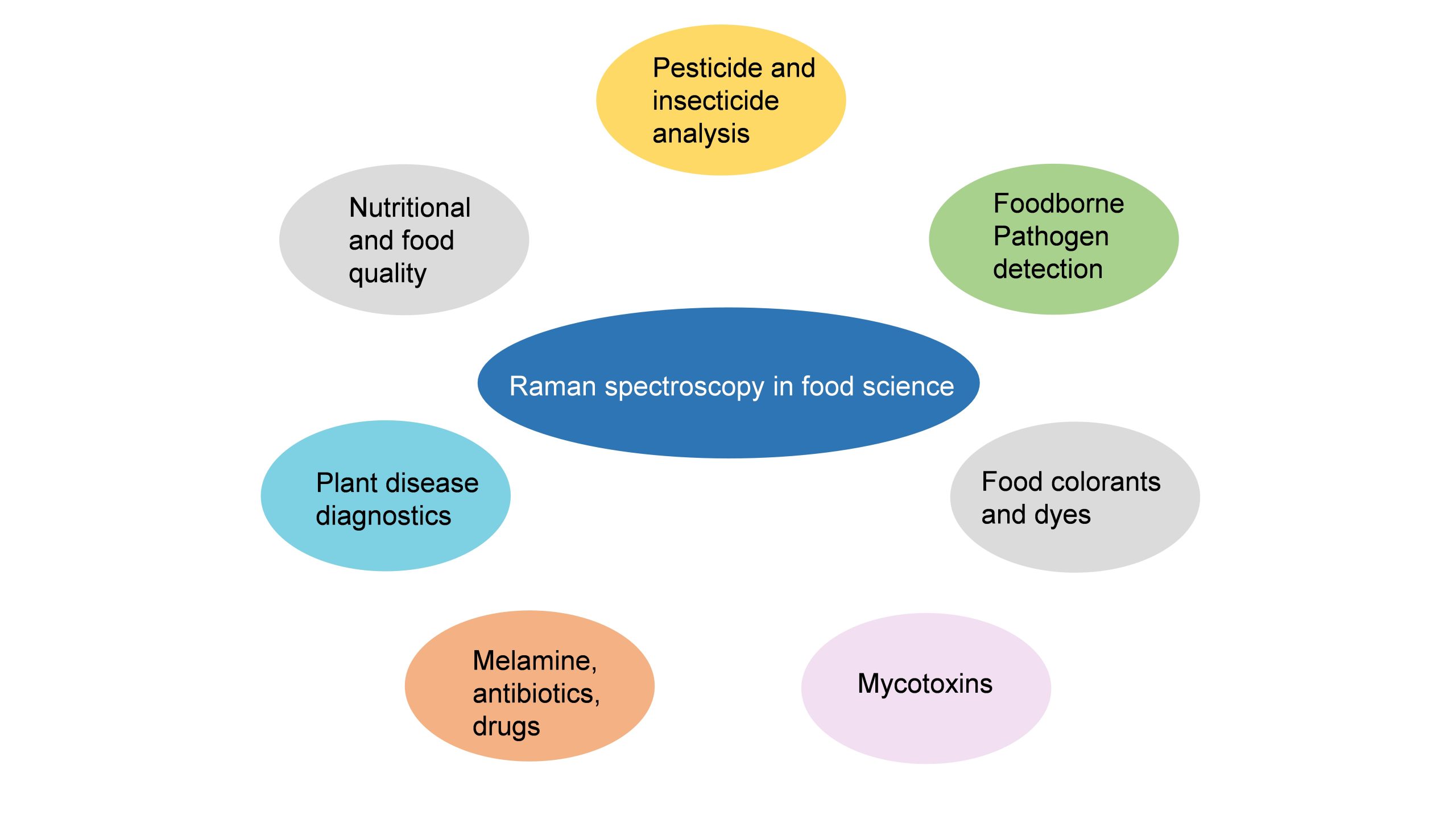
Surface-enhanced Raman Spectroscopy (SERS) is a nuanced chemical technique that amplifies the Raman scattering of molecules by utilising plasmonic nanostructured materials. SERS operates as a powerful detection tool that allows for the structural fingerprinting of a molecule. The ultra-high sensitivity and selectivity of the process offer it a vast array of applications in surface and interface chemistry, nanotechnology, biology, biomedicine, food science, environmental analysis and other areas.
Dr J P Raja Pandiyan and his PhD scholar, Ms Arunima Jinachandran from the Department of Chemistry have been keenly involved in exploring the possibilities of SERS technology in food science and other fields. The safety and quality concerns related to food were the primary reasons that impelled them to step into this domain. Their article “Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy for food quality and safety monitoring” was published in the book Nanotechnology Applications for Food Safety and Quality Monitoring, published by Elsevier. The article was published in collaboration with Dr Selvaraju Kanagarajan from the Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences.
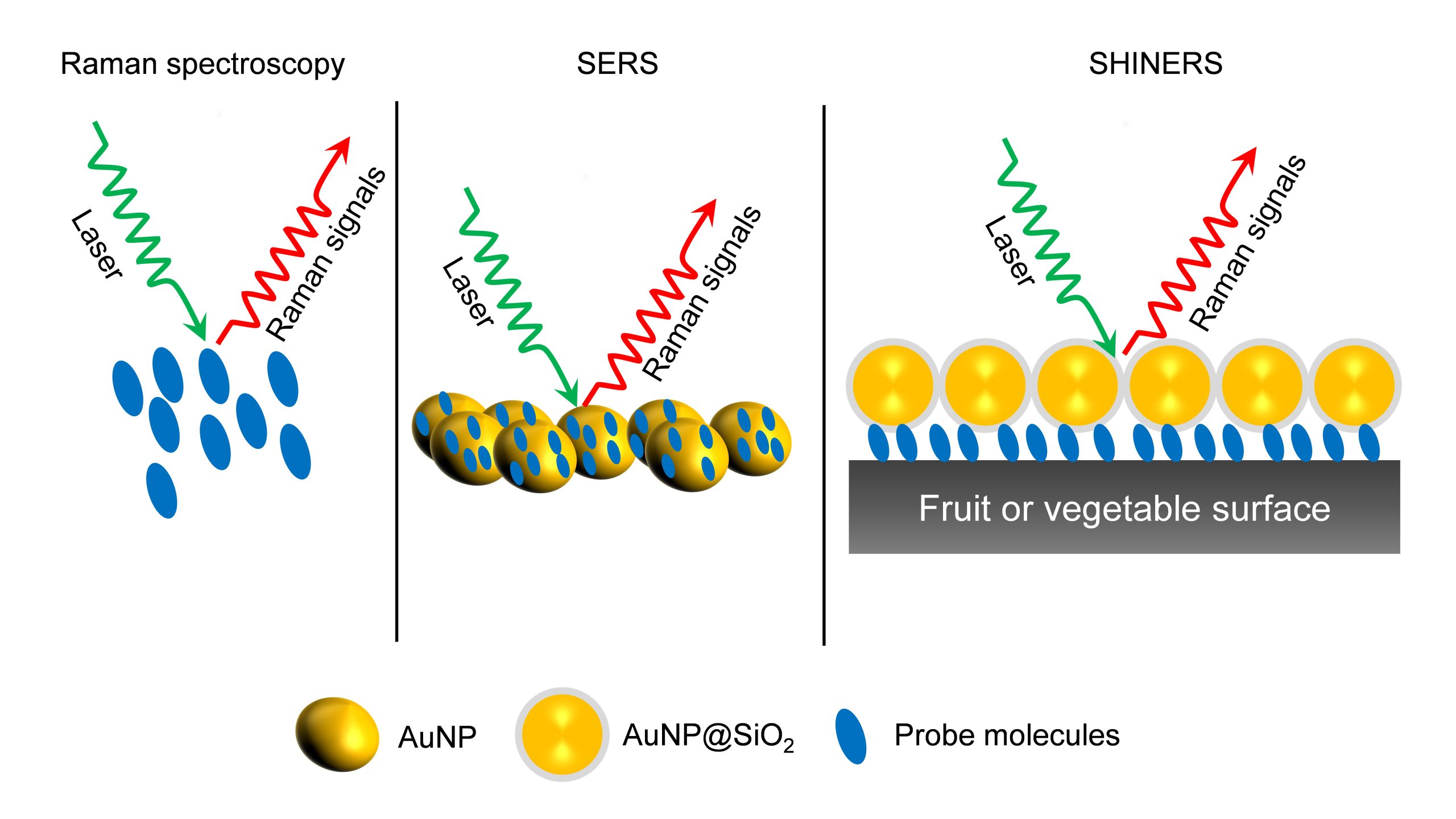 As an analytical technique, SERS possesses several advantages such as non-destructive, sensitive, and selective. In the chapter, the necessity, and applications of SERS in food science are elaborately discussed. They have also discussed all the possible food contaminants and how to identify them using SERS to ensure food quality. This book will serve as an enlightening read to research groups who are working on Raman, surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy, analytical chemistry, and food quality analysis.
As an analytical technique, SERS possesses several advantages such as non-destructive, sensitive, and selective. In the chapter, the necessity, and applications of SERS in food science are elaborately discussed. They have also discussed all the possible food contaminants and how to identify them using SERS to ensure food quality. This book will serve as an enlightening read to research groups who are working on Raman, surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy, analytical chemistry, and food quality analysis.
- Published in Chemistry-news, Departmental News, News, Research News
Enhanced charge transport behaviour of protein-metal nanocluster hybrid
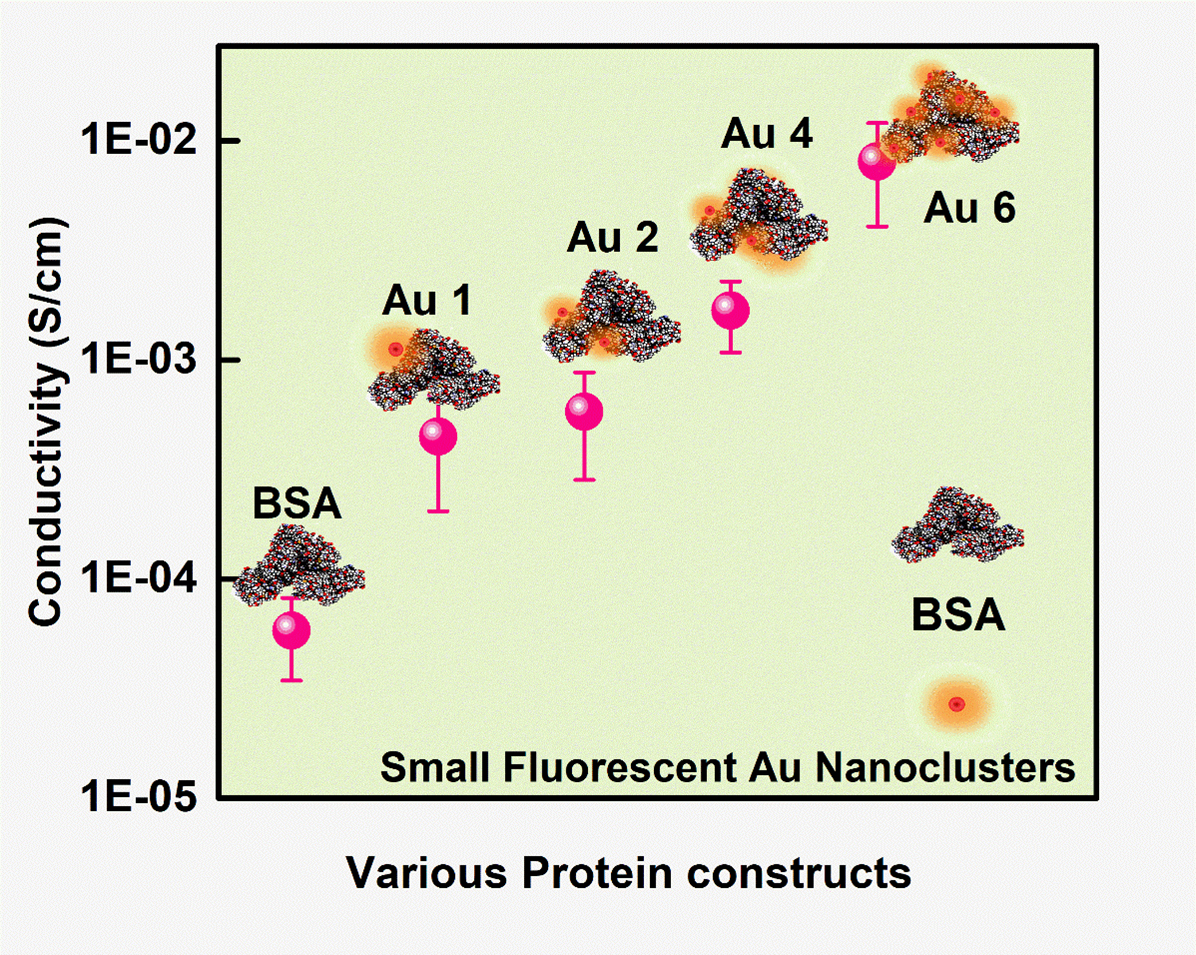
Proteins are the most vital life forms which maintain close coordination with almost living activities through their biological functions. Nevertheless, in most cases, proteins suffer from low charge (electron) transfer efficiency as they are mainly made of insulating organic molecules. The interdisciplinary research publication, of Dr Sabyasachi Mukhopadhyay and Dr Sabyasachi Chakrabortty from the Department of Physics & Department of Chemistry respectively, along with their PhD scholars: Ms Ashwini Nawade, Mr Kumar Babu Busi and Ms Kunchanapalli Ramya, envisions the molecular-level understanding of the charge transport behaviour of various protein-metal nanocluster hybrid.
The article titled ‘“Improved Charge Transport across Bovine Serum Albumin – Au Nanoclusters’ Hybrid Molecular Junction” was featured in the prestigious Q1 journal ACS Omega (IF: 3.512), published by the ‘American Chemical Society’. They successfully incorporated Gold Nanoclusters inside the protein backbone leading to an increase in their conductivity. This will provide new avenues for the rational design of bioelectronic devices with optimized features. The BSA-Au cluster has been a promising model for bioelectronic functionalities. With an increase in their current carrying capacity, they can be used for many more applications, especially as the interface between tissue and organ in biocompatible devices. The research team is also planning to work with various protein dopants to understand their charge transport mechanism. These studies will help in using the protein for various applications mainly in bioimplants or biosensors for drug testing and diagnostics purposes.
Abstract of the Research
Proteins, a highly complex substance, have been the essential element in the living organism where various applications are envisioned due to their biocompatible nature. Apart from protein’s biological functions, contemporary research mainly focuses on their evolving potential associated with nanoscale electronics. Here, we report one type of chemical doping process in model protein molecules (BSA) to modulate its electrical conductivity by incorporating metal (Gold) nanoclusters on the surface or within it. The as-synthesized Au NCs incorporated inside the BSA (Au 1 to Au 6) were optically well characterized with UV-Vis, time-resolved photoluminescence (TRPL), X-ray photon spectroscopy, and high-resolution transmission electron microscopy techniques. The PL quantum yield for Au 1 is 6.8% whereas Au 6 is 0.03%. In addition, the electrical measurements showed ~10-fold enhancement of conductivity in Au 6 where maximum loading of Au NCs was predicted inside the protein matrix. We observed a dynamic behaviour in the electrical conduction of such protein-nanocluster films, which could have real-time applications in preparing biocompatible electronic devices.
- Published in Chemistry-news, Departmental News, News, Physics News, Research News