Patent on CBVR Published by Dr Jatindra Dash
 The Department of Computer Science and Engineering is delighted to announce the publication of a patent titled “A Content-Based Video Retrieval (CBVR) System and Method Thereof,” with application number 202541004749. The invention offers an efficient and accurate approach developed for content-based video retrieval by Dr Jatindra Kumar Dash, Associate Professor in the Department, along with his PhD scholar, Mr Farooq Shaik.
The Department of Computer Science and Engineering is delighted to announce the publication of a patent titled “A Content-Based Video Retrieval (CBVR) System and Method Thereof,” with application number 202541004749. The invention offers an efficient and accurate approach developed for content-based video retrieval by Dr Jatindra Kumar Dash, Associate Professor in the Department, along with his PhD scholar, Mr Farooq Shaik.
Brief Abstract:
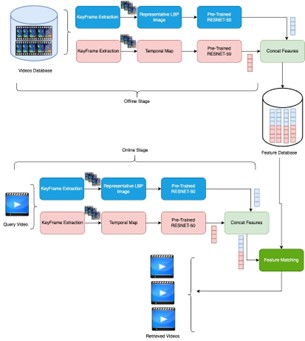
Imagine searching for a specific scene in a movie, not by remembering its title or actors, but by describing the action itself. This is the essence of content-based video retrieval (CBVR), a technique that searches for a video based on what’s inside it, rather than relying solely on manually assigned labels. Unlike traditional methods, which can be time-consuming, error-prone, and struggle with vast datasets, CBVR offers a more efficient and accurate approach. Our proposed system leverages the strong capability of deep learning, a subset of artificial intelligence, to analyse videos and extract their key characteristics. This process occurs in two stages: offline and online. Through the first stage, important features are extracted from all videos in the dataset and stored for future use. When a user submits a query video, its features are extracted in real-time (online) and compared to the stored features of all videos. The videos with features most similar to the query, essentially those with the “closest match” are then presented to the user. To capture the full essence of a video, our system employs a two-stream neural network architecture. This innovative approach allows us to extract both temporal features, which capture the changes and motion patterns within the video (think: someone running or jumping), and spatial features, which pivot about the static visual content of each individual frame (think: the objects and scene depicted).By utilizing a pre-trained neural network called ResNet-60, our system benefits from existing knowledge and can efficiently extract meaningful features from videos. To evaluate its effectiveness, we tested our system on the UCF101 dataset, a widely used benchmark consisting of 101 categorized videos. Our approach obtained accuracy 93,7\% for top 5 retrieval and 95.95\% for top 10 retrieval. The outcomes illustrate that our approach obtains superior accuracy compared to other state-of-the-art video retrieval methods.
Explanation in Layperson’s Terms:
Most of video searching platforms relay on meta data attached to video to search and retrieve videos. For example you tube utilize video name description attached to video while uploading. How ever this approach is time consuming, error prone, and need human intervention. Our proposed CBVR system aims to retrieve videos based on content of video similarity rather than meta tags. Proposed article utilized pre trained Deep neural network particularly ResNet-50 a convolutional neural network with residual skip connections to learn video representation by employing LBP representation and Temporal map of the video.
Practical Implementation and Social Implications
The research focus on CBVR a technique that enables users to search videos based on content rather than meta tags. It has many practical implementations in various industries, such as Surveillance and security (like to search large surveillance feed particular incident), Health care and medical imagining(where doctor retrieve similar medical video for faster diagnosis), Education , Entertainment.
The research has significant social implications such as Improved accessibility to information, enhanced public safety, Advancing ai in daily lifes. Using this system in smart cities and digital systems.
Collaborations
Experiments are conducted on publicly available Dataset on DGX-1 server available at our university premises. In future we may plan to collaborate with local authorities for real time video feed to enhance proposed method capabilities.
Future Research Plans
Further in to research our plan is to propose a robust system that can be scaled and applied to all scenarios of videos may it be Medical videos, Education. Further proposed method is supervised approach, we want to explore unsupervised methods to generalize video retrieval.
- Published in Departmental News, News, Research News
Dr Debajyoti’s Research on Improving Biofuel Production
 In the quest for sustainable energy solutions, Dr Debajyoti Kundu, from the Department of Environmental Science and Engineering, examines the potential of biofuels through his research paper – “Heterogeneous Catalysts for Sustainable Biofuel Production: A Paradigm Shift Towards Renewable Energy.” The paper highlights the importance of heterogeneous catalysts for improving biofuel production efficiency. The research also suggests future research to support sustainable energy practices.
In the quest for sustainable energy solutions, Dr Debajyoti Kundu, from the Department of Environmental Science and Engineering, examines the potential of biofuels through his research paper – “Heterogeneous Catalysts for Sustainable Biofuel Production: A Paradigm Shift Towards Renewable Energy.” The paper highlights the importance of heterogeneous catalysts for improving biofuel production efficiency. The research also suggests future research to support sustainable energy practices.
Brief Abstract:
This study focuses on the use of heterogeneous catalysts for sustainable biofuel production. With the growing concerns around fossil fuel depletion and environmental pollution, biofuels derived from biomass are emerging as promising alternatives. The article explores the significant role of heterogeneous catalysts in enhancing biofuel production by improving conversion efficiency, recyclability, and environmental impact. By analyzing various biomass sources, structural compositions, and the application of catalysts in bioethanol, biobutanol, biodiesel, biogas, and biohydrogen production, the study highlights recent advancements and provides recommendations for future research to drive sustainable energy solutions.
Explanation in layperson’s terms:
This research looks at how we can produce more environmentally friendly fuels from natural materials like plants and waste. Traditional fuels like oil and coal are harmful to the environment, so we are turning to biofuels made from biomass (such as plants) as a cleaner alternative. A key part of making biofuels efficiently is using special catalysts—materials that help speed up chemical reactions. The study examines how different catalysts are used to convert biomass into biofuels such as bioethanol, biodiesel, and biogas. The goal is to improve the processes, making biofuels more sustainable and accessible for the future.
Practical Implementation and Social Implications:
This research has significant implications for advancing renewable energy. The use of heterogeneous catalysts can make biofuel production more efficient and environmentally friendly, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and mitigating climate change. By optimizing biofuel production processes, we can develop cleaner energy solutions that are sustainable, carbon-neutral, and beneficial for the environment. This study also supports the ongoing shift towards renewable energy, ensuring that biofuels can contribute to reducing global energy crises and health risks associated with fossil fuel use.
Future Research Plans
Our future research will focus on the development and optimization of biocatalysts for the bioconversion of biomass into biofuels. We aim to enhance the efficiency and sustainability of biocatalytic processes, exploring new catalysts and reaction conditions that can improve the conversion of various biomass feedstocks into valuable biofuels. This research will contribute to advancing biofuel production technologies, with an emphasis on reducing environmental impact and improving the scalability of bioconversion processes for renewable energy solutions
- Published in Departmental News, ENVS News, News, Research News
Insights into Success in the Corporate Environment

The Department of Management organised a Guest Talk on the topic “The Commercial Real Estate Industry; Trends & Insights” on January 17, 2025. Mr Dibashish Ghosh, Senior Vice President and Country HR Head at Berkadia delivered an insightful session on the transition from Campus to Corporate. With over 18 years of extensive experience in human resources, Mr Ghosh has successfully led global organisations and Indian conglomerates, including GE and Genpact, in key leadership roles. His expertise, spanning organisational culture transformation, change leadership, and talent management, gave professional tips to MBA students by sharing real-world experiences, challenges and strategies for success in the corporate environment.
The session provided a holistic perspective, enabling students to connect theoretical knowledge with real-world applications in the Financial Services and Commercial Real Estate domains. The talk focused on enhancing Real Estate Industry awareness—the trends, challenges, and opportunities; Understanding the Key Financial Components and their integration with real estate investments; Knowledge of Asset classes and opportunities for investing in Commercial Properties; Practical insights into investment and mortgage banking; Impact of Regulatory and economic factors; Networking and mentorship; and Preparation for Corporate Roles.
- Published in Departmental News, News, Paari Current Happenings, paari-guest-lectures
Tech Wizards Claim South Zone Title at Nation Building Competition

In a world where the potential of GenZs is often questioned, two of our students, Md. Hadi Mahmood and Md Ahmed Raza Khan have proven that their engagement can deliver meaningful change. These III-year BTech CSE students have showcased an inspiring display of their intellect and innovative prowess at the Nation Building Case Study Competition, an annual event that aligns with the “Viksit Bharat” initiative led by Hon’ble Prime Minister Shri. Narendra Modi, inviting college teams from across the nation to develop creative strategies aimed at transforming India into a developed country by 20247.
Here’s an excerpt of their interview:
1. What was the competition/event about?
The NationBuilding Case Study Competition is an annual event organised to inspire young college students to contribute to India’s development by addressing critical national issues. Participants engage in a 2-month-long journey involving multiple rounds, including an online quiz, presentation submissions, zonal finals, and the national finals in New Delhi. The competition is judged by a distinguished panel of experts in the given domain.
This year’s competition, NationBuilding Case Study Competition 2025, focused on the problem statement of identifying the gaps in India’s sports environment. Participants were tasked with studying the sports systems of other countries, analysing their strengths, and drafting a model to achieve India’s vision of hosting and winning 100 medals in the Olympics by 2036. This theme aimed to encourage innovative solutions to elevate India’s standing in global sports and align with the broader goal of nation-building.
2. What place did you secure?
We secured the 1st rank in the South Zone during the third round of the competition, competing against teams from multiple prestigious institutions. This achievement has advanced us to the national finals, where we will compete against the top 2 teams from each of the six zones: North, South, East, North East, West, and Central.
3. How did you find out about the competition?
We discovered this opportunity on the Unstop platform. The NationBuilding Case Study Competition is widely recognised and attracts thousands of teams annually, making it a highly sought-after event for students across India.
4. Who were your competitors
In the South Zone, we competed against 10 teams from premier institutions. The competition was intense, as participants brought innovative solutions to the table, reflecting the high level of talent and dedication among the youth.
5. Your feelings on advancing this far and future aspirations.
We are excited to have advanced to the national finals. Competing against the best teams from across the country is both a challenge and an opportunity to showcase our strategic thinking and problem-solving skills. This competition has allowed us to apply our skills & knowledge to real-world issues, which has been incredibly rewarding. We look forward to the final round and hope to contribute meaningfully to the vision of a developed India.
- Published in CSE NEWS, Departmental News, News, Students Achievements



