Dr Tousif Khan N elected as a Joint Secretary of ACDOS
 Dr Tousif Khan N, Head of the Department, Electrical and Electronics Engineering at SRM University-AP, Andhra Pradesh has been elected as a Joint Secretary (2020-2023) of the prestigious Automatic Control and Dynamic Optimization Society (ACDOS), Indian national member organization of International Federation of Automatic Control (IFAC). The objective of ACDOS is to promote automatic control and dynamic optimization fields in academia and industry across India. The society aims to host international conferences and technical workshops regularly in order to promote close interaction between industry professionals and academia. The society also participates in curriculum development for graduate and under-graduate studies in addition to facilitating productive research in this area. The society volunteers to honour eminent persons who excelled in this field in industry and academic circles.
Dr Tousif Khan N, Head of the Department, Electrical and Electronics Engineering at SRM University-AP, Andhra Pradesh has been elected as a Joint Secretary (2020-2023) of the prestigious Automatic Control and Dynamic Optimization Society (ACDOS), Indian national member organization of International Federation of Automatic Control (IFAC). The objective of ACDOS is to promote automatic control and dynamic optimization fields in academia and industry across India. The society aims to host international conferences and technical workshops regularly in order to promote close interaction between industry professionals and academia. The society also participates in curriculum development for graduate and under-graduate studies in addition to facilitating productive research in this area. The society volunteers to honour eminent persons who excelled in this field in industry and academic circles.
Dr Tousif Khan N is an Assistant Professor in the Department of Electronics and Electrical Engineering at SRM University-AP, Andhra Pradesh. He has obtained his PhD from Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati. Apart from performing his duties as a teacher, he is pursuing his research career in Control systems, Power Electronics and Optimization Techniques. The very young and talented professor has been honoured with several awards and recognitions for his pursuits in the domains of Teaching and Research. As a Joint Secretary of ACDOS, Dr Khan wishes to contribute further to the versatile worlds of Research and Academia.
The other members of ACDOS are eminent researchers and scientists such as Prof. Sukumar Mishra (IIT Delhi) as President, Dr Jayesh Barve (GE, Bangalore) as Vice-President and President-Elect, Dr Shaik Faruque Ali (IIT Madras) Vice-President, Prof Bidyadhar Subudhi (IIT Goa) as Vice-President, Dr Arnab Maity (IIT Bombay) as General Secretary, Dr S. N Omkar (IISc-Bangalore) as Treasurer and Prof Radhakant Padhi (IISc Bangalore) as Director of Operations.
To know more about ACDOS, please click the link: https://www.acdos.org/
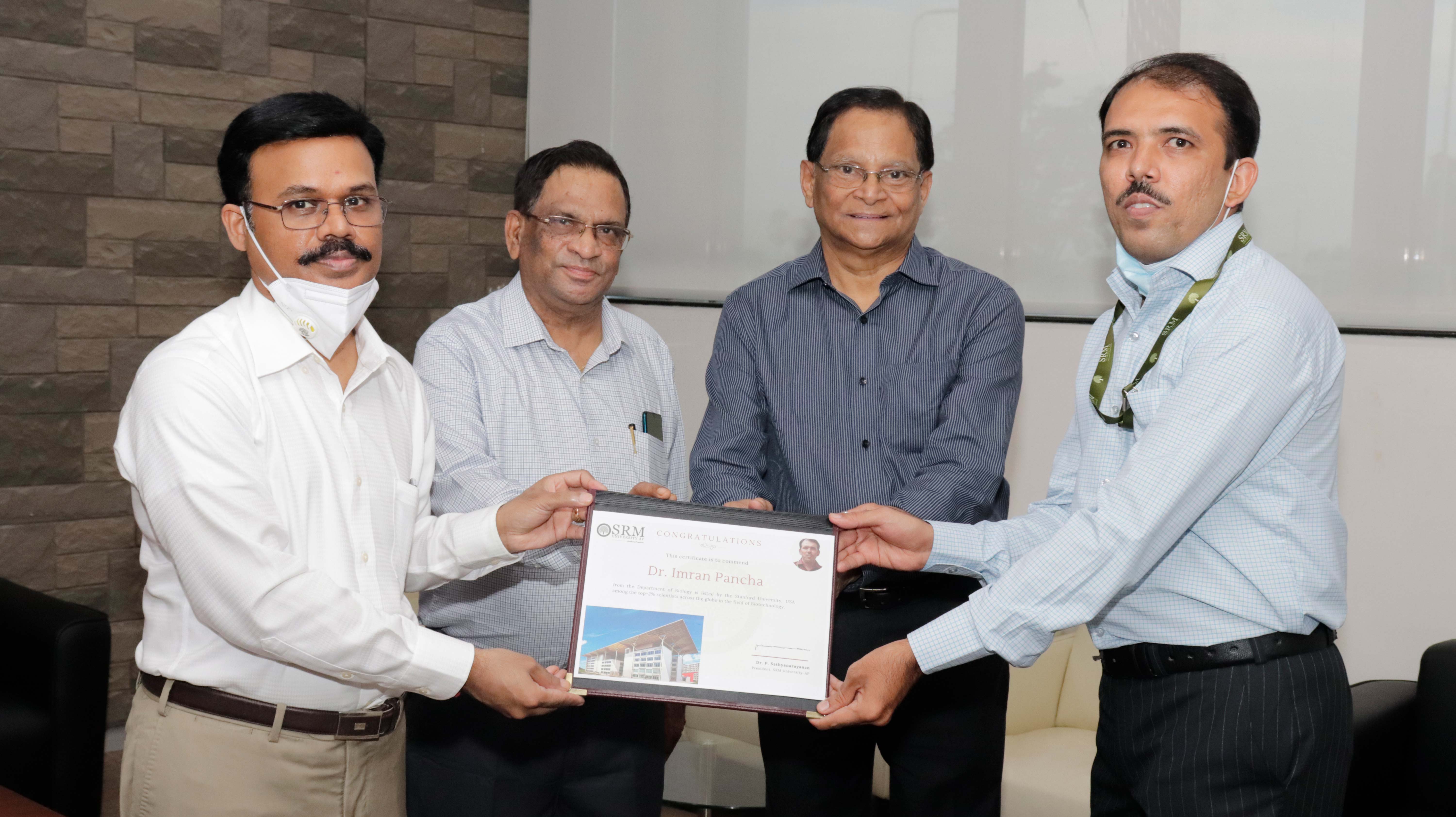
SRMAP faculty recognised by Stanford University among the top Biotechnologists
Dr Imran Pancha from the Department of Biological Sciences, SRM university – AP is recognised in Biotechnology among the top 2% scientists/researchers across the world By Stanford University Researchers. Recently an article has been published in PLOS Biology by Stanford University Researchers on the highly cited researchers in 22 different fields and their subfields. In the Biotechnology field, 1,074 scientists/faculty members were identified, and Dr Imran Pancha is one amongst them. From India, only 77 scientists/faculty members could achieve this honour, and Dr Imran Pancha is one among them. This is an admirable achievement for a young faculty from a nascent University to be in the top 2% scientists of the world. Dr P Sathyanarayanan, the President of SRM University-AP honoured Dr Pancha for bringing this scientific laurel to the university.
Overall, of the top 160,000 scientists from different fields of Science & Technology, India hosts 2,313 scientists/faculty members. This list comprises of the prominent and illustrious scientists from India.

Dr Imran Pancha is a young researcher working as an Assistant Professor in the Department of Biological Sciences in SRM University-AP, Andhra Pradesh. He has obtained his doctoral degree from CSIR-Central Salt and Marine Chemicals Research Institute-Bhavnagar after graduating from Bhavnagar University. He has also worked as a post-doctoral fellow at Japanese Society for Promotion of Science, Japan before joining SRM University-AP.
Dr Pancha’s primary research focus is to produce renewable energy from microalgae. His team is trying to develop integrated microalgal bio-refinery to produce high-value compounds like phycobiliproteins, carotenoids along with biofuel and bio-fertilisers from microalgae. Apart from this, he is also interested to understand algal-bacterial interaction, particularly isolate and characterise the microalgae associated bacteria and finding their role in growth enhancement and inhibition in microalgae.
- Published in Biology News, News, Research News
ECE Student sets sail to King’s College, London for Masters studies
 Nothing brings more pleasure than seeing our students being recognised in the best educational institutions abroad. Ms Abirami Ravishankar has secured a seat in King’s College London for their full-time Master’s Programme in Telecommunications and Internet Technology. She is in the final year of B. Tech in the Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering. The duration of the Master’s programme is one year, and she will be joining her programme in September 2021.
Nothing brings more pleasure than seeing our students being recognised in the best educational institutions abroad. Ms Abirami Ravishankar has secured a seat in King’s College London for their full-time Master’s Programme in Telecommunications and Internet Technology. She is in the final year of B. Tech in the Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering. The duration of the Master’s programme is one year, and she will be joining her programme in September 2021.
King’s College, London is well known throughout the world for its eminence. It is one of the top institutes with high QS ranking. Abirami informed that the admission process in such a reputed institute is very rigorous and challenging. King’s College, London accepts only 10% of all the applications each year. “The sheer credit goes to my professors who briefed me on the admission process and guided to crack it. Thanks to the incredible learning experience at SRMAP, I was able to achieve a thorough understanding in my subjects, which helped me immensely during my application days. King’s College, London minutely judges the applicant’s overall knowledge and depth before offering them admission. However, for me, it was no tough job because of my excellent grooming here at SRMAP. I sincerely thank all my professors for all their efforts in making me a good engineer, and now I wish to avail this opportunity to prosper and make a difference to the world in the coming days,” says Abirami, deeply overwhelmed.
“We are very happy for Abirami for her enrolment in the Master’s programme at King’s College, London. We, the faculty of SRMAP, always strive to provide best guidance and support to our students. Abirami is a meritorious student who aspires to do something for herself as well as for the community. We wish her all the best for her future. She can always count on our support whenever she needs it,” said Prof Siva Sankar Yellampalli, who has closely witnessed Abirami throughout the years of her undergraduate studies. Prof Yellampalli is also the Professor and Head in the Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering.
- Published in Departmental News, ECE NEWS, News, Students Achievements
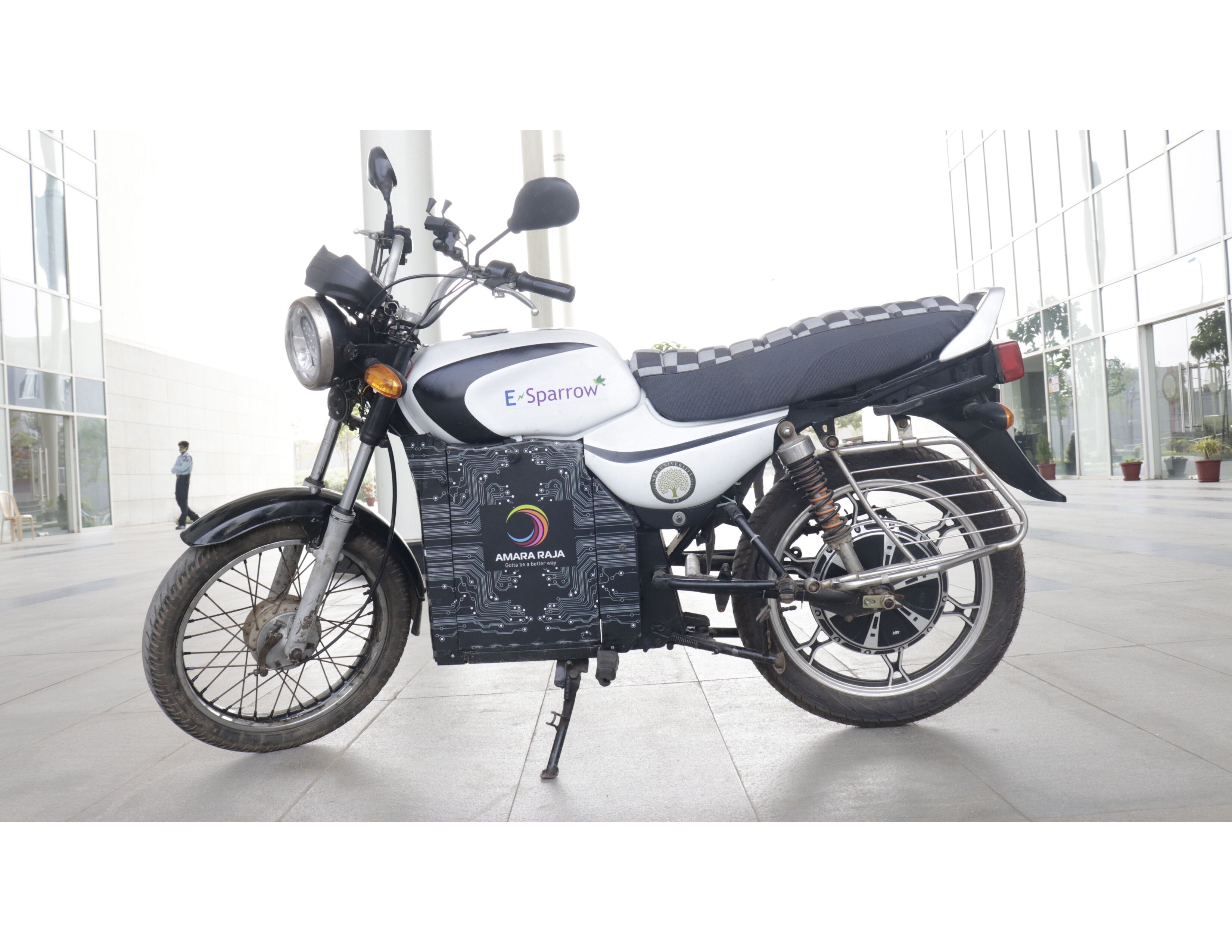
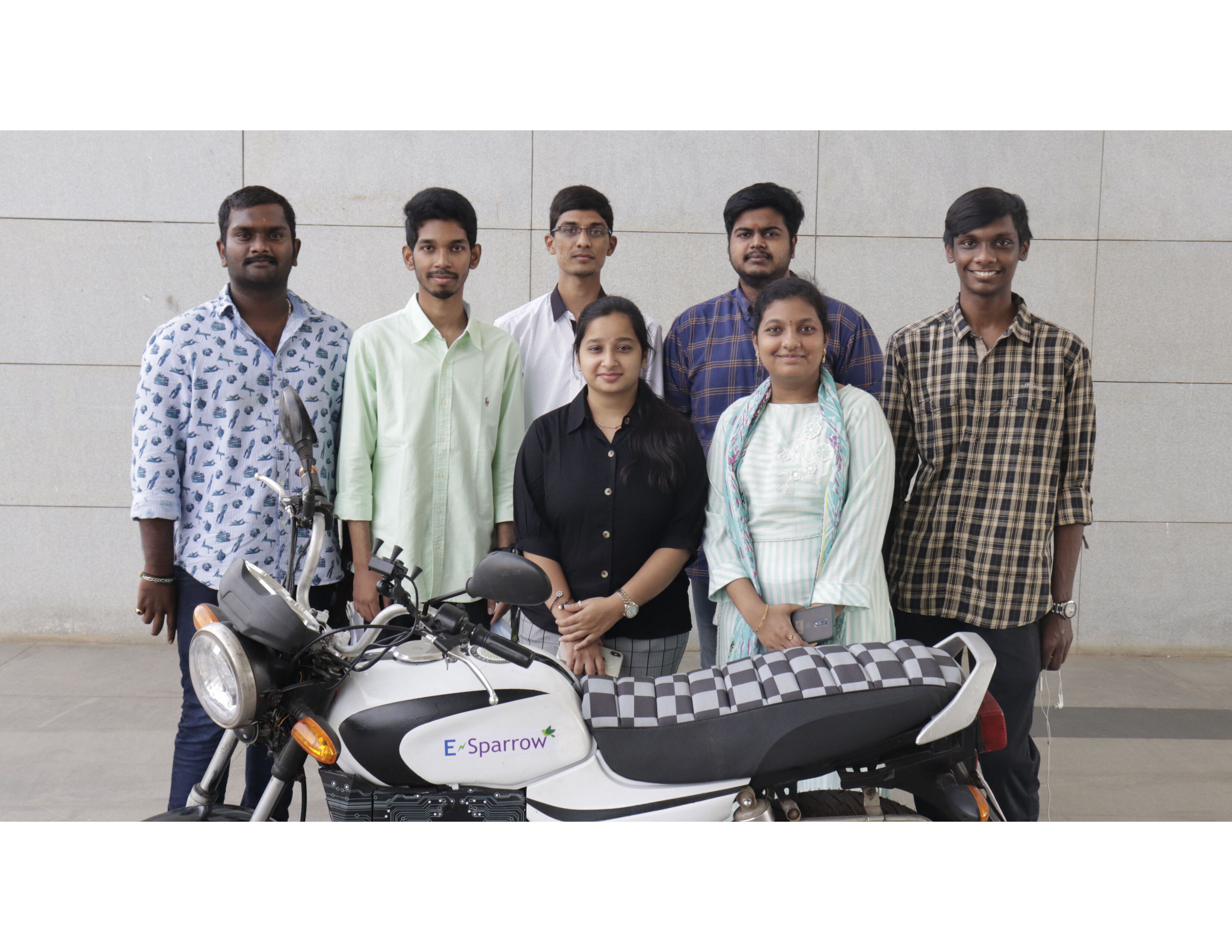
Undergraduate students design e-bike for sustainable environment

Advancing the celebration, Prof D Narayana Rao, Pro Vice-Chancellor, SRM AP took the virtual podium to comment “Science and Technology is the driving force for the economic development of India. We need to encourage young scholars by providing a vibrant and conducive research environment. Expanding the frontiers of knowledge by triggering interest among students must be the priority of the institutions. Also, focus should be on translational research with societal applications through collaborative research to make our nation a global leader.”
The team comprises of undergraduate students – Mr Raviteja Reddy, Mr A Chaitanya, Mr P M Aditya, Mr K Praveen, K Yeshashwini, A Sravya, K Vasu, and G Priyanka along with faculty members – Dr Venkata N Nori, Associate Professor, and Dr Panchagnula Jayaprakash Sharma, Assistant Professor, Department of Mechanical Engineering. Aditya reveals, “We endured several challenges in various aspects of retrofitting the conventional petrol motorcycle. Also, designing a portable battery system, enhancing the performance of the Hub motor, Chassis improvements, etc. enriched our understanding of electric vehicles and manufacturing techniques.”
Conversion of IC engine bike to an e-bike is considered to be a potential business venture by the team. Sharing their forthcoming plans, Aditya informs, “We are working on additional designs and ideas to incorporate the best possible features to make the e-bike more reliable. We heartily thank Prof D Narayana Rao, Pro Vice-Chancellor, for his continuous support. Also, Dr Venkata Nori and Dr Jayaprakash propelled us to create a steadfast model by relentlessly helping us in improving our design to make our model more cost-effective.”
- Published in Mechanical Engineering NEWS, News, Research News
Undergrad student receives envious internship offer from Adobe India with 1 LPM
 Khushboo Sharma is one of the brightest gems in the Department of Computer Science and Engineering. She is currently pursuing her third year in undergraduate studies. She has recently bagged an envious summer internship offer at one of the most reputed companies- Adobe India, a multinational software company. Through their women-only hiring challenge “SheCodes”, Khushboo not only bagged an internship offer but she may also have an opportunity of a Pre Placement Offer, upon successful review after this internship with attractive pay package. She will be joining Adobe India in May 2021 for the internship of 10-12 weeks with a stipend of 1 lakh rupees per month.
Khushboo Sharma is one of the brightest gems in the Department of Computer Science and Engineering. She is currently pursuing her third year in undergraduate studies. She has recently bagged an envious summer internship offer at one of the most reputed companies- Adobe India, a multinational software company. Through their women-only hiring challenge “SheCodes”, Khushboo not only bagged an internship offer but she may also have an opportunity of a Pre Placement Offer, upon successful review after this internship with attractive pay package. She will be joining Adobe India in May 2021 for the internship of 10-12 weeks with a stipend of 1 lakh rupees per month.
Mr Vivekanandan, Assistant General Manager, Department of Corporate Relations and Career Services (CR&CS), says “It is a proud moment for the university. SRM University-AP is full of bright students with huge potential. It is our sincere responsibility to bring out the best in them and help them find the right place in the industry.” Khusboo asserted that the training process in the Department of CR&CS was rigorous. Be it attitude development or interview preparations, the CR&CS department has extended continuous guidance and support along with mock sessions. Mr Vivekanandan further informed that the training programmes of SRM University-AP are designed by the experts to make students prepare for every challenge that they might face in a competitive world. They even organise some training sessions that are company-specific. Needless to say, that the placement department is not ready to leave any stone unturned when it comes to the future of its students. The placement team thoroughly guided Khushboo in the four-month-long hiring process in Adobe.
Khushboo expressed her gratitude, saying that it would not have been possible for her to crack this challenge without the continuous guidance and support provided by her teachers and the placement team. The modernised industry-oriented curriculum helped her gain the necessary in-depth knowledge to excel in her studies. Khushboo is also a part of tech-based clubs of SRM university-AP and always strives to think something out of the box. Her zeal towards scaling new heights and perseverance her made her achieve this offer.
- Published in CR&CS, CR&CS NEWS, CSE NEWS, Departmental News, News, Students Achievements
Young researcher presents research paper amidst scholars at global conference – ICCCS 2020
Nikhila Korivi offers revolutionary approach to ensure Data Security
 Nikhila Korivi, third year, Department of Computer Science and Engineering, SRM University- AP, Andhra Pradesh was steered by Dr Manikandan V M, Assistant Professor, Department of CSE, to present the pioneering research paper “Reversible Data hiding in encrypted images using checkerboard based pixel inversion” in the IEEE International Conference on Computing, Communication and Security (ICCCS-2020), IIT Patna, held on October 14-16, 2020.
Nikhila Korivi, third year, Department of Computer Science and Engineering, SRM University- AP, Andhra Pradesh was steered by Dr Manikandan V M, Assistant Professor, Department of CSE, to present the pioneering research paper “Reversible Data hiding in encrypted images using checkerboard based pixel inversion” in the IEEE International Conference on Computing, Communication and Security (ICCCS-2020), IIT Patna, held on October 14-16, 2020.
Nikhila and her mentor, Dr Manikandan V M, worked on the paper conjointly for which, she is profoundly grateful to the professor. She says, “I thank Dr Manikandan and my other professors at SRM University-AP for their continuedguidance that inspired me to do research. Their encouragement propelled me to successfully present the research paper at ICCCS-2020, a conference revered by the entire scientific community.”
Nikhila has been keen on exploring and broadening her horizon of knowledge. Right from her early undergraduate days, Nikhila was intrigued by Information Security, an emerging discipline in the modern era. Soon she recognized that Reversible Data Hiding is an active research area in the realm of Information Security, which has extensive application in Medical Image Transmission, and Cloud Computing.
On approaching her professor, Dr Manikandan enthused Nikhila to embark on the research work and propose a new Reversible Data Hiding scheme in encrypted images by using a checkerboard pattern-based pixel inversion technique. Nikhila informs, “The proposed scheme ensures a better bit error rate without compromising on the embedding rate. The algorithms were implemented using Matlab-2019 and the experimental studies of the proposed scheme have been carried out using a standard image dataset (USC-SIPI) managed by the University of Southern California.”
This revolutionary approach is immensely beneficial when it comes to Data Security, and it is widely implemented in medical image transmission along with many other sectors. Fostering her interest in pursuing research and advanced studies, Nikhila plans to enhance her research work by focusing on designing and developing new Reversible Data Hiding schemes with better embedding rates without compromising other efficiency parameters such as computational complexity, robustness, and bit error rate.
- Published in CSE NEWS, News, Research News
ECE Undergrads developed AI-based communication app for deaf and blind
Won prestigious i-Hack Alpha with a cash prize of $2300
 Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering rejoices in the exhilarating success of Harsha and Mahesh, the winners at iHack Alpha Hackathon. iHack Alpha was an AI-Hackathon, where developers from all backgrounds were invited to solve real-world problems with innovative AI solutions powered by sentient.io AI and Data platform. Unlike the usual hackathons, it was conducted over three weeks, starting from December 2, 2020, and finished on December 27, 2020, and participants were supposed to present a full-fledged application. Four themes were given to participants to work on in the hackathon- 1) Use of AI in retail 2) Use of AI in Customer service 3) Use of AI in media 4) Use of AI in Accessibility.
Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering rejoices in the exhilarating success of Harsha and Mahesh, the winners at iHack Alpha Hackathon. iHack Alpha was an AI-Hackathon, where developers from all backgrounds were invited to solve real-world problems with innovative AI solutions powered by sentient.io AI and Data platform. Unlike the usual hackathons, it was conducted over three weeks, starting from December 2, 2020, and finished on December 27, 2020, and participants were supposed to present a full-fledged application. Four themes were given to participants to work on in the hackathon- 1) Use of AI in retail 2) Use of AI in Customer service 3) Use of AI in media 4) Use of AI in Accessibility.
Harsha and Mahesh chose to work on the use of AI in the Accessibility theme, where they were asked to build an AI – solution using the sentient.io services. The whole hackathon was divided into three phases 1.) Ideation Phase 2) Build Phase 3) Finals.
Around 1083 teams participated across countries such as India, Malaysia, the Philippines, Indonesia, and Singapore.
Harsha and Mahesh found their inspiration in the story of Helen Keller and decided to build an app with ease of accessibility for the blind and deaf persons. As Annie Sullivan used to help Helen in her communication, Harsha and Mahesh thought, why can’t they create an app which can be installed on the mobile phone and will do the same! The duo turned this crazy idea into reality by developing Artificial Voice- a communication app for the blind and deaf. Artificial Voice is a bidirectional communication app for the deaf and blind to send and receive messages with the help of AI-based technology such as Automatic Speech recognition, Text to speech converter, Audio format converter.
The whole Hackathon was broadcasted online. Harsha and Mahesh’s presentation on Artificial Voice received high praise and acclaims from the judges, and the Team SRMAP(aka Team Square) secured first place in the prestigious i-Hack Alpha hackathon with a grand cash prize of $2300. Harsha is currently pursuing his 3rd year B. Tech Studies whereas Mahesh is in the 2nd year of his undergraduate studies at the Department of Electronics and Communications Engineering. “This success at i-Hack Alpha hackathon has boosted our confidence. We are working on better versions of the app and some other projects that can contribute to society,” said Harsha.
- Published in Departmental News, ECE NEWS, News, Students Achievements
Undergrad CSE student bags envious placement offer with a CTC of 20 Lakh LPA
 Another proud moment for SRM University-AP when Kattamuri Sai Krishna Rohith bagged an envious job offer from ODCEM Technologies Pvt. Ltd. (OneDirect) with a CTC of 20 Lakhs per annum. He is pursuing his B. Tech final year in the Department of Computer Science and Engineering.
Another proud moment for SRM University-AP when Kattamuri Sai Krishna Rohith bagged an envious job offer from ODCEM Technologies Pvt. Ltd. (OneDirect) with a CTC of 20 Lakhs per annum. He is pursuing his B. Tech final year in the Department of Computer Science and Engineering.
Mr Rohith will be joining the company as an intern for six months with monthly compensation of Rs. 20,000. After six months of internship, he will be offered the permanent employee as a Full Stack Developer with a CTC of Rs. 20,00,000 per annum.
Mr Rohith went through rigorous placement training programmes conducted by the Department of Corporate Relations and Career Services to secure the job offer. The job hiring process for this role was conducted in four stages. After preliminary selection, Mr Rohith had to prove his ability in coding, aptitude and other technical domains. The Director of Engineering himself took the final call before offering him a position in the company to see if Rohith is a proper fit for their company.
Rohith expressed his gratitude towards the CR & CS department of SRM University-AP, saying that the training sessions strengthened his core skills and abilities. He was also taught to face interviews and critical questions. Mr Rohith said, “Placement is an arduous process. I was offered another position in other company before, but I was not happy with that offer. I had faith in my abilities, so I continued searching for better opportunities and improve my skill set to secure the Super Dream offer. Keeping nerves in control, not panicking during interviews, excellent communication skills are some essential qualities that everyone should master to get good jobs. I am thankful to the CR & CS department for all their support and customised, personal, need-based assistance, which helped me a lot to prepare for the interviews,” said Mr Rohith.
After five months of determination, Mr Rohith finally secured the job that he was looking for. “The University has provided us with numerous opportunities with a flexible curriculum and Global standards. In addition to all the training, my mentors encouraged me to participate in Hackathons, apply for research internships, and attend conferences. Thanks to the extraordinary faculty that we have, the regular classes were of great help in enhancing my technical knowledge,” asserted Mr Rohith. Mr Rohith was a proud track-winner of Microsoft and EthDenver hackathons and a research Intern at Nanyang Technological University (NTU) Singapore.
He has shared his mantra to success with his fellows. Mr Rohith believes that instead of panicking or comparing with others, one should focus on becoming a better version of oneself, and the success will find him.
- Published in CR&CS, CR&CS NEWS, CSE NEWS, News
Dr Jatindra Kumar Dash devices technique for easy detection of Interstitial Lung Diseases
 Dr Jatindra Kumar Dash, Associate Professor, Computer Science and Engineering, has recently published a paper, “Content-based image retrieval system for HRCT lung images: Assisting radiologists in self-learning and diagnosis of Interstitial Lung Diseases” in the reputed Springer Journal- Multimedia Tools and Applications. The research has been carried out in collaboration with Prof. Sudipta Mukhopadhyay, IIT Kharagpur and Professor & Head, Department of RADIO DIAGNOSIS & IMAGING, Post Graduate Institute of Medical Education and Research, Chandigarh.
Dr Jatindra Kumar Dash, Associate Professor, Computer Science and Engineering, has recently published a paper, “Content-based image retrieval system for HRCT lung images: Assisting radiologists in self-learning and diagnosis of Interstitial Lung Diseases” in the reputed Springer Journal- Multimedia Tools and Applications. The research has been carried out in collaboration with Prof. Sudipta Mukhopadhyay, IIT Kharagpur and Professor & Head, Department of RADIO DIAGNOSIS & IMAGING, Post Graduate Institute of Medical Education and Research, Chandigarh.
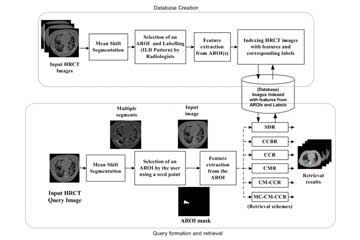 Content-based Image Retrieval (CBIR) is a technique that can exploit the wealth of the data stored in the repository and help radiologists in decision making by providing references to the image in hand. A CBIR system for High-Resolution Computed Tomography (HRCT) lung images depicting the sign of Interstitial Lung Diseases (ILDs) is built, and the system can be used as a self-learning tool by budding radiologists. The system is built by addressing several challenges using advanced machine learning techniques. The objective of this work is to develop a CBIR system for ILDs that is reliable and needs minimal human intervention for ling disease diagnosis.
Content-based Image Retrieval (CBIR) is a technique that can exploit the wealth of the data stored in the repository and help radiologists in decision making by providing references to the image in hand. A CBIR system for High-Resolution Computed Tomography (HRCT) lung images depicting the sign of Interstitial Lung Diseases (ILDs) is built, and the system can be used as a self-learning tool by budding radiologists. The system is built by addressing several challenges using advanced machine learning techniques. The objective of this work is to develop a CBIR system for ILDs that is reliable and needs minimal human intervention for ling disease diagnosis.
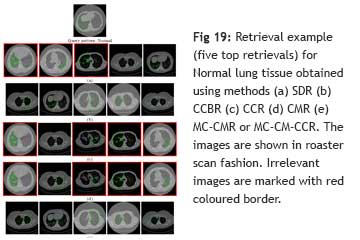 The system developed will act as a helping tool for radiologist by providing a second opinion for the diagnosis of a diverse group of lung diseases called Interstitial Lung Disease. It will help the budding radiologist for self-learning. When used in daily medical practice, the system may reduce the workload of radiologists in countries, having a low number of physicians per inhabitants.
The system developed will act as a helping tool for radiologist by providing a second opinion for the diagnosis of a diverse group of lung diseases called Interstitial Lung Disease. It will help the budding radiologist for self-learning. When used in daily medical practice, the system may reduce the workload of radiologists in countries, having a low number of physicians per inhabitants.
 Dr Dash is associated with SRM University-AP for almost three years. His research interests include Content-Based Image Retrieval, Medical Image Analysis and Texture Analysis. He has currently employed his time into the design and development of a Computer-Aided Diagnosis System for Lung Cancer Screening.
Dr Dash is associated with SRM University-AP for almost three years. His research interests include Content-Based Image Retrieval, Medical Image Analysis and Texture Analysis. He has currently employed his time into the design and development of a Computer-Aided Diagnosis System for Lung Cancer Screening.
Read More: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11042-020-10173-4
- Published in CSE NEWS, Departmental News, News, Research News
An Enthralling Webinar on “Applications of Artificial Intelligence in Aerospace Engineering”
 On April 15, 2021, the Department of Mechanical Engineering, SRM University-AP, Andhra Pradesh, hosted a virtual lecture session with Dr B V N Ramakumar, Professor and HOD, Department of Aerospace Engineering, Dayananda Sagar University, Bangalore. Addressing the Webinar, Dr Lakshmi Sirisha Maganti and Dr Venkata Nori, Faculty, Department of Mechanical Engineering, handed over the podium to Dr Ramakumar. Initiating the discussion with a brief understanding of the background of Artificial Intelligence (AI), Dr Ramakumar described the AI Applications in Space, Civil and Defense industry. Apart from highlighting the overview and functionality of AI Applications in Aerospace Engineering, he outlined the challenges associated with it.
On April 15, 2021, the Department of Mechanical Engineering, SRM University-AP, Andhra Pradesh, hosted a virtual lecture session with Dr B V N Ramakumar, Professor and HOD, Department of Aerospace Engineering, Dayananda Sagar University, Bangalore. Addressing the Webinar, Dr Lakshmi Sirisha Maganti and Dr Venkata Nori, Faculty, Department of Mechanical Engineering, handed over the podium to Dr Ramakumar. Initiating the discussion with a brief understanding of the background of Artificial Intelligence (AI), Dr Ramakumar described the AI Applications in Space, Civil and Defense industry. Apart from highlighting the overview and functionality of AI Applications in Aerospace Engineering, he outlined the challenges associated with it.
Dr Ramakumar completed his bachelor’s from Ranchi University, and he pursued a master’s from Andhra University. Dr Ramakumar holds a Doctorate Degree from IIT Madras and has years of experience in research, academia and industry. Dr Ramakumar worked for Rolls Royce India Pvt Ltd and Honeywell Solutions Pvt Ltd. With contributions to the Auto Mechanics Industrial Sector, he also worked for the DMR Institute of Technology.
Dr Ramakumar was the visiting faculty at Manipal University. In terms of contribution to the field of engineering, he designed, developed, and analysed components for Boeing 777X, Airbus A350 and Honeywell HTF700 Engine Programme. Dr Ramakumar published papers in reputed National and International journals in addition to two patents to his credit.
Dr Ramakumar elucidated, “Artificial Intelligence is the broad sphere covering machine learning and deep learning as well. Moreover, a technique which mimics human behaviour”. Discussing the key players in the aviation industry, he explained the role of the mini-robots to capture the imagery clips of the inaccessible area in an aircraft. Implementation of the Artificial Reality techniques in the civil aviation industry is needed to reduce manual cost and time. AI applications manage the supply chain by gathering data as a part of the predictive measure. With the inclusion of automated tools, the civil aviation industry efficiently controls and optimises the security parameters.
During Dr Ramkumar’s proceeding, he added, “AI Application in aviation optimises the data related to flight scheduling, seat arrangement, cabin crew shift scheduling along with the management of the route mapping”. Starting from taking off to landing, AI Applications are being used widely in the aviation industry.
He further added that “Emerging as the dynamic technology, AI Applications marked their presence in the military intelligence too. Drones for military operations map the routes and record that in imagery forms to apprehend the nearby geographical location. The information stored in databases are sent and received without any manual meddling”.
Advancing to the next part of the discussion, Dr Ramakumar explained that “Speaking of the satellite link and communication, Robonauts are the new humanoid robots that would replicate the actual human beings by assisting in anything from gathering outer space information to exploring it”. Dr Ramakumar also propounds that “Productivity and Investment are few challenges amongst others that are common and would go hand in hand with the development of AI technology.” The discussion came to an end with an engaging Q&A session with the students followed by a Vote of Thanks by Dr Nori.
- Published in Departmental News, Mechanical Engineering NEWS, News, Webinars







