BSc Physics student contributes as the First Author for a research paper
 A research paper titled “First Principle Identification of 2D-MoS2 based Composite Electrodes for Efficient Supercapacitor Application” is published by Samadhan Kapse, PhD student, as First Author and Bennet Benny, BSc Physics Student, (Same Contributed First Author) in the Journal of energy storage, Elsevier having an Impact Factor of 6.583. The paper publication has been guided and supervised by Dr Pranab Mandal (Co-Author) and Prof Ranjit Thapa (Corresponding Author) from the Department of Physics, SRM University-AP.
A research paper titled “First Principle Identification of 2D-MoS2 based Composite Electrodes for Efficient Supercapacitor Application” is published by Samadhan Kapse, PhD student, as First Author and Bennet Benny, BSc Physics Student, (Same Contributed First Author) in the Journal of energy storage, Elsevier having an Impact Factor of 6.583. The paper publication has been guided and supervised by Dr Pranab Mandal (Co-Author) and Prof Ranjit Thapa (Corresponding Author) from the Department of Physics, SRM University-AP.
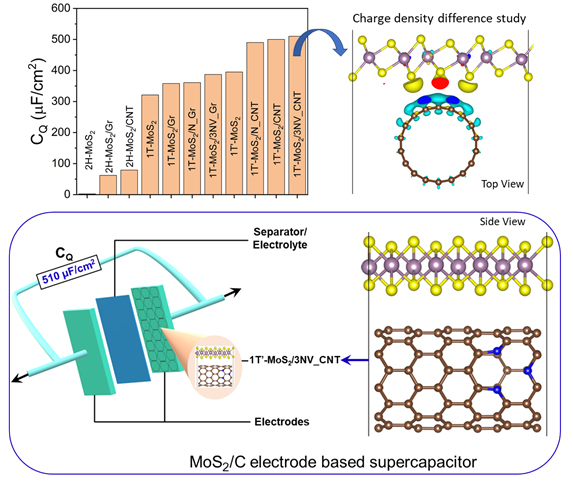
1T Molybdenum disulfide (1T-MoS2) has been widely studied experimentally as an electrode for supercapacitors due to its excellent electrical and electrochemical properties. Whereas the capacitance value in MoS2 is limited due to the lower density of electrons near the Fermi level, and unable to fulfil the demand of industry i.e. quantum capacitance preferably higher than 300 μF/cm2. Here, we investigated the performance of 2H, 1T, and 1T’ phases of MoS2 in its pristine form and heterostructures with carbon-based structures as an electrode in the supercapacitors using density functional theory. Specifically, we reported that the underneath carbon nanotube (CNT) is responsible for the structural phase transition from 1T to 1T’ phase of MoS2 monolayer in 1T’-MoS2/CNT heterostructure. This is the main reason for a large density of states near the Fermi level of 1T’-MoS2/CNT that exhibits high quantum capacitance (CQ) of 500 μF/cm2 at a potential of 0.6 V. Also, we observed that the nitrogen doping and defects in the underneath carbon surface amplify the CQ of heterostructure for a wider range of electrode potential. Therefore, the 1T’-MoS2 /N doped CNT can be explored as an electrode for next-generation supercapacitors.
Today’s increasing demand for energy storage technologies is highly dependent on batteries, fuel cells, supercapacitors, etc. The supercapacitors are greatly efficient due to advantages such as high power density, wide operating temperature range, large charge-discharge cycles. The recent focus of researchers is to find promising electrode materials for supercapacitor application. Among all reported works, the MoS2 nanosheet is found to be a prime candidate for supercapacitors with a high power density as well as energy density. Therefore, it is important to understand the origin of capacitance in MoS2 and their composites to design promising electrodes for supercapacitors. Also, the identification of ideal MoS2 based composites for efficient supercapacitor application is a grand challenge using only experimental approaches.
Using density functional theory, we can identify the promising electrode materials for supercapacitor application based on various graphene, 2D metal chalcogenides and their heterostructures. The quantum capacitance (CQ) is the cost-effective method to estimate the performance of any low density of states materials such as graphene, MoS2, etc towards supercapacitors.
- Published in Departmental News, News, Physics News, Research News
STIP- 2020: “Impartial inclusion will make India global scientific superpower”
“India is moving towards ‘technological self-reliance’ and will emerge as one of the ‘Top 3 scientific superpowers’ through Science, Technology and Innovation Policy (STIP) 2020: A Transformative Science and Technology Agenda,” said Dr Sandeep Verma, Secretary of Science and Engineering Research Board (SERB), in the thirteenth edition of University Distinguished Lecture Series conducted by SRM University-AP, Andhra Pradesh on October 30, 2021.
The objectives of the Distinguished Lecture were enumerated by the Pro-Vice-Chancellor, Prof D Narayana Rao. He further said that the STIP: 2020 will greatly enhance the scientific contributions of Universities, Institutions and National Laboratories. He said that Universities and Institutions are hubs for innovations.
Dr Verma, a recipient of one of the highest Indian awards in the field of Science, the Shanti Swarup Bhatnagar Prize, is known for his contributions towards experimental medicine by working in the areas of bio-chemical interface. Prof Verma felt that the vision behind STIP: 2020 can only be executed through innovative, collaborative, and open science research that is best implemented in Universities and Educational Institutions like SRM University-AP.
Dr Verma elucidated that the primary idea behind STIP: 2020 is Inclusivity. STIP: 2020 will require an uninhibited and indiscriminate free flow of scientific and innovative ideas between all the people with a scientific interest from the Indian diaspora and from rural India, from all genders, from all age groups ignoring any disability physical or otherwise. “We can’t afford to leave anyone behind”, Dr Verma said referring to India’s quest to become a scientific and technological superpower. Prof Sandeep Verma said that the gross spending of the country on R & D increased 3 times during the last 8 years.
Appreciating the efforts made by SRM University-AP, Dr Verma emphasised the need to have the researchers coming out in the open, solving real-life problems and making every individual Indian life better. “It is our Scientific Social Responsibility to conduct such open forums for scientific communication and understanding,” he said, “As India prepares to grow towards technological self-reliance and indigenisation with the support of various schemes under Atmanirbhar Bharat and develop an ecosystem worthy of global benchmark, STIP: 2020 comes as a landmark innovation policy at this crucial juncture.”
Dr Verma ended his talk with the hopeful note that other Universities would follow the example of SRM University-AP and make such conscientious efforts towards innovation to make lives better. The lecture was attended by Dr S Chandrasekhar, Director, CSIR-IICT and over 2300 members from several premier institutions like IITs, NITs, IISERs, Universities and Institutions, CSIR, DST, DBT, DRDO, DAE, ISRO, NARL, MoES and several others from different parts of the country.
Prof V S Rao, Vice-Chancellor and Prof D Narayana Rao, Pro-Vice-Chancellor felicitated Prof Sandeep Verma and presented him with a memento.
- Published in News, Research News
High bars of predecessors for high marches of successors
 We bid adieu to the maiden batch with interesting placements and higher education opportunities in hand. Their farewell was as glorious as it was tearful. On October 23, 2021, SRM University-AP welcomed them back with the intention to aid the current students. In a colourful online ceremony, President Dr P Sathyanarayanan inaugurated the Alumni Connect Programme to help our students stay connected, even after graduation.
We bid adieu to the maiden batch with interesting placements and higher education opportunities in hand. Their farewell was as glorious as it was tearful. On October 23, 2021, SRM University-AP welcomed them back with the intention to aid the current students. In a colourful online ceremony, President Dr P Sathyanarayanan inaugurated the Alumni Connect Programme to help our students stay connected, even after graduation.
In his inaugural speech, Dr P Sathyanarayanan congratulated the graduate students for the rigorous years of studies and the many laurels that they have brought to their alma mater. He further expressed his beliefs that this kind of networking programme will bring the students closer and skillfully aid the existing students in their search for the best jobs, higher studies and other opportunities. “The founding batch has set the bar so high that the following batches will need to strive really hard to make their mark,” asserted Dr Sathyanarayan.
The event progressed with messages from Prof V S Rao, Vice-Chancellor, SRM University-AP and Prof D Narayana Rao, Pro-Vice-Chancellor, SRM University-AP. The eminent dignitaries launched the Alumni Yearbook-2021.
The event sprang to life with the jovial conversations between the alumni and the current students. The current students shared their fears and anxiety with their seniors, while our alumni shared their journey.
Listening to the alumni helped the current students be more confident and focused. The insights shared by the seniors helped the juniors plan their the academic and career trajectories more adequately.
The alumni also reminisced about their time at the University. They guided the current students on making the best use of all the state-of-the-art facilities that the University offers. In addition to that, they taught their juniors about managing academic studies and other activities without compromising with all the fun of college life.
The vigorous event came to an end with the facilitation ceremony by Ms Revathi B, Assistant Director, Student Affairs. Dr Sujith Kalluri, Assistant Director, Alumni Affairs, offered a concluding speech to mark the closing of the event.
- Published in News
Fully automated quality control of rigid and affine registrations of T1w and T2w MRI in Big Data using Machine Learning
 “Research is seeing what everybody else has seen and thinking what nobody else has thought.”
“Research is seeing what everybody else has seen and thinking what nobody else has thought.”
– Albert Szent-Györgyi
“Fully Automated Quality Control of Rigid and Affine Registrations of T1w and T2w MRI in Big Data using Machine Learning” is the latest research paper published by Dr Sudhakar Tummala, Assistant Professor, Electronics and Communication Engineering, SRM University-AP in ‘Computers in Biology and Medicine Journal’ having an Impact Factor of 4.6.
Abstract of the paper:
Background: Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)-based morphometry and relaxometry are proven methods for the structural assessment of the human brain in several neurological disorders. These procedures are generally based on T1-weighted (T1w) and/or T2-weighted (T2w) MRI scans, and rigid and affine registrations to a standard template(s) are essential steps in such studies. Therefore, a fully automatic quality control (QC) of these registrations is necessary for big data scenarios to ensure that they are suitable for subsequent processing.
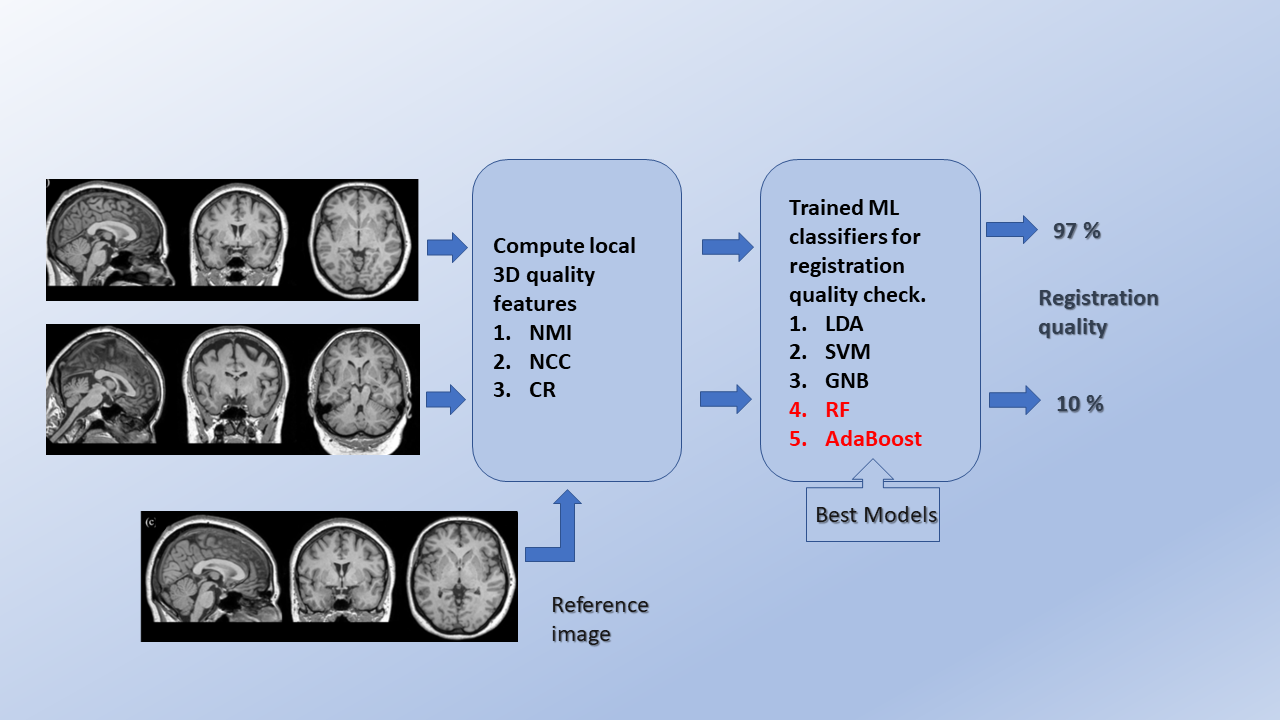
Method: A supervised machine learning (ML) framework is proposed by computing similarity metrics such as normalized cross-correlation, normalized mutual information, and correlation ratio locally. We have used these as candidate features for cross-validation and testing of different ML classifiers. For 5-fold repeated stratified grid search cross-validation, 400 correctly aligned, 2000 randomly generated misaligned images were used from the human connectome project young adult (HCP-YA) dataset. To test the cross-validated models, the datasets from autism brain imaging data exchange (ABIDE I) and information eXtraction from images (IXI) were used.
Results: The ensemble classifiers, random forest, and AdaBoost yielded the best performance with F1 scores, balanced accuracies, and Matthews correlation coefficients in the range of 0.95-1.00 during cross-validation. The predictive accuracies reached 0.99 on Test set #1 (ABIDE I), 0.99 without and 0.96 with noise on Test set #2 (IXI, stratified w.r.t scanner vendor and field strength).
Conclusions: The cross-validated and tested ML models could be used for QC of both T1w and T2w rigid and affine registrations in large-scale MRI studies.
Medical imaging is basically a method to see inside the body non-invasively. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is one of the medical imaging modalities to see inside the body. MRI works on the principles of nuclear magnetic resonance. T1-weighted (T1w) and T2-weighted (T2w) MRI can enable us to see the brain without opening the skull and to monitor brain structural changes that occur in several medical and neurological conditions. It is important to monitor these structural changes over time to understand the disease progression. For example, in Alzheimer’s disease, it is important to monitor the hippocampus (memory storage centre) Recently, due to the advances in computational power such as high-performance GPUs and the availability of publicly accessible big data MRI, scientists around the world now conducting big data research studies. In group-based big data studies, for fair comparison of the brain between healthy and diseased individuals, it is necessary that the brain MRI images are registered to a common coordinate system. Therefore, quality control (QC) of these registrations is necessary to ensure that they are suitable for further processing. Further, in big data studies that involve several thousands of images, manual QC is not feasible and hence there is a need for a fully automated QC mechanism at the pre-processing stage. Checking the quality of rigid and affine registrations is one such task.
The research group implemented a fully automated QC mechanism based on computing several quality metrics local to the image and trained several machine learning classifiers based on these locally computed quality measures. The trained classifiers include linear discriminant analysis, support vector machine, Gaussian naïve Bayes, random forest and adaptive boosting. The developed ML models generalize well to detect misaligned registrations across different MRI scanner vendors and field strengths and even under noisy image situations. Therefore, the classifiers could be employed in big data studies for fully automated QC of registrations, especially T1w and T2w MRI.
Big data MRI studies are generally conducted using a large number of subjects. The conclusions drawn based on big data analysis are more reliable and help to understand the disease mechanics better. The developed method can help to reduce the manual labour for various QC mechanisms required during the pre-processing stage.
This work is done in collaboration with
a. Prof Erik B Dam, Machine Learning Group, University of Copenhagen, Copenhagen, Denmark.
b. Prof Niels K Focke, Clinic for neurology, University Medical Centre, Göttingen, Germany.
In future, the idea is to implement the QC framework using sparse autoencoders in an unsupervised manner and also using Siamese neural networks via deep representation learning.
- Published in Departmental News, ECE NEWS, News, Research News

