SRM-AP All News
ALL News
- SERB- SURE Grants: 10 projects worth 2.50 crores awarded to SRM AP May 16, 2023

The faculty of SRM University-AP have been awarded 10 projects worth 2.50 crores from the Science and Engineering Research Board (SERB-SURE). Department of Science and Technology (DST) received a total of 2000 proposals, of which 466 were sanctioned. Among the 466 projects, 151 projects were awarded to Private Universities. Of the 151 projects approved to state private universities and colleges throughout India, the five-and-a-half-year young varsity was awarded 10 projects. 10 professors from various Science and Engineering Departments brought this incredible achievement to the university.
SERB-SURE is a research grant scheme initiated by the Science and Engineering Research Board (SERB) in India to provide financial support to young researchers in the early stages of their careers. The grants are intended to support research in basic and applied sciences, engineering, and technology and is typically granted for a period of three years.The SERB-SURE scheme is one of several initiatives by SERB to promote scientific research in India and support the development of a strong research community in the country.
“It is a milestone achievement that resonates with the University’s unparalleled commitment for excellence. We are striving towards research-intensive learning to build cutting-edge innovation for a transformative tomorrow”, commented Vice Chancellor, Prof. Manoj K Arora. The Executive Director-Research of SRM Group, Prof. Narayana Rao said that, “SRM University-AP has travailed hard to achieve the world-class scientific temperament that we now advocate, and this achievement is a testimonial recognition of all our efforts.” The prestigious grants were sanctioned to the faculty in the on-going domains of Quantum Kinetic Approach, Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR) Profiling and Changing of Hydroclimatic conditions in Bay of Bengal among 7 others.
Dean-SEAS, Prof. Ranjith Thapa said, “These research could be path-breaking and could offer a solution to many of the societal difficulties.” Prof. Jayaseelan Murugaiyan, Dr Sandeep Singh and Dr Pitchaiah Cherukuri of the Department of Biological Sciences; Dr Sabyasachi Chakrabortty, Dr V S Baswanth Oruganti of the Department of Chemistry; Dr Debabrata Pramanik, Dr Ravi Kumar and Dr Pankaj Bhalla of the Department of Physics ; Dr Sandeep Kumar Verma of the Department of Mathematics; Dr Uma Maheswar Arepalli of the Department of Civil Engineering; and Dr Kousik Das of the Department of Environmental Science and Engineering were awarded the grants.
Continue reading → - A Discourse on Multiscale Modelling of Complex Systems May 11, 2023

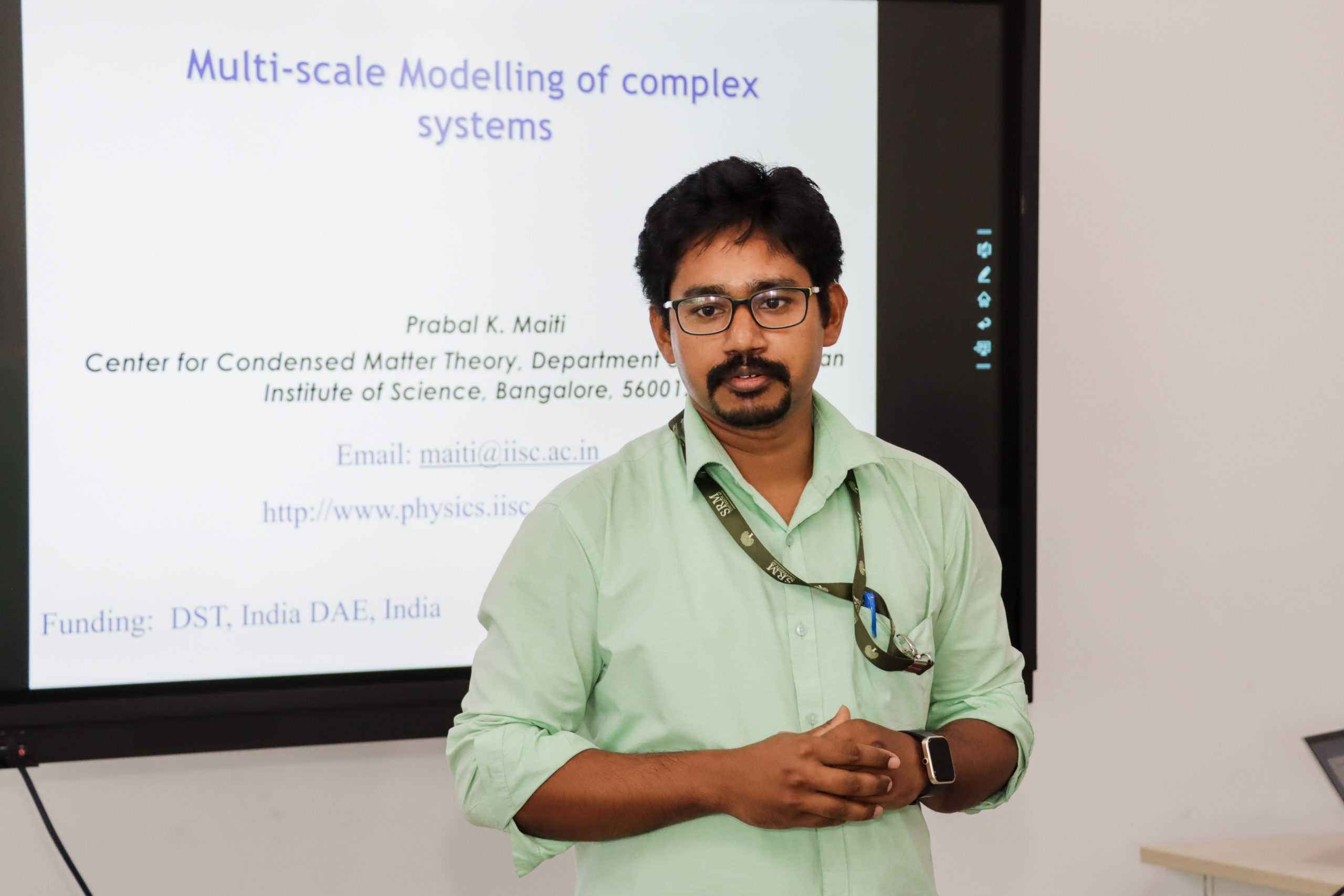
The Department of Physics, SRM University–AP organised the 8th lecture of the “Eminent Guest Lecture Series: An Odyssey of Physics” on May 10, 2023. Prof. Prabal K Maiti from the Department of Physics, Indian Institute of Science (IISc) Bangalore visited the university campus and delivered a talk on “Multiscale Modelling of Complex Systems”. The seminar was held at colloquium level to motivate and encourage young undergraduates and graduates.
More than 60 participants attended the seminar across the disciplines and interacted with the eminent speaker. During his visit, Prof. Maiti also had one-to-one interaction sessions with the faculty members and research scholars. The speaker also enthusiastically interacted with many students informally over breakfast at the university mess hall. Dr Debabrata Pramanik from the Department of Physics coordinated the event with Dr Amit Chakraborty and with active participation from the research scholars, faculty members and supporting staff. Department of Physics plans to conduct more such events where eminent and distinguished scientists will visit the campus and encourage young talents.
Continue reading → - Two-Dimensional Transition Metal Oxide Layers and A method for Their Synthesis May 8, 2023
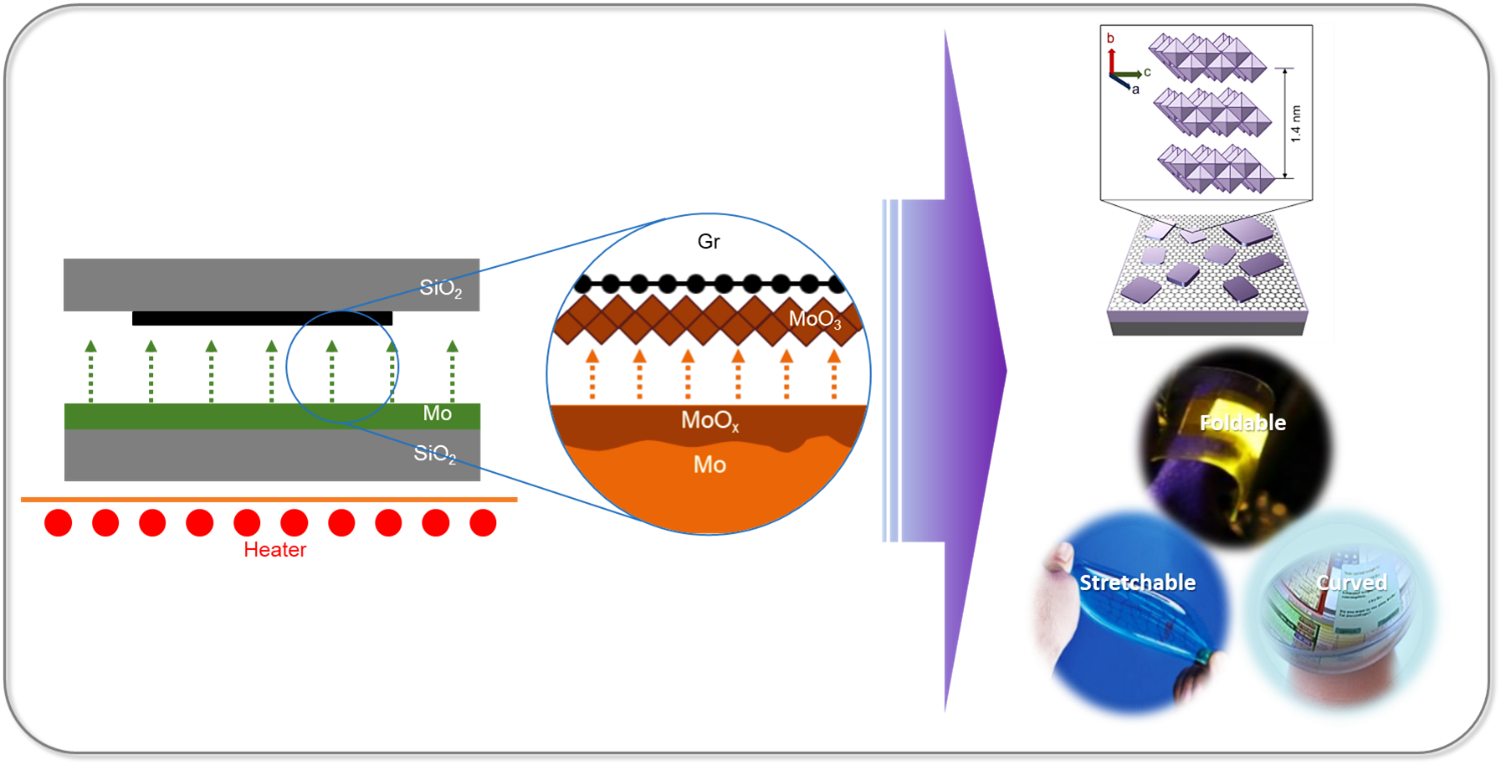 Researchers at the Department of Physics have successfully developed large-area ultra-thin 2D transition metal oxide (TMO) layers using a cost-effective and straightforward method through proximity evaporation under ambient conditions. Associate Professor Dr Jatis Kumar Dash and his students Shaik Md. Abzal, Kurapati Kalyan, and Sai Lakshmi Janga have secured a patent for their research in Two-Dimensional Transition Metal Oxide Layers and A method for their Synthesis (application no: 202241005220). They have integrated the 2D TMO layers with various other 2D materials to create nano-electronic devices. Their work demonstrates the immense potential of ultra-thin TMOs in 2D-material-based flexible electronics.
Researchers at the Department of Physics have successfully developed large-area ultra-thin 2D transition metal oxide (TMO) layers using a cost-effective and straightforward method through proximity evaporation under ambient conditions. Associate Professor Dr Jatis Kumar Dash and his students Shaik Md. Abzal, Kurapati Kalyan, and Sai Lakshmi Janga have secured a patent for their research in Two-Dimensional Transition Metal Oxide Layers and A method for their Synthesis (application no: 202241005220). They have integrated the 2D TMO layers with various other 2D materials to create nano-electronic devices. Their work demonstrates the immense potential of ultra-thin TMOs in 2D-material-based flexible electronics.Patent Background
The two-dimensional (2D) ultrathin hetero-stacked layers show unusual physiochemical properties when reduced to a few atoms in thickness. These 2D heterostructures offer significant benefits for next-generation devices. Firstly, their atomically thin 2D nanosheets provide a larger surface area due to the complete exposure of surface atoms. Secondly, edge sites in 2D nanosheets are chemically more reactive than their basal planes, and open gaps allow for the intercalation of electrolyte ions. In addition, the high mechanical strength and flexibility at atomic dimensions make them suitable for use in next-generation wearable electronics. However, growing and stacking 2D materials is challenging, and existing growth tools are complex and costly.
Future Prospects
2D materials are critical for making flexible, wearable, foldable and transparent self-powered smart electronic devices. The next generation smart electronic devices will be
Continue reading →
made of 2D materials heterostructures which will need less operating power, fewer materials consumption and will have ultimate scalability. - Inculcating Social Awareness May 8, 2023
 Saurvi and Indigo, Student-led communities of Directorate of Leadership, Innovation and Entrepreneurship had conducted a visit on April 19, 2023 to Vasavya Mahila Mandali (VMM) Vijayawada. Vasavya Mahila Mandali(VMM) is a non-profitable and renowned women organization working to transform the lives of women and children since its inception.The NGO has taken part in various activities and is known for its passion and commitment in building a society with happy families and human values.
Saurvi and Indigo, Student-led communities of Directorate of Leadership, Innovation and Entrepreneurship had conducted a visit on April 19, 2023 to Vasavya Mahila Mandali (VMM) Vijayawada. Vasavya Mahila Mandali(VMM) is a non-profitable and renowned women organization working to transform the lives of women and children since its inception.The NGO has taken part in various activities and is known for its passion and commitment in building a society with happy families and human values.Students of SRM University-AP visited the NGO as part of the Corporate Social Responsibility programme. The student-led communities are well-known for promoting leadership and entrepreneurial skills amongst the members and so, the visit proved to be highly motivating. The visit was an initiative by the Directorate to inculcate a sense of awareness and accountability amongst the students. 35 students along with faculty visited the NGO, and interacted with women entrepreneurs. They witnessed the tireless efforts that the social entrepreneurs make to better the lives of others. Interaction with the lesser privileged inhabitants at VMM was an eye-opening experience. Not only did the students learn of societal iniquity, but they also learnt of innovative solutions to these evils.
Students also got to learn about the workings of the startup ecosystem. The students also took a tour of the various centers inside the NGO. The visit to the center provided the students a better understanding of societal problems and helped them expand their horizons.
Continue reading → - One-Day Workshop on Powder X-ray Diffraction May 3, 2023
 A One-Day Workshop on Powder X-ray Diffraction was conducted on April 28, 2023, by the Department of Physics in association with Malvern Panalytical, a division of Spectris Technologies. The workshop was intended to train users on the foundation of the X-ray diffraction technique in solids, the equipment’s hardware, data collection and analysis by software and advanced applications on thin-film and battery measurements.
A One-Day Workshop on Powder X-ray Diffraction was conducted on April 28, 2023, by the Department of Physics in association with Malvern Panalytical, a division of Spectris Technologies. The workshop was intended to train users on the foundation of the X-ray diffraction technique in solids, the equipment’s hardware, data collection and analysis by software and advanced applications on thin-film and battery measurements.More than 60 participants attended the workshop from eight different institutes, including SRM University-AP, VIT-AP, KL University, Vignan’s Foundation for Science, Technology & Research, PB Siddhartha College, VR Siddhartha Engineering College, Raghu Institute of Technology – Visakhapatnam and NIT Andhra Pradesh. Four members from the Panalytical team visited, and the experts, Dr Mangesh Mahajan and Dr Sandeep Nagar, presented technical presentations on the topics.
Advanced features of the HighScore Plus software application and in-situ Powder X-ray diffraction measurement on battery charge-discharge were vital highlights. The external members interacted with participants during the technical sessions and during X-ray diffraction laboratory demonstrations. Participants were awarded a certificate by the varsity and Malvern Panalytical.
Dr Pranab Mandal, Head of the Department of Physics and Mr Soumik Mahapatra from Panalytical coordinated the event. The workshop witnessed active participation from research scholars and faculty from the Department of Physics. The Department plans to conduct more events on advanced research techniques and hands-on training for young researchers.
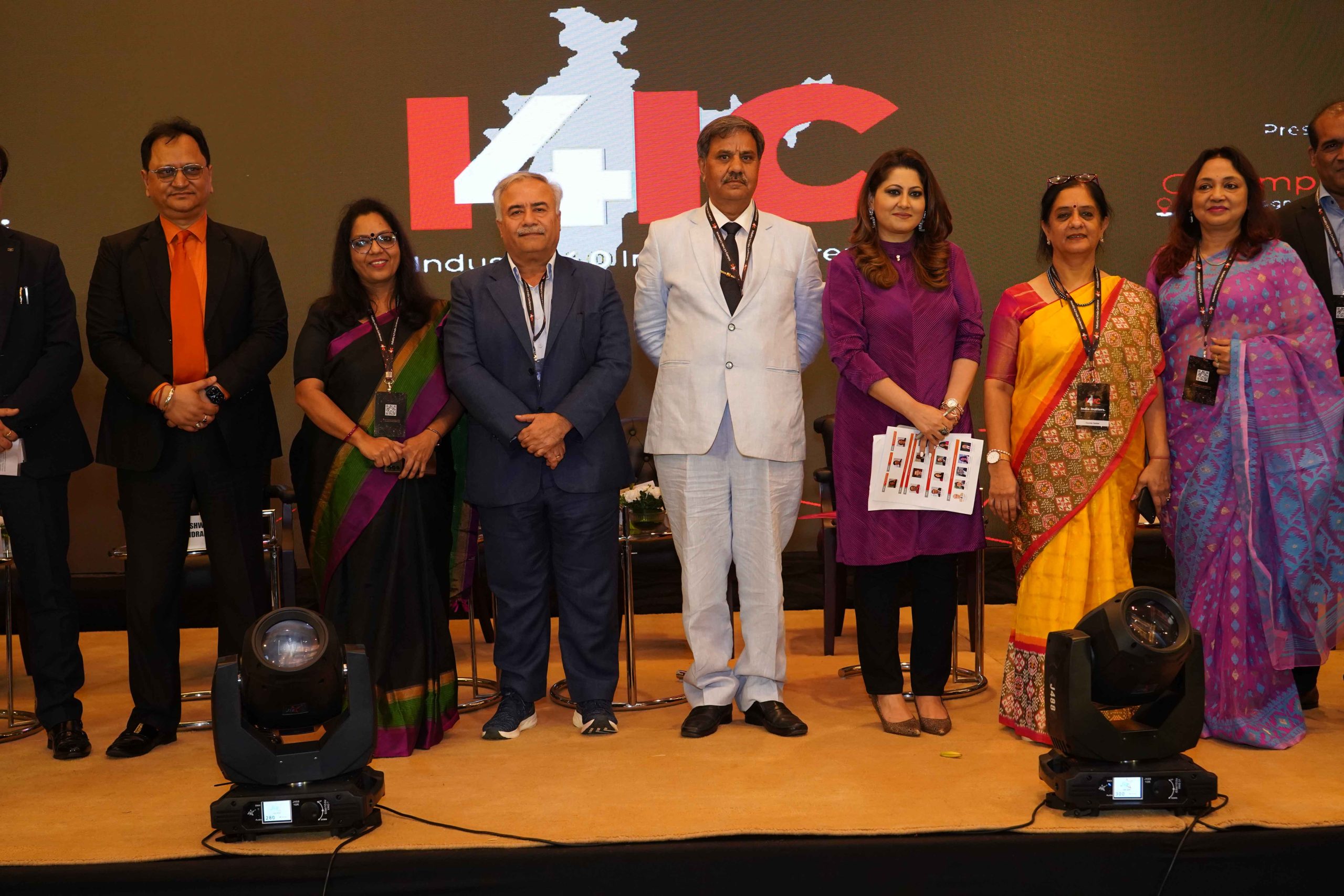
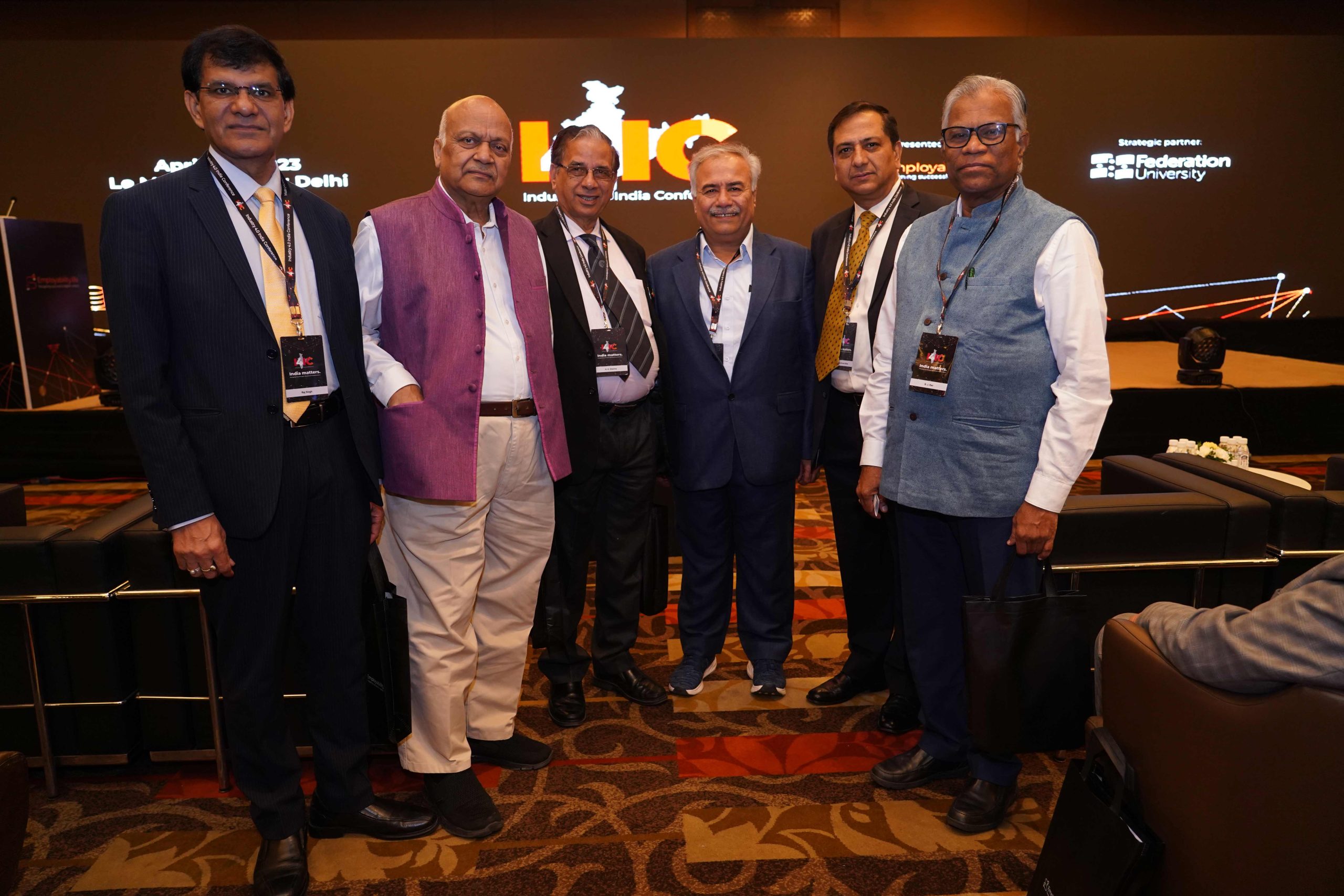
Continue reading → - The 5 ‘I’s of UG and PG Education: Prof. Manoj K Arora at the Industry 4.0 India Conference May 1, 2023
 Honourable Vice Chancellor Prof. Manoj K Arora participated in Industry 4.0 India Conference organised by Employability.life in Delhi from April 25 to 26, 2023. At the Vice Chancellors Workshop on April 25, 2023, he emphasised the need to integrate education with skills and certification. He shared his experiences on how SRM University-AP is revamping the curriculum for all UG and PG programmes from 2023 to 24. The 21st-century skills, co-curricular activities, value education, community services, projects, internships, and field studies will be integral to the curricula, delivered through project-based learning and active learning.
Honourable Vice Chancellor Prof. Manoj K Arora participated in Industry 4.0 India Conference organised by Employability.life in Delhi from April 25 to 26, 2023. At the Vice Chancellors Workshop on April 25, 2023, he emphasised the need to integrate education with skills and certification. He shared his experiences on how SRM University-AP is revamping the curriculum for all UG and PG programmes from 2023 to 24. The 21st-century skills, co-curricular activities, value education, community services, projects, internships, and field studies will be integral to the curricula, delivered through project-based learning and active learning.Extending on this concept, during the panel discussion on Transforming Higher Education for India 2030 on April 26, 2023, he spoke about how SRM University-AP focuses on the 5 ‘I’s of UG and PG education. He proceeded to mention the 5 ‘I’s, such as Integrative Curricula where integration of research with teaching, integration of live problems from society and community in courses, integration of industry and international experts with faculty and integration of technology with teaching-learning processes; Interdisciplinarity where research is at the core as many discoveries happen at the border between disciplines, and therefore being borderless will be crucial for meeting the national challenges; Innovation that goes hand in hand with research leading to an entrepreneurial buzz on the campus; International Cooperation that becomes a necessity not only for high-quality research and innovation but for teaching and learning as well; and Inclusivity by involving global partners, the higher education community, industry partners, civil society, government departments and communities in the learning processes thereby promoting rightful intellect distribution.
Continue reading → - Delivered Lecture at the Two – day National Conference on Youth Development May 1, 2023
 Dr Aehsan Ahmad Dar, Assistant Professor, Department of Psychology, delivered a lecture titled Impact of Childhood Adversity on the Mental Health of Young Adults in Kashmir at the Two – day National Conference on Youth Development held on March 24 and 25, 2023. Youth in the 21st Century: Prospects and Psychosocial Challenges was the theme of the conference, which was organised by the Department of Social Work and Department of Applied Psychology, Rajiv Gandhi National Institute of Youth Development (RGNIYD), Sriperumbudur, Tamil Nadu, in collaboration with ICMR – NIRT, Chennai.
Dr Aehsan Ahmad Dar, Assistant Professor, Department of Psychology, delivered a lecture titled Impact of Childhood Adversity on the Mental Health of Young Adults in Kashmir at the Two – day National Conference on Youth Development held on March 24 and 25, 2023. Youth in the 21st Century: Prospects and Psychosocial Challenges was the theme of the conference, which was organised by the Department of Social Work and Department of Applied Psychology, Rajiv Gandhi National Institute of Youth Development (RGNIYD), Sriperumbudur, Tamil Nadu, in collaboration with ICMR – NIRT, Chennai.Abstract of the Lecture
The study examines the impact of Adverse childhood experiences (ACEs) on mental health among young adults in Kashmir. A cross-sectional research design was followed to study the effect of ACEs on the mental health of Kashmiri youth by employing a multi-stage sampling method. Data were collected from 693 research participants who were studying in different colleges and universities in Kashmir, with the help of the Adverse Childhood Experiences scale and Mental Health Inventory (MHI-18). Findings revealed that various adversities during childhood, including psychological abuse, physical abuse, contact sexual abuse, household substance abuse, violent household treatment of mothers and fathers, household mental illness, and household criminal behaviour, had a significant impact on the mental health of Kashmiri youth in terms of increased anxiety, depression and loss of behavioural control and decreased positive affect.
Practical Implementation of the Findings
ACEs are traumatic events that individuals under 18 have experienced. Various individual, family, and community factors can affect a child’s likelihood of experiencing ACEs, and it causes long-term risks for mental health with the potential to carry over beyond the present generation. ACEs are linked to chronic health problems, mental illness, and adult risk-taking behaviours. There is a “dose-response relationship” between ACEs and health outcomes. Therefore, findings suggest advocating early targeted interventions to reduce ACEs and their impact on young people’s mental health in Kashmir. There is a need to design efficient measures, to enhance ACE resilience programs and ‘trauma-informed’ approaches to tackle the longer-term impact of ACEs on health and wellbeing.
Continue reading → - Research Day 2023: Anchoring an Innovative Research Culture May 1, 2023
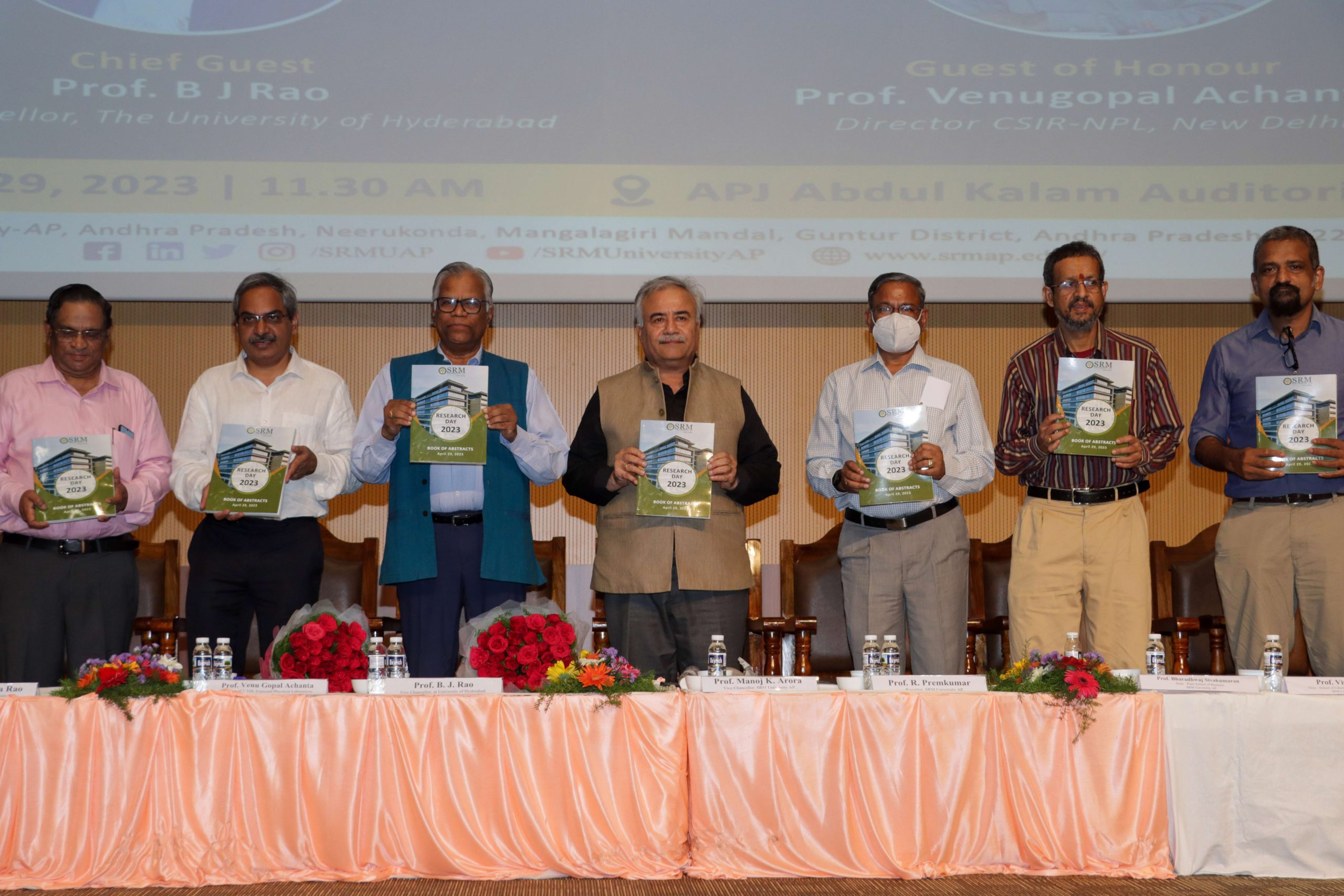
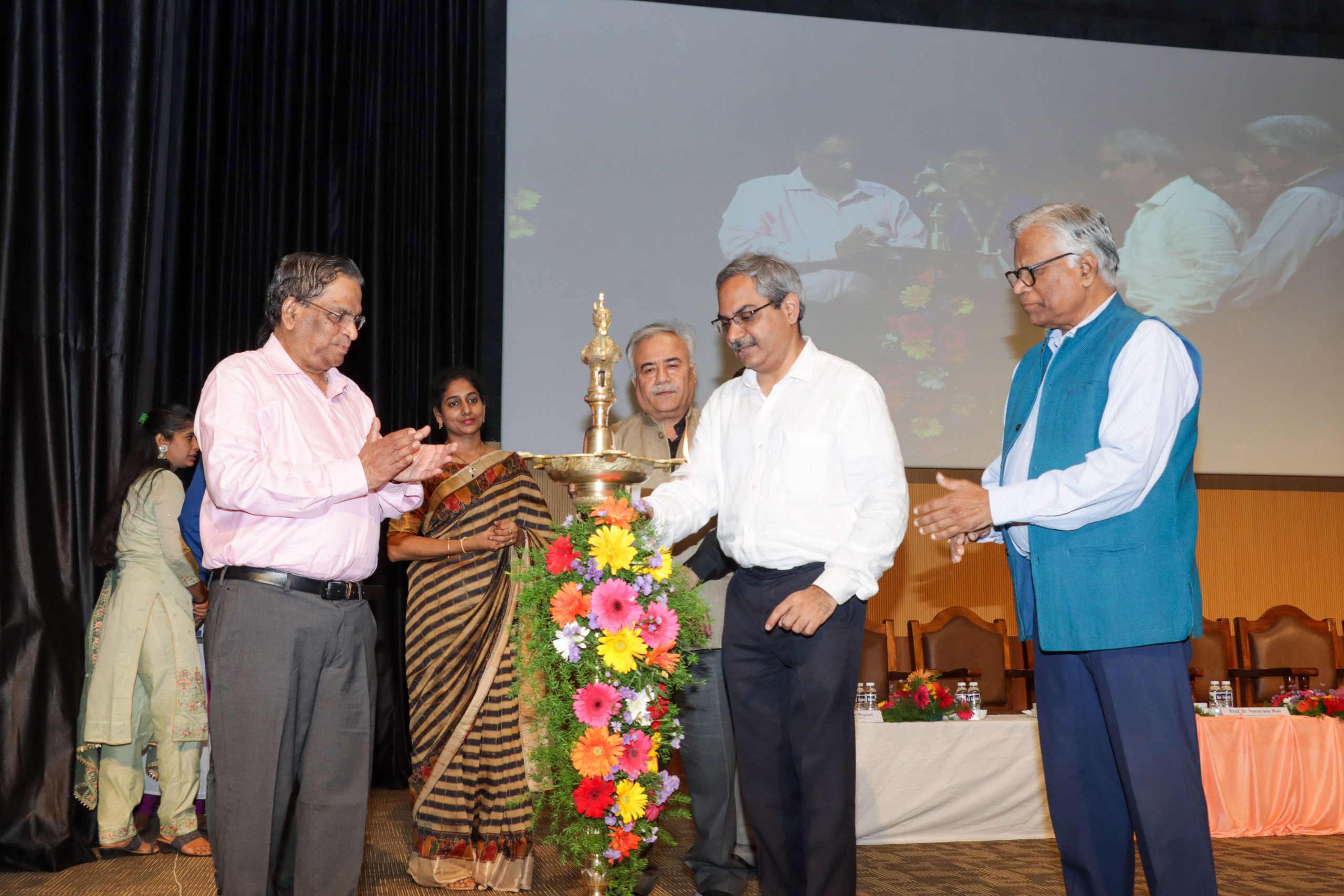
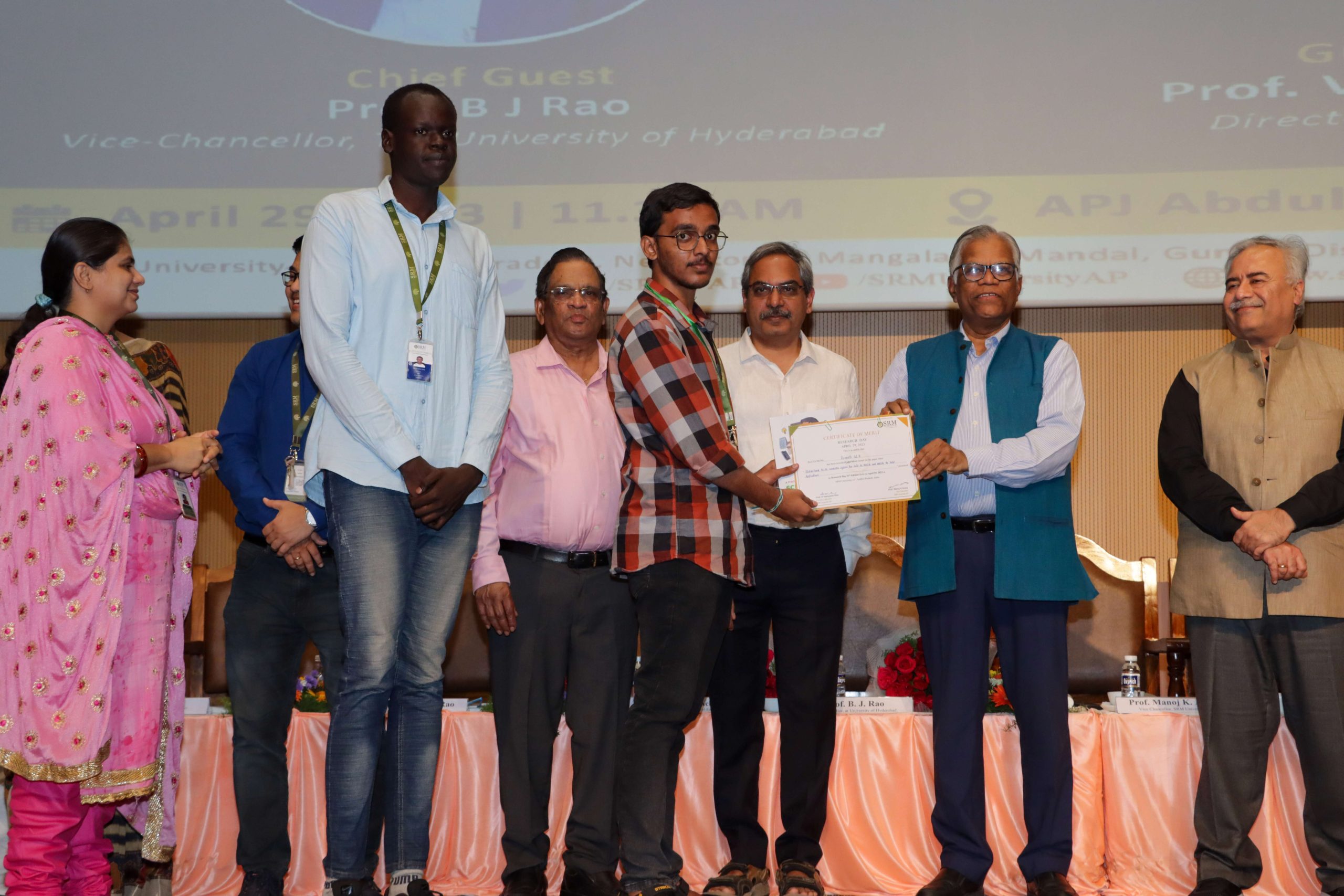
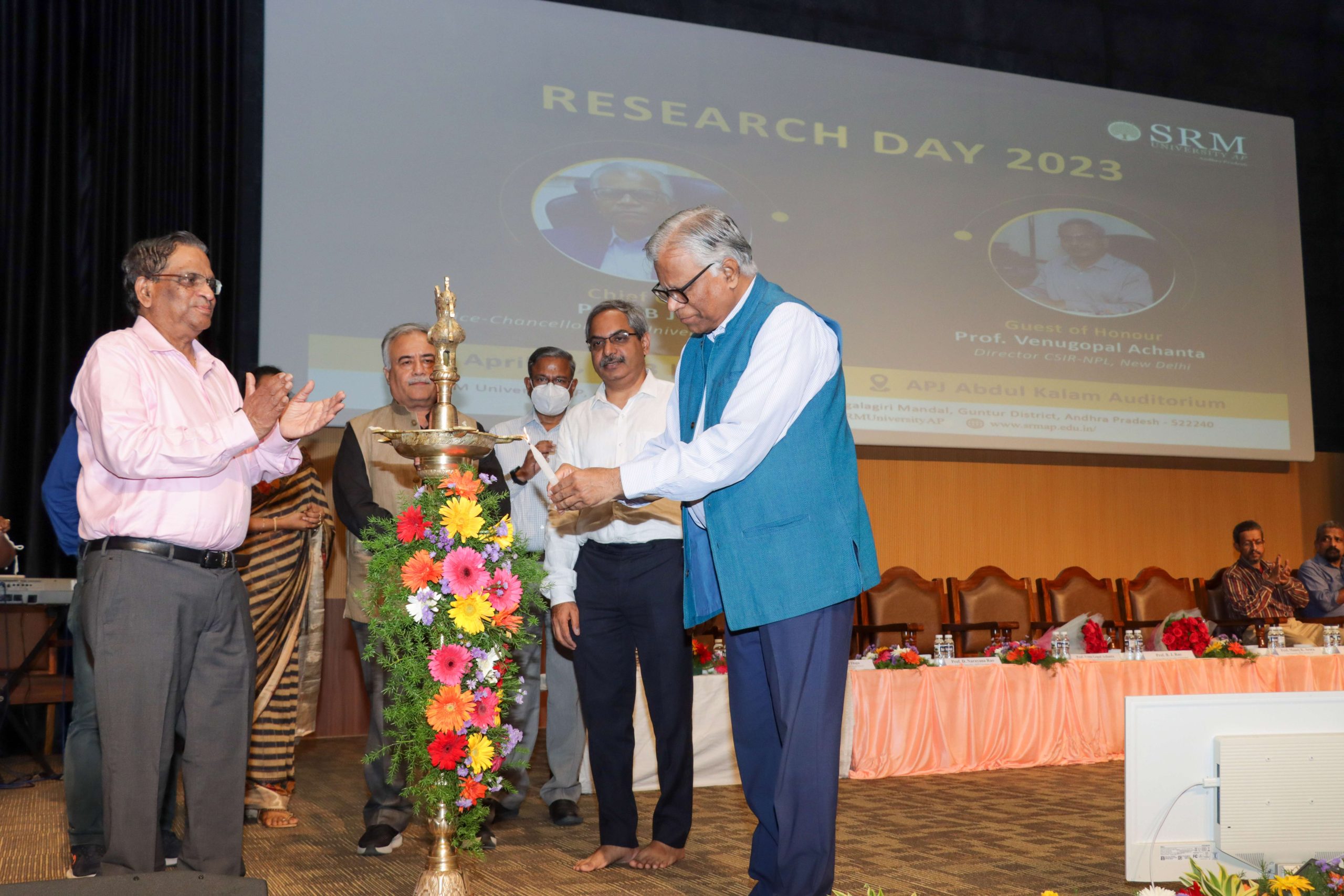
 SRM University-AP observed the 6th edition of Research Day on Saturday, April 29, 2023. Research Day aims to foster the exchange of information across disciplines, encourages extensive research projects, and appreciates innovative efforts in research. Prof. B J Rao, Vice-Chancellor, University of Hyderabad, was the Chief Guest and Prof. Venugopal Achanta, Director, CSIR-National Physical Laboratory, Delhi, was the Guest of honour of the illustrious event held on the campus.
SRM University-AP observed the 6th edition of Research Day on Saturday, April 29, 2023. Research Day aims to foster the exchange of information across disciplines, encourages extensive research projects, and appreciates innovative efforts in research. Prof. B J Rao, Vice-Chancellor, University of Hyderabad, was the Chief Guest and Prof. Venugopal Achanta, Director, CSIR-National Physical Laboratory, Delhi, was the Guest of honour of the illustrious event held on the campus.‘‘There are multiple ways to look at the truth. It is the journey of truth that gives you interest in insights, and it is in that context that Research Day is significant. You are not just a human being when you do research; you become a thinker. When you become a thinker, you discover new things and find the actual purpose of your existence. That is the level of culture we need to generate in our educational ecosystem,’’ stated Prof. B J Rao, Chief Guest of the event. He proceeded to explain why education must be an open process of learning and how it happens only by diffusion. ‘‘Scientific ethics is a big challenge in the country. Whatever I do, it is always looked under the microscope. It will take a longer time. It doesn’t matter. Are you not sure? Do one more experiment,’’ said the Guest of honour Prof. Venugopal Achanta.
The 6th edition of Research Day, for the first time, invited researchers from all SRM Group of Educational Institutions, AIIMS Mangalagiri, Acharya Nagarjuna University, Acharya N G Ranga Agricultural University, and Vignan University. It was an excellent opportunity for research enthusiasts to exchange and exhibit their ideas on research. UG, PG, and PhD students presented their research abstracts which is the culmination of innovative ideas and a sign of continuous contributions to research advancements on April 26, 2023. The various themes covered diverse topics such as AI, Machine learning, Cyber Security, Electric Vehicle, Renewal and Nonrenewal energy, Health Care Technologies, Image Processing and Computer Vision, Communication and Digital technologies, Robotics, VLSI and Embedded Systems, Drone Technologies, and Geoscience etc.
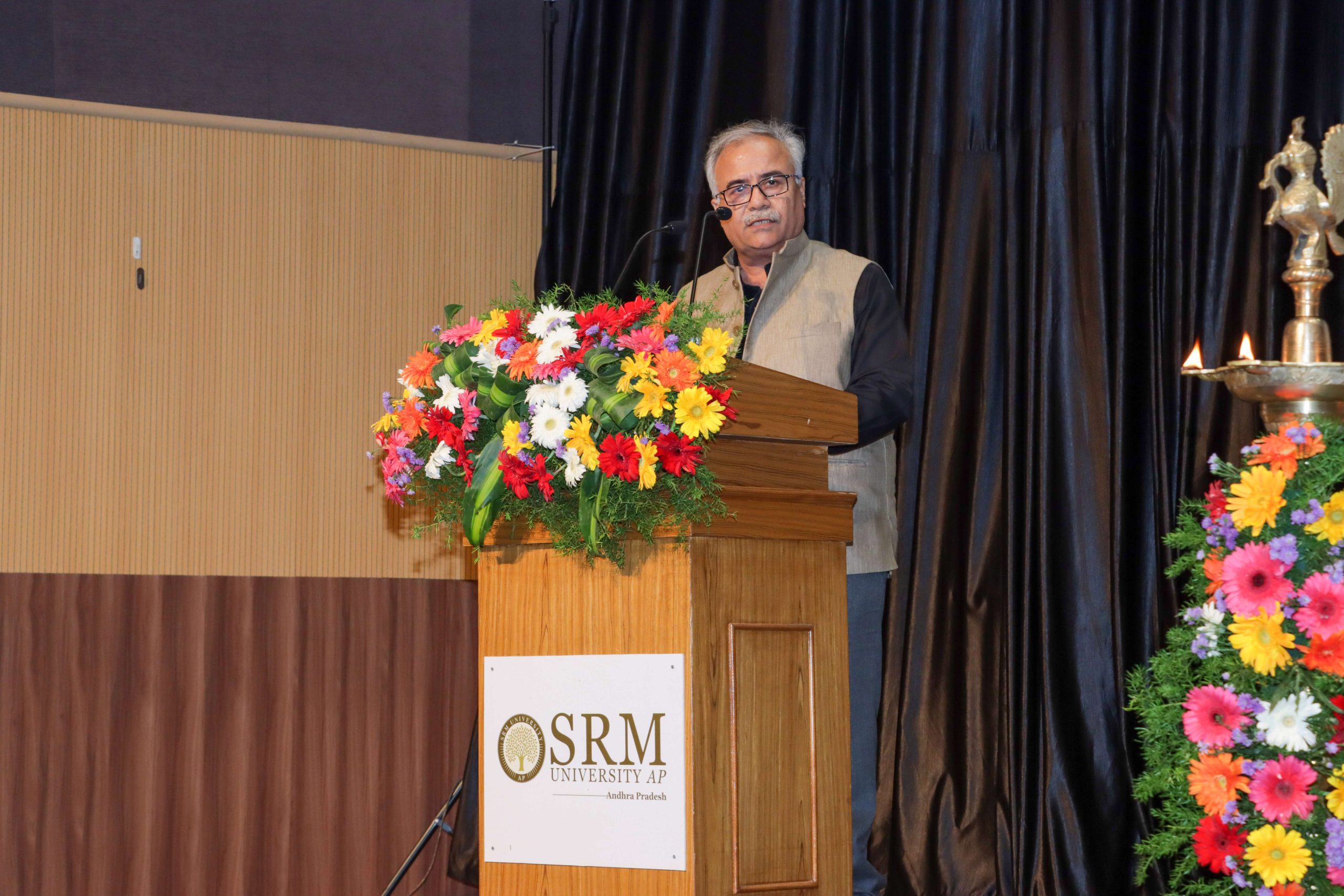
‘‘During the next five years, besides fundamental research, our focus will be on industrial research, research commercialisation, prototype and product development, and technology transfers,’’ said Prof. Manoj K Arora, Vice Chancellor, SRM University-AP, while addressing the gathering. ‘‘We have conceptualised Research Day to provide an opportunity for the students to get a comprehensive knowledge of the diverse research activities being carried out in the university. It is also a chance for enthusiastic students to showcase their research work,’’ added Prof. D Narayana Rao, Pro-vice-chancellor, SRM University-AP.
As part of Research Day, students and research scholars were advised to submit their research abstracts. Over 350 abstracts were received. 181 abstracts from the UG/PG category and 110 abstracts from the PhD category were accepted. A special issue of the research abstracts booklet comprising all selected abstracts was unveiled during the event. Gold and Silver medals and certificates have been awarded to the winners for their research work in various thematic areas. The potential abstracts will be converted into full papers, which will be submitted further to reputed conferences and journal papers.
Continue reading → - AMEYA 2k23: The Signature B-School Fest at SRM University-AP May 1, 2023

The Paari School of Business organised the very first edition of its signature Business Fest “AMEYA 2k23” on April 12 and 13, 2023, at SRM University-AP, Andhra Pradesh. The EMBA programme was also launched during this event. The event was inaugurated on April 12 by Chief Guest, Dr Nagendra V Chowdary in the presence of the Vice Chancellor, Prof. Manoj K Arora; Registrar, Dr R Premkumar; Dean-Paari School of Business, Prof. Bharadwaj Sivakumaran.
The event was launched on a great scale with events being conducted both from the technical as well as non-technical streams. Students from other educational institutions enthusiastically participated in the fest. Technical events such as How’s That (IPL Auction) and Big Bull (Stock Market Simulation), created interest among the participants. There were events from every parallel offered as specialisations by the B-School. A few other events that were conducted are Resultyics, Get Massive Votes, Mock Commercial, Brand Race, and sustainability concept-based Upcycling.
The non-technical events induced a fun and healthy competitive atmosphere in the university. Events like hopscotch, treasure hunt, and separation anxiety had pulled large crowds. The organising committee also encouraged student entrepreneurship by allowing the students to set up food and game stalls.
The business fest concluded on a high note by rewarding the winners from all the events. The winners were given cash prizes of Rs. 5000 and Rs. 3000 for 1st and 2nd place, respectively. Two movie promotions were organised as part of AMEYA 2k23. The film crew and cast of Anni Manchi Sekunalu visited the campus on April 12, adding entertainment and excitement to the already buzzing fest. Team Ugram were a part of the cultural night on April 13. The event was concluded by dance performances, beatboxing and a spectacular DJ night. AMEYA 2k23 was a grand success and a trademark event in the history of the Paari School of Business.
Continue reading → - Workshop on Water Resources in India: Challenges and Hazards April 28, 2023

The availability of water as an elixir of life depends on several factors, including land and climate. The Department of Environmental Science and Engineering organised a 2-Day workshop on “How interactions between climate and land use/land cover changes can affect water resources” on March 27 and 28, 2023, in affiliation with the Department of Earth and Environmental Science, University of Kentucky, USA. The workshop was inaugurated by Vice Chancellor Prof. Manoj K Arora. Distinguished academician and researcher, Prof. Alan Ernest Fryar, Department of Earth and Environmental Science, University of Kentucky, was the resource person for the session.
The workshop was conducted with the aim of providing an overview of water resources in India, water resource challenges and hazards, climate change and projected effects, and mitigation and adaptation strategies. Prof. Fryar also explained the groundwater status across India and regional approaches to exploring it as a drinking water resource. He also explained the impact of climate change on groundwater as a fresh drinking water resource and adaptation strategies.
The workshop saw the participation of over 60 faculty, PhD Scholars and UG students from various educational institutions across the district. UG students from the Department of Geology, Hindu College and Chalapathi Institute of Engineering and Technology, Guntur, participated in the session and interacted with Prof. Fryar.
A field visit to the Krishna Riverbank in Amaravati, Guntur, was also conducted as part of the workshop on March 28, where Prof. Fryar interacted with the research scholars and emphasised the importance of field visits and the scientific and systematic way of sample collection from the field. In addition, Prof. Fryar conducted hands-on training on the field instrument (multi-parameter probe, Hanna) for real-time data collection from the river water and groundwater sources in the field.
Continue reading →

































