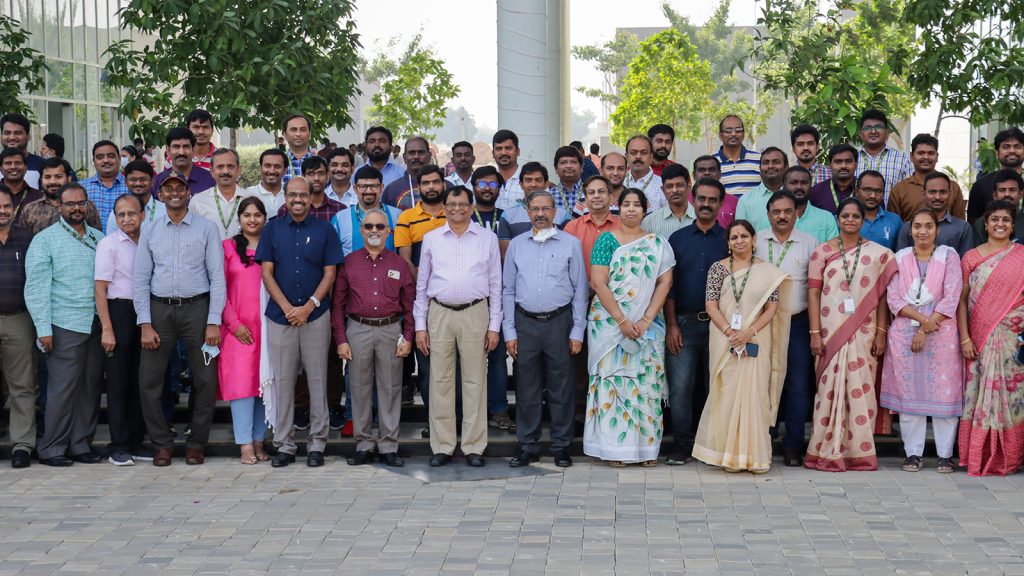
STEM-Research Society Best Paper Award to faculty and undergraduate students
 “As an undergraduate student, I initially faced many difficulties selecting the area of interest, analysing and organising a paper, and academic writing skills. The continuous support from faculty at SRM university-AP helped me overcome these issues. This achievement would have been impossible without the support and efforts of my faculty mentors. My heartful gratitude to Dr Shubh Lakshmi madam and Dr Tousif Khan N sir for their kind support and encouragement in research work. I am grateful to start my research career under their guidance. Also, the management encourages and supports us every time in every possible way by providing scholarships.”
“As an undergraduate student, I initially faced many difficulties selecting the area of interest, analysing and organising a paper, and academic writing skills. The continuous support from faculty at SRM university-AP helped me overcome these issues. This achievement would have been impossible without the support and efforts of my faculty mentors. My heartful gratitude to Dr Shubh Lakshmi madam and Dr Tousif Khan N sir for their kind support and encouragement in research work. I am grateful to start my research career under their guidance. Also, the management encourages and supports us every time in every possible way by providing scholarships.”
–Pendem Manoj Sai
A paper titled “Exhaustive Search Approach to Place PV in Distribution Network for Power Loss Minimization” has been awarded STEM-Research Society Best Paper Award in the recently held conference, Soft Computing: Theories and Applications (SoCTA)-2021, at the Indian Institute of Information Technology, Kota on the dates December 17-19, 2021. The authors of the paper are- P Manoj Sai, M Dhana Sai Baji, Dr Shubh Lakshmi, and Dr Tousif Khan Nizami from the Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, School of Engineering and Sciences, SRM University-AP, Andhra Pradesh, India. The paper is selected for publication in Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems, Springer (Indexed in SCOPUS).
This paper proposes an exhaustive search approach to determine the best location and size of PV placement for power loss minimisation of radial distribution networks. In this approach, the network power loss is determined by placing PV in each location, one at a time, and the size of PV in the same location is varied between a set minimum and maximum limits. The combination of location and size of PV, which provide the minimum network power loss, can be the best location and size of PV for power loss minimisation of radial distribution networks. The forward-backwards sweep load flow algorithm with the PV model is used to determine the power loss for each combination of location and size of PV.
The paper was presented by Mr P Manoj Sai, a BTech EEE 4th year student from SRM University-AP, Andhra Pradesh. He is thrilled to receive the best paper award and extended his gratitude to Dr Tousif Khan N, the Head of the Department, and Dr Shubh Lakshmi, Assistant professor in the Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, for their continuous guidance. Further, he extended his thanks to the management and Pro Vice-chancellor of SRM University-AP for providing financial support.
- Published in Departmental News, EEE NEWS, News, Students Achievements
Welcoming 2022 with joy, hope, and fun
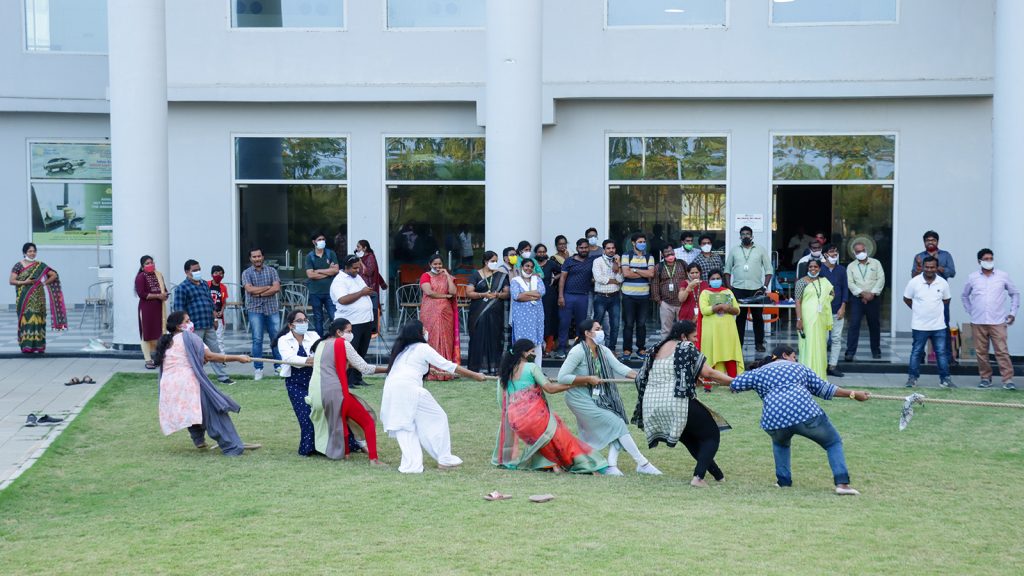
On Saturday morning, students, faculty and administrative staff members at SRM University-AP welcomed the new year with colourful celebrations on campus. Vice-Chancellor Prof V S Rao cut the New year special cake and addressed the gathering. “We shall enter the new year with the hope that pandemic will be endemic in 2022”, he said. He also suggested that everyone take steps in a planned manner to receive the success they hope for in the new year.
Dr R Premkumar, the Registrar, expressed hope that the university would move towards higher standards under the supervision of Professor B V Babu, Dean of the School of Engineering and Sciences. The organisers and participants of the event and various game activities adhered strictly to the Covid-19 protocol. Prizes were given away to the winners of various competitions.
The event was attended by Registrar-Dr R Premkumar, Dean-Prof B V Babu, Controller of Examinations- Dr Vinayak Kalluri, Directors-Mrs Suma N, Dr K Mohan, Wg Cmdr Venkataachalam Sekkappan, Prof Y Siva Sankar and others.
Student ready to climb Mount Everest
 The summit will start in April 2022 in Kathmandu
The summit will start in April 2022 in Kathmandu
G Ram Dheeraj, third-year Civil Engineering at SRM University-AP, has been selected to climb Mount Everest, the world’s highest mountain. The adventurous peak climbing expedition will begin in April 2022. He has already climbed three major peaks in the Himalayan range and is selected for the summit by the Asian Trekking Pvt Ltd. The mountains that he has set foot on are Shitindhar Peak (5358 m), Friendship Peak (5287 m) and Deo Tibba Peak (6001 m). He has also completed a mountaineering course from ABVIMAS in Kulu Manali. Ram Dheeraj, who hopes to reach the summit of Mt. Everest through rigorous preparation, seeks kind sponsors to come forward and fund the expenses of ₹27 lacs. Prof V S Rao, Vice-Chancellor; Prof Narayana Rao, Pro-Vice-Chancellor; and the management of SRM University-AP, congratulated Ram Dheeraj for his exceptional enthusiasm to conquer extremely high altitudes.
- Published in CIVIL NEWS, News, Students Achievements
Dr Lakhveer Singh published in Advanced Functional Materials for Engineered Nanoenzymes
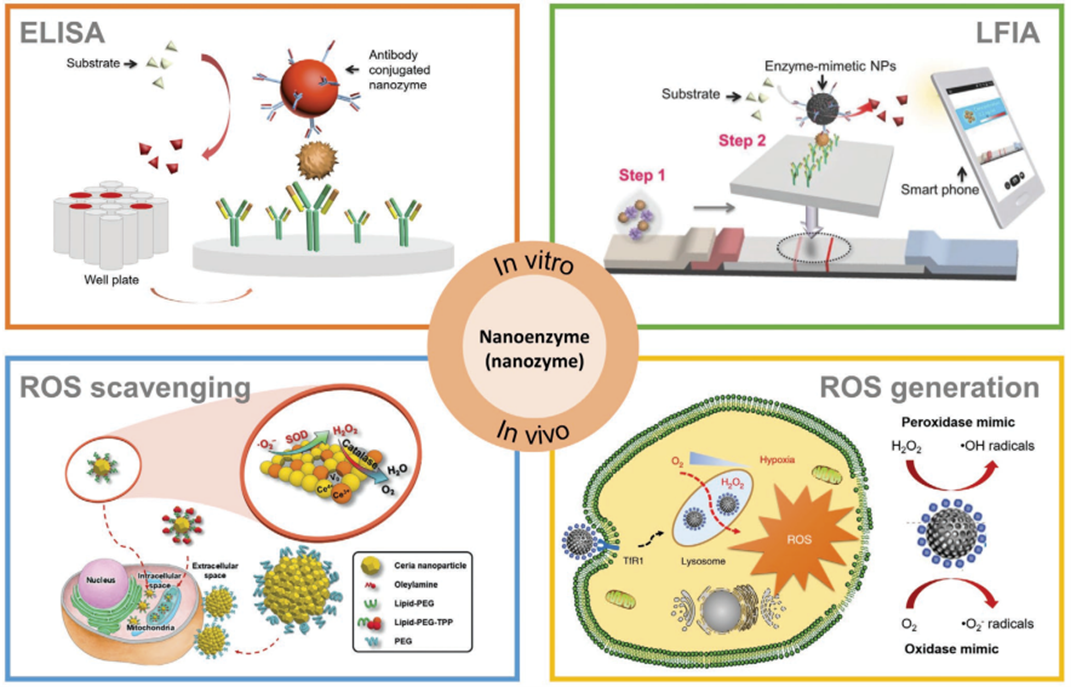 The Department of Environmental Science is proud to announce that Dr Lakhveer Singh has published his paper titled, “Engineered Nanoenzymes with Multifunctional Properties for Next-Generation Biological and Environmental Applications” in Advanced Functional Materials with an impact factor of 18.50.
The Department of Environmental Science is proud to announce that Dr Lakhveer Singh has published his paper titled, “Engineered Nanoenzymes with Multifunctional Properties for Next-Generation Biological and Environmental Applications” in Advanced Functional Materials with an impact factor of 18.50.
About the Paper:
Enzyme mimicking studies took on a new aspect as it turns out that inorganic nanomaterials could have intrinsic enzyme-like activities. The word nanozyme (nanoenzyme) was first coined to describe the ribonuclease-like activity of ligand functionalised gold nanoparticles in 2004. Since then, various research has been continued on nanomaterials with enzyme-like activity. Thus, nanoenzyme has come to describe nanomaterials with enzyme-like activity.
Abstract:
As a powerful tool, nanoenzyme electrocatalyst broadens the ways to explore bioinspired solutions to the world’s energy and environmental concerns. Efforts to fashion novel nanoenzymes or engineering nanoenzymes for effective electrode functionalisation is generating innovative, viable catalysts with high catalytic activity, low cost, high stability and versatility, and ease of production. High chemo-selectivity and broad functional group tolerance of nanoenzyme with an intrinsic enzyme-like activity make them an excellent environmental tool. The catalytic activities and kinetics of nanoenzymes that benefit the development of nanoenzyme-based energy and environmental technologies by effectual electrode functionalisation are discussed in this article. Further, deep insight on recent developments in the state-of-art of nanoenzymes either in terms of electrocatalytic redox reactions (viz. oxygen evolution reaction, oxygen reduction reaction, nitrogen reduction reaction and hydrogen evolution reaction) or environmental remediation/treatment of wastewater/or monitoring of a variety of pollutants. The complex interdependence of the physicochemical properties and catalytic characteristics of nanoenzymes are discussed, along with the exciting opportunities presented by nanomaterial-based core structures adorned with nanoparticle active-sites shell for enhanced catalytic processes. Thus, such modular architecture with multi-enzymatic potential introduces an immense scope of making its economical scale-up for multielectron-fuel or product recovery and multi-pollutant or pesticide remediation as reality.
Collaboration:
The assignment on “Engineered Nanoenzyme” was completed with the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST), 291 Daehak-Ro, Yuseong-Gu, Daejeon 34141, the Republic of Korea, along with other universities.
Social and Industrial Implications:
Trends of nanoenzyme are replacing conventional enzymes, particularly in a microbial bioelectrofuel biosystem, as cheap and efficient electrocatalysts. In this account, various strategies from altering scaffold to point alteration and iterative targeted tailoring have been applied to improve the enzyme-like activity and selectivity of the artificial enzymes.
Future Plans:
Strategies need to be devised to increase the mass loading of both homogenous and heterogeneous nanoenzyme for higher current density. Though, area of nanoenzyme is in its growing stage, engineering nanoenzyme with improved catalytic performance comparable to or even higher than that of the natural enzyme is one of the most concerning issues at this moment. Besides, the future breakthrough in nanoenzyme technology will lead to the development of novel catalysts with wider applications in multiple disciplines.
- Published in Departmental News, ENVS News, News