Dr Sunil Publishes Paper on Ethereum Blockchain Framework in IEEE Access
 We are thrilled to announce that Dr Sunil Chinnadurai, Associate Professor in the Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering has published a significant research paper titled “Ethereum Blockchain Framework Enabling Banks to Know Their Customers” in the esteemed journal IEEE Access. In his paper, Dr Chinnadurai explores the innovative applications of Ethereum blockchain technology in enhancing customer verification processes within the banking sector. His research addresses the growing need for robust and secure methods for banks to comply with Know Your Customer (KYC) regulations while ensuring customer privacy and data integrity.
We are thrilled to announce that Dr Sunil Chinnadurai, Associate Professor in the Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering has published a significant research paper titled “Ethereum Blockchain Framework Enabling Banks to Know Their Customers” in the esteemed journal IEEE Access. In his paper, Dr Chinnadurai explores the innovative applications of Ethereum blockchain technology in enhancing customer verification processes within the banking sector. His research addresses the growing need for robust and secure methods for banks to comply with Know Your Customer (KYC) regulations while ensuring customer privacy and data integrity.
This pioneering work contributes to the ongoing discourse on digital transformation in the banking industry and presents a framework that could potentially revolutionise customer onboarding and identity verification practices.
We extend our congratulations to Dr Chinnadurai for this remarkable achievement and look forward to his continued contributions to the field of electrical and electronics engineering. His research not only enhances the academic reputation of SRM University-AP but also paves the way for innovative solutions in the financial sector.
Abstract of the Research
This paper looks at how blockchain technology can improve the Know Your Customer (KYC) process. It aims to make things more open, secure, and unchangeable. Banks can use the Ethereum blockchain to get and keep customer information, which saves time and money. The solution tries to solve problems with KYC procedures making sure banks follow the rules and stop fraud. The central bank will keep a list of all banks and check if they’re doing KYC right. This spread-out approach gives banks a good long-lasting way to bring in new customers.
Explanation of the Research in Layperson’s Terms
Our study seeks to cause a revolution in the Know Your Customer (KYC) process for banks using Ethereum blockchain technology. Current KYC methods take too long, cost too much, and leave room for cheating. Blockchain offers a clear, safe, and unchangeable platform to store customer data letting banks check and confirm identities. This spread-out approach means customers only need to complete the KYC process one time, which saves a lot of time and money for both banks and customers. Also, blockchain’s safety features make sure that private data stays unchanged and safe from people who shouldn’t see it. Our planned system involves the central bank keeping a full list of all banks and watching to make sure they follow KYC rules. In the future, we plan to put our solution on the real Ethereum network and build a working decentralized app. This system promises to make KYC processes faster, safer, and cheaper, giving a strong answer for banks all over the world.
Practical Implementation or the Social Implications associated
Our research puts blockchain tech to work to improve how banks verify customers. This decentralized system gives everyone access to the same current info through a shared record. This cuts down on middlemen and their costs. Smart contracts that run on their own speed up checks with less human involvement. This lowers the chance of data getting out. It makes transactions faster and keeps data safe from changes it shouldn’t have. This new way of checking customers can save money, make customers happier, and follow rules better. It can make people trust banks more by keeping data safer and being more open. It also means banks don’t have to do the same checks over and over, which is better for them and their customers. In the end, our blockchain answer for customer checks aims to make banking safer, smoother, and cheaper. It should also help build more trust in banks overall.
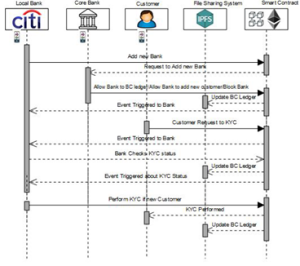
FIGURE 1. Implementation of a blockchain-based KYC process
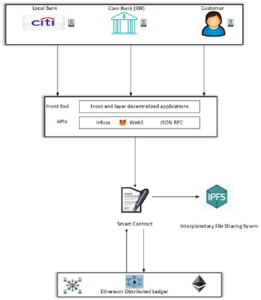
FIGURE 2. Sequential flow diagram illustrating the proposed KYC process using blockchain technology
Future Research Plans
We’re planning to test our idea a lot on the Ethereum network to make sure it works well. We want to build a working DApp that shows our KYC system is doable. We’ll check if people might use it and look at how safe and private it is. By doing this, we hope to make a strong and reliable DApp that’s easy to use, open, safe, and quick. In the end, we want to create something that makes KYC better and sets a new bar for money stuff making banking safer and faster for everyone. Our main goal is to make a system that does not improve how KYC works but also changes how money moves around, making sure banks are safer and work better for people.
- Published in Departmental News, ECE NEWS, News, Research News
Sakura Sangam: Indo Japan Joint Workshop
 In a groundbreaking initiative, the Directorate of IR & HS, along with the Department of Mechanical Engineering and Electrical and Electronics Engineering, successfully hosted the “Sakura Sangam: Indo Japan Joint Workshop,” a two-day virtual event held on July 29 and 30, 2024. This workshop, organised in collaboration with Toyo University, Japan and supported by SRM Global Consulting, aimed to foster academic collaboration and cultural exchange between India and Japan.
In a groundbreaking initiative, the Directorate of IR & HS, along with the Department of Mechanical Engineering and Electrical and Electronics Engineering, successfully hosted the “Sakura Sangam: Indo Japan Joint Workshop,” a two-day virtual event held on July 29 and 30, 2024. This workshop, organised in collaboration with Toyo University, Japan and supported by SRM Global Consulting, aimed to foster academic collaboration and cultural exchange between India and Japan.
During the first day, participants delved into key subjects within Mechanical, Electrical, and Electronics engineering, engaging in dynamic sessions that facilitated knowledge exchange and exploration of the latest advancements in these critical fields. The workshop provided a platform for students and professionals alike to enhance their understanding and contribute to ongoing discussions about innovation and technology.
The second day of the workshop was particularly enriching. It featured talks and seminars highlighting the rich cultural heritage of both nations. Attendees had the unique opportunity to gain a deeper appreciation for the traditions and customs that define the Indo-Japanese relationship. Vice Chancellor Dr Manoj K. Arora explained the meaning of ‘Sakura Sangam.’ He noted that “Sakura” refers to cherry blossoms, which are highly cherished in Japanese culture and symbolise the beauty and fleeting nature of life. ‘Sangam’ means ‘coming together’ in Sanskrit. This introduction set the stage for the workshop’s focus on bringing people together and sharing cultures.
Professor discussed India’s reputation as an IT hub and Japan’s renowned manufacturing expertise. He suggested that by combining these strengths, we could share knowledge and strengthen our bonds. The professor then officially started the workshop with a brief introduction, outlining what we will cover over the next two days.
Dr P Vivekananda Shanmuganathan provided a detailed brief on the research activities at SRMAP, with a particular focus on Mechanical Engineering. He highlighted some of the prominent PhD scholars and their ongoing research projects, showcasing their contributions to advanced topics such as innovative manufacturing processes and robotics. This presentation underscored the university’s dedication to cutting-edge research and its role in advancing the field through the efforts of its talented scholars.
Dr Vitalram Rayankula presented his research on Inverse Kinematics, focusing on the “Two Degree of Freedom Manipulator,” a robotic arm with two independent movements. He discussed the challenges of motion planning, particularly when dealing with line-type obstacles. Dr. Rayankula compared scenarios where the manipulator encounters obstacles without collision to those where collisions occur, highlighting the importance of precise calculations and control algorithms for safe robotic operation.
Dr Kiran Kumar discussed electric vehicles (EVs) and their challenges compared to internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles. He highlighted issues such as the efficiency of ICE components, the longer recharge time for EVs, and the need for additional lead-acid batteries to match the energy density of gasoline. Dr. Kumar emphasized the limitations of current battery technology, which impact the range, weight, and overall efficiency of EVs, while also noting the environmental benefits they offer.
Prof. Shinobu Yamaguchi explored Japan’s changing perspectives regarding India, emphasising the importance of mutual cultural understanding in today’s globalised world. She highlighted how Japan’s view of India has evolved significantly over time.
In addition to technical topics, the workshop also included career-oriented sessions designed to equip students with insights into the professional landscape. Industry experts provided guidance on internships, job prospects, and the latest trends influencing both the Japanese and Indian job markets.
The “Sakura Sangam” workshop proved to be a resounding success, fostering both academic and cultural ties and paving the way for future collaborations between educational institutions in India and Japan.
Dr M Sheikh Mohamed shared insights from his 14-year journey in Japan, focusing on both challenges and growth opportunities.
● Academic Background: Originally from Chennai, Dr. Mohamed completed his B.Sc., M.Sc., and M.Phil. in Biotechnology before moving to Japan.
● Language Challenges: He emphasised the complexity of learning Japanese, especially the kanji script, which can be daunting for newcomers.
● Cultural Adaptation: Dr. Mohamed discussed the importance of mutual respect and understanding in Japan, noting that being polite and helpful can go a long way in overcoming cultural barriers.
● Time Management: He admired the punctuality ingrained in Japanese society, where trains and trams run with remarkable precision.
● Earthquake Preparedness: Recounting an earthquake experience, he observed the calm and orderly manner in which people evacuated buildings, reflecting the nation’s preparedness and resilience.
Thamtoro Elias Dillan, Department of Mechanical Engineering, International Student from Indonesia, provided a detailed account of the key challenges and experiences faced by international students in Japan:
1. Language Barrier: The difficulty of mastering Japanese can be a significant hurdle for international students, impacting daily life and academic success.
2. Student Life: He highlighted the differences in student life between Japan and his home country, including the structure of academic programs and extracurricular activities.
3. Cost of Living: He discussed the relatively high cost of living in Japan, including accommodation, food, and transportation, and offered tips on managing expenses.
4. Location: The choice of university location can greatly affect the student experience, with major cities offering more opportunities but also higher living costs.
5. Help & Support: He stressed the importance of seeking help and support from university resources and local communities to navigate the challenges of living abroad.
Sankar San and Mr. Masahiro Koizumi, Senior Operating Officer of Forum Engineering and Managing Director of Cognavi India, discussed the evolving landscape of educational and career opportunities between Japan and India, focusing on the following aspects:
1. Opportunities in India for Japanese Students: They highlighted the growing interest among Japanese students in India’s IT and engineering sectors, offering diverse opportunities for learning and career growth.
2. Opportunities in Japan for Indian Students: They noted that Japan offers unique opportunities for Indian students, particularly in fields like robotics, engineering, and business management.
3. Identified Gaps: They discussed the gaps in mutual understanding and the challenges students face in adapting to different educational and cultural environments.
4. Changing Trends: They emphasised how initiatives like exchange programs and collaborative projects are bridging these gaps, fostering greater understanding and collaboration.
Sankar San and Jotish San detailed SRM’s strategic initiatives to integrate Japanese language and culture into their curriculum:
● Curriculum Integration: SRM AP has introduced Japanese language courses from the first year, aiming to equip students with the language skills needed for internships and job placements in Japan.
● Destination Japan Program: This program offers students opportunities to experience Japanese culture and work environments, enhancing their global competence.
● Internship and Placement Opportunities: They highlighted partnerships with Japanese companies, providing internships and placements for students, which can be pivotal for career development.
● SRM Group’s Vision: They concluded by sharing SRM’s broader vision of fostering international collaboration and preparing students for a globalized job market.
Ms. Aditi Jain, Director of International Relations and Higher Studies, has eloquently addressed the concept of internationalization and its potential benefits for students from both nations. She highlighted the invaluable partnerships at SRM AP, which foster cross-cultural exchanges and enhance academic collaboration. In her words, “Internationalization not only broadens academic horizons but also cultivates a deeper understanding and appreciation of diverse cultures, preparing students for a globalised world.” These initiatives are not just about enhancing educational experiences; they also empower students to develop a global perspective, essential for succeeding in today’s interconnected environment.
- Published in Departmental News, EEE NEWS, IR-News, Mechanical Engineering NEWS, News
Dr Raviteja K Publishes Book on Sustainable Materials in Civil Infrastructure
 Dr Raviteja K, Assistant Professor in the Department of Civil Engineering, has recently authored a groundbreaking book entitled “Sustainable Materials in Civil Infrastructure.” This publication is set to become a valuable resource for professionals and students in the field, shedding light on the importance of sustainable practices in construction and infrastructure development. His expertise and dedication to promoting environmentally friendly solutions within the realm of civil engineering have culminated in this significant literary contribution. The book delves into the utilization of eco-conscious materials, innovative construction techniques, and the crucial role they play in creating a more sustainable future for infrastructure projects worldwide.
Dr Raviteja K, Assistant Professor in the Department of Civil Engineering, has recently authored a groundbreaking book entitled “Sustainable Materials in Civil Infrastructure.” This publication is set to become a valuable resource for professionals and students in the field, shedding light on the importance of sustainable practices in construction and infrastructure development. His expertise and dedication to promoting environmentally friendly solutions within the realm of civil engineering have culminated in this significant literary contribution. The book delves into the utilization of eco-conscious materials, innovative construction techniques, and the crucial role they play in creating a more sustainable future for infrastructure projects worldwide.
His work is anticipated to inspire a new wave of sustainable practices in the industry and drive positive change towards greener and more resilient civil infrastructure development. Congratulations to Dr. Raviteja K on this remarkable achievement that is sure to make a lasting impact in the field of civil engineering!
Publication details (incl. Publisher, ISBN, Launch date, Edition, etc):
Title: Sustainable Materials in Civil Infrastructure, Publisher: Elseveir, ISBN: 978-0-443-16142-1, Date: July 2024, doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/C2022-0-02477-6.
Brief Introduction the Book:
Sustainable Materials in Civil Infrastructure delves into cutting-edge advancements in eco-materials, offering solutions crucial for building resilient and sustainable infrastructure. It provides profound insights into pioneering research on eco-materials for construction, offering a comprehensive guide on recycled steel, low-carbon concrete, bioconcrete, self-healing concrete, and industrial by-products like fly ash and shape memory alloys. Chapters explore design applications of bioconcrete and the utilisation of eco-materials in landfill liners and masonry, while also addressing obstacles hindering the widespread adoption of green concrete and bioconcrete, proposing practical solutions. This book serves as a cornerstone for the development of sustainable design methodologies, embraced by environmental monitoring bodies worldwide.
Significance of Book
The book “Sustainable Materials in Civil Infrastructure” published by Elsevier is a pivotal resource in the field of sustainable engineering, particularly relevant to my work in developing solutions for geotechnical and geoenvironmental challenges at Sustainable Engineering Research Laboratory (SERL), SRM University AP.
The inclusion of topics such as bioconcrete and the utilization of eco-materials in landfill liners and masonry is particularly significant. Bioconcrete, for instance, exemplifies a pioneering approach by integrating biological processes into construction materials, thereby promoting sustainability and durability. Addressing obstacles to the widespread adoption of green concrete and bioconcrete is also crucial, as it underscores the practical challenges that need to be overcome for these materials to achieve mainstream acceptance.

For my research focus at SERL, this book serves as a cornerstone. It not only provides in-depth insights into the latest research and development in sustainable materials but also offers practical guidance on their design applications and integration into infrastructure projects. Moreover, the emphasis on sustainable design methodologies aligns perfectly with our laboratory’s mission to promote environmentally conscious practices in civil engineering.
Target Audience of the Book
The target audience of the book “Sustainable Materials in Civil Infrastructure” includes a wide range of professionals and researchers involved in civil engineering, sustainability, and materials science. Specifically, the book would be helpful and resourceful for:
Civil Engineers, Researchers and Academics, Environmental Engineers, Policy Makers and Regulatory Bodies, Students, Construction Industry Professionals, and Consultants.
Co-authors
The co-editors include: Thainswemong Choudhury, Lakhveer Singh and Elisa Bertolesi
- Published in CIVIL NEWS, Departmental News, News, Research News
Innovation Alert: Patent on Plant Disease Detection Published by CSE Team
 In an impressive achievement, Dr Ashok Kumar Pradhan, Associate Professor of the Department of Computer Science and Engineering, along with PhD Scholar Ms Ghanta Swetha and BTech CSE students Mr Bandi Sai Harshith, Mr Estamsetty Srikanth, Mr Guduri Venkata Sai Kumar, and Mr Atmakuri Pavan Kumar, has successfully published a patent titled “A SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR AUTOMATED PLANT DISEASE DETECTION.” The application has been officially recognised with Application Number: 202441052706, as recorded in the Patent Office Journal.
In an impressive achievement, Dr Ashok Kumar Pradhan, Associate Professor of the Department of Computer Science and Engineering, along with PhD Scholar Ms Ghanta Swetha and BTech CSE students Mr Bandi Sai Harshith, Mr Estamsetty Srikanth, Mr Guduri Venkata Sai Kumar, and Mr Atmakuri Pavan Kumar, has successfully published a patent titled “A SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR AUTOMATED PLANT DISEASE DETECTION.” The application has been officially recognised with Application Number: 202441052706, as recorded in the Patent Office Journal.
This innovative system aims to revolutionise the agricultural sector by providing an automated mechanism for detecting diseases in plants. Thus, it enhances crop management and ensures healthier yields. The team’s dedication to advancing technology and improving agricultural practices showcases the potential of computer science in solving real-world problems.
The patent not only reflects the hard work and collaboration among the faculty and students but also signifies a step forward in the integration of technology with agriculture. As the world faces challenges related to food security, such innovations play a critical role in safeguarding plant health and agricultural productivity.
Congratulations to Dr Pradhan, Ms Swetha, and the student inventors on this significant milestone in their academic and professional endeavours!
Abstract of the Research:
The innovation that is being presented in this project is a software-based system that is intended to help farmers by offering an automated way to identify plant diseases. This innovation combines a number of technological elements:
Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs): These networks are used to recognise and categorise plant diseases from images of both healthy and sick plants with high accuracy. This is leveraging transfer learning with pre-trained CNN architectures to improve performance even with sparsely annotated data.
MobileNetV2 Architecture: Designed with the specific purpose of classifying agricultural diseases in mind, this model is effective and lightweight, making it ideal for use in resource- constrained settings such as farms.
Weather API Integration: This helps farmers make decisions about crop management and disease prevention by giving them access to real-time weather data.
AI-Powered Website: Acts as a user interface for farmers to communicate with the system, submit plant photos, post queries, and get weather and diagnostic updates.
Chatbot: Utilizes Recurrent Neural Networks (RNN) and Natural Language Processing (NLP) to respond to user inquiries and provide guidance on crop management and disease prevention.
All things considered, this innovation is a system that integrates various software components, artificial intelligence, and data integration to produce a complete tool for raising agricultural productivity and managing diseases.
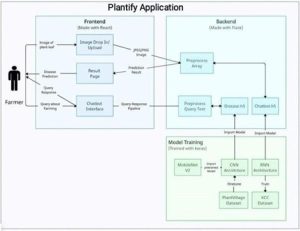
Research in Layperson’s Terms
1. Automated Plant Disease Prediction: Current approaches frequently use traditional diagnostic procedures and manual inspection, which can be laborious and prone to human mistakes. The suggested method uses CNNs to automatically and precisely recognise images, increasing the efficacy and precision of plant disease diagnosis.
2. This project assists farmers in making decisions on crop management and disease prevention by providing them with access to current weather information.
3. Farmers can query various farming issues and receive responses. This is done by leveraging RNNs and NLP.
4. Use of Transfer Learning: The system uses transfer learning to use pre-trained CNN architectures, which enables it to function well even with a small amount of annotated data. Compared to typical machine learning models, which frequently need big datasets and intensive training, this is a major improvement.
Integration with Smart Agriculture Systems: – This method combines disease prediction with smart agriculture systems, allowing for real-time monitoring and decision-making, in contrast to independent diagnostic instruments.
Practical Implementation or the Social Implications Associated
1. Field Diagnosis by Farmers: – Farmers can snap photos of their crops in the fields and instantly receive a disease diagnosis and treatment suggestions by using the platform.
2. Agricultural Extension Services: Using the system, agricultural extension agents may help farmers more effectively by offering guidance and support.
3. Agricultural Research: – Researchers can investigate plant diseases and create novel remedies and management techniques by utilizing the extensive annotated picture library and diagnostic tools.
4. Commercial Farming Operations: – By incorporating the system into their precision agriculture techniques, large-scale farming operations can maximize crop health management and operational effectiveness.
5. Policy Formation and Governance: – Governmental organizations can monitor plant disease outbreaks and create regional or national plans for disease control and prevention using aggregated data from the platform.
Future research plans
We may use privacy and security enhancement tools and techniques to make the data more secure
- Published in CSE NEWS, Departmental News, News, Research News
Faculty and Students Leads to Patent Publication for Intelligent Shelf Management System
 In a groundbreaking collaboration, Dr Banee Bandana Das, Assistant Professor in the Department of Computer Science and Engineering, and Dr Saswat Kumar Ram, Assistant Professor in the Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, have joined forces with Btech-CSE students Mr Rohit Kumar Jupalle, Mr Dinesh Sai Sandeep Desu, and Mr Nikhil Kethavath to develop and patent an innovative invention.,” The team’s invention, titled “A SYSTEM FOR VISION-BASED INTELLIGENT SHELF MANAGEMENT SYSTEM AND A METHOD THEREOF,” has been officially filed and published with Application Number 202441039394 in the Patent Office Journal. This invention showcases the academic excellence and collaborative spirit within the institution, as faculty members and students work together to push the boundaries of technology and create solutions with real-world impact.
In a groundbreaking collaboration, Dr Banee Bandana Das, Assistant Professor in the Department of Computer Science and Engineering, and Dr Saswat Kumar Ram, Assistant Professor in the Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, have joined forces with Btech-CSE students Mr Rohit Kumar Jupalle, Mr Dinesh Sai Sandeep Desu, and Mr Nikhil Kethavath to develop and patent an innovative invention.,” The team’s invention, titled “A SYSTEM FOR VISION-BASED INTELLIGENT SHELF MANAGEMENT SYSTEM AND A METHOD THEREOF,” has been officially filed and published with Application Number 202441039394 in the Patent Office Journal. This invention showcases the academic excellence and collaborative spirit within the institution, as faculty members and students work together to push the boundaries of technology and create solutions with real-world impact.
This significant achievement not only highlights the creativity and dedication of the individuals involved but also underscores the institution’s commitment to fostering a culture of innovation and research. The publication of this invention paves the way for further exploration and development in the field of intelligent shelf management systems, demonstrating the potential for transformative contributions to the industry.
Abstract
This research offers the best solution to improve the business in the retail realm, maintaining On- Shelf Availability (OSA) is vital for customer satisfaction and profitability. Traditional OSA methods face accuracy challenges, prompting a shift to deep learning models like YOLO and CNN. However, data quality remains a hurdle. This research introduces OSA, a novel semi-supervised approach merging ’semi-supervised learning’ and ’on-shelf availability’ with YOLO. It reduces human effort and computation time, focusing on efficient empty-shelf detection. Implementing a Vision-Based Intelligent Shelf Management System empowers retailers with real-time insights, revolutionizing decision-making. The model is optimized for diverse devices and provides practical solutions for efficient retail operations. Balancing model complexity, size, latency, and accuracy, the research paves the way for an advanced, data-driven shelf management approach, contributing to improved shopping experiences and business profitability
Practical Implementation and the Social Implications Associated
1. The present invention is a time-saving method in maintaining the stocks.
2. The use Vision-Based Intelligent Shelf-Management System provide a well alternative in reducing the labor efforts.
3. The system will help in terms of self-management system using machine learning techniques to optimize restocking decisions.
The present invention can be used in shopping malls and business areas for enhancing customer experiences and business and few application areas are:
• Smart City and smart Village
This technique and system can reduce the human efforts in identifying vacant slots for items in business areas and provides necessary inputs to fill the same within a time frame.
• Automobile Industry
The system can be easily integrated with the showrooms to identify the empty spaces and inform to get it fill with products.
Collaborations
SRM AP Faculties and UROP Students
Future research plan
In the future, different deep learning and machine learning methods can be merged to explore better performance in identifying overlapping objects.
- Published in CSE NEWS, Departmental News, ECE NEWS, News, Research News
Dr Soni Wadhwa Publishes Paper on Digital Libraries for Minor Languages in India
 In a significant academic achievement, Dr Soni Wadhwa, Assistant Professor in the Department of Literature and Languages, has recently published a paper titled “Digital Libraries for Minor Languages in India: Frameworks for Addressing Absences in Policy and Governance.” The paper was published in the esteemed Journal Digital Library Perspectives. Dr Wadhwa’s research illuminates the importance of establishing digital libraries for minor languages in India and proposes frameworks to address existing gaps in policy and governance. This pioneering work not only explores the significance of preserving linguistic diversity but also advocates for inclusive and accessible digital resources for all.
In a significant academic achievement, Dr Soni Wadhwa, Assistant Professor in the Department of Literature and Languages, has recently published a paper titled “Digital Libraries for Minor Languages in India: Frameworks for Addressing Absences in Policy and Governance.” The paper was published in the esteemed Journal Digital Library Perspectives. Dr Wadhwa’s research illuminates the importance of establishing digital libraries for minor languages in India and proposes frameworks to address existing gaps in policy and governance. This pioneering work not only explores the significance of preserving linguistic diversity but also advocates for inclusive and accessible digital resources for all.
The publication of this paper not only adds to Dr Wadhwa’s scholarly contributions but also highlights the commitment of SRM University-AP faculty members to engaging in research that can have a positive impact on society.
Abstract
This study aims to deliberate on strategies for enlisting community support for gathering diverse learning resources in different languages and for enlisting participation in activities such as crowdsourcing in initiatives such as annotations and transliteration. This paper calls for interventions that imagine and create infrastructure for the flourishing of smaller libraries that can draw from and feed into large-scale national and international libraries. Offering a conceptual framework to rethink the country’s approach toward minor languages, it first offers an overview of policies and initiatives relevant to the concerns of minor languages in digital libraries in India. Based on the policy analysis, it then goes on to suggest starting points for policy designers and custodians of libraries to help them work toward better representation of languages in their resources.
The existing frameworks analyzed here for the greater or representation of minor Indian languages reveal a culture of silence toward the issue of language. With some advocacy, these frameworks can be mined to craft different ways that are critical not just for enriching libraries but also for preservation of cultural heritage of the communities concerned, thus adding a larger social dimension to the question of access.
Explanation of the Research in Layperson’s terms
Given that Indian languages in general are under-represented on the internet and that languages of minority linguistic groups find very little space on digital platforms, it is imperative for institutions such as libraries to cater to smaller communities and their educational needs while also reaching out to them in their own languages. While a lot of socio-political discourse on minority languages in India exists, this study pushes for their bearing on digital libraries, educational frameworks and cultural heritage. It offers five suggestions for strengthening the presence of minor languages in digital libraries in India.
Details in citation format
Wadhwa, S. (2024), “Digital libraries for minor languages in India: frameworks for addressing absences in policy and governance”, Digital Library Perspectives, Vol. ahead-of-print No. ahead-of-print. https://doi.org/10.1108/DLP-01-2024-0002
Practical Implications
This viewpoint paper can be used to enhance policy and governance around libraries. With National Education Policy 2020, which emphasises the importance of learning in regional/mother/Indian languages, Indian educational system as well as social institutions need stronger platforms to make resources in Indian languages available to students as well as lifelong learners. With more of such research, it will be possible to come up better digital infrastructure for Indian languages.
Social Implications
Indian languages are not widely represented on the Internet and in the knowledge set up. Making existing resources and knowledge available in digital libraries will stimulate further research on generating further research and knowledge production in Indian languages. It is hoped that more research in the domain of Indian languages works towards the digital divide and knowledge divide in India.
Collaborations
This research came out of the researcher’s previous archival work. Her digital archive PG Sindhi Library is dedicated to post-partition Sindhi writing in India. This article is based on an invited talk delivered at the international symposium titled “Digital Libraries: Sustainable Development in Education” held at IIT Kharagpur in India in November 2023. The author is grateful to the organisers and fellow participants for their feedback.
Future Research Plans
The researcher is involved in a sanctioned project titled “Sindhi Sanchaya: Building a Comprehensive and Interactive Database of a Partitioned Literature” funded by IIT Indore. She hopes to build on this work produced in this article as she makes progress in the project.
- Published in Departmental News, English Current Happenings, News, Research News
Groundbreaking Paper Offers Geo-Temporal Visualisation of COVID-19 Spread in India
 In an exciting development, Dr Anirban Ghosh, Dr Anuj Deshpande, and Dr Sibendu Samanta, Assistant Professors from the Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, have recently achieved a significant milestone with the publication of their paper titled “An Indigenous Computational Platform for Nowcasting and Forecasting Non-Linear Spread of COVID-19 across the Indian Sub-continent: A Geo-Temporal Visualization of Data” in the esteemed journal, Procedia Computer Science.
In an exciting development, Dr Anirban Ghosh, Dr Anuj Deshpande, and Dr Sibendu Samanta, Assistant Professors from the Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, have recently achieved a significant milestone with the publication of their paper titled “An Indigenous Computational Platform for Nowcasting and Forecasting Non-Linear Spread of COVID-19 across the Indian Sub-continent: A Geo-Temporal Visualization of Data” in the esteemed journal, Procedia Computer Science.
The paper focuses on the development of a state-of-the-art computational platform specifically tailored for nowcasting and forecasting the non-linear spread of COVID-19 across the Indian sub-continent. This pioneering work promises to offer valuable insights into the geo-temporal visualisation of data related to the COVID-19 pandemic, with potential implications for public health interventions and policy decisions.
The publication of this paper serves as a testament to the innovative research being conducted by the faculty members at the Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering. Their dedication and expertise in the field have not only contributed to advancing scientific knowledge but also hold considerable promise for making a real-world impact in the ongoing fight against the COVID-19 pandemic. We extend our congratulations to Dr Anirban Ghosh, Dr Anuj Deshpande, and Dr Sibendu Samanta for this remarkable accomplishment and look forward to witnessing the continued impact of their research in addressing critical challenges facing the world today.
Abstract
The rapid spread of the COVID-19 pandemic necessitated unprecedented collective action against coronavirus disease. In this light,we are proposing a novel online platform for the visualisation of epidemiological data incorporating social determinants for understanding the patterns associated with the spread of COVID- 19. The current AI computational platform combines modelling methodologies along with temporal, geospatial visualisation of COVID-19 data, providing real-time sharing of graphic analytical simulation of vulnerable hotspots of recurrent (nowcasting) and emergent (forecasting) infections visualised on a spatiotemporal scale on geoportals. The proposed study will be a secondary data analysis of primary data accessed from the national portal (Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR)) incorporating 766 districts in India. Epidemiological data related to spatiotemporal visualisation of the demographic spread of COVID-19 will be displayed using a compartmental socio-epidemiological model, reproduction number R, epi-curve diagrams, as well as choropleth maps for different levels of administrative and development units at the district levels.
Explanation of the Research in Layperson’s Terms
The rapid spread of COVID-19 required quick and coordinated action. To aid the process, we have created a new online platform to help visualise COVID-19 data, including social factors that affect its spread. Our platform uses advanced computer models and shows COVID-19 data over time and across locations. It allows real-time sharing of visual analyses, highlighting areas at risk for current and future infections. The effectiveness of the platform lies in the fact that it is not limited to COVID-19. It can be suitably modified and employed for capturing similar trends for any future pandemic.
Title of the Research in the Citation Format
Priya Ranjan, Dhruva Nandi, Karuna Nidhi Kaur, Rohan Rajiv, Kumar Dron Shrivastav, Anirban Ghosh, Anuj Deshpande, Sibendu Samanta, Rajiv Janardhanan, “An Indigenous Computational Platform for Nowcasting and Forecasting Non-Linear Spread of COVID-19 across the Indian Sub-continent: A Geo-Temporal Visualization of Data”, Procedia Computer Science, Volume 235, 2024, Pages 496-505, ISSN 1877-0509,
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2024.04.049
Practical Implementation and Social Implications Associated
As mentioned earlier, the platform can be used to present real-time data analysis and identify emerging and current hotspots of the COVID-19 pandemic. However, the beauty or robustness of the platform lies in the fact that it can be suitably adapted for similar analysis for any future pandemic with minimum effort.
Collaborations
- University of Petroleum and Energy Studies, Energy Acres, Dehradun, Uttarakhand, India
- SRM Medical College Hospital and Research Centre, SRMIST, Kattankulathur, Tamil Nadu, 603203, India
- Amity Institute of Public Health, Amity University, Noida, Uttar Pradesh, 201303, India
Future Research Plans
The future plan includes improving the visual and graphical presentation of the platform to provide more insightful and intuitive information. Aggregation of data from other international databases would further augment the effectiveness of the platform by not limiting it to only the national scenario.
- Published in Departmental News, ECE NEWS, News, Research News
Dr Sanjay Kumar and Team Publish Digital Image Security Invention in the Patent Office Journal
 In a recent development, Dr Sanjay Kumar, Assistant Professor in the Department of Computer Science and Engineering, along with a team comprising N Ujwala, J Yashwanth Sri Ram, J Lakshmi Prasanna Kumar, and K Heman Rai Choudhary, have successfully filed and published an innovative invention in the Patent Office Journal titled “SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR DISCRETE WAVELET TRANSFORM (DWT)-BASED SECURE IMAGE WATERMARKING” with the application number “202441045387”.
In a recent development, Dr Sanjay Kumar, Assistant Professor in the Department of Computer Science and Engineering, along with a team comprising N Ujwala, J Yashwanth Sri Ram, J Lakshmi Prasanna Kumar, and K Heman Rai Choudhary, have successfully filed and published an innovative invention in the Patent Office Journal titled “SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR DISCRETE WAVELET TRANSFORM (DWT)-BASED SECURE IMAGE WATERMARKING” with the application number “202441045387”.
This invention holds great promise in the field of digital image security and watermarking. The patented system and method are based on the discrete wavelet transform (DWT), a widely used signal processing technique, to embed secure watermarks into digital images. The application of DWT ensures that the watermarking process is robust and secure, making it suitable for a wide range of applications where image integrity and authenticity need to be ensured.
Dr Sanjay Kumar’s expertise as an Assistant Professor, coupled with the team’s skills and dedication, has resulted in the successful development and patenting of this cutting-edge technology. The “SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR DISCRETE WAVELET TRANSFORM (DWT)-BASED SECURE IMAGE WATERMARKING” promises to be a significant addition to the field of digital image security and watermarking, offering enhanced protection against unauthorised tampering and misuse of digital images. It is expected that this invention will garner attention from industry professionals, researchers, and policymakers, paving the way for its integration into diverse digital imaging systems.
Abstract
Our research introduces a robust image watermarking technique that combines Discrete Wavelet Transform (DWT) and chaotic map-based encryption. The method analyzes high-frequency sub-bands derived from DWT applied to the blue channel of an RGB image, selecting the block with the highest energy for embedding a grayscale watermark encrypted with the Henon Map. The alpha blending technique is used to integrate the encrypted watermark, ensuring both imperceptibility and robustness. The method achieves an average PSNR of 43.7211 dB and SSIM of 0.9950. The watermark can be extracted by analyzing patterns in the high-frequency component, even after various attacks, using inverse DWT and Henon Map for decryption.
Explanation of the Patent in Layperson’s Terms
Our research focuses on protecting digital images by embedding a hidden watermark that is hard to remove. We use a mathematical method called the Discrete Wavelet Transform (DWT) to break down an image into different parts and find the best place to hide the watermark. The watermark is further secured by encrypting it with a technique called the Henon Map. Our method ensures that the watermark remains invisible to the naked eye while being resistant to tampering. This means the watermark can be detected and recovered even if the image is altered.
Practical Implementation and the Social Implications
The primary application of our research is in protecting the ownership and integrity of digital images. This technique can be used by photographers, artists, and digital content creators to ensure their work is not copied or altered without permission. By embedding a secure, invisible watermark, they can prove ownership and detect unauthorised use. Additionally, this method can be applied in sensitive fields such as medical imaging and legal documents where tamper detection is crucial.
Collaborations
This research was conducted by the Visual Information Processing Lab at the Department of Computer Science and Engineering, SRM University AP, Guntur, India. The team comprised Nadella Ujwala, Sanjay Kumar, Jayyavarapu Yaswanth Sri Ram, Jetti Lakshmi Prasanna Kumar, and Katragadda Heman Rai Choudhary.
Future Research Plans
Our future research will focus on enhancing the watermarking technique’s robustness against more sophisticated attacks, exploring real-time applications in video watermarking, and developing methods to embed multiple watermarks in a single image. We also aim to reduce the computational complexity to make the algorithm more efficient for practical applications.
- Published in CSE NEWS, Departmental News, News, Research News
CSE Academic Innovators File Patent for AI-Powered Refrigeration System
 In a significant development for the field of artificial intelligence and sustainable technologies, Dr Subhankar Ghatak, Dr Aurobindo Behera, Assistant Professor, and Ms Samah Maaheen Sayyad, an undergraduate student from the Department of Computer Science and Engineering, have collectively filed a patent for an “Artificial Intelligence (AI) Enabled Refrigeration System.” The patent, bearing the Application Number 202441036548, has been officially published in the Patent Office Journal, marking a milestone in their academic and research careers.
In a significant development for the field of artificial intelligence and sustainable technologies, Dr Subhankar Ghatak, Dr Aurobindo Behera, Assistant Professor, and Ms Samah Maaheen Sayyad, an undergraduate student from the Department of Computer Science and Engineering, have collectively filed a patent for an “Artificial Intelligence (AI) Enabled Refrigeration System.” The patent, bearing the Application Number 202441036548, has been officially published in the Patent Office Journal, marking a milestone in their academic and research careers.
This innovative refrigeration system promises to enhance efficiency and reduce energy consumption, potentially revolutionising the way we preserve food and other perishables. The team’s dedication to integrating AI into practical applications is a testament to their commitment to advancing technology for the betterment of society. The academic community and industry experts alike are eagerly anticipating further details on the implementation and impact of this patented technology.
Abstract
The invention is an advanced smart and AI-enabled refrigerator that seamlessly integrates device and software components. Key features include automatic quantity detection, a reminder system, a spoiler alert system, an inbuilt voice system, an inbuilt barcode scanner, an emotion detection system, and a personalised recipe recommendation system based on user preferences, weather conditions, season, location, and precise quantity measurements.
Research in Layperson’s Terms
The invention represents a groundbreaking improvement in traditional refrigerators, providing a new and enriched user experience through AI integration. It addresses food management, user interaction, and personalised recipe recommendations, incorporating user preferences, weather considerations, seasonal variations, location-specific nuances, and accurate quantity measurements.
Practical implementation and the social implications associated with it
The practical implementation of the “AN ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE (AI) ENABLED REFRIGERATION SYSTEM ” involves the seamless integration of advanced hardware and sophisticated AI algorithms to create an intelligent and user-friendly refrigerator. The following steps outline the practical implementation:
Hardware Integration:
Sensors: Install advanced sensors, including thermistors for temperature, humidity sensors, barcode scanners, ultrasonic quantity measurement sensors, cameras, spoilage identification sensors, level sensors, defrost sensors, and weight sensors within the refrigerator compartments.
Voice and Emotion Detection Modules: Incorporate a microphone and speaker system for voice interaction and integrate cameras and emotion analysis algorithms for facial recognition and emotion detection.
Connectivity Components: Equip the refrigerator with Wi-Fi or Bluetooth modules to enable seamless data transfer and communication with other smart devices.
Processor and Memory: Utilize a powerful processor and ample memory to support AI algorithms, data processing, and smooth operation.
Display Panel: Implement an LED or touchscreen display for user interaction, providing real-time information and control over the refrigerator’s functionalities.
Software Development:
AI Algorithms: Develop and integrate AI algorithms for automatic quantity detection using computer vision, sentiment analysis for emotion detection, and collaborative filtering for personalised recipe recommendations.
Natural Language Processing (NLP): Implement NLP algorithms to enable the inbuilt voice system to understand and respond to user commands effectively.
Image Recognition Software: Utilize image recognition software to accurately read barcodes and analyse visual data from the integrated cameras.
Connectivity Software: Develop software protocols to ensure reliable wireless communication between the refrigerator and other devices or cloud services.
User Interface Software: Design a user-friendly interface for the display panel, allowing users to interact with and manage refrigerator contents easily.
Social Implications:
The “AI Enabled Refrigeration System” invention has several profound social implications:
1. Reduction in Food Wastage: The automatic quantity detection, reminder system, and spoilage alert system significantly reduce food wastage by ensuring that users are alerted about unused items and potential spoilage. This contributes to more efficient food management and a reduction in household food waste, addressing a critical global issue.
2. Enhanced Food Safety and Health: By providing real-time alerts about food spoilage and precise quantity measurements, the invention ensures that users consume fresh and safe food. This minimizes health risks associated with consuming spoiled food and promotes overall well-being.
3. Personalized Dietary Support: The personalized recipe recommendation system caters to individual dietary preferences and requirements, promoting healthier eating habits. By suggesting recipes based on user preferences, weather conditions, seasonality, and location, the system encourages balanced and nutritious meal planning.
4. Convenience and Efficiency: The inbuilt voice system, emotion detection, and intuitive user interface enhance the convenience and efficiency of managing refrigerator contents. Users can easily access information, receive reminders, and interact with the refrigerator, making food storage and preparation more streamlined.
5. Technological Advancements: The integration of advanced AI technologies in everyday appliances like refrigerators represents a significant step forward in smart home innovation. This can drive further advancements in the field, encouraging the development of more intelligent and interconnected household devices.
6. Environmental Impact: By promoting efficient food management and reducing wastage, the invention indirectly contributes to environmental sustainability. Less food waste translates to lower carbon footprints and reduced strain on food production resources, aligning with global efforts to combat climate change.
Overall, the “AI Enabled Refrigeration System” invention not only offers practical benefits in terms of food management and user convenience but also holds significant social implications by promoting health, reducing waste, and advancing technological innovation in household appliances.
Future Research Plans
Building on the innovative foundation of the “AN ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE (AI) ENABLED REFRIGERATION SYSTEM, ” future research plans involve enhancing the AI algorithms for even greater accuracy in food quantity detection, spoilage prediction and personalised recipe recommendations. This includes exploring more advanced machine learning techniques and incorporating real-time feedback mechanisms to continuously refine the system’s performance. Additionally, research will focus on integrating the refrigerator with broader smart home ecosystems, allowing for seamless interaction with other smart appliances and IoT devices to create a fully connected kitchen experience. Investigations into more sustainable and energy-efficient sensor technologies will also be pursued to further reduce the environmental footprint of the device. Finally, extensive user studies will be conducted to gather feedback and insights, ensuring that the next iterations of the refrigerator are even more aligned with consumer needs and preferences, ultimately driving widespread adoption and maximising the social benefits of this technology.
Pictures Related to the Research
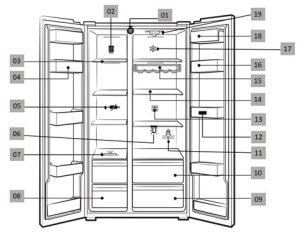
Fig 1: Schematic Arrangement of various Components for adequate operation of the proposed scheme
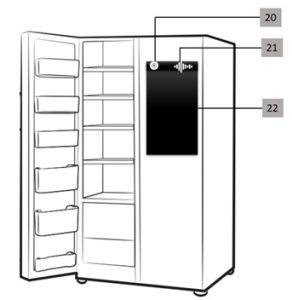
Fig 2: Schematic Arrangement of various Components for user interaction
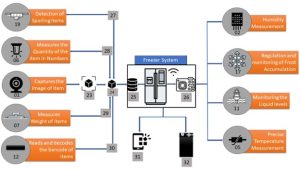
Fig 3: Schematic representation of working of various components in the freezer system
• Pointer Number-27: Spoilage Detection Sensor (19) detects the item that is being spoiled and maps to particular item for alerting the user with the help of the capturing Device (01) and the info associated with that particular item like Expiry date etc.
• Pointer Number-28: The Ultra Sonic Quantity Measurement Sensor (06) senses the quantity of the ITEM “x” (24), and the camera (01) is used to identify what is ITEM “x” through (23).
• Pointer Number-29: Weight Sensor (07), using newly captured item ITEM “x” (24) by capturing device (01), identifies the weight of that item by subtracting the weight obtained after the addition of that item with the initial holding by the cabinet and attaching the value with corresponding ITEM “x” (24).
• Pointer Number-30: Barcode Scanner (12) scans the Barcode associated with the item and maps the corresponding information with that particular item with the help of the capturing device (01).
• Port Number-31: Mobile Application.
- Published in CSE NEWS, Departmental News, News, Research News
Chetna: Awakening Mathematical Minds
 The Department of Mathematics at SRM University-AP successfully conducted a two-week summer programme “Chetna: Awakening Mathematical Minds” from June 17th to June 28th, 2024. This programme aimed to inspire and enhance mathematical understanding among participants from various parts of the country. The programme saw enthusiastic participation from 25 students hailing from different states across India, including West Bengal, Assam, Kerala, Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, Maharashtra, Gujarat, Delhi and Andhra Pradesh.
The Department of Mathematics at SRM University-AP successfully conducted a two-week summer programme “Chetna: Awakening Mathematical Minds” from June 17th to June 28th, 2024. This programme aimed to inspire and enhance mathematical understanding among participants from various parts of the country. The programme saw enthusiastic participation from 25 students hailing from different states across India, including West Bengal, Assam, Kerala, Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, Maharashtra, Gujarat, Delhi and Andhra Pradesh.
The programme featured a diverse curriculum, covering a wide range of mathematical topics. Eleven subjects were taught by eleven distinguished faculty members from the Department of Mathematics. The subjects provided a broad and enriching mathematical experience, designed to ignite a passion for mathematics in the participants.
Insights of the Two-Week Programme
First Week Highlights
1. Number Theory by Prof. Kalyan Chakraborty
The first week began with an in-depth exploration of Number Theory. Prof. Kalyan Chakraborty introduced participants to fundamental concepts such as divisibility, prime numbers, and modular arithmetic. The engaging sessions provided a strong foundation in understanding the properties and applications of numbers.
2. Abstract Algebra by Dr Anirban Bose
Dr Anirban Bose led the sessions on Abstract Algebra, diving into structures like groups, rings, and fields. The course covered essential algebraic concepts and their applications, enhancing the participants’ problem-solving skills and theoretical knowledge.
3. Linear Algebra and Basic Operators by Dr Animesh Bhandari
Dr Animesh’s lectures on Linear Algebra included topics such as vector spaces, linear transformations, and matrices. The sessions aimed to build a solid understanding of linear systems and the role of operators in mathematical computations.
4. Graph Theory by Dr Fouzul Atik
Graph Theory, taught by Dr Fouzul Atik, introduced participants to the study of graphs, which are mathematical structures used to model pairwise relations between objects. Topics included graph traversal, connectivity, and graph colouring, providing insights into the practical applications of graph theory.
5. Ordinary Differential Equation by Dr Nityananda Roy
The week concluded with Dr Nityananda Roy’s sessions on Ordinary Differential Equations (ODEs). This course covered methods of solving first-order and higher-order ODEs, along with real-world applications of differential equations in various fields.
Second Week Highlights
1. Advanced Algebra by Dr Kalyan Banerjee
Building on the first week, this subject delved deeper into algebraic structures, including advanced group theory and ring theory, preparing students for research-level problems.
2. Metric Spaces by Dr Choiti Bandyopadhyay
Dr Choiti’s sessions on Metric Spaces introduced participants to the concepts of distance and convergence in metric spaces. Topics included open and closed sets, continuity, and compactness, providing a deeper understanding of analysis.
3. Foundations of Probability and Statistics by Dr Vijayakrishna Rowthu
Dr. Vijayakrishna covered the Foundations of Probability and Statistics, focusing on probability theory, random variables, and statistical inference. The course aimed to equip participants with the skills needed to analyze and interpret data.
4. Mathematical Modelling by Dr Tapan Kumar Hota
Dr. Tapan’s lectures on Mathematical Modelling demonstrated how mathematics can be used to represent, analyse, and solve real-world problems. The course included case studies and practical applications in various disciplines.
5. Partial Differential Equation by Dr Ram Baran Verma
The sessions on Partial Differential Equations (PDEs) by Dr Ram Baran explored methods of solving PDEs and their applications in physics and engineering. Topics included separation of variables, Fourier series, and boundary value problems.
6. Math Education by Dr Jayasree Subramanian
The final course on Math Education, taught by Dr Jayasree, focused on pedagogical approaches and techniques for teaching mathematics effectively. The sessions aimed to inspire future educators and enhance their teaching methodologies.
Conclusion
The “Chetna: Awakening Mathematical Minds” summer programme was a resounding success, providing participants with valuable insights and knowledge in mathematics. The diverse backgrounds of the participants and the expertise of the faculty created a vibrant and stimulating learning environment, fostering a deeper appreciation for the subject. The Department of Mathematics at SRM University -AP looks forward to organising similar programmes in the future to continue inspiring young mathematical minds across the country.
- Published in Departmental News, Math News, News














