Research News
- Colonial Impact on Pastoral Nomads and Caravan Traders in India July 26, 2022
 Cultural and Post-colonial studies enclose various historical approaches. It ranges from cultural studies and comparative social history to analysis of the means of domination and resistance. Nevertheless, there are communities that didn’t get the space they deserve in the studies of settled communities. Assistant Professor Dr Bikku R from the Department of Liberal Arts published a paper titled Colonial Impact on Pastoral Nomads and Caravan Traders in India: The Raika and the Banjara to analyse the aftereffects of colonialism in the most unexplored communities. The article was published in the book Tribe, Space, and Mobilisation.
Cultural and Post-colonial studies enclose various historical approaches. It ranges from cultural studies and comparative social history to analysis of the means of domination and resistance. Nevertheless, there are communities that didn’t get the space they deserve in the studies of settled communities. Assistant Professor Dr Bikku R from the Department of Liberal Arts published a paper titled Colonial Impact on Pastoral Nomads and Caravan Traders in India: The Raika and the Banjara to analyse the aftereffects of colonialism in the most unexplored communities. The article was published in the book Tribe, Space, and Mobilisation.Abstract
The Raika of Rajasthan and the Banjara or Lambadi tribe of the Deccan region had been self-sustained as nomadic pastoralists and caravan traders, respectively, in pre-British India. Colonial policies imposed several restrictions on nomadic communities and their economic activities by branding them as ‘criminals’ under the Criminal Tribes Act of 1871. As a result, many of the nomadic communities lost their cultural economy and struggled to survive. Colonial and post-colonial studies have primarily focused on settled communities. However, little attention is paid to pastoral nomads and itinerary communities. The present paper focuses on the transformation of traditional nomadic livelihoods, culture, and economy of the two communities; the Raika pastoralist and the Banjara traditional caravan traders and livestock breeders’ as a consequence of colonial policies. It also emphasises current livelihood strategies. Empirical data resulting from ethnographic fieldwork and colonial and post-colonial literature have been examined. An ethnographic study among the Banjaras from the Deccan region during the year 2009- 2010 and the Raika of Rajasthan between 2013- 2015 and 2019 helped to understand their past and present situations. Colonial and post-colonial policies, governance, and their impact on pastoralists and other nomadic communities have been critically examined.
Continue reading → - Sustainable IoT system for freshwater pearl farming July 26, 2022
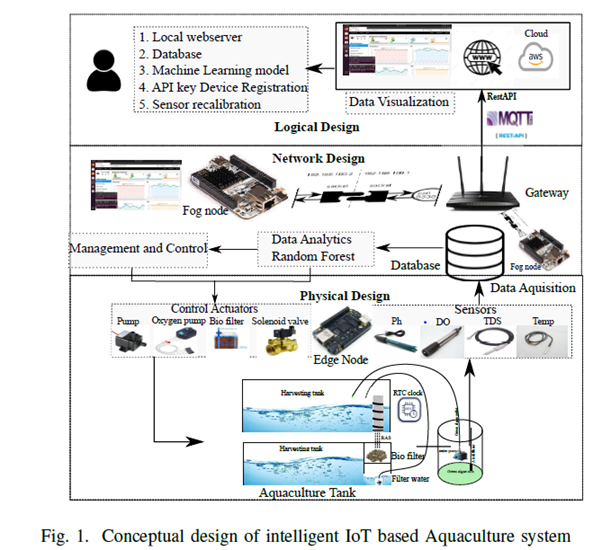
The Department of Computer Science Engineering is glad to announce that Dr Kshira Sagar Sahoo, Assistant Professor, has published an article titled ‘Sustainable IoT Solution for Freshwater Aquaculture Management’ in the Q1 journal, IEEE Sensors, having an Impact Factor of 4.325. The research was published in collaboration with Munesh Singh, from the Department of Computer Science and Engineering, PDPM IIITDM Jabalpur Campus, Madhya Pradesh, and Anand Nayyar, Graduate School, Faculty of Information Technology, Duy Tan University, Vietnam.
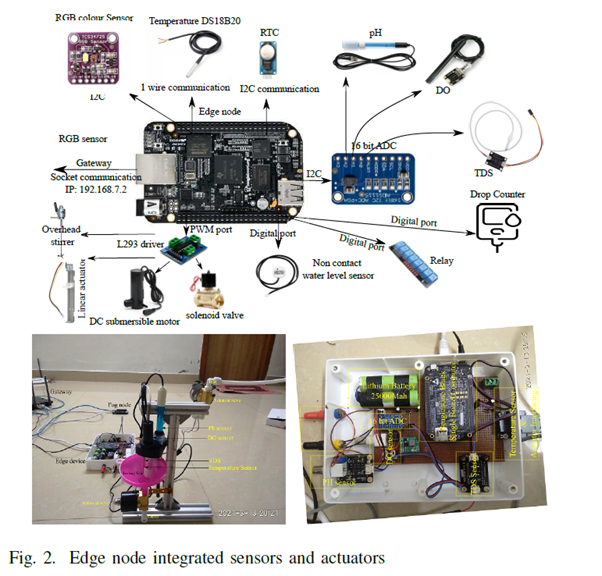 Freshwater pearl farming has the potential to generate an alternative source of income for small farmers. Indian freshwater river bodies have 51 types of species that can produce pearls. Still, India imports 2.4 billion dollars’ worth of pearls from China and Japan. To reduce the import burden on the Indian economy, the government encouraged the farmers to do integrated freshwater pearl farming. Aquaculture-based farming needs a small investment for the initial setup. Although the Indian government promotes aquaculture-based farming through subsidies and free training programs, farmers find it difficult to get success in aquaculture-based farming.
Freshwater pearl farming has the potential to generate an alternative source of income for small farmers. Indian freshwater river bodies have 51 types of species that can produce pearls. Still, India imports 2.4 billion dollars’ worth of pearls from China and Japan. To reduce the import burden on the Indian economy, the government encouraged the farmers to do integrated freshwater pearl farming. Aquaculture-based farming needs a small investment for the initial setup. Although the Indian government promotes aquaculture-based farming through subsidies and free training programs, farmers find it difficult to get success in aquaculture-based farming.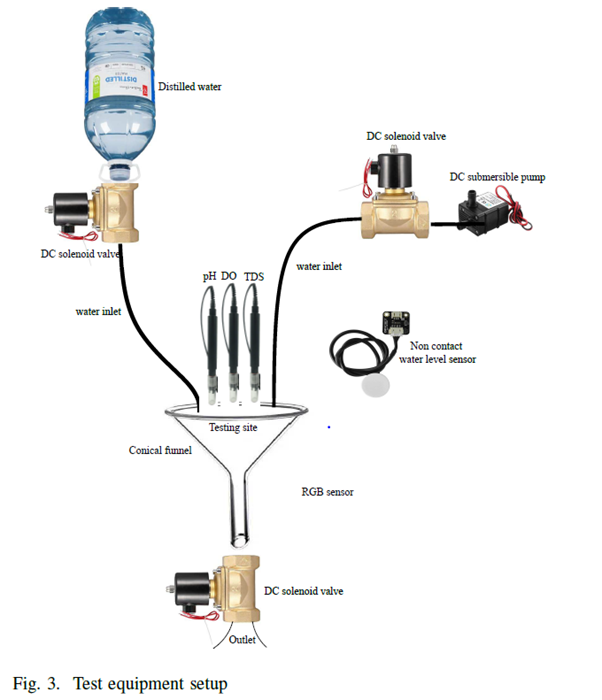 The paper proposes a comprehensive IoT system for freshwater pearl farming which has an intelligent control system for maintaining the aquaculture environment. The proposed system monitors and supports the habitable underwater environments for aquaculture. To train the farmers and educate them in pearl farming business is a time taking and skill-oriented job. The comprehensive IoT system will encourage farmers for freshwater pearl farming and proper utilisation of the government subsidy granted for aqua farming. In future, the researchers will consider more relative water parameters for robust forecast and analyse the best model for predictive analysis.
The paper proposes a comprehensive IoT system for freshwater pearl farming which has an intelligent control system for maintaining the aquaculture environment. The proposed system monitors and supports the habitable underwater environments for aquaculture. To train the farmers and educate them in pearl farming business is a time taking and skill-oriented job. The comprehensive IoT system will encourage farmers for freshwater pearl farming and proper utilisation of the government subsidy granted for aqua farming. In future, the researchers will consider more relative water parameters for robust forecast and analyse the best model for predictive analysis.Abstract of the Research
In recent years, we have seen the impact of global warming on changing weather patterns. The changing weather patterns have shown a significant effect on the annual rainfall. Due to the lack of annual rainfall, developing countries like India have seen a substantial loss in annual crop production. Indian economy largely depends on agro products. To compensate for the economic loss, the Indian government encouraged the farmers to do integrated aquaculture-based farming. Despite government subsidies and training programs, most farmers find it difficult to succeed in aquaculture-based farming. Aquaculture farming needs skills to maintain and monitor underwater environments. The lack of skills for monitoring and maintenance makes the aquaculture business more difficult for farmers. To simplify the pearl farming aquaculture, we have proposed an Internet of Things (IoT)-based intelligent monitoring and maintenance system. The proposed system monitors the water quality and maintains an adequate underwater environment for better production. To maintain an aquaculture environment, we have forecasted the change in water parameters using an ensemble learning method based on random forests (RF). The performance of the RF model was compared with the linear regression (LR), support vector regression (SVR), and gradient boosting machine (GBM). The obtained results show that the RF model outperformed the forecast of the DO with 1.428 mean absolute error (MAE) and pH with 0.141 MAE.
- Pre-existing health conditions and the risk of Covid-19 July 26, 2022
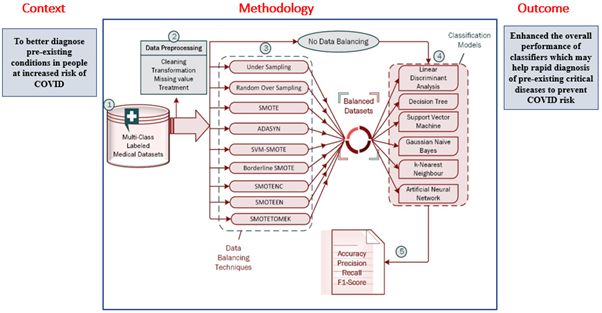 Individuals with pre-existing medical conditions are more vulnerable to Covid-19 and its variants. Patients in countries like India require early testing to diagnose crucial disorders to reduce the risk. Research at the Department of Computer Science and Engineering has come up with a system that automatically identifies and categorises diseases based on the patient’s medical test results. Assistant Professor Dr Ravi Kant Kumar published a paper Improving Performance of Classifiers for Diagnosis of Critical Diseases to Prevent COVID Risk as a co-author in the Q1 journal Computers and Electrical Engineering and has an impact factor of 4.152. With an accurate diagnosis, the required actions can be planned and executed to stop the patients from serious health issues as well as covid risk.
Individuals with pre-existing medical conditions are more vulnerable to Covid-19 and its variants. Patients in countries like India require early testing to diagnose crucial disorders to reduce the risk. Research at the Department of Computer Science and Engineering has come up with a system that automatically identifies and categorises diseases based on the patient’s medical test results. Assistant Professor Dr Ravi Kant Kumar published a paper Improving Performance of Classifiers for Diagnosis of Critical Diseases to Prevent COVID Risk as a co-author in the Q1 journal Computers and Electrical Engineering and has an impact factor of 4.152. With an accurate diagnosis, the required actions can be planned and executed to stop the patients from serious health issues as well as covid risk.Abstract
The risk of developing COVID-19 and its variants may be higher in those with pre-existing health conditions such as thyroid disease, hepatitis C virus (HCV), breast tissue disease, chronic dermatitis, and other severe infections. As a result, early and precise identification of these disorders is critical. A huge number of patients in nations like India require early and rapid testing as a preventative measure. Machine learning methods for automatically identifying and classifying diseases have been created, and they function effectively when the dataset is well specified and balanced at every class level, including “no disease”. The problem of imbalance arises from the skewed nature of data, in which a large number of cases belonging to one class (known as the majority class) are classified correct, while the other class (known as the minority class) has lesser instances; is unfortunately misclassified by many classifiers. When it comes to human life, this kind of misclassification is unacceptable. To solve the misclassification issue and improve accuracy in such datasets, we applied a variety of data balancing techniques to several machine learning algorithms. The outcomes are encouraging, with a considerable increase in accuracy. As an outcome of these proper diagnoses, we can make plans and take the required actions to stop patients from acquiring serious health issues or viral infections.
Explanation of the research
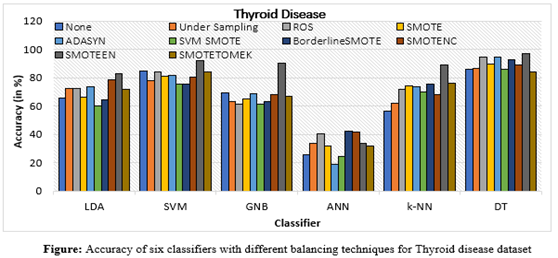 Lethal COVID-19 and its mutant forms may be more likely to arise in patients with pre-existing medical conditions such as thyroid illness, hepatitis C virus (HCV), breast tissue disease, chronic dermatitis, compromised immune systems, obesity, diabetes, heart disease, cancer, etc. For patients, an early and accurate diagnosis of these illnesses is crucial. Based on patient data, machine learning algorithms can assist in the early and quick detection of numerous diseases in a huge population like India. On the other side, machine learning algorithms perform poorly when a dataset has a class unbalanced problem. As a result, we used a variety of smote and its variants in this study to address the problems about the imbalanced class size. The experimental work showed that all six classifiers (DT, SVM, LDA, k-NN, GNB, and ANN) performed better overall on clinical datasets when class balancing strategies and classification techniques were combined. It recommends the use of the recommended classifications and class balancing technique with regard to specific data to identify the disease accurately and automatically
Lethal COVID-19 and its mutant forms may be more likely to arise in patients with pre-existing medical conditions such as thyroid illness, hepatitis C virus (HCV), breast tissue disease, chronic dermatitis, compromised immune systems, obesity, diabetes, heart disease, cancer, etc. For patients, an early and accurate diagnosis of these illnesses is crucial. Based on patient data, machine learning algorithms can assist in the early and quick detection of numerous diseases in a huge population like India. On the other side, machine learning algorithms perform poorly when a dataset has a class unbalanced problem. As a result, we used a variety of smote and its variants in this study to address the problems about the imbalanced class size. The experimental work showed that all six classifiers (DT, SVM, LDA, k-NN, GNB, and ANN) performed better overall on clinical datasets when class balancing strategies and classification techniques were combined. It recommends the use of the recommended classifications and class balancing technique with regard to specific data to identify the disease accurately and automaticallyFor this work, Dr Ravi Kant Kumar has collaborated with Mr Vinod Kumar, Koneru Lakshmaiah Education Foundation, Vaddeswaram,India, and Mr Gotam Singh Lalotra, University of Jammu, India. Their future research will investigate and design the most effective multi-class balancing method to address the multi-class imbalance problem in medical data.
Continue reading → - Decoding the problematic narratives in mainstream Queer cinema July 19, 2022
 The trajectory of trans representation in cinema is essentially critical since the predominant viewers belong to the heteronormative cisgender public. Visual media played a massive role in inculcating the idea of gender identity into the preconditioned entity of heteronormativity. The skill and sympathy of the filmmaker in handling trans issues hold a significant chunk of this representational politics.
The trajectory of trans representation in cinema is essentially critical since the predominant viewers belong to the heteronormative cisgender public. Visual media played a massive role in inculcating the idea of gender identity into the preconditioned entity of heteronormativity. The skill and sympathy of the filmmaker in handling trans issues hold a significant chunk of this representational politics.The popular media in Kerala has reconfigured its space to include people with gender non-conforming identities and sexual orientation as a matter of concern in contemporary times. However, there are times when the filmmakers fail to understand the assignment. The new research chapter of Assistant Professor Dr Anu Kuriakose, Department of English, articulates the discomfort of seeing the misrepresentation of transgender identity in mainstream cinema. The chapter titled The Hetero- Normalisation of Transgender Identity: A Critique on Njan Marykkutty was published by Cambridge Scholars Publishers, UK (WoS) and belongs to the book Theory and the Transformative Humanities.
Problems that face the humanities discipline today have sparked an intense debate across the globe. The Theory of the transformative humanities envisions a domain of inquiry that attempts to transform cultures, individuals, and society. This volume explores different theoretical perspectives and practical orientations through which to perceive, innovate and transform the world in which we live. It opens diverse fields of thinking and research. It offers a broader perspective on how a critical-literary approach could be deployed in addressing the multidimensional and evolutionary nature of the humanities in a way that caters to the needs of the present. A compilation of scholarly essays on topics as diverse as post-millennial theory, trans-humanities, posthumanism, interdisciplinarity, psychoanalysis, and film studies, the book provides an enabling platform for intellectuals, research scholars, and experts in the humanities to tap into the transformative potential of the field.
This chapter critically examines the representational politics of the central transgender character Marykkutty in the 2018 Malayalam film Njan Marykutty. The release of this film marked an unprecedented debate on transgender identity in Kerala’s public sphere, more specifically, about transwomen’s visibility in the public sphere. This is quite significant, as it has been a moment of the culmination of various activist, academic, and governmental interventions in the state attempt to mainstream the trans identity from the margins of society. She has used visual and thematic analysis as a method to critically look at the visualization of a trans feminine body in this film. The chapter analyses the trans identity in terms of Judith Butler’s theory of gender performativity, Julia Kristeva’s ‘abject,’ and Jacques Lacan’s notion of ‘object petit a’ or object of desire. It is argued that the excess in normalisation of the transgender body ironically endorses the heterosexual values of the binary gender performance when the surgically re-appropriated body is celebrated, clapped on the big screen, and sensationalised as an achievement when the central character themselves voices, “I am not a transgender, I am a transsexual.”
Heteronormativity safeguards the normalisation of heterosexuality through myriad practices so as to concrete the notion of a legitimate form of sexuality. Dr Anu Kuriakose attempts to denaturalise and denormalise the excessive lauding of heterosexuality in cinema to open up a less distorted corridor to queer desires and identity.
Continue reading → - Project Sanctioned by Indian National Science Academy July 18, 2022

Yet another moment of pride and honour for SRM University-AP as the Indian National Science Academy (INSA, New Delhi) has sanctioned the Project “Nalanda and Bodhgaya: Understanding the past environment and transnational networks of the World Heritage Sites” to Dr Sharmishtha Chatterjee, Assistant Professor, Department of History with a total outlay of Rs 5 lakhs. The co-investigator of the project is Dr Amrita Saha, Associate Professor and Deputy Director, Amity Institute of Environmental Sciences and Amity Institute of Social Sciences, Amity University, Kolkata. The project is a pioneering initiative to make a comprehensive study of the landscape and environmental factors (physical and cultural) governing the Buddhist World Heritage Sites of Nalanda and Bodhgaya (Bihar, India).
One of the first attempts in South Asia to understand monasteries and monastic complexes in relation to the landscape parameters, the work is distinctive in its scope and methodology because of its multidisciplinary approach involving archaeology, history, and environmental science. It aims for a holistic understanding of the sites and the region. Bodhgaya and Nalanda are two major Buddhist sites of India, the first marking the site of enlightenment of Gautama Buddha and the other being one of the oldest educational institutes of ancient times. Both the sites have been witnessing travellers, pilgrims, students, and religious preachers from the farthest corners of the world.
The foremost objective is to investigate the environmental settings (location, settlement geography, palaeolandscape features, layout of the monastic complexes, dietary patterns) of the monastic sites. This will be executed through the generation of a series of maps by superimposing colonial site plans, old maps, satellite imageries and corroboration of the same with extensive field surveys. The scientific study of the topographic delineations, soil samples, and artefactual evidences would be undertaken in the course of the study.
These attempts would generate a detailed study of the regular lives in the two monastic complexes along with the social and cultural ties established with the lesser-known monasteries and villages of the hinterland area. The project also seeks to explore the local, national, and transnational networks emanating from the sites, thus contributing to a global networking. The project is expected to create frameworks for extending the study to the other monastic complexes across South and Southeast Asia. In the long run the work will be published in the form of an annotated atlas featuring the monastic complexes, the wider geographical hinterland, and the transnational networks between India and Southeast Asia. This would serve as one of the noteworthy contributions that puts forth a holistic study of the cultural landscapes of the World Heritage Sites.
- Towards power quality improvement July 18, 2022
 In future, there is a lot of scope for enhancing the power quality using various controllers whose gains are obtained using different optimisation techniques to mitigate several issues. Assistant Professor Dr Ramanjaneya Reddy, Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, envisions this tomorrow through his new research paper PV/WT Integrated System Using Grey Wolf Optimization Technique for Power Quality Improvement. The paper is published in the Process, and Energy Systems Engineering section of the Frontiers in Energy Research journal and has an impact factor 4.008. For this research paper, he has collaborated with Assistant Professor Srikanth Goud, Anurag College of Engineering Ghatkesar, Telangana.
In future, there is a lot of scope for enhancing the power quality using various controllers whose gains are obtained using different optimisation techniques to mitigate several issues. Assistant Professor Dr Ramanjaneya Reddy, Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, envisions this tomorrow through his new research paper PV/WT Integrated System Using Grey Wolf Optimization Technique for Power Quality Improvement. The paper is published in the Process, and Energy Systems Engineering section of the Frontiers in Energy Research journal and has an impact factor 4.008. For this research paper, he has collaborated with Assistant Professor Srikanth Goud, Anurag College of Engineering Ghatkesar, Telangana.Abstract
This work presents the integration of renewable energy sources such as PV and wind into the grid. Hybrid shunt active power filter (HSHAPF) is optimised with the grey wolf optimisation (GWO) and fractional order proportional integral controller (FOPI) for harmonic reduction under non-linear and unbalanced load conditions. With the use of GWO, the parameters of FOPI are tuned, effectively minimising the harmonics. The proposed model has effectively compensated the total harmonic distortions (THD) when compared with filter, without filter, with passive filter, active power filter with PI controller, and GWO- FOPI-based controller. The performance of the proposed controller is tested under non-linear and unbalanced conditions. The parameters of the FOPI controller are better tuned with the GWO technique. The comparative results reflect the best results of GWO-FOPI based HSHAPF. The suggested controller is built in the MATLAB/Simulink Platform.
Explanation of the research
Power quality (PQ) problems in the distribution system occur when non-linear loads are used. With the development in semiconductor technology, the modelling and usage of power electronic devices are increasing on the end-user side. Because of the usage of power, electronic devices give rise to many problems like a disturbance in reactive power, poor power factor, harmonic distortion, etc. These problems cause severe effects on the distribution system, which results in PQ issues. To mitigate PQ issues, there are many controlling techniques that ensure harmonic free. Initially, passive filter usage was widely considered for harmonic elimination and reactive power compensation. Due to various remarkable disadvantages like constant compensation performance, large size, resonance, etc., the usage became less. To mitigate the reactive power compensation and harmonics, active power filters (APF) became more prominent as the performance characteristics are very effective compared to conventional filters. APF is the device that generally produces an equal quantity of harmonics when compared with the load with a phase shift of 1800. These harmonics are injected into the linear PCC, load current harmonics mitigate, and supply becomes sinusoidal. The active power filters are broadly classified as series APF and shunt APF. The basic structure of shunt APF is illustrated in Figure.1, which mitigates the load current harmonics by inserting equal but opposite harmonic compensating current. Several authors have conducted research on grid integration using RES, active power filters, PQ issues, and various types of controllers designed to mitigate in the hybrid integrated system. In this work, THD reduction under non-linear load, unbalanced load without filter, with passive filter, with active power filter using a PI controller, and the proposed controller is introduced, which results in the best reduction of harmonics under various load conditions.
Practical implementation of the research
The proposed system is designed using both passive and active filters. The designed model improves the filer’s compensation characteristics, reducing the disadvantages of both active and passive filters. In this proposed work, HSHAPF is implemented with the combination of LC passive filter and voltage source PWM converter illustrated in Figure. 2, which illustrates the RES and HSHAPF connected to the grid. This design is tested at various loads, such as non-linear loads and unbalanced loads. Both filters’ characteristics are designed to provide the best performance under different operating conditions. To filter out the harmonics, the designed structure is modelled with storage systems using the battery, DC link and switches with antiparallel diodes. At PCC compensating current is injected using a voltage source converter to mitigate the harmonics. To overcome the power rating required for the PWM converter, the system is modelled using both active as well as passive filters to mitigate the harmonics. Here power MOSFETs are used in designing the PWM converters, which is cost-effective. To eliminate the harmonic at the PCC, equal and opposite magnitude harmonic current has to be injected, which also improves the PQ in the distribution system.
- DST-INSPIRE Subject Expert Committee Meeting July 18, 2022
 A two-day DST-INSPIRE Subject Expert Committee meeting was held on July 14 & 15 at SRM University-AP campus. Experts in the area of Physical Sciences from across the country gathered at the university to evaluate this year’s INSPIRE Fellowship applications in Physical Sciences.
A two-day DST-INSPIRE Subject Expert Committee meeting was held on July 14 & 15 at SRM University-AP campus. Experts in the area of Physical Sciences from across the country gathered at the university to evaluate this year’s INSPIRE Fellowship applications in Physical Sciences.INSPIRE Fellowship component offers 1000 Fellowships every year for carrying out doctoral degrees in both basic and applied sciences, including engineering and medicine, in the age group of 22-27 years.
The Chairperson of the Expert Committee in the area of Physical Sciences was Dr Dinakar Kanjilal, Professor, Inter-University Accelerator Centre (IUAC), New Delhi. “The fellowship ensures geographical distribution of excellence, and we look forward to more applicants from SRM AP”, Prof. Kanjilal said. Since its inception, SRM University-AP has INSPIRE Fellows as faculty members in the various departments of Sciences.
University Pro-Vice-Chancellor Prof D Narayana Rao, who also is the co-chair of the expert committee, said that it is gratifying to know that the PhD students have chosen to enrol in reputed universities and institutes. The applicants have chosen extremely accomplished scientists and faculty members as their research supervisors. “We are glad that 61 are girl students out of the 116 applications we received”, highlighted Prof D Narayana Rao. He expressed his happiness about the increasing number of women representation in Indian academia.
The other eminent scientists in the INSPIRE Fellowship selection committee included Member Secretary Dr Umesh K Sharma, Prof. Shikha Verma, Dr G. Vijaya Prakash, Dr AnandamayeeTej, Dr Rajendra Prasad Pant and Dr Arjit Chowdhuri.
Innovation in Science Pursuit for Inspired Research (INSPIRE)” is a flagship scheme of the Department of Science and Technology (DST), Government of India, which aims to attract meritorious youth to study basic and natural sciences at the college and university level and to pursue research careers in both basic and applied science areas including engineering, medicine, agriculture, and veterinary sciences.
Continue reading → - Optimised copper nanoclusters for bio imaging applications July 15, 2022
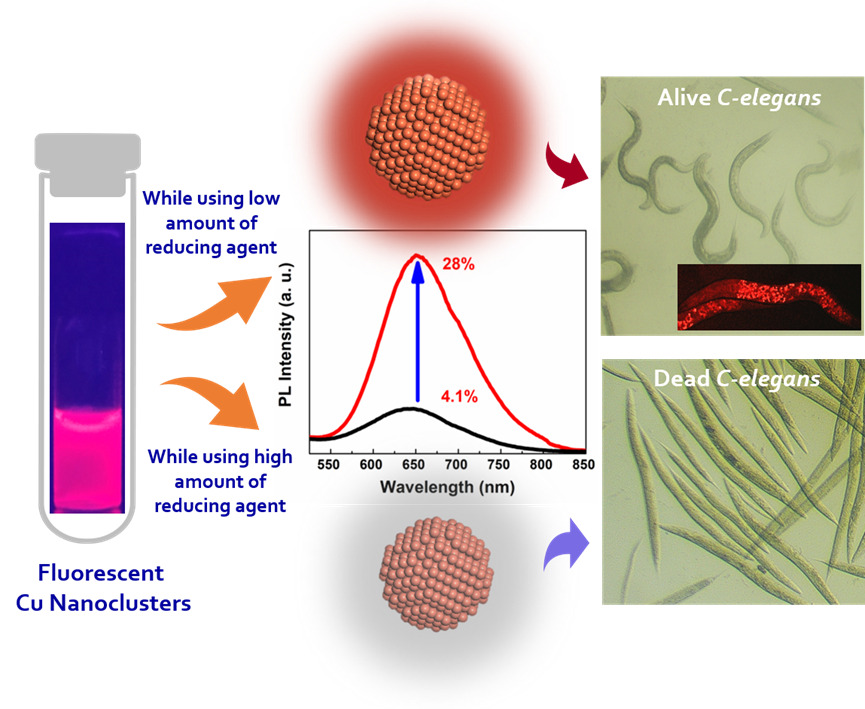
Inspite of being a plentiful and inexpensive metal, the use of copper nanoclusters is limited in bio-medical research because of their toxicity and low stability due to its easily oxidizable nature. It also has a low quantum yield. The interdisciplinary publication of the researchers at SRM University-AP successfully addressed these constraints, resulting in strong fluorescence, superior colloidal stability, and non-toxicity of copper nanoclusters for bio imaging applications. The research was a collective work of Dr Manjunatha Thondamal from the Department of Biological Sciences, Dr Mahesh Kumar Ravva and Dr Sabyasachi Chakrabortty from the Department of Chemistry along with their PhD scholars; Mr Kumar Babu Busi, Ms Kotha Jyothi, Ms Sheik Haseena, Ms Shamili Bandaru and Ms Jyothi Priyanka Ghantasala.
The article titled ‘“Engineering colloidally stable, highly fluorescent and nontoxic Cu nanoclusters via reaction parameter optimization” was featured in the prestigious Q1 journal RSC Advances (IF: 4.036), published by the ‘Royal Society of Chemistry’. They successfully prepared the protein stabilised copper nanoclusters inside the aqueous medium with exceptional optical properties. To the best of their knowledge, the reported colloidal stability and quantum yield of their as-synthesized Cu NCs are the highest reported in the literature, where the emission wavelength is in the red region. Also, optimised copper nanoclusters showed excellent biocompatibility towards solid cancer cell lines and C. elegans as in vitro and in vivo environments. Thus, these red colour luminescent copper nanoclusters were becoming a suitable fluorescent probe for deep tissue penetration, photodynamic, photothermal and diagnostic applications.
Abstract of the Research
Metal Nanoclusters (NCs) composed of the least number of atoms (few to tens) became very attractive for their emerging properties owing to their ultrasmall size. Preparing copper nanoclusters (Cu NCs) in an aqueous medium with high emission properties, strong colloidal stability, and low toxicity has been a long-standing challenge. Although they are earth-abundant and inexpensive, they are comparatively less explored due to their limitations such as ease of surface oxidation, poor colloidal stability, and high toxicity. To overcome these constraints, we established a facile synthetic route by optimizing the reaction parameters, especially altering the effective concentration of the reducing agent to influence their optical characteristics. The improvement of photoluminescence intensity and superior colloidal stability was modelled from a theoretical standpoint. Moreover, the as-synthesized Cu NCs showed a significant reduction of toxicity in both in vitro and in vivo models. The possibilities of using such Cu NCs as a diagnostic probe towards C. elegans were explored. Also, the extension of this approach towards improving the photoluminescence intensity of the Cu NCs on other ligand systems was demonstrated.
Continue reading → - Sustainable biorefinery approaches for a circular economy July 15, 2022
 Worldwide, 1.3 billion tons of bio-waste are generated annually. By 2025, this is predicted to be increased by 2.2 billion tons/year. The emerged biowaste biorefinery has proved as a sustainable approach for integrated bioproducts, such as bioenergy, biopolymers, biochemicals, bioplastics, and biofertilizers further used for industrial, commercial, agricultural, and energy applications. Integrating biorefinery concepts into biowaste management is promising for a circular bioeconomy. Recent research at the Department of Environmental Sciences investigates the potential of sustainable biorefinery approaches. Assistant professor Dr Karthik Rajendran and his PhD scholar Mr. Prabakaran G published a paper, Sustainable biorefinery approaches towards circular economy for conversion of biowaste to value added materials and future perspectives, in Fuel, a Q1 journal, with an impact factor of 8.03. For this paper, they have collaborated with Dr Mukesh Kumar Awasthi from the College of Natural Resources and Environment, Northwest A&F University, China.
Worldwide, 1.3 billion tons of bio-waste are generated annually. By 2025, this is predicted to be increased by 2.2 billion tons/year. The emerged biowaste biorefinery has proved as a sustainable approach for integrated bioproducts, such as bioenergy, biopolymers, biochemicals, bioplastics, and biofertilizers further used for industrial, commercial, agricultural, and energy applications. Integrating biorefinery concepts into biowaste management is promising for a circular bioeconomy. Recent research at the Department of Environmental Sciences investigates the potential of sustainable biorefinery approaches. Assistant professor Dr Karthik Rajendran and his PhD scholar Mr. Prabakaran G published a paper, Sustainable biorefinery approaches towards circular economy for conversion of biowaste to value added materials and future perspectives, in Fuel, a Q1 journal, with an impact factor of 8.03. For this paper, they have collaborated with Dr Mukesh Kumar Awasthi from the College of Natural Resources and Environment, Northwest A&F University, China.Biorefinery is designed to improve the economic potential and achieve a circular bioeconomy by integrating various technologies such as pyrolysis, anaerobic digestion, gasification, incineration, and aerobic composting to gain energy, nutrients, and material recovery. Biowaste biorefinery contributes as a driving force to cope with challenges of resource scarcity, climate changes, and increased demand. The sustainable biorefinery approaches toward circular bioeconomy require a comprehensive understanding of the biowaste across the value chain. Based on the carbon neutralized biowaste biorefinery concept, this paper explained biowaste generation and utilization as a renewable resource through biorefinery techniques from the perspective of energy, nutrients, and material recovery. Meanwhile, clarify the implementation status, public engagement, and prospects of biowaste recycling with the central concept of biorefinery circular bioeconomy.
Abstract
With the colossal energy demand inevitably exacerbating the non-renewable resources depletion and ecological-social challenges, renewable energy has become a crucial participant in sustainable strategy. Biorefinery emerged as a sustainable approach and recognized promising transformation platforms for products to achieve a circular bioeconomy that focuses on biomass efficiency and sustainable valorisation, promotes resource regeneration, and restorative. The emerged biowaste biorefinery has proved as a sustainable approach for integrated bioproducts and further applied this technology in industrial, commercial, agricultural, and energy sectors. Based on carbon-neutral sustainable development, this review comprehensively explained biowaste as renewable resource generation and resource utilisation technologies from the perspective of energy, nutrient, and material recovery in the concept of biorefinery. Integrating biorefinery concepts into biowaste management is a promise for the conversion of biowaste into value-added materials. It contributes as a driving force to cope with resource scarcity, climate changes, and huge material demand in a circular bioeconomy. In practice, the optimal of biorefinery technologies depends on environmentally friendly, economic and technical feasibility, and social and policy acceptance. Additionally, policy interventions are necessary to promote biowaste biorefinery implements for a circular bioeconomy and contribute to a low-carbon cleaner environment.
Continue reading → - Internet of Things – Security and Privacy in Cyber Space July 13, 2022
 Transactions on Computer Systems and Networks is a unique series that aims to capture advances in the evolution of computer hardware and software systems and progress in computer networks. Associate Professor Dr Ashok Kumar Pradhan, Department of Computer Science and Engineering, becomes a part of this book series by publishing the book titled Internet of Things- Security and Privacy in Cyber Space. Edition 1 of the book was launched on May 27, 2022, under the publishing house Springer Nature. The series aims to present leading works on advances in theory, design, behaviour, and applications in computing systems and networks.
Transactions on Computer Systems and Networks is a unique series that aims to capture advances in the evolution of computer hardware and software systems and progress in computer networks. Associate Professor Dr Ashok Kumar Pradhan, Department of Computer Science and Engineering, becomes a part of this book series by publishing the book titled Internet of Things- Security and Privacy in Cyber Space. Edition 1 of the book was launched on May 27, 2022, under the publishing house Springer Nature. The series aims to present leading works on advances in theory, design, behaviour, and applications in computing systems and networks.This book covers major areas of device and data security and privacy related to the Internet of Things (IoT). It also provides an overview of lightweight protocols and cryptographic mechanisms to achieve security and privacy in IoT applications. Besides, the book also discusses intrusion detection and firewall mechanisms for IoT. It also covers topics related to embedded security mechanisms and presents suitable malware detection techniques for IoT. The book also contains a unique presentation on heterogeneous device and data management in IoT applications and showcases the major communication-level attacks and defense mechanisms related to IoT.
The book is beneficial for the students who pursue under graduation, post-graduation, and PhD as a reference to get the fundamental as well as research ideas about IoT/ cyber security/ Blockchain technology and their application areas.
Continue reading →

