Dr Uma Maheswar to work on an overseas-funded project

Yet another moment of pride and honour for SRM University-AP as Dr Uma Maheswar Arepalli, Assistant Professor, Department of Civil Engineering in collaboration with Dr Ali Shirazi, Assistant Professor, Department of Civil Engineering, University of Maine, USA received a research project award from the Maine Department of Transportation, Maine, USA. The project titled “Comprehensive review of flexible pavement design approaches suitable to Maine conditions” received a total project outlay of $26,396 (Rs. 21.12 Lakhs).
This is the first of its kind project in India that receives funding directly from the foreign (United States) entity unlike the typical Department of Science & Technology (DST) International Bilateral Joint Project Schemes. This 8-month-long project will review the various existing flexible pavement design approaches in the USA and will provide recommendations to the Department of Transportation on a suitable design approach conducive to the conditions of Maine.
The outcome of the project will help the Department of Transportation to decide on a suitable pavement design approach that enhances the performance of pavements in Maine. The project engenders an opportunity for two under-graduate students of SRM University-AP to work as paid interns and receive international exposure in their prospective research areas. It also involves the scope for industry translatory research.
- Published in CIVIL NEWS, Departmental News, News, Research News
Dr Raviteja KVNS Received the Best Paper Award at TRACE 2022
 Soil and groundwater contamination is closely interlinked with human society because of its direct impact on population health and socioeconomic activities. The design and implementation of site remediation can be expensive, time-consuming, and may require much human effort. Emerging technologies such as Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, and Deep Learning have the potential to make site remediation cost-effective with reduced human effort.
Soil and groundwater contamination is closely interlinked with human society because of its direct impact on population health and socioeconomic activities. The design and implementation of site remediation can be expensive, time-consuming, and may require much human effort. Emerging technologies such as Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, and Deep Learning have the potential to make site remediation cost-effective with reduced human effort.
Assistant Professor Dr Raviteja KVNS, Department of Civil Engineering, has received the Best Paper Award at the Fourth International Conference on Trends and Recent Advances in Civil Engineering (TRACE) 2022 for his paper Application of artificial intelligence, machine learning and deep learning in contaminated site remediation. The conference was held at Amity University, Uttar Pradesh, on October 18 and 19, 2022. His research reports the applications of AI and ML in contaminated site remediation.
Dr Raviteja’s future research plan includes studying potential applications of various AI, ML and DL techniques for Geotechnical and Geo-environmental design and testing applications so as to reduce the labours of physical and repetitive testing and associated human effort. This further improves precision as well as aids in decision-making. He has collaborated with Prof. Krishna R Reddy, University of Illinois Chicago, for this research work.
Abstract
Soil and groundwater contamination is caused by improper waste disposal practices and accidental spills, posing a threat to public health and the environment. It is imperative to assess and remediate these contaminated sites to protect public health and the environment as well as to assure sustainable development. Site remediation is inherently complex due to the many variables involved, such as contamination chemistry, fate and transport, geology, and hydrogeology. The selection of remediation method also depends on the contaminant type and distribution and subsurface soil and groundwater conditions. Depending on the type of remediation method, many systems and operating variables can affect the remedial efficiency. The design and implementation of site remediation can be expensive, time-consuming, and may require much human effort. Emerging technologies such as Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, and Deep Learning have the potential to make site remediation cost-effective with reduced human effort. This study provides a brief overview of these emerging technologies and presents case studies demonstrating how these technologies can help contaminated site remediation decisions.
- Published in CIVIL NEWS, Departmental News, Faculty Achievements, News, Research News
Employing Information Entropy in Determining the Water Body’s Health Status
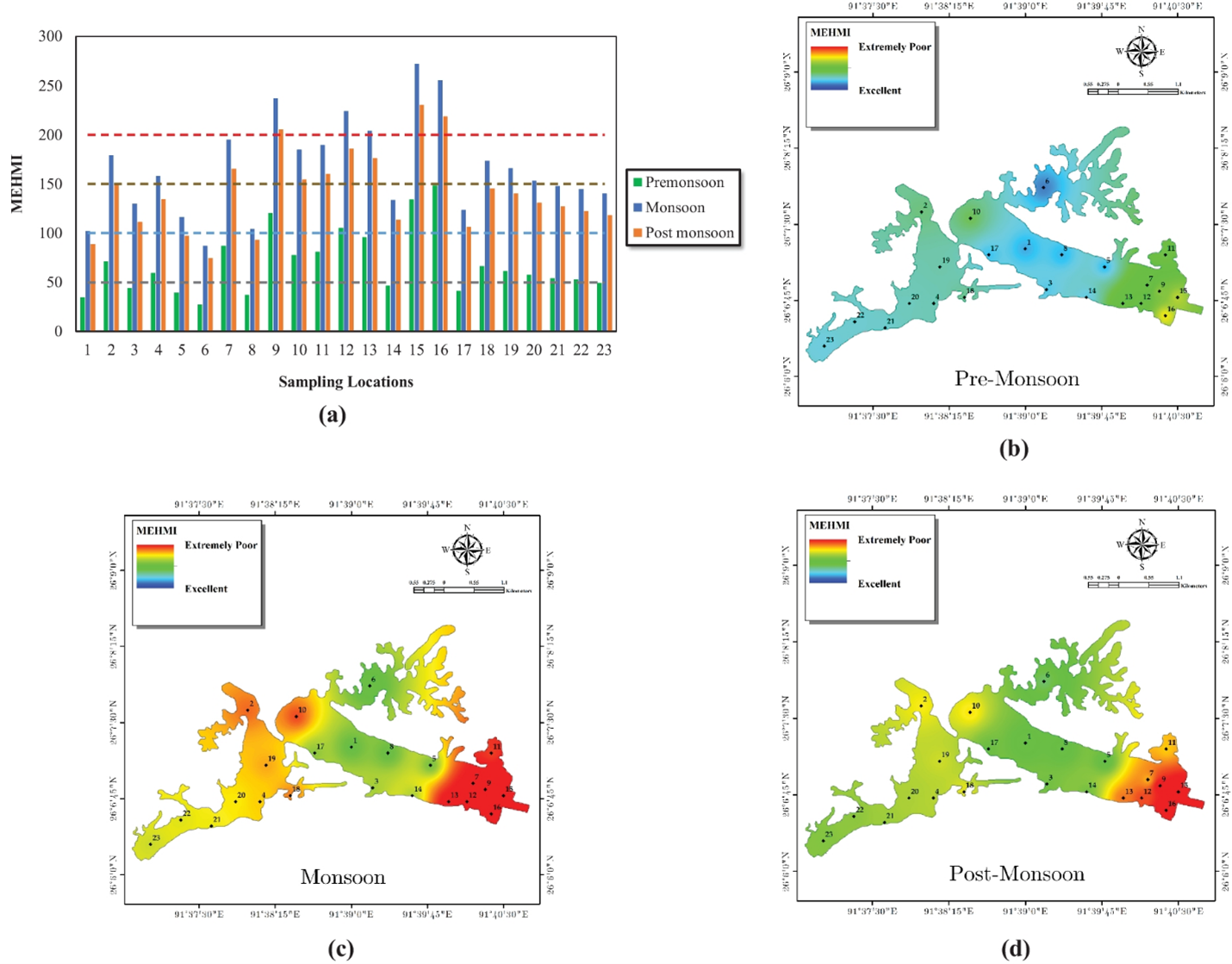 The global population is changing drastically, increasing at an alarming rate of more than 80 million per year. This growing population has led to enormous pressure on land-use patterns and, to a greater extent, the natural ecosystems, especially water bodies. The water bodies are getting depleted considerably, and their quality is significantly deteriorating. Assistant Professor Dr Siddhanth Dash from the Department of Civil Engineering has published the paper Development of function-specific indices for assessing water quality based on the proposed modifications of the expected conflicts on existing information entropy weights in the journal Environmental Monitoring and Assessment with an impact factor of 3.307. He has collaborated with Dr Ajay S Kalamdhad, a Professor at the Department of Civil Engineering, IIT Guwahati, for the research.
The global population is changing drastically, increasing at an alarming rate of more than 80 million per year. This growing population has led to enormous pressure on land-use patterns and, to a greater extent, the natural ecosystems, especially water bodies. The water bodies are getting depleted considerably, and their quality is significantly deteriorating. Assistant Professor Dr Siddhanth Dash from the Department of Civil Engineering has published the paper Development of function-specific indices for assessing water quality based on the proposed modifications of the expected conflicts on existing information entropy weights in the journal Environmental Monitoring and Assessment with an impact factor of 3.307. He has collaborated with Dr Ajay S Kalamdhad, a Professor at the Department of Civil Engineering, IIT Guwahati, for the research.
Explanation in Layperson’s Terms
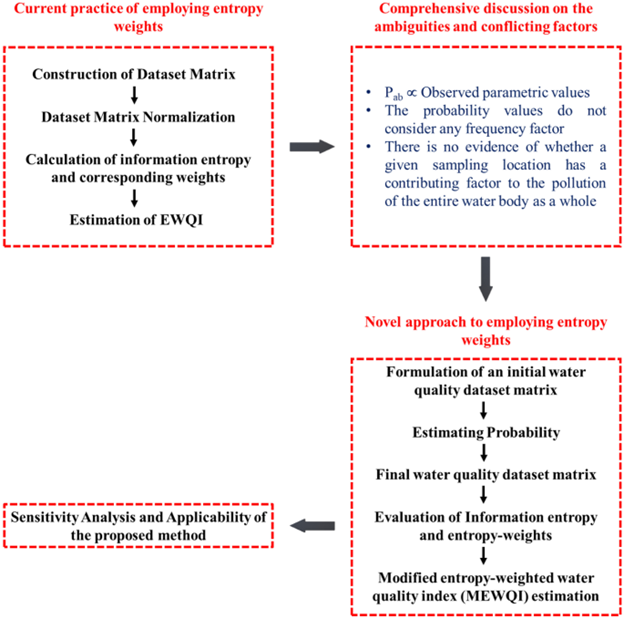
Waterbody contamination is attributed to a various number of reasons: primarily anthropogenic contamination, such as extensive industrial (small as well as large-scale) discharges, leaching of chemical fertilisers from the agricultural grounds, the release of toxic chemicals such as heavy metals and pesticides, and discharge of untreated sewage water from residential complexes (primary constituents being nutrients such as N, P, and K and pathogens). These depletions of the natural water systems have affected the entire aquatic ecosystem. Indexing tools have proved to be the most significant of all the techniques developed. Water quality indices (WQIs) are mathematical representations of a particular body’s water quality, providing a singular numeric denomination reflecting its health status. Specific indices are unique indices which provide information regarding the overall anthropogenic contamination and are broadly target-specific. Over the years and extensive studies carried out worldwide, while multivariate statistics have proved its reliability, the existing approach of using entropy weights suffers from various ambiguities.
Dr Dash’s study addresses vital issues relating to the existing use of entropy weights in WQIs, thus proposing a novel approach to employing information entropy in determining the water body’s health status.
 Practical Implementation and Social Implication of the Research
Practical Implementation and Social Implication of the Research
Water quality assessment remains paramount when providing safe and potable water as per the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). This study’s results would pave the way for a more reliable and time-conserving manner of assessing water quality and a broader context and health status of a water body that will help protect and preserve different water bodies globally. The present study will also benefit the researchers and policymakers in making sustainable decisions toward restoring water bodies and preventing them from plausible future deterioration.
Working on sustainable and effective treatment techniques to remediate emerging contaminants in aquatic ecosystems is the future research plan of Dr Dash.
Abstract
Water serves numerous purposes besides drinking, such as irrigation and industrial usage. Most water quality indices developed have primarily focused on drinking water quality. However, assessing other functionalities of water bodies is also equally essential. The present study proposes a novel technique to measure water quality for two highly specific water use, i.e., assessing heavy metal contamination and irrigation suitability. The ambiguities in the current practice of entropy weights were identified, and a novel method was proposed, considering a three-dimensional approach instead of the conventional two-dimensional procedure. Weights to different parameters were assigned based on the probability estimates obtained from the frequency of observed values within acceptable limits. The proposed method’s reliability, correctness, and applicability were tested using Deepor Beel’s water quality dataset. Results were highly consistent with the experimental values and correlated well with other established methods. The efficacy of the method was determined by employing sensitivity analyses. Both indices showed high reliability and correctness, as no single parameter was found to be highly sensitive compared to others. Therefore, the proposed methodology proved to be the most reasonable, incorporating all the factors required for a reliable water quality monitoring program.
Citation of the Article
Dash, S., & Kalamdhad, A. S. (2022). Development of function-specific indices for assessing water quality based on the proposed modifications of the expected conflicts on existing information entropy weights. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 194(12), 1-17.
- Published in CIVIL NEWS, Departmental News, News, Research News
Industry Visit for Hands-on Exposure
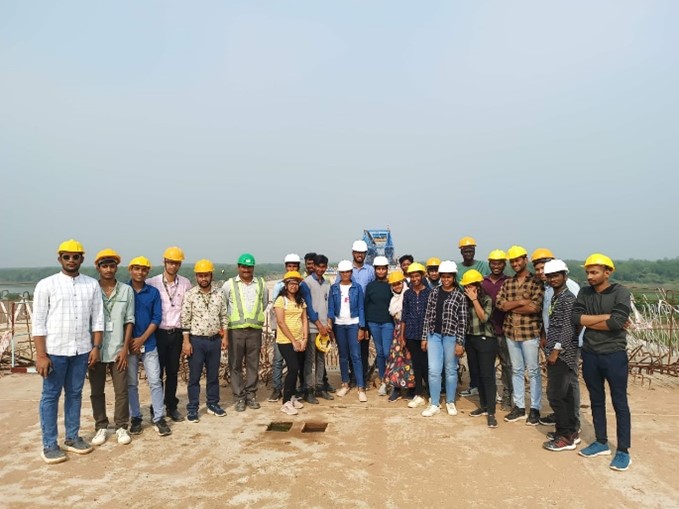

The Department of Civil Engineering of SRM University-AP conducted the second industrial visit for the Civil Engineering students of all semesters on November 30, 2022.
Details of the industrial site
An 18-kilometre stretch bridge over the Krishna River in the Chinakakani-Gollapudi highway is under construction jointly by the Adani group and Navayuga Engineering Company Limited. Hands-on practical insight was provided by experienced site Engineers on the topic of the post-tensioned precast bridge and the launching arrangement of each precast segment using advanced technological equipment. Students were also exposed to the different units of the site (i.e., the Safety class was delivered by the site officials, the Concrete batching plant, Quality control laboratories, and the Casting yard of the precast units).
Coordinating faculty: Dr Nishant Sharma and Dr Arijit Saha
- Published in CIVIL NEWS, Departmental News, News
Industrial Visit to MEIL

The Department of Civil Engineering has organised an industrial visit to Megha Engineering & Infrastructure Limited (MEIL) for engineering students to harbour them with the practical skillsets demanded by profession. The field visit was guided by senior engineers working on respective sites and co-ordinated by the faculty.
Project: Six-Laning of Vijayawada Bypass from Chinna Autupalli (Design Ch. 0.000) to Gollapudi (Design Ch. 30.000) Section of NH-16
Construction Company: Megha Engineering & Infrastructures Limited (MEIL)
Visit Highlights:
- Safety training by MEIL
- Quality Control Lab tour
- Soil, Aggregate, Bitumen, and Cement Concrete Testing
- Quality Control Aspects
- Batching Plant visit
- WMM and Concrete batching plants
- Site Tour
- Earthworks, Embankment, and WMM Construction
Coordinating faculty: Dr A Uma Maheswar
- Published in CIVIL NEWS, Departmental News, News
Academic Trio Secures Second Prize at Aakaar Symposium
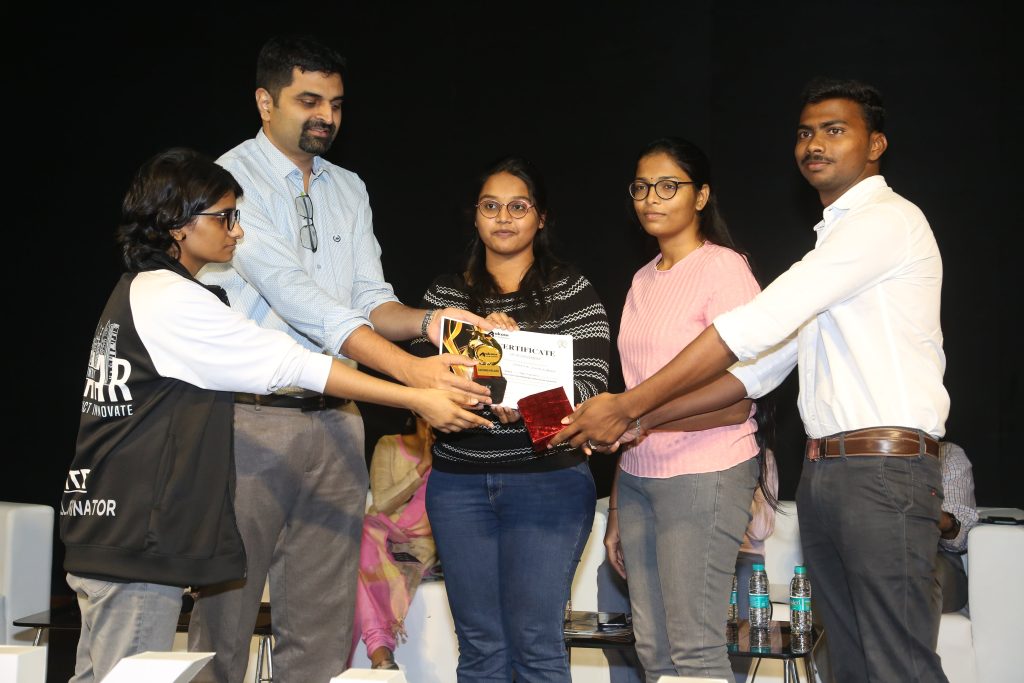

The students of SRM University-AP are nurtured in a conducive educational ecosystem that moulds them into competent candidates ensuring research and academic success at national and international frontiers. The Department of Civil Engineering proudly congratulates Tanoogna Mallarapu, Jonnalagadda Cheritha and Gade Venkata Reddy, Final year BTech students for securing the second prize in the Paper presentation contest at the prestigious Aakaar Symposium held by The Department of Civil Engineering, IIT Bombay on March 17 and 18, 2023. The trio presented their paper titled “Study of alternative flexible pavement design approaches suitable for Maine conditions” which was part of the students’ paid internship on an overseas (USA) research project funded by the Maine Department of Transportation, USA. A total of 47 groups participated in the contest from various domains of civil engineering from all over India. The academic cohort bagged the position of runners-up under the guidance and mentorship of the faculty advisor, Dr Uma Maheswar Arepalli, Assistant Professor, SRM Univeristy-AP.
About the Symposium
Aakaar is an annual symposium organized by the Department of Civil Engineering at IIT Bombay. The event comprises workshops, lecture series, panel discussions, industrial talks, exhibitions, and other activities. The festival also includes the Seventh International Civil Engineering Symposium (ICES), which aims to encourage young research enthusiasts to engage in rigorous research in civil engineering. ICES includes poster presentations, 3-minute thesis talks, city planning, and paper presentations. The symposium offers young and promising students enthusiastic about research the opportunity to present their work in front of experienced professors, civil engineering leaders, and industrialists.
The team had the incredible opportunity to meet renowned academicians and industrialists and learn about various projects in the civil engineering domain. Their work was highly praised by the judges with Dr Dharmaveer, Associate Professor, Civil Engineering Dept., IIT Bombay commenting that, “I enjoyed their presentation. I like their exposure to new tools and techniques, exploring new terms, learning, and understanding, which made them worthy.”
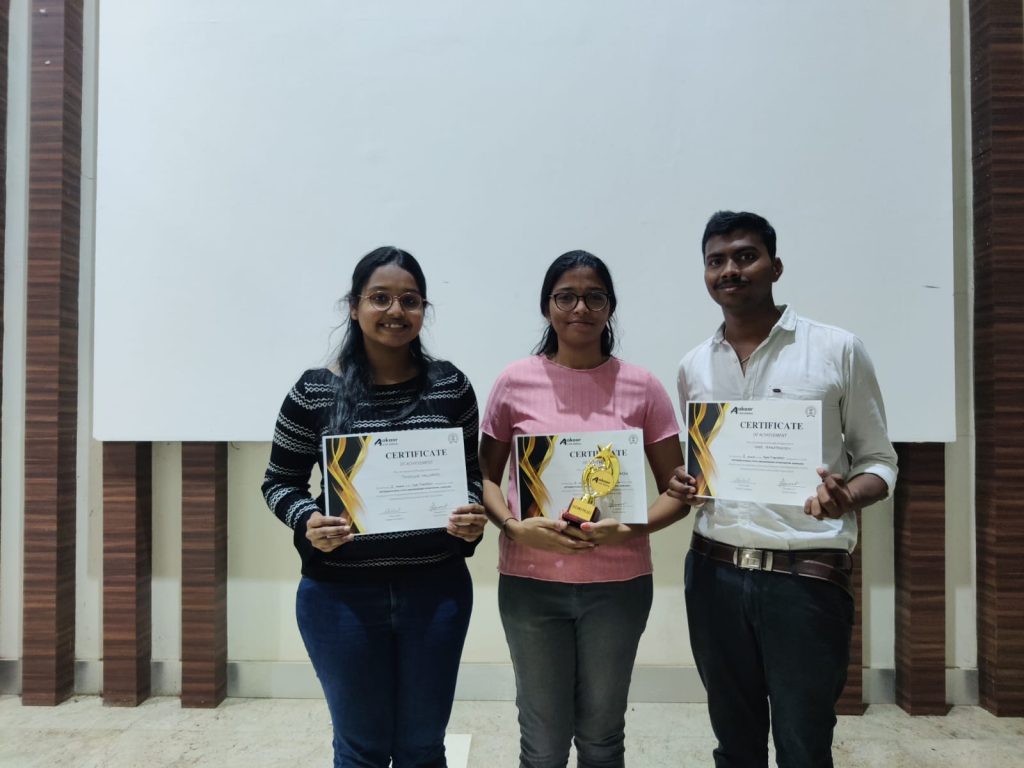

Tanoogna from the team stated her elevation in acquiring this success. “From the outset, I was motivated to participate in the competition and showcase my skills. Our advisor, Dr Uma Maheswar was always available to answer our questions, provide feedback on our work, and offer valuable insights that helped us refine our approach. His mentorship has played an integral role in our success, and we could not have accomplished this without his assistance. We are grateful for this opportunity and the platform that IIT Bombay provided us. It has been a fantastic journey, and I look forward to participating in more competitions and pushing my limits further,” said the young scholar.
Cheritha also expressed her gratitude towards her team’s accomplishment and the valuable experience the symposium had provided. “We were able to show case our work and was able to present it effectively and secured 2nd place in the category of paper presentation. Participating in this event is an incredible experience for me to gain knowledge. I am very grateful for my advisor and my teammates Tanoogna and Venkata Reddy for their hard work towards the accomplishment of the project and for being there in difficult situations.”
Venkat also commented that the event was beneficial in gaining knowledge and to present the project. The students thanked their mentor, Dr Uma Maheswar for the opportunities he had provided and his constant encouragement to strive for excellence.
Dr Uma Maheswar, Assistant Professor, Department of Civil Engineering, SRM University-AP also voiced delight in the incredible performance of his students. “From the beginning, I had the feeling that the topic has the potential to win this competition. But this team of students has made it a reality with their excellent technical and soft skills. It was a moment of immense pride and happiness for us in the civil engineering department when our students won the contest at a prestigious platform like IITB. Heartful congratulations to Tanoogna, Cheritha, and Venkat. I wish them the best of luck in their future career endeavours.”
Abstract of the Paper
AASHTOWare Pavement Mechanistic-Empirical Design (PMED) has been introduced to overcome the limitations of the AASHTO 1993 pavement design approach in the United States. However, due to the data requirements and work involved with accurate local calibration of PMED performance models, PMED seems challenging from a benefit-cost standpoint, especially for the states with low traffic volumes and limited resources. This study aims to understand the current flexible pavement design practices in the United States and recommend an alternative design approach for a state department of transportation. The methodology included an online survey with practitioners, a literature review, and a comparative analysis of selected alternative design approaches. Two approaches were chosen as an alternative design approach based on the online survey results, interviews, and literature review. One is updating layer coefficients for AASHTO 1993, and the second is developing its mechanistic-empirical (M-E) based pavement design approach for Maine. A layered elastic analysis using winJULEA or similar combined with standard performance empirical equations was considered a proposed M-E design tool for preliminary analysis. A sensitivity analysis using the range of design input values for Maine conditions and validation with a historical project database is planned. The presentation will discuss this study’s findings and the final recommendations derived from the comparative analysis.
- Published in CIVIL NEWS, Departmental News, News, Students Achievements
Site visit to Railway Project
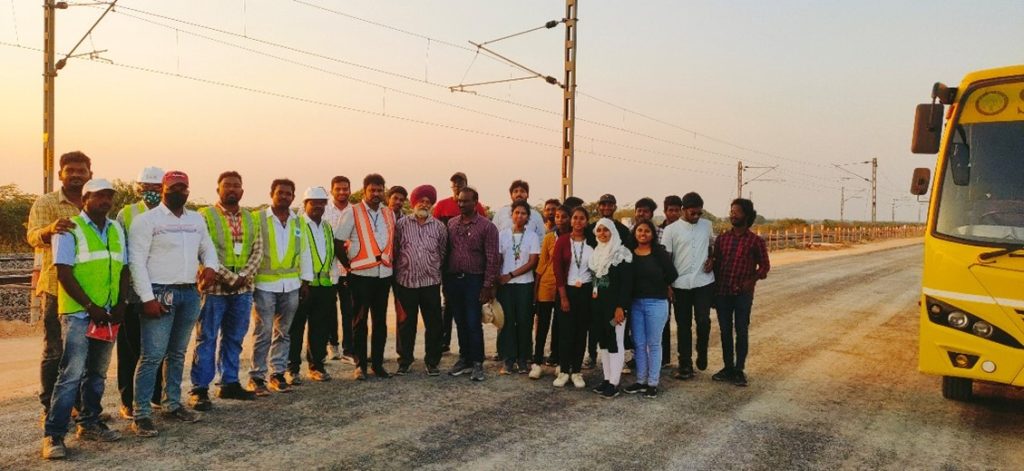

The Department of Civil Engineering has organised the third industrial visit to the ongoing railway project, “Construction works of 3rd railway line between Vijayawada and Gudur”. The tour was arranged with the support of Mr Basha, AGM, Rail Vikas Nigam Limited (RVNL) and coordinated by Mr Lakwanth Singh Khalsa, Project Manager, Systra, India. The field visit was guided by engineers from Systra and GR Infra (GRIL) working on respective sites and coordinated by the faculty.
Visit Highlights:
- Construction activities of Railway Under Bridge (RUB) at LC225: Understanding the difficulties due to black cotton soil and water seepage, diversion works of existing natural streams of irrigation channels, dewatering and pumping arrangements, alignment challenges, and girder design challenges.
- Erection of Foot Over Bridge (FOB) at Chirala Railway Station
- GRIL Laboratory Camp: Batching plant, Ready Mix Concrete, Quality Control tests, Concrete Permeability Test, etc.
- Steel Bridge at BR. NO. 612: Procedure of fabrication, inspection, and erection of girders, components of the girder, etc.
- Railway Formation: Earthwork, Blanket, Tests to be conducted at the site, and Method of laying.
Coordinating faculty: Dr A Uma Maheswar

- Published in CIVIL NEWS, Departmental News, News
SERB- SURE Grants: 10 projects worth 2.50 crores awarded to SRM AP

The faculty of SRM University-AP have been awarded 10 projects worth 2.50 crores from the Science and Engineering Research Board (SERB-SURE). Department of Science and Technology (DST) received a total of 2000 proposals, of which 466 were sanctioned. Among the 466 projects, 151 projects were awarded to Private Universities. Of the 151 projects approved to state private universities and colleges throughout India, the five-and-a-half-year young varsity was awarded 10 projects. 10 professors from various Science and Engineering Departments brought this incredible achievement to the university.
SERB-SURE is a research grant scheme initiated by the Science and Engineering Research Board (SERB) in India to provide financial support to young researchers in the early stages of their careers. The grants are intended to support research in basic and applied sciences, engineering, and technology and is typically granted for a period of three years.The SERB-SURE scheme is one of several initiatives by SERB to promote scientific research in India and support the development of a strong research community in the country.
“It is a milestone achievement that resonates with the University’s unparalleled commitment for excellence. We are striving towards research-intensive learning to build cutting-edge innovation for a transformative tomorrow”, commented Vice Chancellor, Prof. Manoj K Arora. The Executive Director-Research of SRM Group, Prof. Narayana Rao said that, “SRM University-AP has travailed hard to achieve the world-class scientific temperament that we now advocate, and this achievement is a testimonial recognition of all our efforts.” The prestigious grants were sanctioned to the faculty in the on-going domains of Quantum Kinetic Approach, Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR) Profiling and Changing of Hydroclimatic conditions in Bay of Bengal among 7 others.
Dean-SEAS, Prof. Ranjith Thapa said, “These research could be path-breaking and could offer a solution to many of the societal difficulties.” Prof. Jayaseelan Murugaiyan, Dr Sandeep Singh and Dr Pitchaiah Cherukuri of the Department of Biological Sciences; Dr Sabyasachi Chakrabortty, Dr V S Baswanth Oruganti of the Department of Chemistry; Dr Debabrata Pramanik, Dr Ravi Kumar and Dr Pankaj Bhalla of the Department of Physics ; Dr Sandeep Kumar Verma of the Department of Mathematics; Dr Uma Maheswar Arepalli of the Department of Civil Engineering; and Dr Kousik Das of the Department of Environmental Science and Engineering were awarded the grants.
- Published in Biology News, Chemistry-news, CIVIL NEWS, Departmental News, ENVS News, Math News, News, Physics News, Research News
Best Paper Award: Conferred to Dr Raviteja KVNS at RAISE 2023

The Department of Civil Engineering is glad to announce that Dr Raviteja KVNS, Assistant Professor, has received the Best Paper Award for his paper titled “Compressibility Characteristics of Bentonite Amended Fly Ash Liners Exposed to Phosphate Contamination” at the 2nd International Conference RAISE 2023 (Recent Advances in Sustainable Environment) held on May 15-16, 2023. Dr Raviteja collaborated with Dr Janga Jagadeesh Kumar and Dr Krishna R Reddy, Civil, Materials and Environmental Engineering, University of Illinois Chicago for the research paper. Their cutting-edge research focused on developing alternate liner materials for waste containment systems.
Abstract
Waste containment systems like landfills, and impoundments are often lined with low permeable clays of hydraulic conductivity less than 10-7 cm/s. However, it is often challenging to get large volumes of low permeable clays near the project site. Conveyance of large volumes of clay from distant locations can be unsustainable due to the associated carbon emissions and energy costs, and not viable financially. Hence, there is a need to identify alternative liner materials without compromising on the containment capabilities. This study proposes the use of fly ash, amended with bentonite, as an alternative to the traditional liner systems. From preliminary studies, it is understood that a mixture of 80% fly ash amended with 20% bentonite is optimal to function as an effective liner material. However, the hydro-mechanical stability of liners needs to be investigated under different contamination scenarios. The present study reports the compressibility behavior of the proposed liner system under phosphate contamination, typically found in landfill leachate, impoundments, and stormwater retention ponds. One-dimensional consolidation tests were conducted on pure bentonite and fly ash with water to study the compressibility characteristics of individual materials. The optimum mix (80-20) was then tested at three different solutions exposure: water, 3.2 mg/L PO4-3-P and 12 mg/L PO4-3-P. It is depicted that the addition of 20% bentonite to fly ash did not affect the compressibility significantly, while the presence of phosphate contamination did not compromise the hydro-mechanical stability of the proposed liner system.
- Published in CIVIL NEWS, Departmental News, Faculty Achievements, News, Research News
- 1
- 2













