 Dr Om Jee Pandey Two research papers of Dr Om Jee Pandey, Assistant Professor, Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, have been accepted in reputed IEEE Journals. The papers titled “Multiuser Full-Duplex IoT Networks with Wireless-Powered Relaying: Performance Analysis and Energy Efficiency Optimization,” and “Time Synchronized Node Localization Using Optimal H-Node Allocation in a Small World WSN” are going to be published in IEEE Transactions on Green Communications and Networking and IEEE Communications Letters, respectively. The paper “Multiuser Full-Duplex IoT Networks with Wireless-Powered Relaying: Performance Analysis and Energy Efficiency Optimization,” was pursued in collaborations with Prof. Ha H. Nguyen, Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Saskatchewan, Saskatoon, Canada, and Dr Mahendra K. Shukla, who is associated with Macau University of Science and Technology as a Post Doctoral Fellow.
Dr Om Jee Pandey Two research papers of Dr Om Jee Pandey, Assistant Professor, Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, have been accepted in reputed IEEE Journals. The papers titled “Multiuser Full-Duplex IoT Networks with Wireless-Powered Relaying: Performance Analysis and Energy Efficiency Optimization,” and “Time Synchronized Node Localization Using Optimal H-Node Allocation in a Small World WSN” are going to be published in IEEE Transactions on Green Communications and Networking and IEEE Communications Letters, respectively. The paper “Multiuser Full-Duplex IoT Networks with Wireless-Powered Relaying: Performance Analysis and Energy Efficiency Optimization,” was pursued in collaborations with Prof. Ha H. Nguyen, Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Saskatchewan, Saskatoon, Canada, and Dr Mahendra K. Shukla, who is associated with Macau University of Science and Technology as a Post Doctoral Fellow.
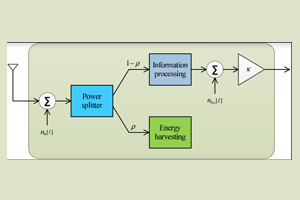 Block diagram of the full-duplex
Block diagram of the full-duplex
wireless-powered relay based on power splitting There has been a growing interest in improving energy efficiency for next-generation Internet of Things (IoT) networks due to the increasing demand for green communications. Motivated by this demand, energy efficiency maximization has been investigated for several networks. Specifically, without considering simultaneous wireless information and power transfer networks, various works have extensively studied energy efficiency maximization for half-duplex networks and full-duplex networks. Further, by considering simultaneous wireless information and power transfer networks, several works have examined energy efficiency maximization in half-duplex networks. Moreover, energy efficiency for next-generation IoT networks with simultaneous wireless information and power transfer has also been studied by considering half-duplex transceivers. It appears that energy efficiency problems for multiuser full-duplex IoT networks have not been studied in the open literature.
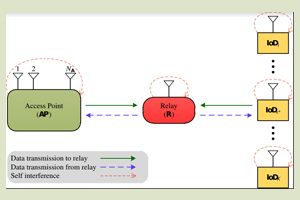 Multiuser FD-IoT network with
Multiuser FD-IoT network with
wireless-powered TWR Motivated by the above discussion, in this work we consider a full-duplex IoT network in which a multi-antenna access point and several single antenna IoT devices exchange information bidirectionally with the aid of a wireless-powered single-antenna relay, under generalized Nakagami-m fading channels. In particular, we consider the power splitting protocol at the full-duplex relay terminal, and each communication terminal operates in the full-duplex mode. For such a network, we first formulate the instantaneous end-to-end signal-to-interference-plus-noise ratios (SINRs) by employing maximum-ratio transmission (MRT) beamforming and maximum-ratio combining (MRC) at the access point A, as well as IoD scheduling. Then, based on the obtained SINRs, we evaluate the overall outage probability and ergodic sum-rate of the network. Furthermore, we develop an optimal power allocation to maximize the network’s EE.
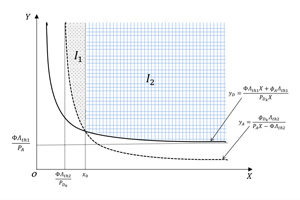 Integral area for the
Integral area for the
overall outage probability Recently, with many technological advancements in wireless data transmission, IoT is expected to affect all aspects of our daily lives with its ever-growing and emerging applications. Traditional wireless communication networks are usually limited by the operational time of energy-constrained devices, and therefore energy consumption minimization is a crucial factor in IoT networks. Simultaneous wireless information and power transfer have emerged as a sustainable solution to the scenarios where replacing or recharging batteries is very costly, and may even be impossible. The basic idea of simultaneous wireless information and power transfer is that since radio frequency signals can carry information and energy at the same time, the received radio frequency signals can be utilized for energy harvesting to keep the energy-constrained devices operational. Existing studies adopt two different protocols, namely time switching and power switching, to implement simultaneous wireless information and power transfer receiver architecture. With these protocols, either the power or time of the received signal is split so that one part is used for information processing, and the other is used for energy harvesting.
The proposed research can play a crucial role in societal development as it can be applied in developing many state-of-the-art applications in the areas related to green healthcare systems, energy-efficient agriculture systems, green transportation, low power home automation, green manufacturing, low power smart utilities, and energy-efficient industries etc.
His other paper “Time Synchronized Node Localization Using Optimal H-Node Allocation in a Small World WSN”, DOI (identifier) 10.1109/LCOMM.2020.3008086, has been done in collaborations with Prof. Rajesh M Hegde, Department of Electrical Engineering, IIT Kanpur and Dr Mahendra K. Shukla, Post Doctoral Fellow at Macau University of Science and Technology. To know more about Dr Pandey’s work in the domain of Small-World Wireless Sensor Network, visit- https://srmap.edu.in/news/dr-om-jee-pandey-small-world-wireless-sensor-network-help-making-smart-applications-industries/.
Dr Pandey is now not only working for the commercial applications of his current research but also has devoted himself to his future projects, that include-
Full-Duplex Network Development for Green Healthcare Systems.
Energy-Efficient Cyber-Physical Systems and Internet of Things.
Development of Energy-Efficient Agriculture Systems.
Green and Intelligent Transportation over Full-Duplex Context-Aware Pervasive Systems.

