Delivered Lecture at the Two–day National Conference on Youth Development at RGNIYD
 During the Two-day National Conference on Youth Development titled Youth in the 21st Century: Prospects and Psychosocial Challenges, organised by Rajiv Gandhi National Institute of Youth Development (RGNIYD), Sriperumbudur, Tamil Nadu, in collaboration with ICMR – NIRT, Chennai, Dr Dhamodharan, Assistant Professor, Department of Psychology, presented a lecture on Status of the Youth in Fishing Community in Terms of Education, Health, and Violence.
During the Two-day National Conference on Youth Development titled Youth in the 21st Century: Prospects and Psychosocial Challenges, organised by Rajiv Gandhi National Institute of Youth Development (RGNIYD), Sriperumbudur, Tamil Nadu, in collaboration with ICMR – NIRT, Chennai, Dr Dhamodharan, Assistant Professor, Department of Psychology, presented a lecture on Status of the Youth in Fishing Community in Terms of Education, Health, and Violence.
Abstract
Over sixty percent of the fisher population in India is Below Poverty Line (BPL). For traditional fishers, fishing is their primary source of income, and they have no other options. Hence, families in the coastal village are socially, financially, and educationally disadvantaged and frequently face financial difficulties. Additionally, the literacy level of the fishing community is deficient. Fishers have met an unbalanced diet, tension, excessive drinking, tobacco usage, and harmful behaviours. Fisher communities are often underprivileged and constitutionally and communally isolated from other communities. Limited research has been conducted on the fishing community youth, particularly in Tamil Nadu and Pondicherry. Hence, the study needs to be understood and conducted for the fishing community youth regarding education, health, and violence. The empirical study combined quantitative and qualitative approaches to Tamil Nadu and Pondicherry fishing community youth. The study tools used for the data collection are a semi-structured questionnaire for youth for their perspective on health care, school, violence, and family support and a semi-structured questionnaire to the parents regarding their perspective on their children’s education, health, violence, and family support. Twenty case studies were conducted in the selected clusters. Also conducted were key informant interviews with fishing community leaders in four clusters. The results showed that more than 50 % of participants face verbal violence, more than 80 % face physical violence, and nearly 25% face sexual violence. The fishing community is an under-educated, predominantly nuclear family, and the family income is less than ten thousand rupees monthly. Physical abuse had significantly associated with place of residence, Puducherry residing youth had more physical abuse than Tamil Nadu. The social-economic condition of the family and the parental education seemed to be better in the state of Tamil Nadu as compared to Puducherry. Youths from Puducherry had a greater risk of experiencing physical and verbal abuse. Parents had a relatively low level of awareness and understanding of child rights and laws. The study’s results helped to understand the problem of fisher community youth and their perception of parental care, education, health, and violence.
Practical Implementation of the Findings
- Social welfare department and local NGOs to take up need-based intervention programmes for the welfare of the fishing community and youth.
- The youth welfare department understands the problems of youth in the fishing community.
- Policymakers to develop policies and legislation for the youth of fishers in the education and health sectors.
- Understanding the problems and violence against the youth of the fisher community, as well as helping the Non-Government Organisations for making intervention programs at the community level.
- Assist the school administration in better understanding the Fisher community students’ situation and creating counselling centres in school settings.
- Published in Departmental News, News, Psychology News, Research News
An Algorithm to Assess Employee Attrition Rate in Organisations

Socially relevant and community-centric research is of primal focus at SRM University-AP leading to innovations that transpire into transforming society. Dr Vimal Babu and his research scholar Ms Rukma R, Paari School of Business, have undertaken creative research to understand employee attrition in organisations critically. The research cohort employed a modified Random Forest Algorithm for assessing employee attrition and analysing its findings and benefits to Human Resource departments of corporate houses. Their groundbreaking invention and research titled “A System to generate a Model Predicting an Employee Attrition Rate and a Method Thereof” with Application No: 202341031320 has recently been filed and published under the Patent Office Journal.
Abstract
The problem of employee attrition in every organization concerns the employee turnover ratio, thereby increasing the cost of investment in human resources. Various factors are reasonable for the rapid attritions at different phases. The purpose of the current study is to predict the employees who are likely to leave the organization. The factors that lead to attrition are identified using the Random Forest algorithm. Random Forest algorithm is one of the widely used supervised machine learning technique for both classification and prediction. However, the random forest algorithm has specific issues, such as it is too slow and ineffective for real-time predictions. i.e., the large number of trees can make the algorithm, which results in a slower model. Therefore, the study proposes a new alternative for choosing the appropriate decision trees based on the concept of fractional factorial design of experiments. The different performance criteria were compared across the modified random forest algorithm, existing random forest algorithm, Support Vector Machine (SVM), Logistic Regression (LR), Navie Bayes (NB), K – Nearest Neighbour (K-NN), Decision Tree, XG Boost tree and Neural Network (NN). It was found that the modified random forest algorithm excelled in all criteria and performed better than the existing ones.
The findings of this study offer valuable assistance to human resources departments by providing necessary insights into potential employees’ decisions to leave the company. By analysing the identified factors or reasons for leaving the organisation, HR professionals can better understand attrition patterns and make informed decisions to improve employee retention. The proposed method not only assists in identifying the factors contributing to employee attrition but also predicts the likelihood of attrition based on employee signals. This predictive capability enables organisations to proactively address potential attrition cases and take preventive measures to retain valuable employees.
Practical implications of the research
Overall, the practical applications include designing retention strategies, predicting attrition cases, tailoring employee engagement initiatives, developing HR policies, optimising recruitment and selection processes, benchmarking attrition rates, and implementing continuous improvement measures. These applications can collectively contribute to reducing employee attrition and enhancing overall employee retention in organizations.
Collaborations and Future research plans
The applicants, viz. Ms Rukma, R.; Dr Vimal Babu and Dr Vijaya Prabhagar, M. plan to collaborate in the intersecting area of HR and analytics to arrest employee attrition by employing sophisticated analytics models and explore the future scope of our research to come up with impactful research outputs benefitting the industry.
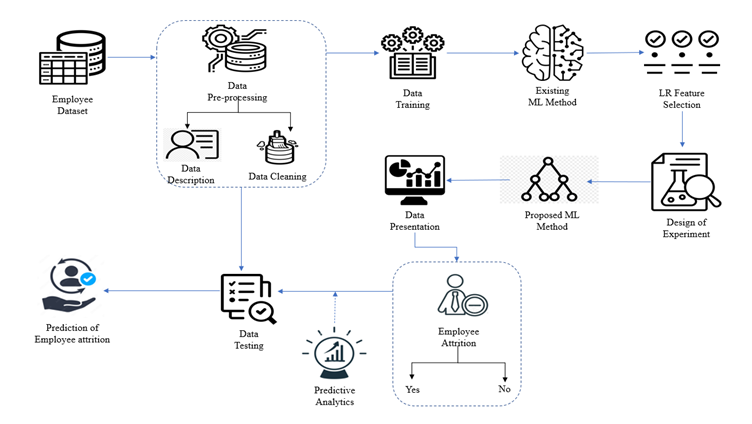
Phases of prediction of employee attrition
- Published in Departmental News, News, Paari Current Happenings, Research News
Elected as General Secretary of ACDOS NMO-IFAC

The Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering is glad to announce that Dr Tousif Khan, Associate Professor and HOD, has been selected as the General Secretary of the Prestigious Automatic Control and Dynamic Optimization Society (ACDOS), National Member Organisation of the International Federation of Automatic Control (IFAC), at the Governing Council meeting held on June 22, 2023.
Automatic Control & Dynamic Optimization Society (ACDOS) was established in 2011 with the noble objective to promote automatic control and dynamic optimization discipline in academia and industry across India. The society aims to host international conferences and technical workshops regularly in order to promote close interaction between industry and academia. The society also participates in curriculum development for graduate and undergraduate studies and facilitates productive research in this field. The society also volunteers to honour eminent persons who excelled in this field in industry and academic circles.
Congratulations to Dr Tousif for this remarkable accomplishment and for further contributing to the university’s rising reputation among national and international frontiers!
- Published in Departmental News, EEE NEWS, Faculty Achievements, News
Patent Filed for Person Identification System and Method

Today, biometric systems are widely used across all major domains, but alarmingly these systems are vulnerable to various security attacks. However, Dr Banee Bandana Das and Dr Saswat Kumar Ram, Assistant Professors at the Department of Computer Science and Engineering, SRM University-AP, have jointly come up with a solution that is more efficient and robust. The faculty duo have also filed and published the patent titled- “A System and A Method For Person Identification” with Application Number: 202341036899.
Abstract
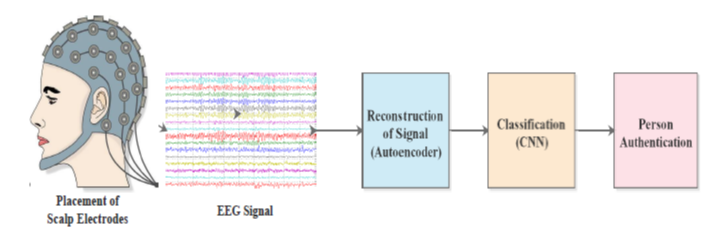
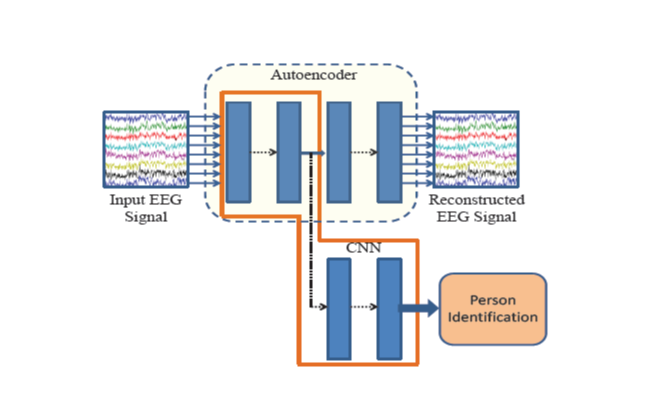
Biometric representation of humans deal with tasks such as identification and verification. It can be done through various methods like fingerprint, face, retina, voice, etc. However, existing biometric systems are vulnerable to various security attacks. EEG-based biometrics are putting forward solutions because of their high-safety capabilities and handy transportable instruments. Motor imagery EEG (MI-EEG) is a broadly centred EEG signal exhibiting a subject’s motion intentions without actual actions. This invention proposes an unsupervised framework for feature learning based on autoencoders. It learns sparse feature representations for EEG-based person identification. Autoencoder-CNN exhibits the person identification task for signal reconstruction and recognition. The framework proved to be a practical approach in managing the massive volume of EEG data and identifying the person based on their different tasks in resting state. The experiments have been conducted on the standard publicly available Motor imagery EEG dataset with 109 subjects. This invention proposes an unsupervised framework for feature learning based on autoencoder to learn sparse feature representations for EEG-based person identification. Autoencoder and CNN do the person identification task for signal reconstruction and recognition. The outcomes imply that the implementation of an autoencoder-CNN architecture for person identification was intensely successful with improved recognition performance with the most notable autoencoder architecture. Eye open and closed resting state data as training data is used while four different motor imagery tasks have been considered test data in this biometric model. Training and testing of different state data of the same person have been proved to be the most robust and versatile EEG-based biometric system.
Practical Implementation of the Research
The present invention can be used in smart city applications, considering that the population of cities is increasing by the day, in which case, the security and privacy of people are at high risk in all sectors. The application of this technology will be in areas like:
Smart Office
The workflow and working efficiency of the employees can be enhanced with various innovative features and technology in an intelligent environment like smart offices of smart cities. Biometric-based methods involving fingerprints, retina, voice, and face recognition for secure authentication and identification of employees, clients, and different types of machinery are helpful. Various security attacks are the most severe issue related to these methods. Brain signals (EEG) are more secure and difficult to copy and steal, efficiently used for security needs and authentication.
Smart Healthcare
The laboratory and the data related to the health sectors are always important. The privacy and restricted access are must to secure it. By using the proposed invented model, the security can be enhanced as compared to the traditional biometric traits.
Smart Defence
The use of biometric in defence is not discussed in public but is undoubtedly an essential parameter in this domain. Many countries rely on biometric data like faces, irises, fingerprints, etc., for identification. A unique and trusted database is a must in defence for identifying persons involved in various operations. These include authenticating scientists, pilots, engineers etc., and to identify criminals in specific places. EEG-based person identification can be a secure alternative in this domain.
As a future prospect, Dr Das and Dr Ram are planning to develop a more secure and reliable biometric authentication system that will be based on Multimodal Techniques using Machine learning Methods.
- Published in CSE NEWS, Faculty Achievements, News, Research News
MoU with APIS Opens Doorway to Entrepreneurial Ecosystem

It is a moment of immense pride for SRM University-AP and its entrepreneurial affiliate, the HatchLab Research Centre as they sign an MoU with the Andhra Pradesh Innovation Society (APIS).
HatchLab Research Centre is an innovation and start-up incubator of SRMAP, while APIS is a State Nodal Agency that promotes the growth of innovation, entrepreneurship, and the startup ecosystem in the state. The MoU signed by the two organisations will significantly impact innovations and benefit hundreds of individuals. Also, through this collaboration, the varsity aims to cultivate an environment that nurtures creativity, fosters entrepreneurship, encourages innovative thinking, and drives tangible results. The combined expertise and vision of APIS and HatchLab Research Centre will undoubtedly lead to groundbreaking advancements in various fields, pushing boundaries, unlocking new possibilities, and making a lasting difference.
- Published in Departmental News, IDEA NEWS, MoU, News
Cracking the Code: How Congress Scripted Its Victory In 2023 Karnataka Assembly Elections
 Assistant Professor Dr Vineeth Thomas, from the Department of Liberal Arts, has recently made a publication in the Q2 journal called Economic and Political Weekly. The paper titled Cracking the Code: How Congress Scripted Its Victory In 2023 Karnataka Assembly Elections contributes to comprehending and examining the political landscape of Karnataka, shedding light on the various elements that shape voter behaviour and election outcomes within the context of Indian democracy.
Assistant Professor Dr Vineeth Thomas, from the Department of Liberal Arts, has recently made a publication in the Q2 journal called Economic and Political Weekly. The paper titled Cracking the Code: How Congress Scripted Its Victory In 2023 Karnataka Assembly Elections contributes to comprehending and examining the political landscape of Karnataka, shedding light on the various elements that shape voter behaviour and election outcomes within the context of Indian democracy.
Abstract
The Congress party secured a much-awaited thumping majority in the 2023 Karnataka Assembly elections. The election result gave a much-required lifeline to the existential crisis faced by the Congress party and opened the eyes of the BJP to recognise that the Modi-factor and Hindutva card does not always get converted into votes. In this context, this article provides an in-depth analysis of the factors that led to the Congress party’s victory in the 2023 Karnataka assembly elections.
Explanation of the Research in Layperson’s Terms
Due to multiple reasons, it is worth examining the ingredients of Congress’ magical recipe for winning the Karnataka assembly elections. The Congress’ victory in the Karnataka assembly elections in 2023 is a significant political event, as it marked the party’s return to power in the state after a gap of several years. The result provided a new lease of life for the Indian National Congress and it helped to cement the Congress’ position as a key player in the politics of southern India in general and Karnataka in particular. The victory boosts the spirit of Congress party workers on the ground, who are so used to losing that they sometimes give up before the combat even begins. It also allows the party to generate resources in a situation where the Congress controls only three additional states (Himachal Pradesh, Rajasthan and Chhattisgarh). It also enhances the Congress’s profile within the greater national opposition and may persuade some other parties, who have been sceptical of the party’s political judgement and ability, to consider working together. It may help the Congress, which won only one Lok Sabha seat in Karnataka in 2019, to increase its score in 2024. Understanding the components of the Congress’ electoral strategy in Karnataka might therefore provide light on the party’s overall approach to the future assembly and Lok Sabha elections. Examining the reasons that influenced the Congress’ win in Karnataka can give useful insights into India’s larger political scene and shed light on the anticipated outcomes of future elections in the nation.
- Published in Departmental News, Liberal Arts News, News, Research News



