SRM University-AP Celebrates Janmashtami with Devotion and Joy
 Sweeter than honey, tastier than curd, pleasanter indeed than any happiness, and joy is the company, is the power of the name of Krishna. Janmashtami is celebrated as the birthday of Lord Krishna, one of the most powerful and famous reincarnations of Lord Vishnu.
Sweeter than honey, tastier than curd, pleasanter indeed than any happiness, and joy is the company, is the power of the name of Krishna. Janmashtami is celebrated as the birthday of Lord Krishna, one of the most powerful and famous reincarnations of Lord Vishnu.
To seek the blessings of Lord Krishna, the Directorate of Student Affairs at SRM University-AP celebrated Janmashtami on August 23, 2024, with mirth and joy. The campus was filled with the fragrance of flowers, the soothing aroma of camphor, and the jingle of bells, creating a divine atmosphere.
While the religious significance of Janmashtami was deeply honoured, the day also symbolised much more for modern India. It was a day of excitement, euphoria, and a joyous spirit of enthrallment. The celebration brought together devotion, creativity, enjoyment, and fun.
Additionally, the event featured a captivating story recital narrating Lord Krishna’s divine leelas, which enchanted the audience. Devotional singing by the devotees of ISKCON further elevated the spiritual ambience, making the celebration truly memorable. The Janmashtami celebration wasn’t just a series of events; it was a testament to the power of unity, tradition, and the true spirit of Janmashtami. The Auditorium was alive with laughter and enthusiasm during the fun activities, complemented by the elegant area adorned for Krishna Pujan, creating a serene backdrop for our spiritual observance.
This event beautifully showcased the ability of communal celebrations to bring our community together, fostering an appreciation for the significance of Lord Krishna’s birth in a joyous and meaningful manner. As we reflect on the joy and unity of Janmashtami 2024, our hope is that the blessings of Lord Krishna continue to guide and inspire our community throughout the year.
- Published in Departmental News, News, student affairs news
Naga Sravanthi Explores the Role of Blockchain in Food Marketing
 In a significant contribution to the field of food marketing and consumption, Ms P Naga Sravanthi, an Assistant Professor Ad hoc in the Department of Computer Science and Engineering, has recently published a book chapter titled “Blockchain-Based Food Influencer Verification.” The chapter is part of the book “Innovative Trends Shaping Food Marketing and Consumption,” shedding light on the emerging use of blockchain technology in authenticating food influencers.
In a significant contribution to the field of food marketing and consumption, Ms P Naga Sravanthi, an Assistant Professor Ad hoc in the Department of Computer Science and Engineering, has recently published a book chapter titled “Blockchain-Based Food Influencer Verification.” The chapter is part of the book “Innovative Trends Shaping Food Marketing and Consumption,” shedding light on the emerging use of blockchain technology in authenticating food influencers.
In the rapidly evolving world of food marketing, trust and authenticity have become more critical than ever. The book chapter delves into how blockchain technology can revolutionise the way food influencers are verified and trusted by their audiences. Blockchain technology, known for its transparency and security features, has been making waves across various industries, and its application in the food sector is no exception.
Ms Naga Sravanthi’s work focuses on utilising blockchain to verify the credibility and authenticity of food influencers, a vital aspect in today’s digital era, where influencer marketing plays a significant role in consumer decision-making. The book chapter explores how blockchain can address issues of trust and reliability in food marketing by providing a secure and immutable record of influencers’ endorsements and partnerships. This innovative approach not only benefits consumers by ensuring they receive genuine recommendations but also helps food brands collaborate with legitimate and reputable influencers.
The publication of this book chapter underscores SRM University-AP’s commitment to fostering cutting-edge research and innovation in diverse fields, positioning its faculty members as thought leaders in their respective domains. Ms Naga Sravanthi’s work serves as a testament to the university’s dedication to academic excellence and pushing the boundaries of knowledge in emerging technologies.
Brief Description of the Book Chapter:
This chapter explores the integration of blockchain technology into the verification process of food influencers, providing a transparent and tamper-proof method to authenticate their influence and endorsements. By leveraging blockchain, the chapter outlines how the food industry can ensure that influencers are genuine, their endorsements are credible, and their impact is accurately measured. The chapter also delves into case studies and practical applications, demonstrating how this technology can reshape the landscape of influencer marketing in the food sector.
Significance of the Book Chapter
The significance of this chapter lies in its exploration of a cutting-edge application of blockchain technology in a field that deeply influences consumer behaviour in food marketing. As the digital space becomes more saturated with influencers, the need for a reliable verification system becomes paramount. This chapter is particularly meaningful because it addresses the growing concern of authenticity in influencer marketing, a crucial factor in maintaining consumer trust and brand integrity. For those passionate about the intersection of technology, marketing, and food, this chapter offers insights into how blockchain can be a game-changer in ensuring that the voices consumers trust is, indeed, trustworthy.
Target Audience
The book is primarily targeted at professionals in the food industry, including marketers, brand managers, and digital strategists, who are keen on understanding the latest trends shaping consumer behaviour and marketing practices. Additionally, this chapter will be valuable to academics and students in the fields of marketing, food science, and technology, as well as tech enthusiasts interested in the practical applications of blockchain.
Startups and entrepreneurs looking to innovate within the food sector will also find this book to be a vital resource, providing both theoretical insights and practical examples of how technology can redefine industry standards.In essence, “Innovative Trends Shaping Food Marketing and Consumption” and its chapter on blockchain-based influencer verification is an essential read for anyone looking to stay ahead of the curve in the dynamic world of food marketing.
- Published in CSE NEWS, Departmental News, News, Research News
SRM University-AP Hosts Transformative Aadigyan 2024 for Malaysian Students
 The Directorate of International Relations &Higher Studies recently concluded the Aadigyan—Indian Immersion Program 2024, a comprehensive five-day event held from August 16th to 20th. This program was designed to provide bachelor students from UTP Malaysia with an immersive experience of Indian culture, economy, and technological advancements.
The Directorate of International Relations &Higher Studies recently concluded the Aadigyan—Indian Immersion Program 2024, a comprehensive five-day event held from August 16th to 20th. This program was designed to provide bachelor students from UTP Malaysia with an immersive experience of Indian culture, economy, and technological advancements.
The program offered a rich blend of academic lectures, hands-on workshops, industry visits, cultural experiences, and recreational activities. Over the course of five days, students engaged in cultural exchange and understanding through interactive sessions and cultural tours, fostering a deeper connection between Indian and Malaysian students.
Participants were introduced to various facets of Indian history, economy, business models, and technological advancements, broadening their intellectual horizons. Industry visits provided insights into the Indian industrial landscape, promoting an understanding of emerging trends and opportunities.
Highlights of Aadigyan IIP 2024:
- Design Thinking Workshop: Conducted by Prof. Satyanarayana Duvvuri, Associate Director – Directorate of Executive Education and Professional Studies & Professor of Practice, Paari School of Business.
- Essence of Entrepreneurship: A session by Prof. Sidharth Tripathy, Director of Entrepreneurship and Innovation, highlighting the importance of creating new products and ideas to meet market needs. Prof. Tripathy explained that entrepreneurship is derived from the Sanskrit words “antah” (innermost) and “prerna” (inspiration).
- Climate Change Solutions: Students were tasked with providing solutions for contemporary climate change issues, enhancing their understanding of the scope and impact of these problems.
- Customer-Centric Product Development: Emphasized the need for a deep understanding of customers, empathy, and creative problem-solving. Students learned the importance of observing market dynamics to connect with customers effectively.
- Business Insights: AVS Kamesh from PSB provided an introduction to key elements of business and career paths in marketing and management.
- Digital Marketing: Kirti Krishna conducted a session on digital marketing tools and the differences between traditional and digital marketing.
The program concluded with a valedictory address by Sandeep Samala. During the ceremony, students and professors from the IR council shared heartfelt experiences, reflecting on their journey together. The event was marked by the exchange of mementos and the capturing of photographs, commemorating this significant event in their academic careers. Aadigyan IIP 2024 aimed to inspire, educate, and empower the next generation of leaders from Malaysia, preparing them to tackle the challenges and opportunities of the 21st-century global landscape.
The “Aadigyan – Indian Immersion Program 2024” at SRM University-AP stands as a testament to the institution’s commitment to fostering global understanding and preparing future leaders for success in the interconnected world.
- Published in Departmental News, International Relations, IR-News, News
Dr Vineeth Thomas Analyses Challenges Ahead for Modi’s Third Term
 Dr Vineeth Thomas, an Assistant Professor in the Department of Political Science, has recently published a thought-provoking paper titled “Why Modi’s Third Term as India’s Prime Minister Will Be Tough” in the distinguished journal Asian Affairs. In his comprehensive analysis, Dr Vineeth delves into the political landscape of India and the various challenges Prime Minister Narendra Modi may face if he seeks re-election for a third consecutive term in 2024. Drawing on an array of political theories and current socio-economic indicators, the paper examines the underlying factors shaping Indian politics and public sentiment.
Dr Vineeth Thomas, an Assistant Professor in the Department of Political Science, has recently published a thought-provoking paper titled “Why Modi’s Third Term as India’s Prime Minister Will Be Tough” in the distinguished journal Asian Affairs. In his comprehensive analysis, Dr Vineeth delves into the political landscape of India and the various challenges Prime Minister Narendra Modi may face if he seeks re-election for a third consecutive term in 2024. Drawing on an array of political theories and current socio-economic indicators, the paper examines the underlying factors shaping Indian politics and public sentiment.
Dr Thomas argues that while Modi’s leadership has been marked by significant economic reforms and a robust foreign policy, the landscape is shifting in a manner that could complicate his re-election bid. Key issues explored in the paper include rising economic disparities, increasing urban unrest, and the challenge of maintaining communal harmony in a diversely populated nation.
The findings of this research are particularly pertinent in light of ongoing debates surrounding economic policy, agrarian distress, and the role of civil liberties – a backdrop that could significantly influence electoral dynamics heading into 2024.
The publication of this paper not only highlights Dr Thomas’s expertise in political science but also underscores the vital role academic discourse plays in contemporary political analysis. His insights contribute to a deeper understanding of India’s complex interplay between governance and public perception.
Abstract of the Research
On 9 June 2024, Narendra Modi became India’s Prime Minister for a third consecutive term, a feat previously accomplished only by Jawaharlal Nehru. However, this historic victory also began one of the most uncertain periods of his prime ministership. The fractured outcome of India’s 18th general election has created a fundamentally different political landscape. Modi’s Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) secured just 240 seats, a significant drop from its 2019 tally, and was therefore short of an absolute majority. Although the BJP-led National Democratic Alliance (NDA) did win a majority, Modi will now be dependent upon coalition partners, necessitating a shift towards a more collaborative governance style.
Research in Layperson’s Terms
In the recent election, Modi’s party, the BJP, won only 240 seats, much fewer than in the last election and not enough for a clear majority. Although the broader alliance led by the BJP still has a majority, Modi now needs to rely more on other parties in the alliance to govern. This means he will have to work more closely with his coalition partners and be more collaborative in his leadership style.
Research Paper in the Citation Format
Vineeth Thomas, Agney GK & Arsha V Sathyan (2024), Why Modi’s Third Term As India’s Prime Minister Will Be Tough, Asian Affairs, ISSN: 0306-8374
(Routledge, SCOPUS/WoS Indexed)
Practical implementation or the social implications associated with Research
The practical implementation of my research lies in shaping policies that promote gender equality in political representation. By identifying barriers and proposing solutions, it aims to enhance women’s participation in politics, leading to more inclusive governance. The social implications include fostering a more equitable society with diverse perspectives in decision-making.
Your collaborations
Electoral Politics
Your Future Research Plans
Indian govt and politics
- Published in Departmental News, News, Political Science News, Research News
SRM AP Partners with ISF as Regional Hub for Rural Ankura Yatra Semi-Finals
 In a pioneering move to promote innovation and entrepreneurship at the grassroots level, SRM University-AP is proud to announce its partnership with the International Startup Foundation (ISF) as the regional hub for conducting the semi-finals of the Rural Ankura Yatra. This ambitious initiative by ISF seeks to ignite the entrepreneurial spirit across tier 2 and 3 cities and rural areas, identifying and nurturing latent entrepreneurial talent.
In a pioneering move to promote innovation and entrepreneurship at the grassroots level, SRM University-AP is proud to announce its partnership with the International Startup Foundation (ISF) as the regional hub for conducting the semi-finals of the Rural Ankura Yatra. This ambitious initiative by ISF seeks to ignite the entrepreneurial spirit across tier 2 and 3 cities and rural areas, identifying and nurturing latent entrepreneurial talent.
The Rural Ankura Bus Yatra, spearheaded by ISF, is more than just a journey—it’s a celebration of the entrepreneurial potential nestled within the heart of rural Andhra Pradesh. By uniting global CXOs, mentors, investors, researchers, and educators, this statewide yatra aims to strengthen the rural startup ecosystem, ultimately catalysing job creation and fostering economic growth in underserved regions.
The startup pitch contest, a key component of the Yatra, will serve as a platform for rural innovators to showcase their ideas and solutions to local problems. This initiative aligns seamlessly with SRM University-AP’s mission to drive innovation and entrepreneurship across the country.
Vice-Chancellor of SRM University-AP, Prof. Manoj K Arora, expressed his enthusiasm for the partnership, stating, “At SRM University-AP, we are deeply committed to fostering a culture of innovation and entrepreneurship. Partnering with ISF for the Rural Ankura Yatra allows us to extend our mission beyond urban centres, empowering rural innovators to drive meaningful change within their communities.”
The regional semi-finals at SRM University-AP are scheduled for September 11, 2024. The event is expected to draw over 500 participants from various districts, with the top 20 teams—10 from each category—advancing to the final demo day. These teams will have the opportunity to exhibit their ideas and solutions at SRM University-AP, vying for the support and investment needed to bring their ventures to life.
A distinguished panel of high-profile delegates, including professors from SRM University-AP and leaders from ISF, will serve as the jury, selecting the most promising ventures for the finals. Notably, five offers from venture capitalists associated with ISF will be extended to the top ventures.
Dr Siddharth Shankar Tripathi, Director of Entrepreneurship and Innovation at SRM University-AP, added, “The Rural Ankura Yatra is a remarkable initiative that aligns with our vision of holistic development. By nurturing entrepreneurial talent in rural areas, we are not only fueling economic growth but also promoting sustainable development.”
Mr J.A. Chowdary, Founding Director of Software Technology Parks of India and former IT Advisor and Special Chief Secretary to the Chief Minister of AP, emphasised the importance of the Yatra, stating, “The Rural Ankura Yatra is a vital step towards unlocking the vast potential of rural India. By bringing together global expertise and local talent, we aim to create a thriving ecosystem that supports innovation and entrepreneurship at the grassroots level.”
SRM University-AP has consistently championed entrepreneurship as an economic growth and social change catalyst. One of the university’s flagship initiatives, ADITRI, stands as a testament to this commitment. As a pioneering CSR project, ADITRI is dedicated to supporting and empowering rural women entrepreneurs in Andhra Pradesh. With funding of ₹2 crores, the project aligns with the university’s mission to promote innovation and social responsibility, focusing on economic empowerment, job creation, gender equality, and community development.
Through initiatives such as Micro Entrepreneurship Bootcamps and the Rural Women Innovation and Entrepreneurship Hub (RWIEH), SRM University-AP continues to make a significant impact, having already reached over 1400 women across various mandals in Andhra Pradesh. As the university steps into the role of a regional hub for the Rural Ankura Yatra, it reaffirms its commitment to nurturing the next generation of entrepreneurs who will drive India’s socio-economic transformation.
- Published in Departmental News, IDEA NEWS, News
New Chapter Begins: Over 3000 Students Start Their Journey at SRM AP
 SRM University-AP extends a warm welcome to its newest cohort of students as it kicks off the much-anticipated “UDAAN 2024” orientation programme. This 10-day event, running from August 12 to August 23, is meticulously crafted to seamlessly integrate more than 3000 freshers from more than 20 states of India into the vibrant campus life and academic environment.
SRM University-AP extends a warm welcome to its newest cohort of students as it kicks off the much-anticipated “UDAAN 2024” orientation programme. This 10-day event, running from August 12 to August 23, is meticulously crafted to seamlessly integrate more than 3000 freshers from more than 20 states of India into the vibrant campus life and academic environment.
The event began with the traditional lighting of the lamp and an invocation ceremony, setting a tone of reverence and inspiration. During the inaugural session, students were given an overview of the university’s various directorates, schools, and the academic ecosystem, providing them with essential knowledge about their new environment. Deans and directors from all departments were present, underscoring the importance of this milestone in the student’s academic journey.
Pro-Chancellor, SRM University-AP Dr P Sathyanarayanan, extended his warmest wishes to the students, stating “At SRM AP, we are dedicated to shaping the next generation of leaders, innovators, and change-makers. With UDAAN 2024, we are excited to empower our students as they embark on this transformative educational journey. It is our hope that this experience inspires each of you to achieve excellence and make a meaningful impact on the world. Welcome to a vibrant community where your future truly begins.”
Vice Chancellor, SRM University-AP, Prof. Manoj K Arora, addressed the new students, encouraging them to embrace self-reliance and to make the most of every opportunity during their time at the university. He motivated the students and said that they have an opportunity to learn new things, acquire new knowledge, grow new competencies, develop new skills and enhance their personal attributes in profound ways that will shape their character for the rest of their lives. Prof. Arora further added that the students have an opportunity to weave new friendships that will impact their lives in incredible ways and that education is not only about acquiring knowledge and skills, but it also prepares us for life.
The programme was honoured by the presence of Indian Ambassador Deepak Vohra ji, Special Advisor to Prime Minister in Africa and Ladakh, who was the chief guest for the event. His address to the students motivated them on how to attain great heights in their careers even in adverse situations through relentless goal setting, hard work, dedication and determination. He further told the students that if we are divided, we can go fast, but if we are united, we can go far. Deepak Vohra concluded his speech with this line, “The future of India is the future of the world. The whole world trusts India because we are intrinsically good people. You are the hope for the future of a safe and secure world.”
Throughout this 10-day programme, students will participate in a series of sessions designed to familiarise them with the university’s offerings. These include introductions to the academic departments, faculty, and administrative staff, as well as insights into the various clubs and associations that contribute to a holistic educational experience at SRM University-AP.
- Published in News, student affairs news
AI-Based Remote Fetal Heart Rate Monitoring Published in Leading Journal
 Dr Sibendu Samanta, Assistant Professor in the Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, and Ms Radha Abburi, a PhD Scholar, have made significant strides in the field of fetal health monitoring. Their paper, titled “Adopting Artificial Intelligence Algorithms for Remote Fetal Heart Rate Monitoring and Classification using Wearable Fetal Phonocardiography,” has been published in the prestigious Q1 Journal, Applied Soft Computing, which boasts an impressive impact factor of 7.2.
Dr Sibendu Samanta, Assistant Professor in the Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, and Ms Radha Abburi, a PhD Scholar, have made significant strides in the field of fetal health monitoring. Their paper, titled “Adopting Artificial Intelligence Algorithms for Remote Fetal Heart Rate Monitoring and Classification using Wearable Fetal Phonocardiography,” has been published in the prestigious Q1 Journal, Applied Soft Computing, which boasts an impressive impact factor of 7.2.
This pioneering study addresses the critical gaps in the analysis of Fetal Heart Rate (FHR) recordings by leveraging wearable Phonocardiography (PCG) signals and advanced AI algorithms. The primary goal of the research is to achieve accurate classification results through the remote monitoring of fetal heartbeats. Additionally, the study tackles complex issues related to data quantity and the inherent complexity of FHR analysis. Dr Samanta and Ms Abburi’s work represents a significant advancement in the field, promising to enhance the accuracy and reliability of fetal health monitoring, ultimately contributing to better prenatal care.
Abstract of the Research:
Fetal phonocardiography (FPCG) is a non-invasive Fetal Heart Rate (FHR) monitoring technique that can detect vibrations and murmurs in heart sounds. However, acquiring fetal heart sounds from a wearable FPCG device is challenging due to noise and artefacts. This research contributes a resilient solution to overcome the conventional issues by adopting Artificial Intelligence (AI) with FPCG for automated FHR monitoring in an end-to-end manner, named (AI-FHR). Four sequential methodologies were used to ensure reliable and accurate FHR monitoring. The proposed method removes low-frequency noises and high-frequency noises by using Chebyshev II high-pass filters and Enhanced Complete Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition with Adaptive Noise (ECEEMDAN) in combination with Phase Shifted Maximal Overlap Discrete Wavelet Transform (PS-MODWT) filters, respectively.
The denoised signals are segmented to reduce complexity, and the segmentation is performed using multi-agent deep Q-learning (MA-DQL). The segmented signal is provided to reduce the redundancies in cardiac cycles using the Artificial Hummingbird Optimization (AHBO) algorithm. The segmented and non-redundant signals are converted into 3D spectrograms using a machine learning algorithm called variational auto-encoder-general adversarial networks (VAE-GAN). The feature extraction and classification are carried out by adopting a hybrid of the bidirectional gated recurrent unit (BiGRU) and the multi-boosted capsule network (MBCapsNet). The proposed method was implemented and simulated using MATLAB R2020a and validated by adopting effective validation metrics.
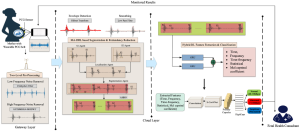
The results demonstrate that the proposed method performed better than the current method with accuracy (81.34%), sensitivity (72%), F1-score (83%), Energy (0.808 J), and complexity index (13.34). Like other optimization methods, AHO needs precise parameter adjustment in order to function well. Its performance may be greatly impacted by the selection of parameters, including population size, exploration rate, and learning rate.
The title of the Research Paper in the Citation Format:
R. Abburi, I. Hatai, R. Jaros, R. Martinek, T. A. Babu, S. A. Babu, S. Samanta, “Adopting artificial intelligence algorithms for remote fetal heart rate monitoring and classification using wearable fetal phonocardiography”, Applied Soft Computing, vol. 165, pp. 112049, 2024, ISSN 1568-4946.
Practical Implementation or the Social Implications Associated with the Research
- Chebyshev filter and EC2EMDAN-PS-MODWT reduce low and high frequency noises.
- MA-DRL and optimization algorithms reduce complexity during classification.
- Machine learning spectrogram conversion to capture time, frequency, and spectral variations.
- Hybrid deep learning algorithms can be used to reduce positive rates.
Collaborations:
- Dr. Indranil Hatai (Signal Processing and FPGA, Mathworks, Bangalore, India)
- Dr. T. Arun Babu (HoD, Dept. of Pediatrics, All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS), Andhra Pradesh, India)
- Dr. Sharmila Arun Babu, MBBS, MS (HoD, Dept. of Obstetrics and Gynecology, All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS), Andhra Pradesh, India)
- Dr. Rene Jaros (Dept. of Cybernetics and Biomedical Engineering, Faculty of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, VSB–Technical University of Ostrava, 708 00, Ostrava, Czechia)
- Prof. Radek Martinek (Dept. of Cybernetics and Biomedical Engineering, Faculty of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, VSB–Technical University of Ostrava, 708 00, Ostrava, Czechia)
Future Research Plans:
- Design a low cost for continuous fetal heart rate (FHR) monitoring system
- Develop a proper deep learning algorithm to get a proper understanding of fetal’s abnormality.
- Published in Departmental News, ECE NEWS, News, Research News
Dr Vineeth Publishes Paper on Policy Responses to Caste Violence in Tamil Nadu
 Dr Vineeth Thomas, Assistant Professor in the Department of Political Science, has recently published a paper titled “Policy Responses to Caste Violence in Tamil Nadu” in the esteemed journal Economic and Political Weekly (EPW). In the paper, Dr. Thomas offers valuable insights into the crucial issue of caste violence in Tamil Nadu and examines various policy responses aimed at addressing this complex societal challenge.
Dr Vineeth Thomas, Assistant Professor in the Department of Political Science, has recently published a paper titled “Policy Responses to Caste Violence in Tamil Nadu” in the esteemed journal Economic and Political Weekly (EPW). In the paper, Dr. Thomas offers valuable insights into the crucial issue of caste violence in Tamil Nadu and examines various policy responses aimed at addressing this complex societal challenge.
Dr Thomas’s research illuminates the dynamics of caste violence and provides a comprehensive analysis of the policy measures adopted to tackle this pressing issue. His work in the EPW is expected to significantly contribute to the discourse on caste-based conflicts and policy formulation in the region. The publication of this paper not only exemplifies Dr. Vineeth Thomas’s scholarly prowess but also underscores SRM University—AP’s commitment to fostering impactful research in the realm of social and political sciences. It is anticipated that this publication will stimulate further academic dialogue and influence policy considerations in the domain of caste relations and violence in Tamil Nadu.
Abstract of the Research
This study examines the policy response to caste violence in schools in Tamil Nadu, particularly through the recommendations of a committee led by retired Justice K. Chandru. The committee’s report highlights pervasive caste discrimination in schools and proposes various measures, including teacher transfers, banning caste markers, and implementing orientation programs on caste-related issues. The report also suggests the establishment of School Welfare Officers and Social Justice Student Forces, along with a robust grievance redressal mechanism. Despite opposition and criticism, these recommendations represent a significant step toward addressing caste discrimination in Tamil Nadu’s educational institutions.
Research in Layperson’s Terms
This research focuses on the problem of caste discrimination in schools in Tamil Nadu, India. Despite the state’s reputation for promoting social justice, caste-based violence still occurs, even among students. A committee led by retired Justice K. Chandru made several recommendations to address this issue, such as banning caste markers like wristbands and educating students and teachers about discrimination. The report also suggests having specific officers to ensure these measures are followed. While these recommendations aim to create a fairer school environment, their success depends on proper implementation and support from the community.
Practical Implementation and the Social Implications Associated
Implementing this research can lead to more inclusive and equitable school environments by eliminating caste-based discrimination. By enforcing bans on caste markers, educating students and teachers, and establishing grievance mechanisms, schools can foster a culture of equality, reducing social tensions and promoting a just society for future generations.
Collaborations
Electoral Politics
Future Research Plans
Indian govt and politics
- Published in Departmental News, News, Political Science News, Research News
Exploring the Impact of Welding Processes on Duplex Stainless Steel Parts in Additive Manufacturing
 In a recent publication in the prestigious Journal Metals and Materials International, Dr Maheshwar Dwivedy, Associate Professor in the Department of Mechanical Engineering and Dr B Prasanna Nagasai, Post-Doctoral Researcher, delve into the intricate relationship between welding processes and the resulting microstructure and mechanical properties of Duplex Stainless-Steel parts fabricated through Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing.
In a recent publication in the prestigious Journal Metals and Materials International, Dr Maheshwar Dwivedy, Associate Professor in the Department of Mechanical Engineering and Dr B Prasanna Nagasai, Post-Doctoral Researcher, delve into the intricate relationship between welding processes and the resulting microstructure and mechanical properties of Duplex Stainless-Steel parts fabricated through Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing.
The research paper, aptly titled “Influence of Welding Processes on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Duplex Stainless-Steel Parts Fabricated by Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing,” illuminates the crucial factors that influence the quality and performance of components produced using this innovative manufacturing technique.
This collaborative effort not only enriches the academic community but also holds promising implications for the advancement of additive manufacturing technologies, particularly in the realm of Duplex Stainless-Steel fabrication. By unravelling the impact of different welding processes on the microstructural characteristics and mechanical behaviour of such components, the researchers offer valuable insights that can potentially enhance the efficiency and reliability of the manufacturing process.
The publication of this paper signifies a significant milestone in the ongoing exploration of material science and additive manufacturing techniques, highlighting the dedication and expertise of Dr Maheshwar Dwivedy and Dr B Prasanna Nagasai in pushing the boundaries of knowledge and innovation in the field.
Abstract
Direct energy deposition (DED) is an advanced additive manufacturing (AM) technique for producing large metal components in structural engineering. Its cost-effectiveness and high deposition rates make it suitable for creating substantial and complex parts. However, the mechanical and microstructural properties of these components can be influenced by the varying heat input and repeated thermal treatments associated with different welding procedures used during the deposition process. This study employed gas metal arc welding (GMAW) and cold metal transfer (CMT) arc welding techniques to fabricate cylindrical components from 2209 duplex stainless steel (DSS).
The research investigated the impact of these welding methods on the microstructure and mechanical properties of the 2209 DSS cylinders. The intricate thermal cycles and cooling rates inherent in the DED process significantly influenced the primary phase balance, ideally comprising 50% austenite and 50% ferrite. In components processed using GMAW, σ-phase formation was noted at the grain boundaries. Additionally, a slower cooling rate and extended time for solid-state phase transformations led to an increase in austenite content from the bottom to the top of the component. The cylinder fabricated using the CMT process exhibited fine austenite morphologies and a higher ferrite content compared to the GMW-processed cylinder.
Furthermore, the cylinder produced using the CMT process showed consistent properties across the building direction, unlike the components manufactured with the GMW process. In terms of tensile properties, hardness, and impact toughness, the cylinder produced using the CMT technique outperformed the one made with the GMW process.
Research in Layperson’s Terms
Over the last ten years, a new way of making things called additive manufacturing (AM) has become really popular, especially in industries like aerospace, oil, and gas. This technology builds parts layer by layer, which is a big change from traditional methods that often involve cutting away material to shape a part. One specific method of AM, called Directed Energy Deposition (DED), is particularly good at creating complex metal parts quickly and efficiently. A special kind of stainless steel called duplex stainless steel (DSS) is made of two types of microstructures, ferrite and austenite, which give it great strength and resistance to corrosion. This makes it ideal for use in demanding environments like the oil and gas industry.
A technique within DED called Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing (WAAM) is becoming a popular way to make large, strong metal parts like pipes and storage tanks. WAAM uses the same equipment as welding and can build parts by melting wire with an electric arc. It’s faster and cheaper than other AM methods. However, the process can change the structure of the metal, which affects its properties. For example, too much heat can reduce the amount of ferrite in the metal, making it less strong.
Researchers have been studying how different methods of WAAM, including ones that use less heat, affect the metal’s structure and properties. They’ve found that controlling the heat can lead to better mechanical properties, like higher strength and toughness. They’ve also looked at new technologies like digital twins (virtual models of the manufacturing process) to improve the stability and consistency of the process. In this study, researchers focused on making cylindrical parts from 2209 DSS using two different welding processes within WAAM: Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW) and Cold Metal Transfer (CMT).
They studied how these processes affected the metal’s structure and properties, like tensile strength, hardness, and toughness. The goal was to understand which process produces the best quality parts for industrial use. In summary, the research aims to improve the manufacturing of strong, corrosion-resistant metal parts using advanced AM techniques, making them more efficient and cost-effective for industries that need durable components.
Practical Implementation or the Social Implications Associated
The practical implementation of this research can revolutionise industrial manufacturing, especially in sectors like aerospace, oil and gas, automotive, and marine applications. Using WAAM with DSS, industries can produce lightweight, high-strength parts that withstand extreme environments, significantly improving efficiency and cost-effectiveness. WAAM’s ability to quickly produce customized and high-quality components also makes it ideal for rapid prototyping and repair, reducing lead times and overall production costs. Furthermore, WAAM is a more sustainable manufacturing method, generating less waste and utilizing recycled materials, contributing to eco-friendly production practices. The social implications are substantial, including the creation of new job opportunities and the need for specialized training programs to equip workers with advanced skills.
The economic impact is also notable, as WAAM enhances the competitiveness of companies, driving economic growth in high-tech industries. Innovation is fostered through advancements in manufacturing processes and materials science, leading to improved product performance and longevity, particularly in safety-critical applications. Additionally, the environmental benefits of reduced waste and potential use of recycled materials align with global sustainability goals. Overall, the adoption of WAAM can democratize the manufacturing landscape, making advanced technologies more accessible and affordable for smaller companies and startups, thereby fostering a more inclusive and innovative industrial environment.
Future Research Plans:
The upcoming work will focus on creating Functionally Graded Materials (FGMs) using Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing (WAAM) by merging various metals, including nickel, stainless steel, mild steel, Inconel 718, and AISI 410 MSS. The goal is to optimise material interfaces, refine deposition processes, and ensure structural integrity for high-performance applications.
- Published in Departmental News, Mechanical Engineering NEWS, News, Research News
Unraveling Chaos Dynamics in Cancer: Dr Koyel Chakravarty’s Breakthrough Research
 Dr Koyel Chakravarty, Assistant Professor in the Department of Mathematics, has made a significant contribution to the field of cancer research with her paper “Analysis and Regulation of Chaos Dynamics in a Cancer Model through Chemotherapeutic Intervention and Immune System Augmentation,” which was recently published in the International Journal of Dynamics and Control. In her paper, Dr Chakravarty delves into the intricate world of chaos dynamics within a cancer model and explores the potential for regulating these dynamics through the combined approach of chemotherapeutic intervention and immune system augmentation.
Dr Koyel Chakravarty, Assistant Professor in the Department of Mathematics, has made a significant contribution to the field of cancer research with her paper “Analysis and Regulation of Chaos Dynamics in a Cancer Model through Chemotherapeutic Intervention and Immune System Augmentation,” which was recently published in the International Journal of Dynamics and Control. In her paper, Dr Chakravarty delves into the intricate world of chaos dynamics within a cancer model and explores the potential for regulating these dynamics through the combined approach of chemotherapeutic intervention and immune system augmentation.
Her research offers insights into understanding the complex behaviour of cancer cells and how such insights can be leveraged to develop more effective treatment strategies. Dr Chakravarty’s work marks a crucial step forward in the ongoing efforts to combat cancer, shedding light on the dynamic interplay between therapeutic interventions and the body’s immune response.
The publication of this paper not only underscores Dr Koyel’s expertise in the field of mathematical analysis in cancer research but also signifies a promising advancement in the collective pursuit of understanding and addressing the challenges posed by cancer.
Abstract
The focus of the current investigation lies in the formulation and analysis of a dynamic model depicting cancer growth, incorporating the joint influences of chemotherapy and immune system augmentation. The primary emphasis of this study revolves around the analysis of the dynamic behaviour within a living-cell closed carcinoma system, specifically one devoid of external vitamin support, with a particular exploration of chaos dynamics. Subsequently, the authors aim to scrutinise the pivotal impact of infused vitamins in attaining stable system dynamics through the application of chaos control techniques.
The formulated model exhibits fundamental mathematical properties, revealing a spectrum of co-dimension one and co-dimension two bifurcations. The identification of specific bifurcation types relies on algebraic criteria techniques, where conditions necessary and sufficient for bifurcation types are developed. Notably, these criteria are distinct from traditional approaches based on the characteristics of the eigenvalues of the Jacobian matrix, instead relying on coefficients derived from characteristic equations. The accuracy of the analytical conclusions is validated through numerical findings, elucidating diverse bifurcation structures. The article enriches its contribution by delving into the control of chaos through the reinforcement of the internal immune system and the maintenance of the biological system’s stability. This work culminates in proposing future directions aimed at advancing a more realistic approach to eradicating cancer.
Research in Layperson’s Terms
This study focuses on developing and analysing a model that simulates how cancer grows, considering both chemotherapy and the immune system’s response. The main goal is to understand how cancer behaves over time in a system that doesn’t have external vitamin support, especially looking at how chaotic or unpredictable the growth can become. The researchers also investigate how adding vitamins might help stabilise this chaotic system using specific control techniques. The model they created has certain mathematical features that show different types of changes, called bifurcations, which can occur under specific conditions.
Additionally, the study explores how strengthening the immune system might help control this chaos and stabilise the biological system. The paper concludes by suggesting future research directions that could lead to more effective cancer treatment strategies.
Practical implementation
The practical implementation and social implications of analysing and regulating chaos dynamics in a cancer model through chemotherapeutic intervention and immune system augmentation can be profound. Insights gained from this research could be applied to optimize cancer treatment protocols, potentially leading to more effective therapies with reduced side effects. By understanding and controlling the chaotic behaviour in cancer systems, patient outcomes could be improved through personalized treatment strategies.
Socially, the adoption of these findings may lead to increased public confidence in advanced cancer treatments, as well as a broader acceptance of integrating immune system support with traditional therapies. The potential for more stable and predictable treatment outcomes may also reduce the emotional and financial burden on patients and healthcare systems. Additionally, this approach may encourage further interdisciplinary research, bridging gaps between Mathematics, Biology, and Medicine, thus fostering innovation in cancer therapy development.
Collaborations
Dr Lakshmi Narayan Guin, Associate Professor, Department of Mathematics, Siksha Bhavana, Visva-Bharati
Future research plans
Potential areas for further exploration include:
- Personalised Medicine: Developing patient-specific models that consider individual biological variations could lead to more tailored and effective cancer treatments, minimising side effects and improving outcomes.
- Integration with Advanced Therapies: Combining the insights from chaos dynamics with emerging therapies such as immunotherapy, targeted therapy, and gene editing could enhance the precision and efficacy of cancer treatments.
- Published in Departmental News, Math News, News, Research News


































