8th Research Day: A Pathway to Research and Innovation

“Research is a passion. We must lay a strong foundation of basic research to further develop, grow and produce a high-quality research output. Focus on translational research as it is the way forward for an innovative world,” said Prof. Rajeev Ahuja, Chief Guest of the 8th Research Day, while addressing the research community of SRM University-AP.
The university hosted the 8th Research Day on April 26, 2024, in the august presence of Chief Guest Prof. Rajeev Ahuja, Director-IIT Ropar and Officiating Director-IIT Guwahati, Guest of Honour Prof. Amlan Chakrabarti, Director–A. K. Choudhury School of Information Technology, University of Calcutta; Vice Chancellor Prof. Manoj K Arora, Registrar Dr R Premkumar, Dean-Research Prof. Ranjit Thapa, Deans of all schools, faculty, research scholars and students. “Research Day at SRM AP is the celebration of our students’ innovative thought and applauding them in their developing research acumen”, remarked Prof. Arora in his welcome address. He encouraged students to take their research to the next level and become entrepreneurs who will transform the Indian market and economy.
Prof. Amlan Chakrabarti, the designated guest of honour for the day, tremendously appreciated the efforts put forth by the SRM AP in propelling a research-centric education. He remarked that research is the pursuit of thought and the product of innovation. Prof. Chakrabarti also delivered distinguished lectures on the intriguing realm of quantum machine learning and exploring generative AI, shedding light on the latest advancements and potential applications in both fields.
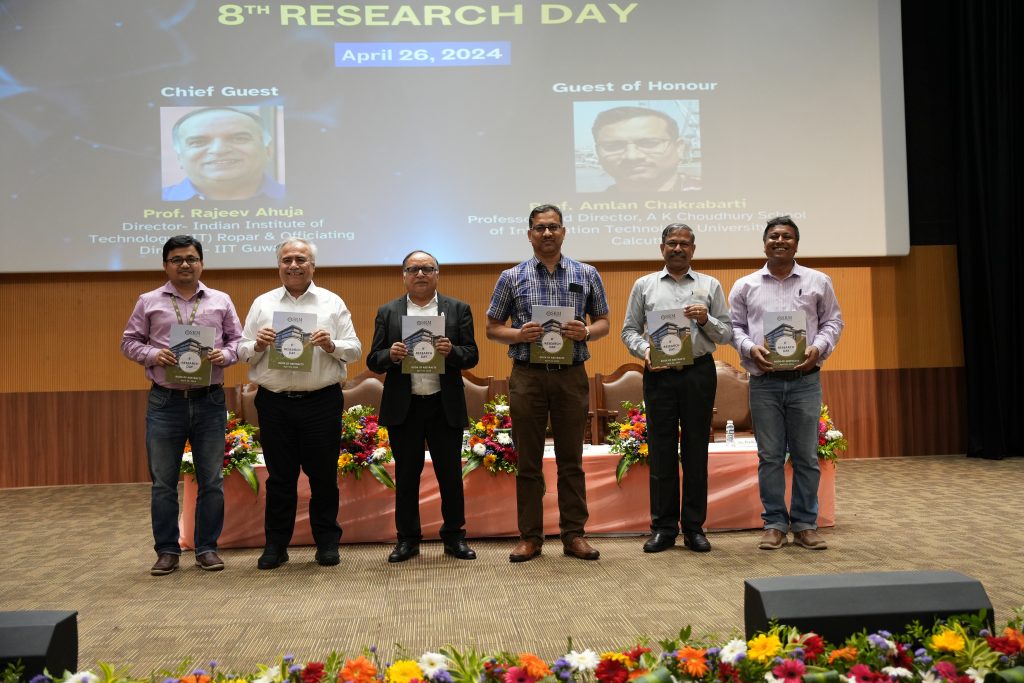

The 8th Research Day was commemorated to celebrate research and innovation in the emerging fields of science, technology, humanities, social sciences, management and commerce. 350+ research abstracts were submitted by undergraduate/postgraduate students and research scholars from across the country, which were culminated and unveiled as an Abstract Book. Selected papers were presented, and medals were awarded to the winners. The paper presentation witnessed 27 participants bagging gold medals and 7 participants securing silver medals. Five esteemed faculty of the university, Dr K M Divya Chaturvedi, Dr Mahesh Kumar Ravva, Prof. G S Vinod Kumar, Dr Ghanshyam Pandey and Dr Ramanjeya Reddy Udumula, were awarded prestigious awards for their stellar contributions and ingenious inventions in their respective domains.
The dignified guests of the events were presented with mementos as a token of gratitude by the university leaders, Dean-Research Prof. Ranjit Thapa and Convenor of the 8th Research Day, Dr Pradyut Kumar Sanki, Associate Professor, Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering. Dr R Premkumar delivered the Vote of Thanks, concluding the spectacular event.
Ranked Third among all private universities in India for two consecutive years according to Nature Index Ranking, SRM University-AP has a total of 2040+ research publications, 200 published patents, 24 granted patents, 43 Nature Index publications and a total outlay of Rs. 37+ crores in projects. The research environment is anchored by Eight Interdisciplinary Research Centres of Excellence. Research Day is a testament to the varsity’s commitment to building a strong research culture and research capacity among the faculty and students across different domains.
- Published in News, Research News
Accelerated Academic Leadership Workshop
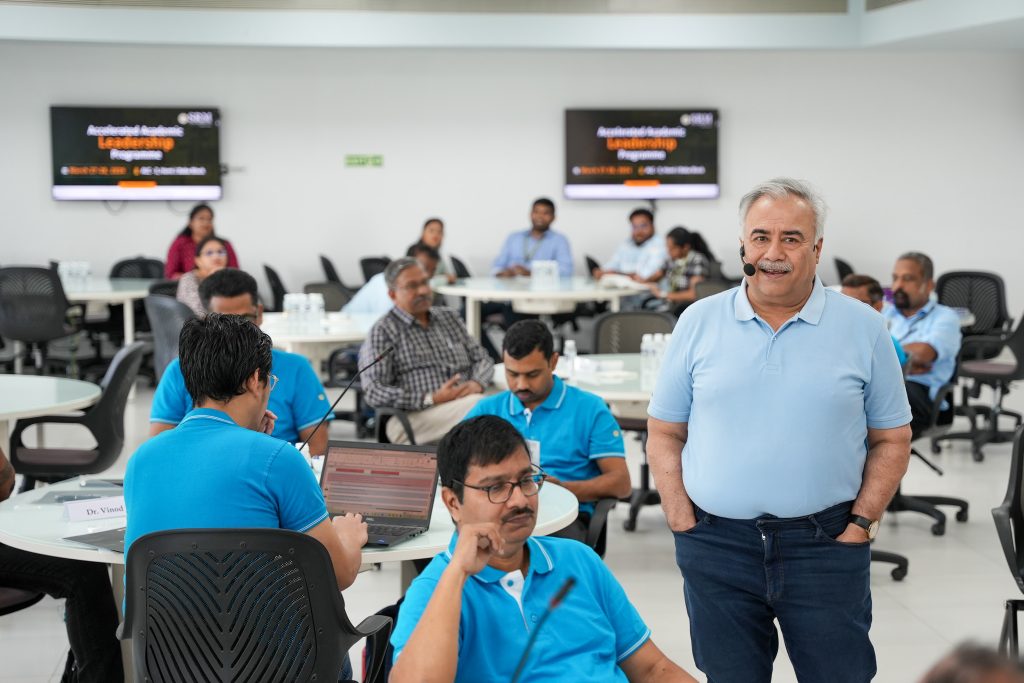

The Directorate of Human Resources organised a 2-day Accelerated Academic Leadership Programme 2024, on March 27 and 28, 2024, bringing together the academic community to align with the institute’s mission and strategic goals. This landmark event, organised in collaboration with People Business Consulting, has brought together Mr Kadapa Hanumantha Rao Muralidhar and Vinish Soman from People Business Consulting, Vice Chancellor Prof. Manoj K Arora, Registrar Dr R Premkumar R, Deans and Associate Deans of all schools and HoDs and faculty from all departments.
“Building on the foundation set by last year’s Alignment 360 Workshop, we are focused on achieving our strategic objectives for 2023-28. Our aim is not only to enhance operational excellence but also to foster individual and collective growth within our community of over 7,000 students and 300 faculty members. Our ambitious targets are to position SRM University-AP among the Top 30 universities in India by 2027-28. We are setting benchmarks that reflect our commitment to excellence and the development of our academic team,” said Prof. Manoj Arora.
Prof. Arora also commented on how the university is dedicated to nurturing a vibrant team of young professors, with an average age of 34, signifying the university’s belief in youthful innovation and dynamic leadership. He also spoke exclusively on SRM AP’s culture of continuous learning and growth, guided by 6 core values integral to our institutional ethos.
- Published in Departmental News, News, Workshop
Leading the Next Generation of Creators and Innovators: Inauguration of Tech Fest 2024
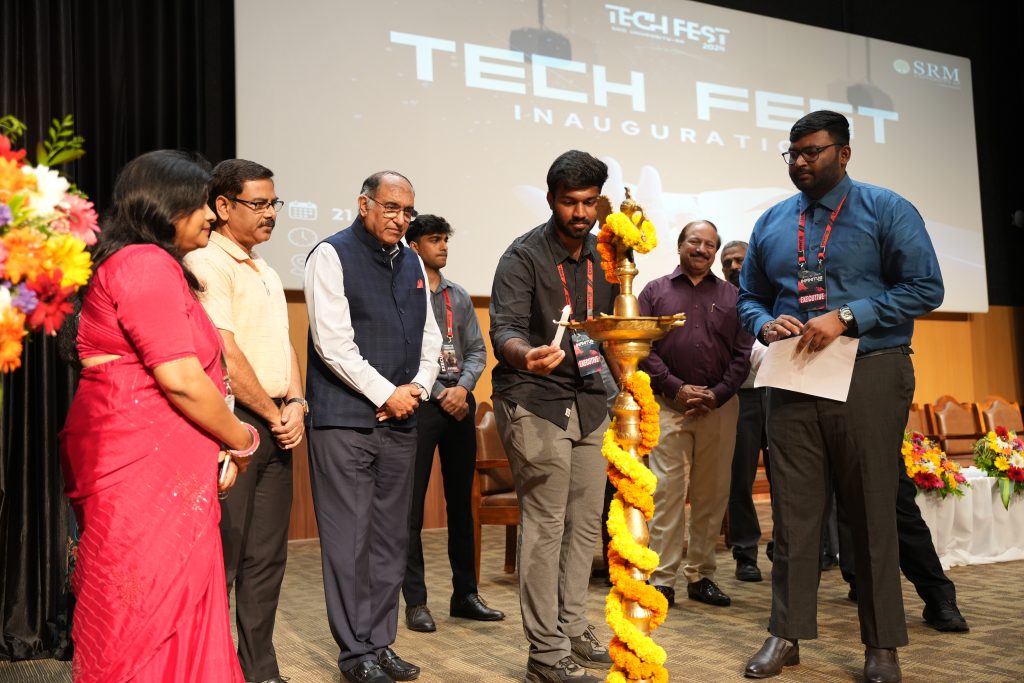

“Tech fests are your platform to explore, learn and thrive. Your spirit to compete and succeed is immaterial without learning, ” remarked Mr Sanjiv Bhavnani, distinguished guest at SRM University-AP Tech Fest 2024.
SRM University-AP kick starts its Tech Fest with glamour, zeal and endless exuberance. The student-led national fest, held from March 21-22, 2024, was inaugurated in the gracious presence of Guest of Honour, Mr Dinesh Dua, Executive Director on Board at Nectar Lifesciences Limited, esteemed guests, Mr Sanjiv Bhavnani, founder of Mentorpreneur & Infotecniques and Dr Deepak Pandit, Chair Professor – Innovation and Entrepreneurship, BML Munjal University, Vice Chancellor, Prof. Manoj K Arora, Registrar, Dr R Premkumar, Director-Student Affairs, Mr Anil Kumar Nigam, Chief Club Advisor, Dr Priyanka, Deans of different schools, leaders and representatives from the Student Council, and all students of the varsity.
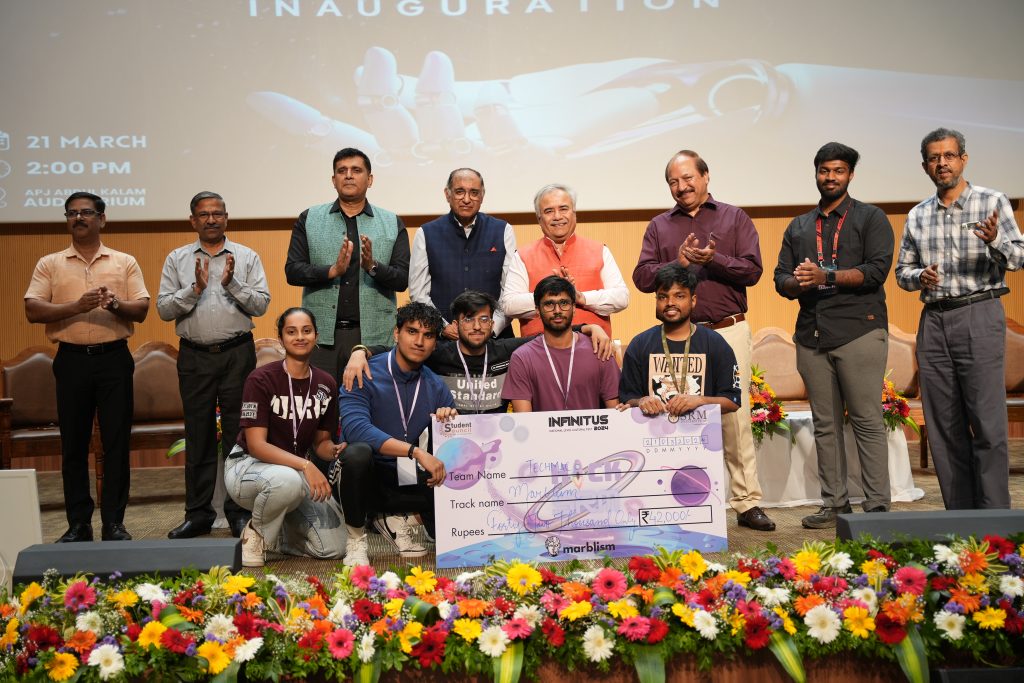

Vice Chancellor, Prof. Manoj K Arora stated in his welcome address that technical fests are magnificent learning platforms. He said, “This is your opportunity to collaborate, network and learn 21st-century skills such as creativity, critical thinking, and problem-solving leadership that will equip you to be the tech leaders of tomorrow.” Mr Dinesh Dua, Guest of Honour, encouraged budding students to take advantage of the upsurge of technology to recalibrate themselves to the new age of intelligence. He expressed his genuine delight in inaugurating the Tech Fest with an interactive discourse on Artificial Intelligence.
The thrilling university fest embarked on its two days of electrifying events and activities with a mega Hackathon challenge, “Hack SRM”, with a prize pool of Rs 4 Lakhs. The 24-hour hackathon challenge saw dynamic participation from colleges around the nation, with young techies from VIT-AP, Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham-Amaravati, SRM University Ramapuram, VISAT Maharashtra bagging the top prizes worth Rs 5000/-, Rs 10,000/-, Rs 40,000/- and Rs 50,000/-.
Tech Fest 2024 is the university’s testament to celebrating innovation, creativity, and boundless possibilities. The four-day fest features technical competitions, non-technical events, workshops, hackathons, ideathons and expos on every technology domain enhancing students’ learning experience.
- Published in News, student affairs news
Breakthrough in Lead-Free Brass Manufacturing: Patent Granted to Prof. G. S. Vinod Kumar

The Department of Mechanical Engineering are excited to share a significant milestone achieved in the field of material science and metallurgy. Prof. G S Vinod Kumar, Professor and Head of the Department, has been granted a patent jointly with Titan Company, Bangalore, for the invention “METHOD OF MANUFACTURING LEAD-FREE BRASS” (Patent Grant Number: 452003). This industrial patent was created through a collaboration between SRM University-AP and Titan Company Limited.
This groundbreaking discovery not only transforms the manufacturing of lead-free brass, but it also highlights the collaborative spirit that drives advances in materials engineering.
Abstract
The present disclosure relates to a field of material science and metallurgy. In particular, the present disclosure discloses a method for manufacturing lead-free brass alloy. The method includes preparation of first master alloy by melting copper and a transition element, and a second master alloy by mixing molten zinc and molten copper. The lead-free brass is obtained by meting a predetermined proportion of the first master alloy and second master alloy along with elemental copper in a furnace under an argon atmosphere. The lead-free brass alloy is then subjected to a precipitation hardening process to improve hardness. The lead-free hard brass alloy containing titanium exhibits improved hardness in comparison to bare lead-free brass mainly due to the presence of intermetallic nanoscale precipitates, which are distributed throughout the lead-free brass matrix.
SRM University-AP continues pushing the limits of scientific discovery and industrial innovation.
- Published in Departmental News, Mechanical Engineering NEWS, News, Research News
Deep Transfer Learning for Green Environment Security in Smart Cities

The Department of Computer Science and Engineering is pleased to announce an extraordinary research paper titled “A Deep Transfer Learning Model for Green Environment Security Analysis in Smart City“, authored by Dr Sambit Kumar Mishra, Assistant Professor, was published in the Journal of King Saud University – Computer and Information Sciences that falls within the Q1 quartile with an Impact Factor (IF) of 6.9. The study introduces a model to automatically classify high-resolution scene images for environmental conservation in smart cities. By enhancing the training dataset with spatial patterns, the model improves green resource management and personalised services. It also demonstrates the effectiveness of LULC classification in smart city environments using transfer learning. Data augmentation techniques improve model performance, and optimisation methods enhance efficiency, contributing to better environmental management.
Abstract
The research addresses the importance of green environmental security in smart cities and proposes a morphologically augmented fine-tuned DenseNet121 (MAFDN) model for Land Use and Land Cover (LULC) classification. This model aims to automate the categorisation of high spatial resolution scene images to facilitate green resource management and personalised services.
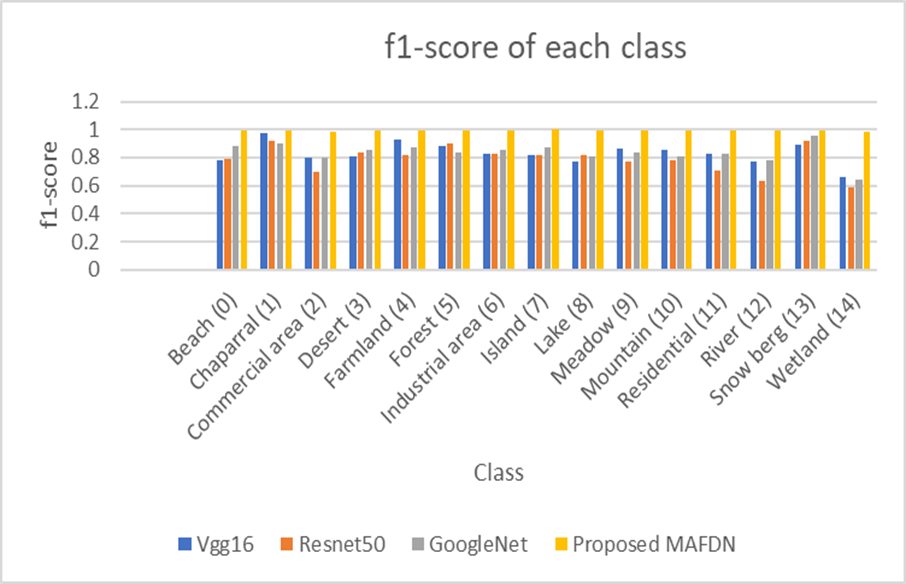
Dr Mishra collaborated with Dr Rasmita Dash and Madhusmita Sahu from SoA Deemed to be University, India, as well as Mamoona Humayun, Majed Alfayad, and Mohammed Assiri from universities in Saudi Arabia.
His plans include optimising the model using pruning methods to create lightweight scene classification models for resolving challenges in LULC datasets.
- Published in CSE NEWS, Departmental News, News
Tracing a Translator’s Journey: An Interview with V Ramaswamy

A translated work must retain the essence and flavour of regional culture and locales. A good translator tries to reproduce the particularities that are ingrained within the texts. On this note, Dr Bidisha Pal, Assistant Professor from the Department of Literature and Languages, has published a paper, “Delving into a Translator’s Journey of Translating Marginalised Voices of Bengal: An Insightful Discussion with V Ramaswamy” in Meta Journal des traducteurs Translators’ Journal. This research revolves around a discussion with the well-known translator V Ramaswamy, a noted name in Bengali Dalit literature and translation. Ramaswamy shares his thoughts on working on the translation projects that he enjoys doing and that establish the cause of the marginalised people of Bengal.
Abstract
In this interview discussion with Bidisha Pal and Md. Mojibur Rahman, translator V Ramaswamy focuses on the journey of his translation and tryst with the marginalised Dalit voice(s) in Bengal. He speaks about the writings that propel him to choose translating and to carry voice(s) beyond the Bengal arena, thus dissolving language barriers. The deliberate choice to translate various pieces representing various periods acts as a witness to his existence as an independent translator. According to him, translation is also a source of healing to deal with a tragic past and the complicacies that life often presents to him. He shares his experience translating Subimal Mishra, the powerful poet who speaks for marginalised people. Ramaswamy, as he states in the interview, makes a vow to translate Mishra’s whole writing career. He talks about translating Manoranjan Byapari, a Bengali Dalit prize-winning author and political persona who has also championed the Dalit cause in Bengal, Adhir Biswas, the story-writer and publisher of a publishing house in Kolkata Gangchil that publishes writings by those literary personas who do not fall, as such, into the category of the mainstream, Bangladeshi writer Shahidul Zahir whose revolutionary voice and zeal reverberate in the literary world of Bangladesh, as well as Ansaruddin, a writer and farmer by profession whose works Ramaswamy is currently translating. Despite not being a part of the literary world, Ramaswamy has built an intense connection with literature and has gradually become part of the world. For him, translation is something that has to remain faithful to the source text, especially if people are doing literary translation.
Practical implementation/social implications of the research
The research contains elements that are connected with the values of the society. It discusses the nuances of translation of the writings of marginalised people, which contain many unforeseen truths of society, and depicts the struggles for the existence of the people. The translator is doing a commendable job compiling the writing thorough translation that will act as a bridge to the unfamiliar audience who could feel connected with the marginalised people.
Dr Bidisha aims to publish many more articles in the diverse interdisciplinary fields of literature, edit books, and attend conferences.
- Published in Departmental News, English Current Happenings, English news, News, Research News
Igniting the Flame of Democracy: ‘Mera Pahala Vote Desh ke Liye’ Initiative
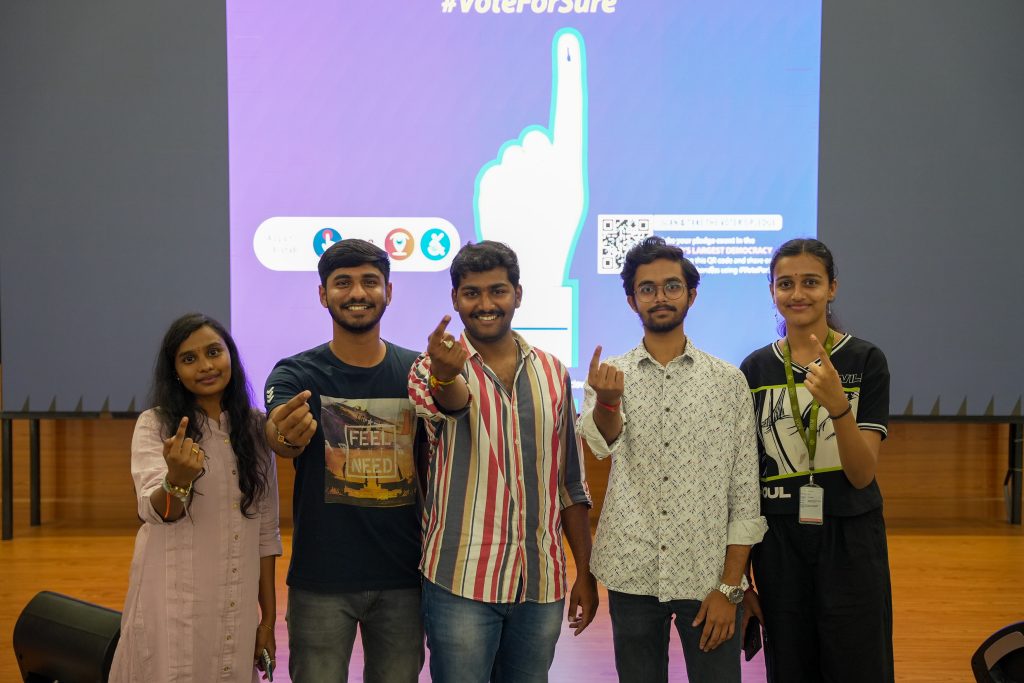

The campus of SRM University-AP was abuzz with a palpable energy as the Directorate of Student Affairs hosted the electrifying “Mera Pahala Vote Desh ke Liye” (My First Vote for the Nation) initiative on March 07, 2024. In a powerful display of civic engagement, students rallied together to celebrate the essence of democracy and ignite the flame of active citizenship.
The event kicked off with a captivating video screening that transported attendees on a journey through India’s vibrant democratic tapestry. Stories of ordinary citizens whose votes reshaped destinies unfolded before their eyes, reminding them of the transformative power they wield with a single mark on the ballot.
As the last frame faded, a solemn hush fell upon the gathering, and a collective pledge echoed through the halls. Students’ voices, united in purpose, vowed to exercise their constitutional rights and make their voices heard in the democratic process. The atmosphere crackled with determination and a renewed sense of responsibility.

But the celebration didn’t stop there! In a burst of youthful enthusiasm, a dedicated selfie point sprung to life, capturing the infectious energy of the moment. Students eagerly posed, their smiles radiating pride and purpose as they immortalised their commitment to shaping the nation’s future.
SRM University-AP‘s commitment to nurturing responsible citizens was displayed as the institution partnered with the Election Commission of India to kindle the flame of democratic participation. With each selfie shared and pledge taken, a powerful message resounded: the future belongs to those actively shaping it.
As the event drew to a close, the campus hummed with a renewed sense of purpose, a collective awakening to the responsibilities and privileges of being citizens of the world’s largest democracy. The ‘Mera Pahala Vote Desh ke Liye’ initiative has undoubtedly left an indelible mark, igniting a fire within the hearts and minds of SRMites – a fire that will guide them as they navigate the intricate tapestry of India’s democratic journey.
- Published in News, student affairs news, Students Affairs Events
SOFEEM-2024: A National Conference on Functional Energy and Electronic Materials

SRM University-AP hosted a national conference on “Status and Opportunities in Functional Energy and Electronic Materials” (SOFEEM-2024) on March 02-03, 2024. The conference was organised by the Department of Physics and was supported by the Department of Science and Technology, Government of India. The conference brought together about 100 participants from various reputed institutions, national laboratories, and universities from India. They shared their research outcomes and discussed the various frontier energy technologies and smart electronic devices.
The main theme of the conference was to boost the development and optimal use of renewable energy and to promote sustainable energy and intelligent electronics. The conference focused on fostering collaboration among researchers and practitioners to explore cutting-edge developments in these domains and pave the way for innovative solutions. A diverse array of topics was covered, including:
- Synthesis and processing of novel energy and electronic materials
- Modelling of low-dimensional materials
- Materials and catalysts for green hydrogen production
- Electrolyte and electrode materials for high-performance batteries and fuel cells
- Functional materials for supercapacitors
- Device fabrication using novel energy materials for energy conversion and storage
- Low-dimensional materials in electronics and photonics
The conference was inaugurated by Prof. Manoj K Arora, Vice Chancellor, who welcomed the guests and the delegates and highlighted the university’s achievements and vision. He also emphasised the importance of interdisciplinary research and innovation in addressing the global energy and environment challenges.

The conference featured keynote lectures, invited talks, oral presentations, and poster sessions by experts and young researchers. Distinguished Keynote speakers from IIT Madras, along with Invited speakers from prestigious institutions such as the Indian Institute of Science (IISC) Bangalore, IIT Tirupati, IIT Hyderabad, University of Hyderabad, IISER Bhopal, and the CSIR – Central Electrochemical Research Institute (CECRI) in Tamil Nadu, among others from esteemed state universities, shared their groundbreaking research. The conference provided a good platform for the participants to interact with the eminent researchers to enrich and share their knowledge in their respective fields of research and engage in potential collaboration to develop innovative technologies in the areas of sustainable energy, advances in materials research and computational sciences. In addition, research scholars from nearby universities (such as VIT-AP, Vignan University, Acharya Nagarjuna University, and SRM-IST) participated in the conference and showcased their current research works.
The conference concluded with awards for the best poster and oral presentation by research scholars, celebrating their significant contributions to the field. The conference concluded with a valedictory session, where the best oral and poster presentations were awarded, and feedback from the participants was collected. The conference was well-received by the attendees, who appreciated the quality and diversity of the scientific discussions, as well as the university’s hospitality and facilities.
- Published in Departmental News, News, Physics News
A Pathbreaking Cross Between Medicine and Technology

The advent of scientific research and technologies in the domain of medicine has recently taken limelight due to its immense benefit on humankind and the medical community. The expert faculty and scholars have recently published a patent, “A System and a Method for Early and Accurate Diagnosis of Cataracts” with Application no.: 202341072058 has put forth an engaging invention on utilising technology for early cataract recognition. Hearty congratulations to Prof. Siva Sankar Yellampalli, Professor, Dr Ramesh Vaddi, Associate Professor, and their Ph.D. Scholars Ms P L Lahari, Mr P Rahul Gowtham, and Mr A Vinod Kumar from the Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering for this groundbreaking achievement!
Abstract
Cataracts are a common eye condition in which the lens of the eye gets clouded, impairing vision. Early cataract detection is crucial for prompt treatment and vision preservation. We have classification and prediction algorithms like VGG, ResNet, DenseNet, Xception, Inception, and other object detection techniques like Yolo, Fast R-CNN, and SSD. Various pre-trained models are employed for cataract categorisation and prediction. Several attempts to detect cataracts have been made, but none have proven effective. A clinical examination by eye specialists is used to diagnose cataracts. An edge board can be used instead of a clinical examination to diagnose cataracts.
We created a method for real-time cataract recognition using the present pre-trained weights of the object detection model YoLoV5. We employ pre-trained YoLo V5 weights for model training, testing, and validation. Connect the Jetson Nano board and Lenovo HD USB camera to the CPU, which serves as the CPU. The monitor is used for programming, and the output is presented on the monitor owing to the board communicating with the camera. The result shows the image with an eye labelling box that tells if the eye is normal or cataract.
- Published in Departmental News, ECE NEWS, News, Research News
Young Investors Workshop for Management Graduates

The Paari School of Business has organised a transformative two-day Young Investor Education Workshop on “Financial Education for Young Citizens” for MBA students on February 26-27, 2024, led by finance expert Dr Vijaya Kumar Chilukuri from NISM. The sessions covered diverse finance intricacies and career strategies. Certificates were awarded to participants who cleared the examination, adding value to their academic journey. A Pre-assessment and post-assessment were conducted, which helped students understand their learning journey. Dr Chilukuri’s expertise and his interactive sessions left a lasting impact on all the students, and they actively participated in learning many key concepts of savings and investments. These workshops conducted by the school align with SRM AP’s commitment to holistic education and student success.
- Published in Departmental News, News, Paari Current Happenings, paari-events

















