Innovating Human Resources: A Blockchain Technology Bibliometric Analysis
 In a significant academic achievement, Dr Vimal Babu, Associate Professor at the Department of Management, Paari School of Business, and Ms Rukma Ramachandran, a PhD Scholar, have co-authored a book chapter titled “Revolutionizing HR through the Deployment of Blockchain Technology: A Bibliometric Review.” The chapter is included in the book Blockchain and Digital Twin Enabled IoT Networks: Privacy and Security Perspectives, published by Routledge: A Taylor and Francis Group.
In a significant academic achievement, Dr Vimal Babu, Associate Professor at the Department of Management, Paari School of Business, and Ms Rukma Ramachandran, a PhD Scholar, have co-authored a book chapter titled “Revolutionizing HR through the Deployment of Blockchain Technology: A Bibliometric Review.” The chapter is included in the book Blockchain and Digital Twin Enabled IoT Networks: Privacy and Security Perspectives, published by Routledge: A Taylor and Francis Group.
The research work delves into the potential of blockchain technology in transforming Human Resources practices, offering a bibliometric review to shed light on the impact and future possibilities within the field.
The publication adds valuable insights to the growing discourse on blockchain applications in various industries, particularly focusing on HR management. This collaborative effort between Dr Vimal Babu and Ms Rukma Ramachandran highlights their dedication to exploring innovative solutions at the intersection of technology and management. Their contribution to the book aims to contribute to the ongoing dialogue on privacy, security, and efficiency in IoT networks, with blockchain technology playing a pivotal role in shaping the digital landscape.
The chapter’s publication signifies a notable milestone in the academic pursuits of both scholars, solidifying their expertise and thought leadership in the realm of blockchain technology and its implications for HR practices. Their contribution is expected to resonate with professionals, researchers, and students interested in the evolving dynamics of digital innovation and its impact on organisational processes.
Brief Introduction of the Book Chapter
The adoption and implementation of Blockchain in Management have been gaining increasing attention. The rise in the number of studies on Blockchain in managerial applications invites a greater number of research contributions in this field. This chapter describes the gap in the present studies using a hybrid review system through the means of systematic literature review and bibliometric analysis.
Publication details (incl. Publisher, ISBN, Launch date, Edition, etc)
Publisher- Taylor & Francis
ISBN- 9781003403791
Launch date- 19 July 2024
Edition- 1st
Target Audience of the Book Chapter
This book emphasizes and facilitates a greater understanding of various data security privacy approaches using the advances in Blockchain and data analysis using machine/deep learning, federated learning, edge computing and the countermeasures to overcome these vulnerabilities.
Link to the Book Chapter
Blockchain and Digital Twin Enabled IoT Networks | Privacy and Securit (taylorfrancis.com)
- Published in Departmental News, News, Paari Current Happenings, Research News
Decoding Investment Perceptions in India: Dr Lakshmana Rao’s Recent Publication
 In a significant contribution to the academic discourse on corporate frauds and investment behaviour, Dr A Lakshmana Rao, Head of the Department and Associate Professor in the Department of Commerce, has published an insightful book chapter titled “Perception of Investment Behaviour in the Light of Corporate Frauds with Special Reference to India,” the chapter is a part of the book “Cybersecurity, Law and Economics: The Case of India,” published by Routledge, a prestigious Taylor and Francis Group.
In a significant contribution to the academic discourse on corporate frauds and investment behaviour, Dr A Lakshmana Rao, Head of the Department and Associate Professor in the Department of Commerce, has published an insightful book chapter titled “Perception of Investment Behaviour in the Light of Corporate Frauds with Special Reference to India,” the chapter is a part of the book “Cybersecurity, Law and Economics: The Case of India,” published by Routledge, a prestigious Taylor and Francis Group.
Dr Rao’s work delves into the intricate dynamics of investor psychology and market trust, particularly in the aftermath of corporate scandals. His research provides a nuanced understanding of how investors navigate the complex landscape of financial decision-making when confronted with corporate malfeasance.
The chapter is poised to serve as a valuable resource for students, academics, and professionals interested in the intersections of finance, law, and cybersecurity. It also underscores the importance of robust legal frameworks and transparent corporate governance in maintaining investor confidence in the Indian market. With this publication, Dr Rao has made a notable contribution to the literature on economic security and investment strategies, offering a timely examination of the challenges and considerations unique to the Indian context.
A Brief Introduction of the Book Chapter
This book examines the intersection between cybersecurity and India’s law and economy and offers a course of action for designing efficacious policies against emerging cybercrimes in the country.
It reviews the boom in infrastructure growth in India and the security challenges this presents to the domestic economy and legal system. Contributors conduct a risk assessment of the potential economic impacts and security vulnerabilities, as well as identify the current regulatory and legal gaps regarding cryptocurrency, e-commerce and digital banking. The book also considers the subject of data localisation and sovereignty, and the challenges of establishing an indigenous data architecture. By discussing the economic impact of cybersecurity and incorporating recommendations from scholars, activists, academics, young legal intellectuals, and professionals in the field, the chapters propose new measures and protections for lawmakers and policymakers to adopt.
Significance of the Book Chapter
The book chapter titled “Perception of Investment Behaviour in the Light of Corporate Frauds with Special Reference to India” is a survey-based study that examines the general investor’s intentions regarding their investment behaviour in various investment options and their behavioural changes in the case of corporate frauds.
Co-authors of the Book Chapter
Two co-authors, Dr G Ramakrishnan and Dr Nikhil Kulshrestha, helped conduct the research and survey.
Link to the Book Chapter publication
Publication Details (incl. Publisher, ISBN, Launch date, Edition, etc)
ISBN 9781032852454
232 Pages 8 B/W Illustrations
October 1, 2024, by Routledge
Price: £ 135
- Published in Commerce Current Happenings, Departmental News, News, Research News
Innovative Aquaculture Monitoring System Patented by Dr K A Sunitha and Team
 In a significant advancement for aquaculture technology, Dr K A Sunitha, Associate Professor in the Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, along with her B.Tech ECE students Ms B Harshitha and Mr B Taraka Rameswara Kanaka Durga Prasad, have made headlines with their latest invention. The team has successfully filed and published a patent for “A Fully Automated System for Real-Time Monitoring of Aquaculture Environment and a Method Thereof.” The application number 202441034671, has been officially recorded in the Patent Office Journal, marking a milestone for the team and the institution they represent.
In a significant advancement for aquaculture technology, Dr K A Sunitha, Associate Professor in the Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, along with her B.Tech ECE students Ms B Harshitha and Mr B Taraka Rameswara Kanaka Durga Prasad, have made headlines with their latest invention. The team has successfully filed and published a patent for “A Fully Automated System for Real-Time Monitoring of Aquaculture Environment and a Method Thereof.” The application number 202441034671, has been officially recorded in the Patent Office Journal, marking a milestone for the team and the institution they represent.
This pioneering system promises to revolutionise the way aquaculture environments are monitored by leveraging automation to ensure real-time, accurate assessments. The invention stands as a testament to the innovative spirit and dedication of Dr Sunitha and her students, who are now recognised as contributors to the technological advancements in the field of aquaculture.
Abstract
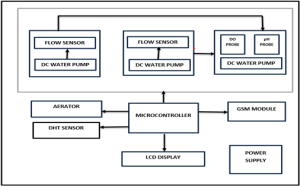
This project involves the design and development of an Automated water quality analysis system to assist aquaculture farmers. The proposed system is tailored for aquatic environments, particularly ponds to monitor crucial parameters say Dissolved Oxygen (DO), PH, Temperature and Humidity levels, signaling when concentrations drop below the predefined threshold set by the user every thirty minutes. The system features autonomous activation and deactivation of aerators to ensure continual oxygenation of water and aids in energy optimisation. Utilising advanced sensors and a microcontroller, the device offers continuous monitoring of parameters to facilitate pond operators with timely insights into water quality dynamics, enabling proactive interventions to protect aquatic ecosystems.
Brief Explanation of the Project
India is the second-largest aquaculture nation in the world, and this sector provides livelihood support to about 280 lakh people. The aquaculture industry globally faces numerous challenges, such as Viral, bacterial, and fungal diseases and Suboptimal water quality. One crucial criterion for evaluating the quality of water is measuring the Dissolved Oxygen level. Water and other liquids contain free, non-compound oxygen, which is measured as dissolved oxygen (DO).
Long-term exposure to low DO levels increases stress and infections and, in certain situations, causes the death of the organism because dissolved oxygen is essential for the health and reproduction of many fish and invertebrates. This project highlights the design of a timer based automated water quality analysis system which can be used in the inland aquaculture farms to continuously monitor the water parameters and automate the calibration process and the operation of aerators without human intervention.
Practical Implications of the Research
The main objectives of this research are
1) To monitor the parameters, say Dissolved Oxygen, PH, Temperature and Humidity levels
every thirty minutes.
2) To automate the Calibration process to maintain accuracy and reliability of the system.
3) To automatically turn ON/OFF the aerators in the event of Low/High oxygen levels detection in the pond.
4) To send notifications to the technician or farmer every thirty minutes to help them monitor.
Future Research Plans
The developed prototype is currently validated with standard DO meter during experimental trials. Moving forward, further research and development efforts may focus on refining the system’s functionality, expanding its sensor capabilities, and integrating advanced analytics for predictive monitoring and decision support, thereby advancing the state-of-the-art in aquaculture management technology and promoting the long-term viability of inland aquaculture operations.
Pictures Related to Research
- Published in Departmental News, ECE NEWS, News, Research News
Exploring Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing

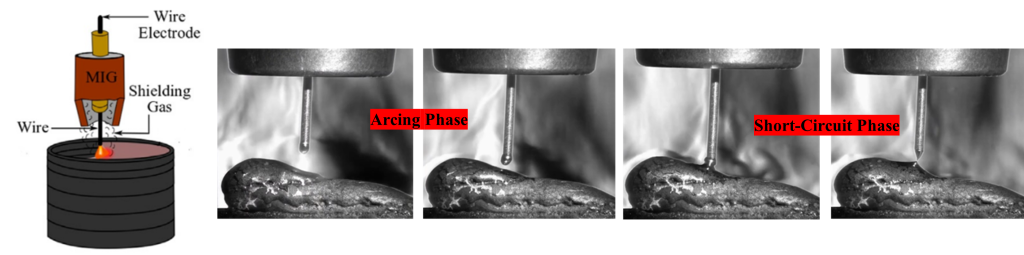
Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing (WAAM) is revolutionizing how we make metal components, especially when it comes to materials like 304L austenitic stainless steel—a popular choice in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and healthcare due to its durability and corrosion resistance. The research paper titled “Microstructural Characteristics and Properties of Wire Arc Additive Manufactured 304L Austenitic Stainless Steel Cylindrical Components by Different Arc Welding Processes” published by Dr Maheswar Dwivedy, Associate Professor, Department of Mechanical Engineering and his post-doctoral scholar Dr B Prasanna Nagasai explores this innovative manufacturing method in detail, focusing on how different welding techniques affect the end product.
Overall, this research indicates that WAAM, with its different welding techniques, can produce 304L stainless steel cylinders that potentially outperform those made by conventional forging, both in terms of material efficiency and mechanical properties. Such findings are significant as they point towards more sustainable and cost-effective manufacturing methods that do not sacrifice quality.
Abstract
Wire arc additive manufacturing (WAAM) is an advanced additive manufacturing (AM) technology that offers low cost and high deposition rates, making it suitable for building large metal parts for structural engineering applications. However, various welding procedures result in differing heat inputs and repetitive heating treatments throughout the deposition process, which can affect the microstructural and mechanical characteristics of the parts. In the current study, cylindrical parts made of 304L austenitic stainless steel (ASS) were manufactured using the WAAM technique, employing both gas metal arc welding (GMAW) and cold metal transfer (CMT) processes. This study explores the correlation between WAAM techniques and their effects on the bead geometry, microstructure and mechanical properties. The paper presents detailed analyses of the microstructure using techniques such as optical microscopy, scanning electron microscopy (SEM), energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS) and X-ray diffraction (XRD). The research findings suggest that the choice of arc welding process significantly affects the grain size, phase distribution, and defect formation within the 304L stainless steel, thereby influencing the mechanical properties and overall performance of the manufactured components. The WAAM-processed 304L ASS cylinders showed better performance compared to those manufactured using traditional industrial forging standards, indicating that WAAM-processed 304L ASS cylinders are suitable for industrial applications. This comprehensive evaluation provides insights into optimising welding processes for enhanced quality and performance of stainless steel cylindrical parts.
Highlights of the research
- Controlling heterogeneous microstructures in WAAM-processed 304L stainless steel is challenging.
- GMAW vs. CMT impacts on 304L ASS microstructure analysed.
- The upward growth of coarse austenite/ferrite morphologies is controlled by the wire retraction mechanism.
- CMT produced finer dendrites and more ferrite morphologies.
- WAAM 304L ASS components outperformed the wrought 304L ASS and forged 304L ASS.
Practical implementation/Social implications of the research
The practical implementation of Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing (WAAM) for 304L austenitic stainless steel could revolutionise multiple industries, including aerospace, automotive, medical devices, maritime, and energy, by allowing the production of complex, custom, and durable components with greater efficiency and reduced material waste. This shift not only promises economic benefits like cost reduction and job creation in advanced manufacturing sectors but also carries significant environmental advantages by minimising waste and the carbon footprint associated with traditional manufacturing processes. Furthermore, the technology enhances supply chain resilience by enabling local, on-demand production, which could be crucial during global disruptions. Socially, WAAM could increase access to customised medical aids in low-income regions, fostering greater equality. The adoption of WAAM thus holds the potential to impact manufacturing practices profoundly, driving innovation, sustainability, and inclusivity across various sectors.
Collaborations
Dr V Balasubramanian, Professor & Director, Centre for Materials Joining & Research (CEMAJOR), Annamalai University, Tamilnadu.
In the future, the research team plan to focus on developing Functionally Graded Materials (FGMs) of nickel and stainless steel using Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing (WAAM). This research will aim to leverage the unique properties of each metal to create components with tailored functional performance for demanding applications. Key challenges will include optimising material interfaces, controlling deposition processes, and ensuring structural integrity.
- Published in Departmental News, Mechanical Engineering NEWS, News, Research News
“Destination Japan”- An Indo-Japanese Alliance for International Recruitment of SRM AP Graduates

SRM University-AP, with its uniquely curated “Destination Japan” program for its highly skilled Engineering & Non-engineering Students, is an initiative by the university to address the growing demand for human resources in Japan. The ‘Destination Japan’ program provides well-equipped engineers with valuable industry skills and well acquainted with Japanese culture. Under the programme, students are trained in the Japanese language, Japanese traditions, and work culture from the first year onwards, which helps them easily assimilate into the country’s workforce. The initiative also welcomes reputed companies from Japan to directly hire skilled engineering graduates from core engineering fields to enhance their manpower.
SRM University–AP has also signed MOUs with multiple universities in Japan for faculty & student exchange programs, collaborative R&D projects, Hi-tech & innovative labs and other academic initiatives complementing the “ Destination Japan “ program.
To further enhance this mutual alliance, the Director of Corporate Relations & Career Services of SRM AP, Dr Vivekanandan M S, has visited prospective companies and industries in Hamamatsu, Japan, during which he presented the stellar record of engineering graduates being nurtured at the varsity and the possible partnership for recruitment and employment.
SRM University-AP has also signed an agreement with the Shizuoka Government to foster Indo-Japanese academic and recruitment partnerships. These partnerships enable internships in Japanese organisations, admissions to universities for higher studies, and good career placement opportunities for their students in Japan.
Under the “Destination Japan” program, direct campus recruitment has begun with the visit of recruitment teams from two reputed Japanese companies, Forum Engineering Inc. and CRESCO Ltd., to hire proficient engineering graduates. This is a remarkable accomplishment for the university to ensure international placements for its students.
A recruitment team of four from CRESCO Ltd, including the Managing Director, and a team of two from Forum Engineering Inc. visited the university campus. The team included engineers, HR Executives and other professionals.
Many more Japanese companies are lined up for campus visits & recruitment in the coming months.
In an interaction with the recruitment teams from Japan, Mr Satoshi Iwami, MD of CRESCO, remarked, “As we are facing a shortage of IT engineers not only in our company but all over Japan, and with the SRM AP harbouring excellent IT engineers, we decided that an alliance would greatly benefit both parties.”
Ms Saho Funahashi, UI/UX Designer at CRESCO, said, “The students’ Japanese skills have impressed me. SRM University-AP has helped students understand the practical way of studying engineering through its impressive resources. This would greatly benefit them in a techno-driven country like Japan.”
Mr Mitsutaka Sekino, Operating Officer at Forum Engineering and Director of Cognavi India stated, “Due to the population crisis, the Japanese economy is getting weaker, but we believe hiring an able workforce from SRM AP to Japan will help improve the economy. We have come to hire excellent students from the university, and I’m greatly impressed by their proficiency in Japanese and their work attitude.”
Mr Masahiro Koizumi, Senior Executive Officer at Forum Engineering and Managing Director of Cognavi India, opined, “We, from Forum Engineering, have come here with the intention of recruiting high-skilled engineers. Furthermore, the clients of Forum Engineering, the manufacturers of electrical and mechanical equipment in Japan, have been facing a shortage of engineers. They desire Indian students to come to Japan and help resolve the problem.”

This program is guided and driven by SRM Global Consulting Private Limited, a consulting company of SRM Group established in Japan. Speaking on this, Mr Sankar Karunanidhi, Country Manager, SRM Global Consulting, mentioned, “SRM Group has had a long-standing relationship with Japan for over 25 years. This association has helped us design this unique program and training for our university students”.
This flagship initiative by SRM University-AP is helping Japan alleviate its labour shortage in various industries. Highly skilled graduates from India can get lucrative placements in Japan, ensuring a good work-life balance and career growth opportunities. SRM University–AP, continuing its success of placing students in Japan with the dedicated program and the team behind Destination Japan, envisions placing a minimum of 120 Highly Skilled students in Japan year-on-year.
Vice Chancellor of SRM University-AP, Prof. Manoj K Arora, said this remarkable venture by the two parties would enrich the student’s academic experience, moulding them into global citizens with exceptional industry acumen. “We have established a prolific alliance with Japan. We plan to extend our collaborations to place our students in Taiwan, Canada, Germany and other European countries,” stated the head of the institution.
The continuous dedication and support from the team’s leading both nations guarantee prospective Indian graduates a once-in-a-lifetime opportunity to secure their dream careers in Japan.
- Published in CR&CS, CR&CS NEWS, Departmental News, News
Dr Chinmoy Das’s Groundbreaking Research Unveils Promising Discoveries

Dr Chinmoy Das, Assistant Professor at the Department of Chemistry at SRM University-AP, has made an impactful contribution with the publication of his research paper, “Insights into the Mechanochemical Glass Formation of Zeolitic Imidazolate Frameworks” in the prestigious Angewandte Chemie International Edition with an impact factor of 16.6. His paper unveils a rapid, eco-friendly, and efficient mechanochemical approach to transform glasses from their crystalline zeolitic imidazolate frameworks. This pioneering work opens new doors for sustainable and effective glass formation, showcasing the power of innovation in the field of chemistry.
Abstract:
We describe a rapid, ecofriendly, and efficient mechanochemical approach to transform glasses from their crystalline zeolitic imidazolate frameworks (ZIFs). We exposition mechanochemical technique through which the traditional melt-quench preparation of glassy phases can be replaced. In this study, we explore that Zn(II), Co(II), and Cu(II)- based crystalline ZIFs transformed into the glassy phases within five minutes through the mechanical ball milling technique. The appearance of glass transition temperature(T g ) upon mechanical milling of crystalline states demonstrated by different characterization techniques, such as X-ray powder diffraction (XRPD), differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), simultaneous thermogravimetric and differential thermal analyses (TG/DTA), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), X-ray total scattering and its deduced pair distribution functions (PDFs). We characterized the porosity and density of the glassy phases through CO 2 gas sorption techniques which aligned with the observation of thermal, structural, and textural features of the ZIFs after varying ball milling times beyond five minutes.
Practical implementation
We can prepare bulk ZIF glasses within five minutes of the mechanochemical approach that will guide the greater feasibility to produce the glass materials for industrial implications. In addition, the greater the accessibility of glassy materials, the greater the fabrication of glassy materials-based device fabrication.
Collaborations
This article has been published with the collaboration of Prof. Sebastian Henke (Henke Group), Department of Chemistry and Chemical Biology, TU Dortmund University, Dortmund, Germany.
Future Research Plans
Recently, we established our research group in SRM University-AP, and our group has started to explore an emergent research area of crystal-glass composite materials towards the applications of atmospheric water harvesting, solid-state electrolytes (Alkali and Alkaline metal ions-based), photovoltaics, and conversion of gaseous Carbon-dioxide molecules to industrially relevant liquids, such as methanol or ethanol.
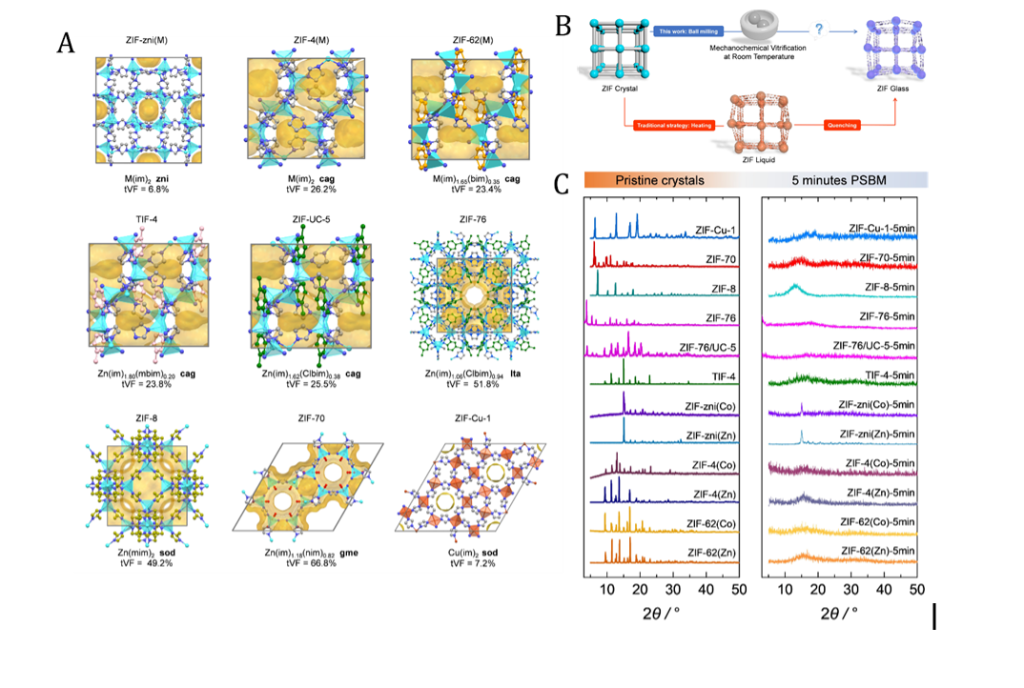
- Figure 1. (A) Single crystal structures of various ZIFs indicated in the figure. (B) Schematic representation of the traditional route to ZIF glass formation (red line) and the mechanochemical vitrification approach followed in this work (blue line). (C) PXRD patterns of the pristine ZIF polycrystalline materials and after five minutes of mechanical ball milling.
- Published in Chemistry-news, Departmental News, News, Research News
Developing Biosensors using Photonic Crystal Fibres and Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR)

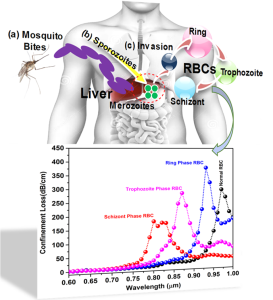
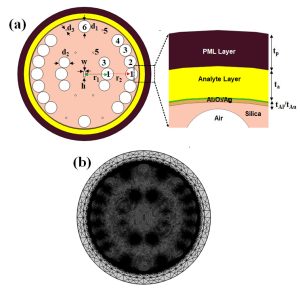
Dr Sanjeev Mani Yadav, Assistant Professor from the Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, has published a cutting-edge research paper titled “Au-Al2O3 Coated Highly Sensitive Broad Range Refractive Index Sensor for Detecting Malaria Disease in Human Blood” in the IEEE Sensors Journal with an impact factor of 4.3. This research focuses on developing a highly sensitive biosensor using photonic crystal fibres and a technique called surface plasmon resonance (SPR) to detect changes in the refractive index, which is how much light bends when it enters a material. This biosensor can also detect malaria in the human body.
Abstract
The paper represents the photonic crystal fibre-based surface plasmon resonance (SPR) biosensor for broad-range refractive index sensors along with the detection of malaria disease in the human body. α-Al2O3-Au dielectric-metal interface has been proposed to stimulate the free electron on the metal surface via evanescent to result in an SPR phenomenon. The proposed sensor shows a sufficient shift in resonance wavelength for the change in external RI from 1.32 to 1.40 for an optimised Al2O3/Au thickness of 50nm/12nm. The broad-range sensing applicability of the designed sensor shows a maximum sensitivity of 6000 nm/RIU when the external RI changes from 1.38 to 1.40. The detection accuracy of the designed sensor is reported to be 1.66×10-5 (RIU) and reported compatible in comparison to broad RI sensors. The proposed SPR sensor has been utilised to sense the malaria diseases in the human body by filling infected RBC samples on the dielectric-metal surface. The proposed study aids in detecting various stages of malaria-infected RBCs, including the Ring phase, Trophozoite phase, and Schizont phase, by measuring the shift in resonance wavelength. The sensor’s wavelength sensitivity varies across the phases: 5714.28 nm/RIU for the Ring phase, 5263.15 nm/RIU for the Trophozoite phase, and 5931 nm/RIU for the Schizont phase. The sensor exhibits the highest reported sensitivity among other biological sensors in this category. The proposed sensor fulfils all the requirements for a diagnosis of early malaria disease in the human body, along with its high sensitivity, low detection limit, and capability of sensing broad RI.
How does the sensor work?
1. Biosensor Basics: The sensor uses a combination of a special crystal fibre and a metal surface (a mix of aluminium oxide and gold) to create a reaction when light hits it. This reaction is called SPR and it helps in detecting tiny changes.
2. Detecting Changes: When the external refractive index (a measure of how light bends in a substance) changes, the sensor detects this by a shift in the wavelength (colour) of the light. The study found that the sensor is very sensitive to changes in the refractive index between 1.32 and 1.40.
3. Sensitivity: The sensor is incredibly sensitive, with a maximum sensitivity of 6000 nm/RIU (nanometres per refractive index unit). This means it can detect very small changes very accurately.
4. Malaria Detection: The sensor can also detect malaria by analysing infected red blood cells. Different stages of malaria infection (Ring, Trophozoite, and Schizont) cause different shifts in the wavelength, which the sensor can measure. The sensor’s sensitivity varies slightly with each stage but is consistently high.
5. High Performance: This sensor is reported to have the highest sensitivity compared to other similar sensors and meets all the requirements for early malaria diagnosis due to its high sensitivity, low detection limit, and ability to detect a wide range of refractive indices.
In essence, this sensor is a powerful tool for detecting both refractive index changes and malaria in the human body with high accuracy and sensitivity.
Practical implementation/Social implications of the research
The photonic crystal fibre-based SPR biosensor represents a significant advancement in medical diagnostics with wide-ranging practical applications and social implications. Its high sensitivity and accuracy in detecting malaria and potentially other diseases can lead to better health outcomes, economic benefits, and improved access to healthcare, particularly in regions that need it the most.
Dr Sanjeev Mani Yadav acknowledges Dr Amritanshu Pandey, Electronics Engineering Department, IIT (BHU) Varanasi, for his continuous support and guidance throughout this research.
- Published in Departmental News, ECE NEWS, News, Research News
Unveiling the Dynamics of Labour Market Outcomes

In the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic, societies across the globe were pushed into acute constraints, especially in the absence of employment security and consistency. In this regard, Dr Boddu Srujana, Assistant Professor at the Department of Economics through her research paper titled, Women’s Labour Market Outcomes and Contours of Subnationalism: A Comparison Across Four States in India, scrutinises the impact of the pandemic on women’s employment and thereby explores whether these outcomes were uniformly impacted or if they reveal variations attributable to the political dynamics within these states.
Read the exciting excerpt followed by the link to the article, featured in Economic and Political Weekly
Abstract:
Using, the Periodic Labour Force Survey data for 2018–19 and 2020–21, the article explores shifts in women’s employment outcomes pre- and post-pandemic across four Indian states. The article finds that the states with stronger subnational politics fare better in creating quality employment outcomes for women compared to their counterparts, even during times of crisis such as the recent COVID pandemic. This stands true even for women with disadvantaged social, economic and educational backgrounds.
Practical implementation of research and social implications:
The research highlights the effectiveness of governance and emphasizes social policies over time that can create better job opportunities for women, where they can secure against vulnerabilities even during challenging times such as crises. This leads to greater economic independence, reduces poverty, and promotes social equity.
Collaborators:
The research paper is co-authored with Anagha Tobi and Sipoy Sarveswar.
Anagha Tobi is an Assistant Professor at the Department of Humanities and Social Sciences, Mahindra University, Hyderabad. Sipoy Sarveswar is an Assistant Professor at the Department of Anthropology, Vidya Bhavana, Visva-Bharati, Santiniketan.
Future Plans:
As part of her future research projects in this area, Dr Srujana plans on studying the urban informal labour markets, urbanisation, the dynamics of informalisation, the future of work, and the impact of public policy on labour markets. She is eager to extend her work in these areas by engaging in collaborative research while also partnering with academic institutions, policymakers and NGOs, whereby she aims to contribute to the changing world of work and develop actionable insights that can inform policy and practice
Link to the article.
https://www.epw.in/journal/2024/23/perspectives/womens-labour-market-outcomes-and-contours.html
- Published in Departmental News, Economics News, News, Research News
A System for Visually Impaired Navigation

A dedicated team of researchers and professors have developed an innovative patent titled “System and a Method for Assisting Visually Impaired Individuals” that uses cutting-edge technology to significantly improve the navigation experience for visually impaired individuals, fostering greater independence and safety.
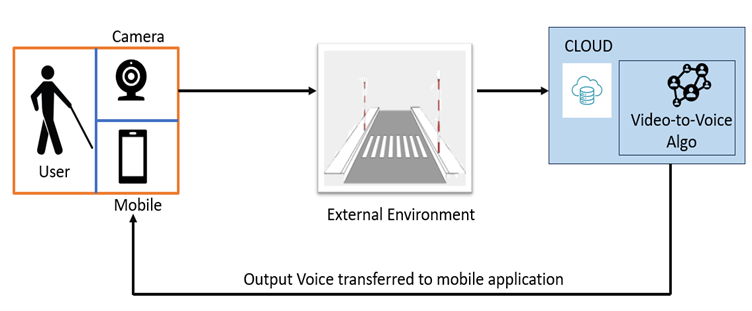
The team, comprising Dr Subhankar Ghatak and Dr Aurobindo Behera, Assistant Professors from the Department of Computer Science and Engineering, and students Ms Samah Maaheen Sayyad, Mr Chinneboena Venkat Tharun, and Ms Rishitha Chowdary Gunnam, has designed a system that transforms real-time visual data into vocals via a mobile app. It will utilise wearable cameras, cloud processing, computer vision, and deep learning algorithms. Their solution captures visual information and processes it on the cloud, delivering relevant auditory prompts to users.
Abstract
This patent proposes a novel solution entitled, “System and a method for assisting visually impaired individuals aimed at easing navigation for visually impaired individuals. It integrates cloud technology, computer vision algorithms, and Deep Learning Algorithms to convert real-time visual data into vocal cues delivered through a mobile app. The system
employs wearable cameras to capture visual information, processes it on the cloud, and deliver relevant auditory prompts to aid navigation, enhancing spatial awareness and safety for visually impaired users.
Practical implementation/Social implications of the research
The practical implementation of our research involves several key components. Firstly, we need to develop or optimise wearable camera devices that are comfortable and subtle for visually impaired individuals to wear. These cameras should be capable of capturing high-quality real-time visual data. Secondly, we require a robust cloud infrastructure capable of processing this data quickly and efficiently using advanced computer vision algorithms and Deep Learning Algorithms. Lastly, we need to design and develop a user-friendly mobile application that delivers the processed visual information as vocal cues in real-time. This application should be intuitive, customisable, and accessible to visually impaired users.
The social implications of implementing this research are significant. By providing visually impaired individuals with a reliable and efficient navigation aid, we can greatly enhance their independence and quality of life. Navigating city environments can be challenging and hazardous for the visually impaired, leading to increased dependency and reduced mobility. Our solution aims to mitigate these challenges by empowering users to navigate confidently and autonomously. This fosters a more inclusive society where individuals with visual impairments can participate actively in urban mobility, employment, and social activities.
In the future, we plan to further enhance and refine our technology to better serve the needs of visually impaired individuals. This includes improving the accuracy and reliability of object recognition and scene understanding algorithms to provide more detailed and contextually relevant vocal cues. Additionally, we aim to explore novel sensor technologies and integration methods to expand the capabilities of our system, such as incorporating haptic feedback for enhanced spatial awareness.
Furthermore, we intend to conduct extensive user testing and feedback sessions to iteratively improve the usability and effectiveness of our solution. This user-centric approach will ensure that our technology meets the diverse needs and preferences of visually impaired users in various real-world scenarios.
Moreover, we are committed to collaborating with stakeholders, including advocacy groups, healthcare professionals, and technology companies, to promote the adoption and dissemination of our technology on a larger scale. By fostering partnerships and engaging with the community, we can maximize the positive impact of our research on the lives of visually impaired individuals worldwide.
- Published in CSE NEWS, Departmental News, News, Research News
Teacher-Student Duo Collaborate to Achieve Scientific Excellence

The Department of Mechanical Engineering at SRM University-AP is proud to present its research paper titled, Study on Properties and Microstructure of Wire Arc Additive Manufactured 2209 Duplex Stainless Steel by Dr Maheshwar Dwivedy and post-doctoral researcher, Dr B Prasanna Nagasai. Below is a brief write-up on their research.
Abstract:
This study investigates the properties and microstructure of 2209 duplex stainless steel (DSS) components fabricated using the wire arc additive manufacturing (WAAM) technique, specifically employing the gas metal arc welding (GMAW) process. The research focuses on the mechanical properties and microstructural characteristics of the produced cylindrical components. Detailed examination revealed that the microstructure varied from the bottom (region ①) to the top (region ②) of the cylinders, with hardness measurements ranging from 301 HV0.5 to 327 HV0.5, and impact toughness values from 118J to 154J. The tensile properties exhibited anisotropic behavior, with ultimate tensile strength and yield strength ranging from 750 to 790 MPa and 566 to 594 MPa, respectively. The study highlights the significant influence of complex heat cycles and cooling rates on the primary phase balance, resulting in a 50/50 austenite/ferrite distribution. Additionally, σ-phase precipitation was observed at the ferrite grain boundaries. The observed increase in austenite content from region ① to region ② is attributed to reduced cooling rates and extended time for solid-state phase transformation. This research provides valuable insights into optimizing the WAAM process for enhanced performance of 2209 DSS components.
Citation Format:
Prasanna Nagasai, B, Maheshwar Dwivedy, Malarvizhi, S. et al. Study on Properties and Microstructure of Wire Arc Additive Manufactured 2209 Duplex Stainless Steel. Metallogr. Microstruct. Anal. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13632-024-01089-8
Practical implementation:
The practical implementation of this research on Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing (WAAM) for Duplex Stainless Steel (DSS) has significant implications for industries requiring high-strength, corrosion-resistant components, such as construction, marine, and chemical processing. By optimizing the WAAM process to produce DSS parts with balanced microstructures, manufacturers can create durable and efficient parts more cost-effectively and with less material waste than traditional methods. This advancement could lead to more sustainable manufacturing practices, reducing the environmental impact and operational costs associated with producing large metal components. Socially, the widespread adoption of this technology could drive innovation, create new job opportunities in advanced manufacturing, and contribute to the development of stronger, longer-lasting infrastructure and machinery, ultimately benefiting the economy and society at large.
Collaborations:
Dr V Balasubramanian,
Professor & Director,
Centre for Materials Joining & Research (CEMAJOR)
Annamalai University, Annamalai Nagar-608002, Tamilnadu.
Dr P Snehalatha,
Associate Professor & Head
Department of Mechanical Engineering,
Sri Padmavathi Mahila Visvavidyalam, Tirupati, Andhra Pradesh-517502, India.
Future Research Plans:
In our upcoming work, we will focus on developing Functionally Graded Materials (FGMs) using Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing (WAAM), combining nickel and stainless steel. This research aims to harness the unique properties of each metal to create components tailored for specialized applications requiring high performance. Key challenges include optimizing material interfaces, refining deposition processes, and ensuring robust structural integrity throughout production.
The link to the article– https://doi.org/10.1007/s13632-024-01089-8
- Published in Departmental News, Mechanical Engineering NEWS, News, Research News