SRM-AP All News
ALL News
- Breakthrough in Autism Detection: A New System Patent by CSE Researchers October 14, 2024
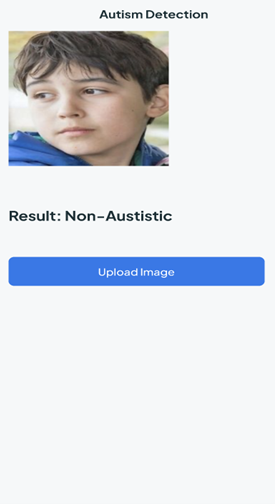
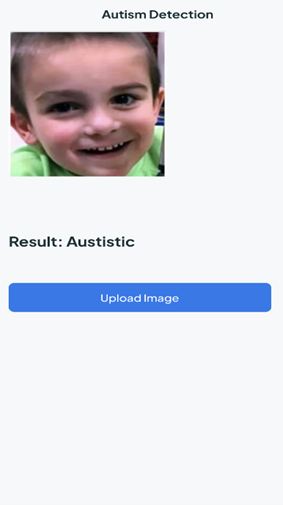
 In a significant advancement for neurodevelopmental research, Dr Nitul Dutta, Associate Professor in the Department of Computer Science and Engineering, along with PhD scholar Ms Surya Samantha Beri and BTech student Mr Nallamothu Sai Karthik, have successfully filed and published a patent titled “A System for Autism Spectrum Disorder Detection.” The application, numbered 202441053505, has been officially documented in the Patent Office Journal.
In a significant advancement for neurodevelopmental research, Dr Nitul Dutta, Associate Professor in the Department of Computer Science and Engineering, along with PhD scholar Ms Surya Samantha Beri and BTech student Mr Nallamothu Sai Karthik, have successfully filed and published a patent titled “A System for Autism Spectrum Disorder Detection.” The application, numbered 202441053505, has been officially documented in the Patent Office Journal.The innovative system aims to enhance the early detection of Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), providing a more efficient and accessible method for diagnosis. By integrating advanced algorithms and machine learning techniques, the system promises to analyse behavioural data effectively, allowing for timely interventions and support for individuals on the spectrum. Dr Dutta emphasised the importance of early detection, stating, “The earlier we can identify ASD, the better the outcomes for individuals and their families. Our system is designed to make this process more accurate and user-friendly.”
Ms Beri and Mr Karthik contributed significantly to the research, which reflects a collaborative effort between academia and technology. Their work not only demonstrates the potential for technological solutions in healthcare but also highlights the critical role of interdisciplinary approaches in addressing complex challenges.
This patent represents a crucial step forward in the field of autism research and is expected to pave the way for further innovations aimed at improving the lives of those affected by ASD.
Abstract of the Research
The system for autism spectrum disease detection incorporates a server with a hybrid application comprising several key modules: a capturing module receiving images from image-capturing devices , a data collection module gathering a dataset of images from multiple capturing devices, and a pre-processing module standardising and normalising images to generate a standardised dataset. Additionally, a feature extraction module collaborates with the pre-processing module to identify autism-indicative features in standardised images, preparing labelled standardised images stored in the data collection module.
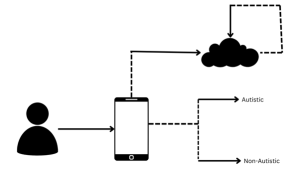
Furthermore, a data segmentation module segments standardised images into training and testing data, including a training module for real-time training of a convolutional neural network model and a testing module to evaluate the convolutional neural network model’s accuracy in detecting autism based on testing data.
Explanation of the Research in Layperson’s Terms
The background information herein below relates to the present disclosure but is not necessarily prior art. Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a neurological or developmental disorder that profoundly impacts communication skills, social interaction, and cognitive abilities in individuals. Those with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) often exhibit challenges in social interaction, limited eye contact, difficulty understanding social cues, and impaired language skills. Additionally, repetitive behaviours and sensory sensitivities are common characteristics.
The disorder arises from developmental changes in brain structure and can have various causes, including genetic factors, familial history of autism spectrum disorder (ASD), advanced parental age, or low birth weight. The prevalence of autism spectrum disorder (ASD), as reported by the World Health Organization (WHO), stands at one in every 160 children. Early detection and intervention are crucial for managing autism spectrum disorder (ASD) effectively, as interventions such as medical and neurological examinations, cognitive and language assessments, and frequent observations, including blood and hearing tests, can significantly improve outcomes. Detecting Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) in children below the age of 10 is comparatively easier than in adults, underscoring the importance of early diagnosis to facilitate timely interventions.
Current diagnostic processes for autism spectrum disorder (ASD) often present significant challenges, particularly for young children, due to their limited ability to communicate and cooperate during assessments. Traditional diagnostic methods rely heavily on structured interviews, behavioural observations, and standardised tests, which can be daunting and stressful for children, leading to inaccurate results. Moreover, these procedures are time-consuming and often require multiple visits to specialised clinics or healthcare facilities, causing inconvenience and financial strain for families. Also, the cost associated with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) diagnosis can be prohibitive for many families.
Therefore, there is a pressing need for more accessible, less intrusive, and cost-effective methods for detecting autism spectrum disorder (ASD) in its early stages to ensure timely and effective intervention. Therefore, there is a need for a system for autism spectrum disorder detection that alleviates the drawbacks.
Practical and Social Implications Associated with the Research
Current diagnostic procedures for Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) face considerable technical challenges, particularly concerning young children’s limited ability to engage in conventional assessment methods. These methods typically rely on structured interviews, behavioural observations, and standardised tests, all of which can be arduous and distressing for children with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), potentially leading to unreliable outcomes. Furthermore, these procedures are resource-intensive, requiring multiple visits to specialised clinics or healthcare facilities, thereby causing logistical challenges and financial burdens for families. Current diagnostic processes for Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) often present significant challenges, particularly for young children, due to their limited ability to communicate and cooperate during assessments. Traditional diagnostic methods rely heavily on structured interviews, behavioural observations, and standardised tests, which can be daunting and stressful for children, leading to inaccurate results. Moreover, these procedures are time-consuming and often require multiple visits to specialised clinics or healthcare facilities, causing inconvenience and financial strain for families. Also, the cost associated with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) diagnosis can be prohibitive for many families. Therefore, there is a pressing need for more accessible, less intrusive, and cost-effective methods for detecting Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) in its early stages to ensure timely and effective intervention.
Collaborations
This research was done in collaboration with Professor George, Brunel University, London, United Kingdom
Future Research Plans
In the future, we will also try to diagnose the disorder by speech therapy using Natural Language Processing and integrate it with real-time industry in health care, which can be used by many doctors in their respective practices
Continue reading → - 1st Private University in India to Send a Student Expedition to Mt. Everest Base Camp October 14, 2024
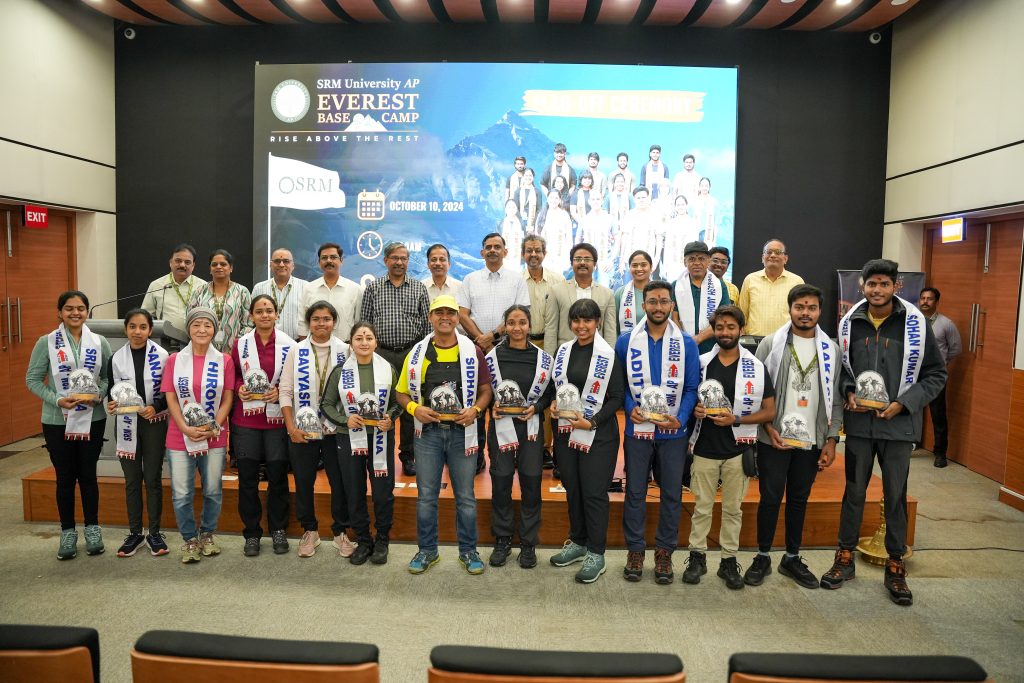

SRM University-AP flagged off the much-awaited Everest Base Camp Expedition that will take place from October 12 – 27, 2024. This is India’s first initiative by any private university in India to send a team of 18 students and faculty under the leadership of Mr Sidharth Tripathy, Director-Entrepreneurship and Innovation, to conquer Mt. Everest Base Camp. The audacious adventure was flagged off by Dr R Premkumar, Registrar, and Prof. Bharadhwaj Sivakumaran, Dean of Paari School of Business, in the presence of Mr Anil Kumar Nigam, Director-Student Affairs, Mr Udayan Bakshi, Associate Director-Entrepreneurship & Innovation, Prof. C V Tomy, Dean-SEAS and the cheering students of the university.
“To enhance the quality of entrepreneurship, it is pivotal to foster a mindset that can take risks, tackle huge challenges and overcome tribulations from a broader perspective. Our motive as a 21st-century university is to cultivate this mindset through this thrilling adventure and to become the harbingers of transformation among students,” remarked the expedition leader, Mr Sidharth Tripathy. The 15-day exhilarating expedition jointly organised by the Directorate of Entrepreneurship & Innovation and the Directorate of Student Affairs will begin from Kathmandu and will reach Everest Base Camp, covering a distance of about 134 km and scaling a height of 17,598 ft.
In his address to the voyagers, Dr R Premkumar wished the group a safe and successful journey and opined, “This is an adventure of a lifetime that will teach you to live as a group, to grow as a team and contribute to each other for a common goal”. In addition to providing students with exemplary academic, research and entrepreneurial resources, SRM University-AP also emphasises the significance of nurturing 21st-century skills through experiential projects and initiatives. The Everest Base Camp expedition is a one-of-a-kind adventure that will ensure that students imbibe the value of belief, the significance of planning, training and camaraderie to develop essential leadership skills.
Continue reading → - Breakthrough in Mathematical Research: Dr Subha Sandeep Repaka’s Innovative Study on Unitary Groups October 10, 2024

The Department of Mathematics, SRM University-AP, is pleased to announce that Assistant Professor Dr Subha Sandeep Repaka has published a significant research paper titled “On Reducibility of Induced Representations of Odd Unitary Groups: The Depth Zero Case.” This accomplishment reflects Dr Repaka’s expertise and dedication to advancing mathematical research, further enriching the academic contributions of the department and the university.
Abstract:
We study a problem concerning parabolic induction in certain $p$-adic unitary groups. More precisely, for $E/F$ a quadratic extension of $p$-adic fields the associated unitary group $G=\mathrm{U}(n,n+1)$ contains a parabolic subgroup $P$ with Levi component $L$ isomorphic to $\mathrm{GL}_n(E) \times \mathrm{U}_1(E)$. Let $\pi$ be an irreducible supercuspidal representation of $L$ of depth zero. We use Hecke algebra methods to determine when the parabolically induced representation $\iota_P^G \pi$ is reducible.
Future Research Plans:
We would like to solve the same problem which I had solved in this paper for the groups U(n,n) and U(n,n+1) over p-adic fields using L-Functions which is a very novel approach.
The link to the article:
http://nyjm.albany.edu/j/2024/30-50.html
Continue reading →
- Celebrating Sporting Excellence at Inter School Sports Championship October 10, 2024
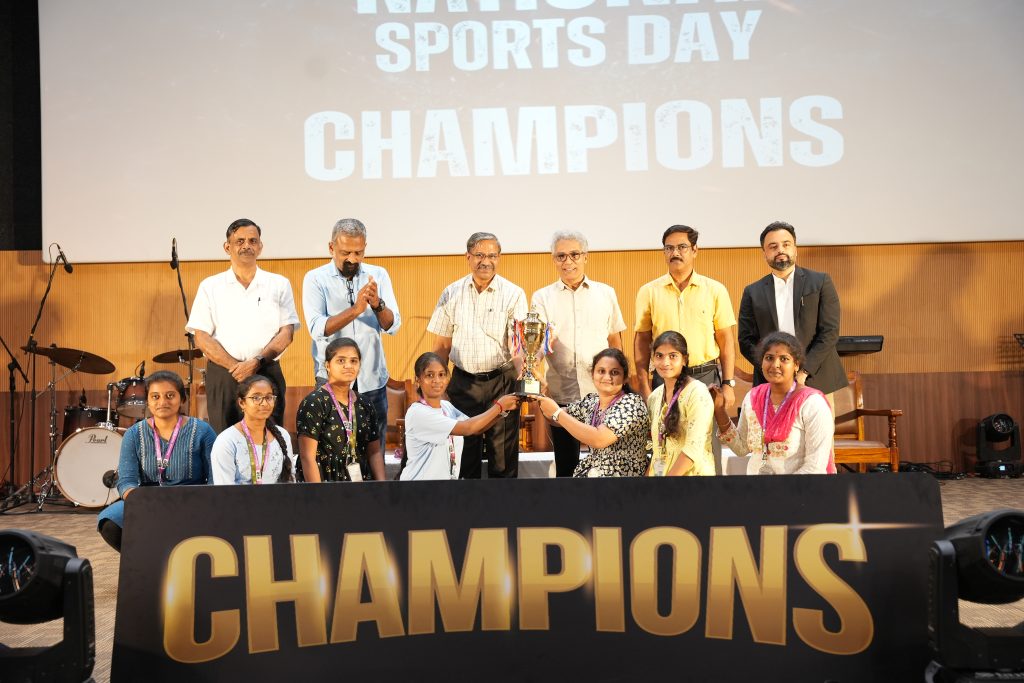 The Directorate of Sports at SRM University-AP proudly hosted the grand closing ceremony of the Inter School Sports Championship (ISC), a celebration of sportsmanship, teamwork, and dedication among students. The event, attended by esteemed guests including Chief Guest Naveen Chary, a renowned fitness influencer, Registrar Dr R Premkumar, Deans, Directors, and a vibrant crowd of students, marked the culmination of a remarkable four-week journey.
The Directorate of Sports at SRM University-AP proudly hosted the grand closing ceremony of the Inter School Sports Championship (ISC), a celebration of sportsmanship, teamwork, and dedication among students. The event, attended by esteemed guests including Chief Guest Naveen Chary, a renowned fitness influencer, Registrar Dr R Premkumar, Deans, Directors, and a vibrant crowd of students, marked the culmination of a remarkable four-week journey.The ISC Championship witnessed the enthusiastic participation of 2,247 students from all three schools: the School of Engineering and Sciences, the Paari School of Business, and the Easwari School of Liberal Arts. Participants showcased their skills in a variety of sports, promoting camaraderie and school spirit throughout the event.
Among the games, cricket was the most popular, attracting 900 participants; Badminton followed with 482 participants and volleyball with 256 participants. The football, basketball, and chess competitions also saw enthusiastic participation, with 180, 102, and 167 players, respectively. The School of Engineering and Sciences (SEAS) emerged as the triumphant winner of the prestigious rolling trophy.
“This championship has not only highlighted our students’ athletic abilities but has also been instrumental in cultivating a culture of sportsmanship at SRM University-AP,” said Dr Dhiraj Parasher, Director of Sports, SRM University-AP. “It has opened pathways for students to consider sports as a viable career option, enriching their overall university experience.”
The closing ceremony featured an engaging live performance by Band Kadali, along with captivating classical and Western dance performances by talented students.
In his address, Registrar Dr R Premkumar reflected on the significance of the event: “As we celebrate these achievements, let us carry forward the enthusiasm and lessons learned during this championship into all our future endeavours, both in sports and academics. The friendships forged and experiences gained here will resonate within our community for years to come.”
The ISC Championship has proven to be more than just a competitive event; it has served as a platform for personal growth, team spirit, and the forging of lasting bonds among students, making it a memorable chapter in the SRM University-AP journey.
Continue reading → - Master the Art of Communication with Media Studies Courses October 9, 2024
- Dr Narayanamoorthy’s Review on Pt-based Electrocatalysts Features in Elsevier Journal of IF 20.8 October 9, 2024

With the rising frequency of climate crises and to address growing energy demands and environmental concerns, a shift from conventional fossil fuels to sustainable alternatives is essential. As Hydrogen fuel cells are a viable and sustainable alternative to conventional fossil fuels, various research is being conducted in maximising the efficiency of fuel cells.
Dr Narayanamoorthy Bhuvanendran, Assistant Professor from the Department of Environmental Science and Engineering, works extensively in this field and has recently reviewed the advancements in Pt-based electrocatalysts that can reduce the Oxygen reduction rate (ORR) in Hydrogen fuel cells in his research paper. The paper titled “Recent progress in Pt-based electrocatalysts: A comprehensive review of supported and support-free systems for oxygen reduction” was published in the Q1 journal Coordination Chemistry Reviews with an impact factor of 20.8.
Abstract
Recent advancements in Pt-based catalysts for the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) have improved energy conversion efficiency in fuel cells and metal-air batteries. However, balancing electrocatalyst activity and stability remains challenging. Due to Pt’s high cost and limited availability, research focuses on Pt alloys, hybrid catalysts, and nanostructured materials to enhance catalytic performance using cost-effective methods. Hybridising Pt with other active components offers synergistic effects and aligns with the U.S. Department of Energy’s 2025 targets. This review examines recent developments in supported and support-free Pt-based electrocatalysts, highlighting carbon, inorganic, and hybrid support materials, as well as support-free metal nanostructures, for superior ORR performance in energy applications.
Explanation of the Research in Layperson’s Terms
Hydrogen, with its abundance and eco-friendly properties, is a promising fuel for sustainable energy systems, powering vehicles like electric cars and buses through efficient energy conversion devices such as fuel cells. While fuel cells effectively convert hydrogen into electricity, further advancements in electrocatalysts and cost-efficiency are needed to make this technology commercially viable. The oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) in fuel cell cathodes requires efficient catalysts for better performance. Pt is the top ORR catalyst for low-temperature fuel cells due to its ability to break O-O bonds efficiently. However, issues like Pt nanoparticle dissolution, surface impurities, and structural changes during reactions limit its effectiveness. This review explores improving electrocatalysts by increasing active sites, boosting metal-support interaction, and enhancing stability for better performance.
Practical Implementation/ Social Implications of the Research
Several challenges remain in scaling Pt-based electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction reaction (ORR), particularly around cost, performance, and environmental impact. Platinum’s high cost and scarcity drive up production costs, and synthesis methods are complex and hard to scale. Catalyst durability also degrades over time in industrial conditions. Efforts are focused on developing green synthesis methods, recovering platinum from used catalysts, and exploring alternatives like atomic layer deposition to reduce Pt usage while enhancing efficiency. New nanostructures, such as 2D layers and hybrid materials, could balance performance and cost. Future research aims to meet the U.S. Department of Energy’s 2025 targets for improved performance and durability, essential for advancing Pt-based electrocatalysts and enabling widespread fuel cell adoption.
Collaborations
- Prof. Huaneng Su, Institute for Energy Research, Jiangsu University, Zhenjiang, China
- Prof. Sae Youn Lee, Department of Energy and Materials Engineering, Dongguk University, Seoul, Republic of Korea
- Dr Srinivasan Arthanari, Research Professor, Chungnam National University (CNU), Daejeon, Korea
- Dr Sabariswaran Kandasamy, Assistant Professor, Department of Biotechnology, PSGR Krishnammal College for Women, Coimbatore, India
Dr Narayanamoorthy will continue to work in this domain, developing novel nanostructured hybrid electrocatalysts for energy and environmental applications.
Continue reading →
- Patent Filed for Innovative Load Balancing System in Cloud Computing October 8, 2024
 In a significant advancement for cloud computing technologies, Dr Kakumani K C Deepthi and Dr Prasanthi Boyapati, Assistant Professors in the Department of Computer Science and Engineering, alongside B Tech student Ms Yarra Khyathisree, have successfully filed and published a patent titled “SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR AUTOMATIC LOAD BALANCING FOR BANK OF CLOUD SERVERS.” The patent, registered with Application Number 202441057273, was officially published in the Patent Office Journal.
In a significant advancement for cloud computing technologies, Dr Kakumani K C Deepthi and Dr Prasanthi Boyapati, Assistant Professors in the Department of Computer Science and Engineering, alongside B Tech student Ms Yarra Khyathisree, have successfully filed and published a patent titled “SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR AUTOMATIC LOAD BALANCING FOR BANK OF CLOUD SERVERS.” The patent, registered with Application Number 202441057273, was officially published in the Patent Office Journal.As cloud computing continues to expand, effective load balancing has become critical for optimizing distributed environments. Load balancing is essential for distributing data and services across a scalable network of nodes, ensuring that no single node becomes overwhelmed. This is particularly important as data storage needs in cloud environments grow exponentially.
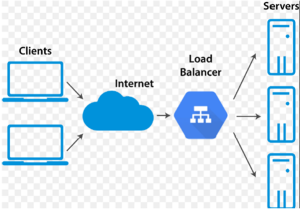
The newly patented system aims to enhance load balancing and job scheduling, addressing the increasing demand for efficient services. The article highlights various notification algorithms designed to improve these processes, comparing the latest methods to boost performance and user satisfaction.
This innovation marks a promising step forward in cloud computing technology, paving the way for more robust and efficient systems to meet the evolving needs of users and organizations alike.Abstract of the Research
Load balancing is crucial for the efficient operation of distributed environments, especially with the rapid growth of cloud computing and increasing customer demands for more services and positive outcomes. Cloud load balancing involves transparently sharing data and delivering services through a scalable network of nodes. Due to the open and distributed nature of cloud computing, the amount of data storage grows rapidly, making load balancing a critical issue. Managing load information in such a vast system is costly. A major challenge in cloud computing is distributing dynamic workloads across multiple nodes to prevent any single node from becoming overwhelmed. Numerous algorithms have been proposed to effectively allocate customer requests to available cloud nodes. These methods aim to enhance the overall performance of the cloud and provide users with more satisfying and efficient services. This article reviews various notification algorithms to address cloud computing load balancing and job scheduling issues, comparing the latest methods in the field.
Practical Implementation or the Social Implications Associated with the Research
In this patent, the common load-balancing algorithms in cloud computing include:
• Round Robin
• Least Connection
• Randomized
• Load Balancing Challenges in Cloud Computing
• Automated Service Provisioning
• Virtual Machine Migration
• Energy Management
• Stored Data ManagementFuture Research Plans
To implement automatic load balancing for not only banks but also some other applications where cloud servers can be designed by ensuring optimal resource utilization, performance, and reliability.
Continue reading → - Revisiting Clément Baloup’s Comics through Dr Gusain’s Research October 8, 2024

SRM University-AP is proud to announce that Dr Abhilasha Gusain, Assistant Professor in the Department of Literature and Languages has made an outstanding contribution to the academic world with her recent publication. Her research paper, “Illustrating Memory: Clément Baloup’s Vietnamese Memories and the Visual Representation of the Past,” featured in 3L: The Southeast Asian Journal of English Language Studies, a Q1-ranked journal known for its high impact in the field.
Abstract
The present study aims to highlight the role that Clément Baloup’s comics, Vietnamese Memories: Leaving Saigon (Volume 1) and Vietnamese Memories: Little Saigon (Volume 2), play in the creation of an alternate archive that validates the forgotten tales and the memories of a neglected past. These texts provide an alternate form of remembrance by materialising the past in the form of images. The two volumes present the unheard experiences of the Vietnamese diaspora that Baloup recorded during his travels to the different parts of France and the U.S. Such experiences bring to the forefront memories that are otherwise kept at the margins or suppressed by the dominant discourse. If not recorded, they will be lost forever. The counter-memory, thus, calls for a reassessment of the idea of a singular past that denies the marginalised memories. It claims representation and restoration in the cultural memory. As works of postmemory, these texts form a link between the past and the present through mediation and give memorability to unremembered accounts. The memories are illustrated, and hence, visual representation becomes important to the task of postmemory here.
Explanation of the Research:
This study emphasises the significance of visual representation in postmemory, showing how the two graphic narratives create a space for counter-memory and contribute to a reassessment of cultural memory by including marginalised experiences. Postmemory is a term used to describe how the memories of one generation are shaped by the stories and experiences of the previous generation. It often relates to events that people haven’t directly experienced, like wars or significant historical events, but feel a strong connection to through family stories, photographs, or cultural narratives. The paper illustrates how Baloup’s works serve as an alternate archival repository, creating a dynamic and inclusive cultural memory that reflects the complex, polyphonic nature of human experience; thus contributing significantly to the fields of comics studies and memory studies.
Continue reading → - B Tech Students Pave the Path for Future Entrepreneurs with Vascan Solutions October 8, 2024
 SRM University-AP is honoured to recognise the impressive accomplishments of B Tech CSE third-year students Sai Tharun Nelluru and Mahendra Kumar Velicheti, co-founders of Vascan Solutions, a startup aiming to disrupt the retail space. This is especially so when one considers that the decision to venture into entrepreneurship entails taking risks that the norm would prescribe against – seeking employment graduates.
SRM University-AP is honoured to recognise the impressive accomplishments of B Tech CSE third-year students Sai Tharun Nelluru and Mahendra Kumar Velicheti, co-founders of Vascan Solutions, a startup aiming to disrupt the retail space. This is especially so when one considers that the decision to venture into entrepreneurship entails taking risks that the norm would prescribe against – seeking employment graduates.Vascan Solutions, as a company, is a clear Shiff economics and architecture in Context business solving real problems in the business of retailing. Understanding the pain points that exist for both shoppers and retailers, Sai Tharun and Mahendra created a mobile app intending to improve retailing activity. Shoppers can search for items, navigate inside the store accurately and use their phones to pay for items. This improves the ease of shopping for customers. On the one hand, retailers get valuable information from consumers about what they choose and how often they come. With this information, it is easy for marketers to reorganise the store improve customer service and increase sales.
The creation of Vascan Solutions is a testament to the vision and commitment of SRM AP students. However, their success story also highlights the importance of mentorship, an integral aspect of SRM AP’s entrepreneurial ecosystem. Sai Tharun and Mahendra were guided by Dr Shobin CC and Dr Randhir Singh, who provided technical expertise that helped refine their product and strategy. Additionally, Mr Siddharth Shankar Tripathy, Director of Entrepreneurship & Innovation, SRM University-AP, played a pivotal role in mentoring the co-founders, offering them the support needed to navigate the complexities of launching a startup.
SRM University-AP’s commitment to fostering entrepreneurship is evident in the success of Vascan Solutions. The university takes pride in cultivating an environment where students are encouraged to think creatively, innovate, and challenge the status quo. Sai Tharun and Mahendra’s decision to build their own business demonstrates the transformative potential of this environment. Their entrepreneurial journey serves as an inspiration not only to their peers but also to future generations of students who wish to explore non-traditional career paths and make a meaningful impact on society.
The establishment of Vascan Solutions aligns with SRM AP’s vision of empowering students to become leaders and innovators. The university strongly believes that entrepreneurship is not only a viable career option but also a path that can contribute to societal and economic development. Sai Tharun and Mahendra have proven that with determination, innovation, and the right mentorship, young entrepreneurs can turn challenges into opportunities.
Looking ahead, SRM University-AP is excited to see the continued growth of Vascan Solutions. With a solid foundation and a clear vision, the startup has the potential to scale and expand beyond the retail sector, further solidifying the impact of Sai Tharun and Mahendra’s contributions. As Vascan Solutions evolves, SRM AP remains committed to supporting entrepreneurial initiatives that empower students to become changemakers in their respective fields.
Continue reading → - Dr Jaidev Advances Green Chemistry with New Acetic Acid Production Technique October 8, 2024
 In a remarkable contribution to the field of green chemistry, Dr Jaidev Kaushik, Assistant Professor in the Department of Chemistry, has published a significant research paper titled “Green Light Promoted Photoreduction of Carbonate to Acetic Acid by Zinc Ash-Derived ZCu@ZnO” in the prestigious Q1 journal, ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, with an impressive impact factor of 7.1.
In a remarkable contribution to the field of green chemistry, Dr Jaidev Kaushik, Assistant Professor in the Department of Chemistry, has published a significant research paper titled “Green Light Promoted Photoreduction of Carbonate to Acetic Acid by Zinc Ash-Derived ZCu@ZnO” in the prestigious Q1 journal, ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, with an impressive impact factor of 7.1.Dr Kaushik’s research addresses the pressing need for sustainable methods of producing acetic acid, a widely used chemical in various industrial applications. The study explores an innovative photoreduction process that utilises green light to convert carbonate compounds into acetic acid using a novel catalyst derived from zinc ash. This approach not only showcases the potential for an eco-friendly production method but also emphasises the recycling of zinc waste, turning a byproduct into a valuable resource.

The paper highlights the efficiency of Zinc Ash-Derived ZCu@ZnO as a catalyst in the photoreduction process, demonstrating its effectiveness under green light conditions. The findings could pave the way for more sustainable practices in chemical manufacturing, aligning with global efforts to reduce carbon emissions and promote environmentally friendly technologies.
This publication underscores the commitment of SRM University – AP to fostering innovative research that addresses contemporary environmental challenges. Dr. Kaushik’s work exemplifies the university’s focus on sustainability and its aspiration to lead in the field of scientific research.
As the demand for sustainable chemical processes grows, Dr Kaushik’s research will likely inspire further investigations and developments in green chemistry, contributing to a more sustainable future.
Abstract of the Research
Mineralized carbon (carbonate) is the readily available carbon dioxide (CO2) source in acidic aqueous conditions. The photoreduction of carbonate to value-added hydrocarbons could be a novel finding performed in the presence of monochromatic visible light and waste-derived photo-active nanomaterials. In this report, we have synthesized ZnO particles from the zinc ash generated as waste in the galvanization process in the steel industry; ZnO particles were decorated with CuO nanoparticles and then further activated by reducing them to get a heterojunction photocatalyst (ZCu@ZnO). After that, ZCu@ZnO is utilized to photoreduce carbonate to acetic acid (AcOH) in a peroxy-rich solvent as a hydrogen-rich solvent under various monochromatic light sources and sunlight. Additionally, different physical and chemical parameters, such as solvent mixture, light sources, photocatalysts, time, etc., were optimized to get the maximum yield of AcOH under monochromatic light of 525 nm wavelength (Green light).
Explanation of the Research in Layperson’s Terms
This report is proposing the solution of two problem statements; first, utilization of zinc ash generated as a by-product after galvanization process; and second, cost-effective and energy efficient process for conversion of carbonates to value-added C2 hydrocarbon.
Practical Implementation and the Social Implications associated with the Research
The process adds value by converting low-value waste into high-value nanomaterials, potentially offering new revenue streams for recycling and waste management industries. It supports the principles of a circular carbon economy and green chemistry focusing on synthesis of hydrocarbons from carbonates.
Collaboration
Dr Sumit Kumar Sonkar (MNIT Jaipur, India)
Future Research Plans
1. The adsorption/photodegradation-assisted quick and efficient removal of next generation advanced pollutants such as microplastic, pesticides, pharmaceutical waste, etc. by hydrophobic carbon aerogel and their doped and functionalized versions.
2. Utilizing waste derived heterogeneous catalysts in organic transformation reactions.
3. Selective sensing of toxic metal ions/biomarkers/biomolecules using fluorescent nanomaterials.
4. Upcycling of carbonates/CO2 via photo/thermal assisted catalyzed reactions to get C1 and C2 hydrocarbons (green fuel).
Continue reading →