All Management Events
- 2nd Convocation ceremony: Proudly honouring the graduates of 2022 October 10, 2022
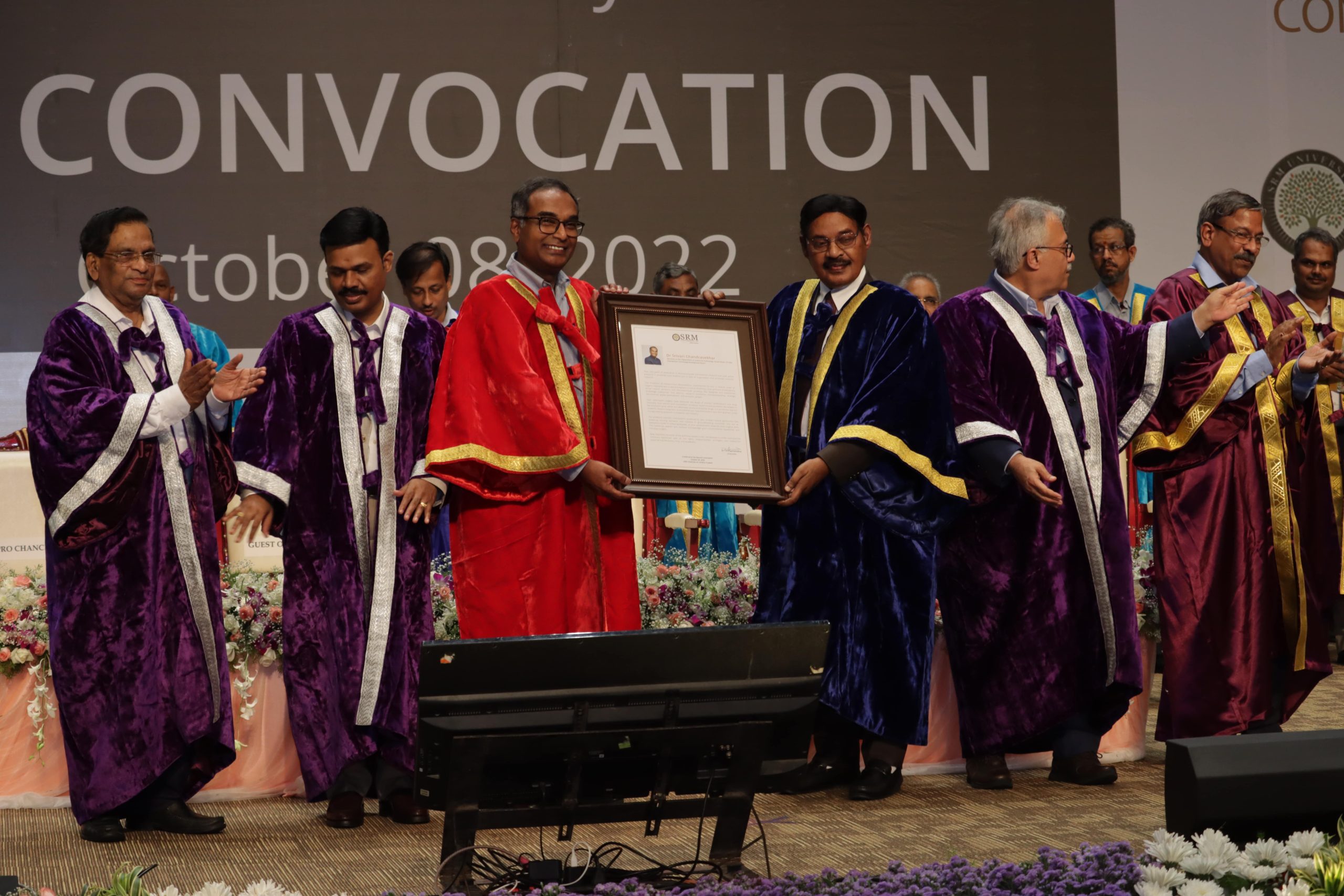 SRM University- AP conducted its 2nd convocation ceremony for the Class of 2022 on Saturday, October 08, 2022, at 3 pm. A total of 1149 students were awarded their graduate degrees at the glorious event held at the APJ Abdul Kalam Auditorium. “As you look forward to the future, I wish you taking action on the key technical, social, and environmental issues that our world is facing today,” said the chief guest of the day, Dr K Radhakrishnan, former ISRO Chairman, in his address.
SRM University- AP conducted its 2nd convocation ceremony for the Class of 2022 on Saturday, October 08, 2022, at 3 pm. A total of 1149 students were awarded their graduate degrees at the glorious event held at the APJ Abdul Kalam Auditorium. “As you look forward to the future, I wish you taking action on the key technical, social, and environmental issues that our world is facing today,” said the chief guest of the day, Dr K Radhakrishnan, former ISRO Chairman, in his address.The ceremony commenced with the welcome address and annual report by Vice-Chancellor Prof Manoj K Arora. “In our objective of being a globally connected, nationally relevant, and regionally transformative university, we are on the path of excellence in knowledge creation and dissemination,” commended him while highlighting the university’s performance and achievements in the academic milieu.
The event continued with the convocation address of Founder Chancellor Dr T R Paarivendhar and Pro-Chancellor, Dr P Satyanarayanan. They enunciated how SRM sets out on its journey with an unflinching vision to grow into a trailblazer in higher education, offering learning par excellence and keeping in line with global academic standards.
“We have always envisioned being a changemaker in the areas of research, placement, entrepreneurship, and higher studies, and we are immensely proud of the profuse accomplishments of our students in these fields, be it the inspiring research endeavours, enviable placement offers, innovative startup plans and exciting opportunities for higher learning,” said Dr P Satyanarayanan.
Pro Vice-chancellor of SRM AP, Prof D Narayana Rao, read out the Citation and Chancellor, Dr T R Paarivendhar conferred the honorary doctorate on Dr S Chandrasekhar, Chairperson, TDB, and Secretary, DST. In his acceptance speech, Dr S Chandrasekhar congratulated the graduands and talked about his vision of a sustainable planet where India becomes an innovation-driven country in the next 20 years. He further called upon the girl students of SRM AP to be the next generation leaders of tomorrow.
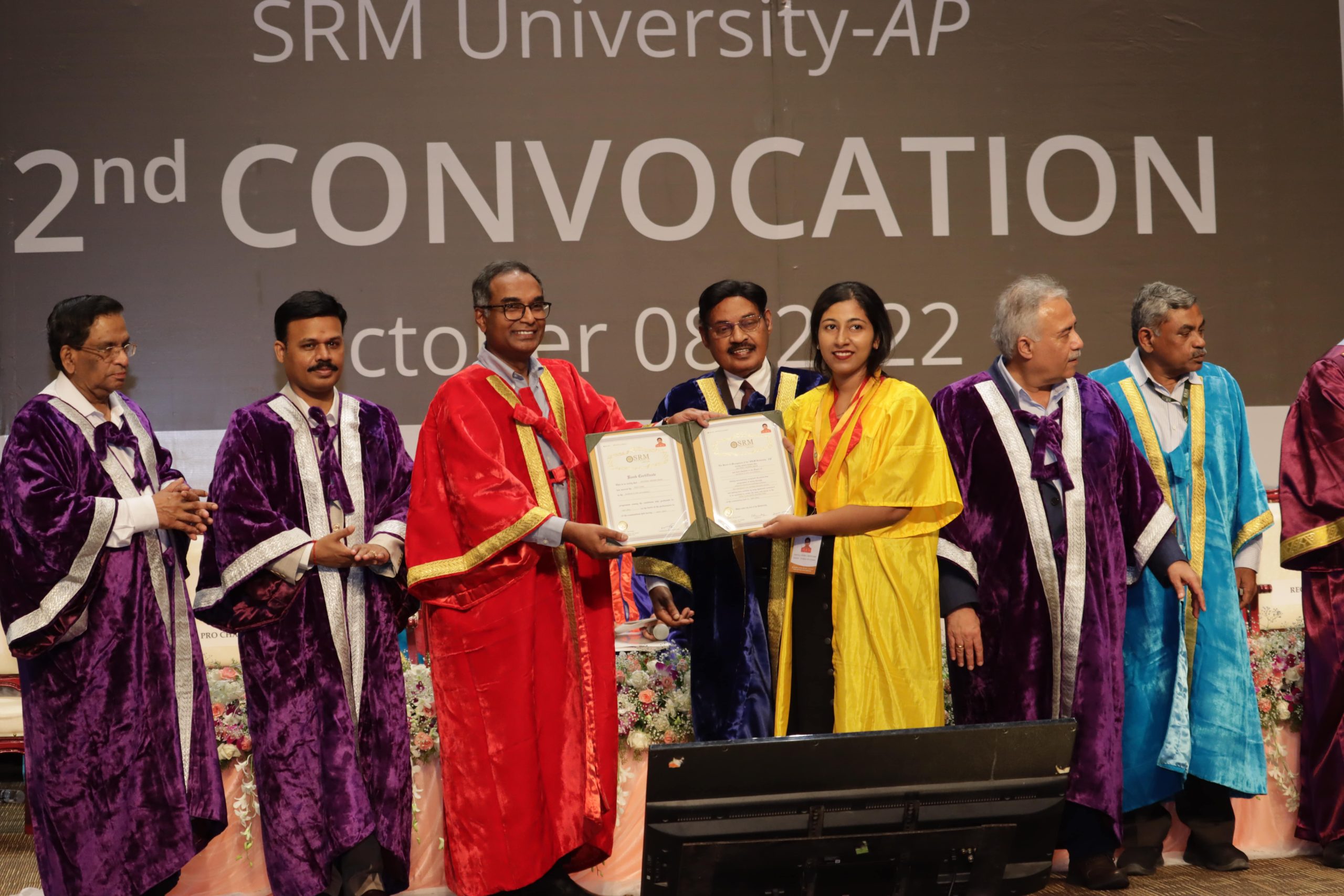 The ceremony proceeded to hand the degrees of merit to the deserving students. Over the years, SRM University- AP has carved a niche for itself in the realm of higher education. The learning destination has achieved numerous milestones for its phenomenal academic performance and purpose-driven endeavours in the Indian educational scenario. SRM AP has earned an enviable reputation of being one of the finest emerging universities in the country within a short span of time. “The university campus has become a breeding ground for excellence and is becoming a revolution in the academic landscape of the country,” remarked the students when asked about their feelings after graduating from SRM University- AP.
The ceremony proceeded to hand the degrees of merit to the deserving students. Over the years, SRM University- AP has carved a niche for itself in the realm of higher education. The learning destination has achieved numerous milestones for its phenomenal academic performance and purpose-driven endeavours in the Indian educational scenario. SRM AP has earned an enviable reputation of being one of the finest emerging universities in the country within a short span of time. “The university campus has become a breeding ground for excellence and is becoming a revolution in the academic landscape of the country,” remarked the students when asked about their feelings after graduating from SRM University- AP.Awards, degrees, and medals were presented for BTech, BBA, BA, BSc, MBA and PhD programmes, and the pledge was administered. Members of the Board of Management and Academic Council, Pro Vice-Chancellor Prof D Narayana Rao, Registrar Dr R Premkumar, Former Vice-Chancellor and Advisor of the university Prof V S Rao, Deans, Directors, Heads of the departments, faculty and staff members, alums, parents of graduands were present on the occasion.
The ceremony culminated with the National anthem, and all the graduates dispersed in exuberant joy!
Know More Continue reading → - Prof K Narayana Chandran Visiting Professor October 7, 2022
- Advantages of global immersion programmes in Malaysia October 7, 2022
 Global Immersion Programme is a unique abroad learning programme instituted at SRM University-AP, enabling students to acquire an all-encompassing learning exposure at an international university. The programme intends to acquaint students with varied approaches of learning while gaining exposure to a foreign cultural, political, and social milieu.
Global Immersion Programme is a unique abroad learning programme instituted at SRM University-AP, enabling students to acquire an all-encompassing learning exposure at an international university. The programme intends to acquaint students with varied approaches of learning while gaining exposure to a foreign cultural, political, and social milieu.The Directorate of International Relations and Higher Studies is organising a webinar on the topic Advantages of Global Immersion Programmes in Malaysia to give students a brief overview of the Global Immersion Programmes in Malaysia and the benefits of undertaking them. Dr Geevaneswary Saththasivam, Director of Business Development, AIMST University, will be the keynote speaker for the event.
Date: October 10, 2022
Time: 4.00 pm to 5.00 pm
Speaker’s Profile
Dr Geevaneswary Saththasivam was the former lecturer and programme coordinator for UG and PG programmes from the faculty of Business and Management. Prior to that, she has 15 years of industry experience in the fields of Supply Chain Management and Shop Floor Management systems and 4 years of experience working in the field of Project Management in multinational corporations.
Join the webinar to know the prospects of doing global immersion programmes in Malaysia.
Continue reading → - In-situ Al–5ZrB2 composite foams : Comparable alternative for conventional Al foams October 7, 2022
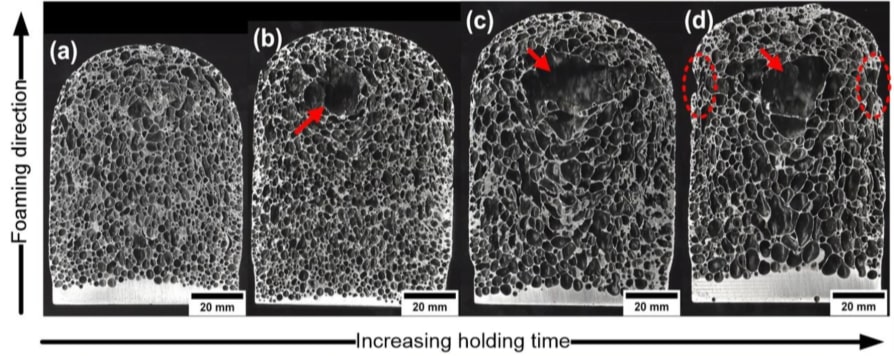
Closed-cell metal foams are crucial to heavy industry machinery as they primarily function as impact-absorbing materials. Stabilizing closed-cell metal foams is a pivotal element in the process of manufacturing closed-cell metal foams. On this note, Prof GS Vinod Kumar from The Department of Mechanical Engineering has published a paper entitled Production, stability, and properties of in-situ Al–5ZrB2 composite foams in the journal Materials Science and Engineering: A with an impact factor of 6.044.
Abstract
Stabilization is an essential requirement to produce closed-cell metal foams. In the melt route of foaming, usually ceramic particles are used as foam stabilizers. For the first time, the present study introduces ZrB2 particles as foam stabilizers. We demonstrate the foaming of in-situ based Al composite containing submicron ZrB2 particles. The effect of foaming temperature and holding time on the structural and mechanical properties of the foams was studied. The composites and foams were characterized using XRD, SEM/EDS, and optical scanning techniques. The mechanical properties of the foams were determined by subjecting the foams to a quasi-static compression test. Submicron ZrB2 particles present in the cell wall and at the gas-solid interface promoted foam stability. All the foams exhibited a good cellular structure with high expansion. Among the foams, the foams prepared at 680 ºC with a holding time of 120 s exhibited the smallest cell size and the best mechanical properties. The structural and mechanical properties of the Al–5ZrB2 foams were found to be comparable to conventional foams.
Novel in-situ ZrB2 particles were produced to form Al-5ZrB2 composites. ZrB2 particles present in the melt tend to stabilize the H2 gas bubbles produced from the decomposition of TiH2. The macrostructure was best observed when foamed at 680 ºC and held for 120 sec. Because of its finer pores ( ̴ 3mm ), excellent compressive strength and energy absorption capacity was exhibited comparable to conventional Al foams.
The paper observes a wide-range of possibilities for the application of in-situ Al–5ZrB2 composite foams to modify bullet proof vests, car body parts, sound and heat proof walls in theatres, naval ship bodies, etc.
Prof Vinod Kumar also discusses the future application of this technique in use of metallic powders as blending agent for effective dispersion of blowing agent in the melt and in the field of compressive and energy absorption studies for Al composite foams.
Continue reading → - SRM University- AP announces Elon Fellowship for budding entrepreneurs October 7, 2022
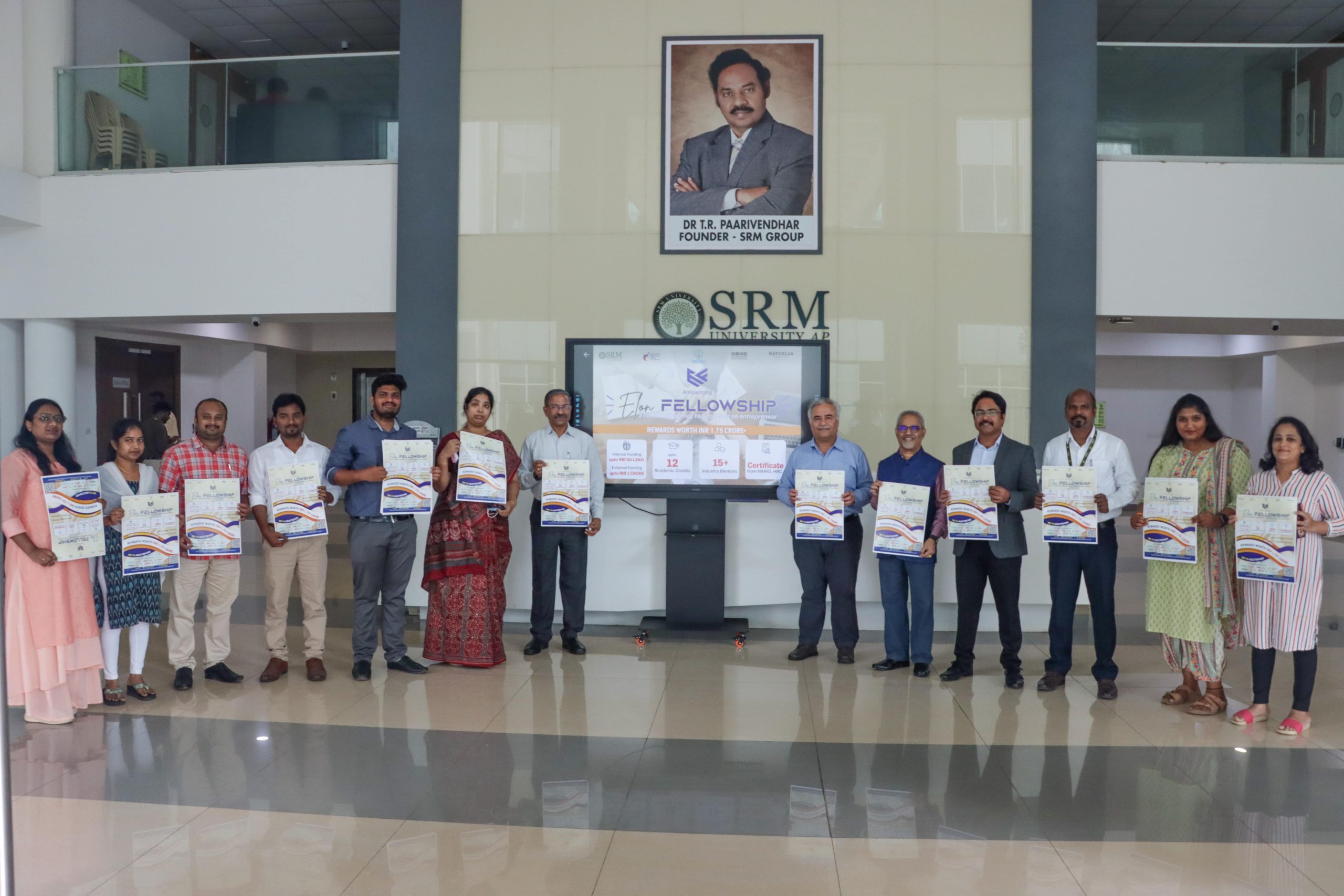

SRM University- AP inaugurated Elon Fellowship on September 30, 2022. It is a novel cohort that aspires to create a startup ecosystem. The Fellowship launched will onboard 60+ venture teams and provide extensive training for four months to facilitate the development of their idea to the prototype stage and beyond. Selected venture groups would receive internal funding up to INR 50 lakhs and external funding upto INR 1 crore for their project development.
The Elon Fellowship poster was launched by the Vice Chancellor of SRM University- AP, Prof Manoj K Arora; Registrar, Dr R Premkumar; and other dignitaries. “The Fellowship opens up new avenues in the domain of entrepreneurship and innovation. It provides students with a well-funded scheme that facilitates fruitful development of their creative ventures”, asserted Prof Arora.
Mr Udayan Bakshi, the Associate Director of Entrepreneurship, SRM AP commented that more than seven portfolio startups of the university have crossed a total revenue of 25 crores annually, making our institution a formidable pioneer in the field of entrepreneurship.
The Andhra Pradesh Innovation Society, Government of Andhra Pradesh, congratulated this innovative scheme. Mr Anil T, the CEO of APIS, extended his support in furthering the cause in promoting young entrepreneurs. The Elon Fellowship grants students a supportive cohort for their journey to entrepreneurship.
Continue reading → - Dr Arijit Datta October 6, 2022
- The Young Leaders Programme October 6, 2022
 The Young Leaders Programme is a foundation that helps high-potential college students secure admission to India’s #1 MBA, the Post Graduate Programme in Management (PGP), at the Indian School of Business (ISB). The Directorate of International Relations and Higher Studies is conducting a seminar, The Young Leaders Programme, to give the students at the university a broader exposure to the programme. Renowned higher education Marketing Professional Mr.Arun Prakash will be the key speaker at the event.
The Young Leaders Programme is a foundation that helps high-potential college students secure admission to India’s #1 MBA, the Post Graduate Programme in Management (PGP), at the Indian School of Business (ISB). The Directorate of International Relations and Higher Studies is conducting a seminar, The Young Leaders Programme, to give the students at the university a broader exposure to the programme. Renowned higher education Marketing Professional Mr.Arun Prakash will be the key speaker at the event.Date: October 11, 2022
Time: 9.45 AM to 10.45 AM
Venue: Tiered Classroom, Fifth Floor, Admin Block
The Young Leaders Programme is meant for pre-final or final year undergraduate or postgraduate students. It equips college students with multidisciplinary perspectives, thinking skills, and research tools and provides clarity on career goals before they begin the PGP in Management.
The seminar will deal with areas including ISB overview, ISB Value Proposition, PGP- YLP Overview etc. It will help students understand how to strengthen the MBA application to crack India’s #1 PGP in Management. A Q & A or discussion on MBA in India Vs MBA abroad and MS vs MBA, and much more are the other attractions of the event.
About the speaker
Mr Arun Prakash leads the Young Leaders Programme at the Indian School of Business. He has rich experience working in top brands like Naukri.com, Butterfly Appliances, and Eenadu and served in premier educational institutions in various managerial roles. His area of interest lies in Career Counselling, Marketing Strategy, Branding, Digital Marketing, Admissions, Outreach, Students’ Life, and Alumni Relations.
Join the seminar for an insightful talk!
Continue reading → - The Saurvi initiative – A new wave for women empowerment October 6, 2022

Upliftment of women is the chief requisite that leads the way to empowerment of a community as well as the nation. The representation of womankind on multitude spheres is imperative for a progressive society to advance into a fair and just future.
Saurvi, the woman leadership and entrepreneurship student community under the Home of Leaders, has become a torch-bearer in creating a novel path for women empowerment by encouraging women into the field of entrepreneurship. The student initiative has recently conducted a bootcamp at Maris Stella Women’s College, Vijayawada AP, to help them create a startup and leadership ecosystem. The interaction between the budding entrepreneurs and students has fostered a positive outlook towards entrepreneurship, leadership and engaging in creative business ventures.
The Saurvi initiative aims at empowering women by cultivating livelihood skills among the women communities and promoting leadership opportunities and business propositions among women from all walks of life. They collaborate with numerous NGOs to generate awareness as well as to nurture impactful women leaders in the field of entrepreneurship.

The initiative has begun to gather momentum and recognition, for their vision, mission and commitment for the cause. Smt KGV Saritha, Superintendent of Police, Andhra Pradesh, offered her words of appreciation for the ingenuity of the initiative to promote women empowerment. The Saurvi enterprise has in view to create 10 women entrepreneurs by the end of 2023, 15 by 2024 and aims to double the number for every consecutive year.
Continue reading → - 15 Lakh investment for Manideep’s Hatchlab venture SPOCSQ Pvt October 6, 2022
 Making an impact on society through revolutionary innovations is not an everyday thing. Manideep Surusomayajula from the Department of Computer Science and Engineering bagged an investment of 15 Lakh for his Hatchlab venture SPOCSQ Pvt. This is the first investment that has been secured by the startup project.
Making an impact on society through revolutionary innovations is not an everyday thing. Manideep Surusomayajula from the Department of Computer Science and Engineering bagged an investment of 15 Lakh for his Hatchlab venture SPOCSQ Pvt. This is the first investment that has been secured by the startup project.His startup deals with chip-based certification processes using Blockchain Technology. SPOCSQ is in the process of developing a tamper-proof certificate system based on chip and blockchain technology.
The investing company ThredzIT Information Technology Pvt. Ltd is willing to invest 20-30 Lakh for the final version of the product. This achievement is a milestone in Manideep’s career as it demonstrates his passion for entrepreneurship and innovation.
Continue reading → - Learn the importance of higher education October 4, 2022

Pursuing higher education is a prerequisite for a distinctive and successful career path. The completion of tertiary education expands deep critical and reasoning skills through an experiential learning process. It also enhances employment prospects in a highly competitive job market.
The Directorate of International Relations and Higher Studies is organising a seminar on the topic Higher Education’s Importance discussing the significance of ensuing tertiary education in upskilling their knowledge assets to inflate one’s career opportunity. Mr Rajesh Balasubramanian will address the gathering.
Date : October 6, 2022
Time : 10.50 am to 11.40 am
Venue : ALC – 1, Third floor, Admin Block
The seminar would provide a brief and comprehensive outlook on the various objectives of mastering a higher degree.
- MBA as an option for Higher Education
- MBA abroad vs MBA in India
- Top B-Schools in the country and how to get admitted into these B-Schools
- The exams a candidate can take – Eg: XAT, SNAP, IIFT, GMAT, GRE.
- What is CAT? (Exam patterns and syllabus)
Speaker’s Profile
Mr Rajesh Balasubramanian is an Electrical Engineer from IIT, Madras, Class of 2001 and completed his PGDM from IIM Bangalore in 2003. He runs 2IIM’s CAT program and has built most of the content for the 2IIM CAT Online Course.
He scored 100th percentile in CAT 2011, CAT 2012, CAT 2014 and CAT 2017. Rajesh scored 99.77 in CAT 2018, 99.99th percentile in CAT 2019, 99.98th percentile in CAT 2020, and 99.79th percentile in CAT 2021.
Rajesh also runs PiVerb – an Ed-Tech company that focuses on teaching maths intuitively to students from class V to class X. Prior to his stint in education, Rajesh had spent a few years as an investment banker.
Join the seminar to anchor your dreams for higher education.
Continue reading →













