Three patent publications from the Department of CSE
The Department of Computer Science and Engineering is pleased to announce the publication of three different patent applications from the department. The patent applications were submitted by the BTech students; Mr Kandala Sree Rama Murthy, Ms Padmaja Buggaveeti, Ms Yadlapalli Sai Harshini, Mr Jagruth K, Ms Shikha Chauhan, and Ms Ravi Srihitha under the guidance of Assistant Professor Dr V M Manikandan. They are making the institution proud with their passion and enthusiasm for the research domain.
 The invention of a new scheme that will help to retrieve relevant videos from a large pool based on the given keyword is an impressive concept with societal relevance. Dr V M Manikandan and BTech students; Ms Yadlapalli Sai Harshini, Mr Jagruth K, Ms Shikha Chauhan, and Ms Ravi Srihitha got their patent application titled A novel video retrieval system and method based on textual information (application number: 202241002653) published.
The invention of a new scheme that will help to retrieve relevant videos from a large pool based on the given keyword is an impressive concept with societal relevance. Dr V M Manikandan and BTech students; Ms Yadlapalli Sai Harshini, Mr Jagruth K, Ms Shikha Chauhan, and Ms Ravi Srihitha got their patent application titled A novel video retrieval system and method based on textual information (application number: 202241002653) published.
The conventional video retrieval system uses the metadata to retrieve the appropriate videos. The new scheme processes the video and identifies the text information within the video, which will be compared with the given keyword. They introduced a scene change detection technique to select the frames for further processing in the new system to reduce the overall processing time.
The new scheme will help to retrieve appropriate educational videos from a large video pool based on the given keyword. The processing time is a significant concern in the scheme proposed. The researchers’ future work will be focused on improving the time complexity of the scheme.
 The other research team invented a prediction error histogram shifting-based approach to hide secret messages in a cover image. The patent application submitted by Dr V M Manikandan and Third-year BTech-CSE Student, Ms Padmaja Buggaveeti, is titled A reversible data hiding system and method for image transmission (application number: 202241002654). The method ensures the lossless recovery of the original image during data extraction. The researchers considered the overflow issues in the histogram shifting approach and proposed an efficient method to handle this.
The other research team invented a prediction error histogram shifting-based approach to hide secret messages in a cover image. The patent application submitted by Dr V M Manikandan and Third-year BTech-CSE Student, Ms Padmaja Buggaveeti, is titled A reversible data hiding system and method for image transmission (application number: 202241002654). The method ensures the lossless recovery of the original image during data extraction. The researchers considered the overflow issues in the histogram shifting approach and proposed an efficient method to handle this.
Reversible Data Hiding (RDH) provides a way to embed some data in a selected image so that in the future, the hidden data can be extracted along with the recovery of the original image. The new RDH scheme invented by the researchers can be used in the healthcare sector to embed patient reports in medical images, or cloud service providers can use it to embed metadata in the digital data. Their future work will focus on designing and implementing robust reversible data hiding schemes capable of resisting attacks.
 A system to facilitate secure transmission of an image along with embedded text (application number: 202241005221) is the third patent application that got published and was submitted by Dr V M Manikandan and Final year B.Tech-CSE Student Mr Kandala Sree Rama Murthy. The researchers invented a method to embed a message into a selected image during the image encryption process, which provides secure transmission of messages. The receiver will be able to extract the hidden message during decryption. The presented method is useful in medical image transmission to store patient details in the medical image.
A system to facilitate secure transmission of an image along with embedded text (application number: 202241005221) is the third patent application that got published and was submitted by Dr V M Manikandan and Final year B.Tech-CSE Student Mr Kandala Sree Rama Murthy. The researchers invented a method to embed a message into a selected image during the image encryption process, which provides secure transmission of messages. The receiver will be able to extract the hidden message during decryption. The presented method is useful in medical image transmission to store patient details in the medical image.
The transmission of medical images and health reports from one hospital to another is widespread in the healthcare sector. Hospitals may want to handle many medical images and health reports every day and ensuring the one-to-one correspondence between them is a tedious task. The invented method will help embed health reports in medical images during encryption. The encrypted medical images (embedded with health reports) can be transmitted securely. The receiver will be able to extract the hidden message after medical image decryption. The researchers’ future work will focus on improving the invented method’s embedding capacity so that lengthy reports can be embedded into the medical images.
- Published in CSE NEWS, Departmental News, News, Research News
Green hydrogen to combat global warming
‘Energy Conversion & Management’ is a journal that belongs to the top 2% of the “Renewable Energy, Sustainability, and the Environment” subject category. Publishing a paper with an impact factor of 9.7 in such a journal is a considerable achievement. Assistant Professors Dr Sabyasachi Chakrabortty and Dr Mahesh Kumar Ravva and their PhD scholar Ms Mounika Sai Ambati from the Department of Chemistry have accomplished this by publishing a paper titled Photovoltaic/Photo-Electrocatalysis Integration for Green Hydrogen: A review in this Q1 journal.
Abstract of the research
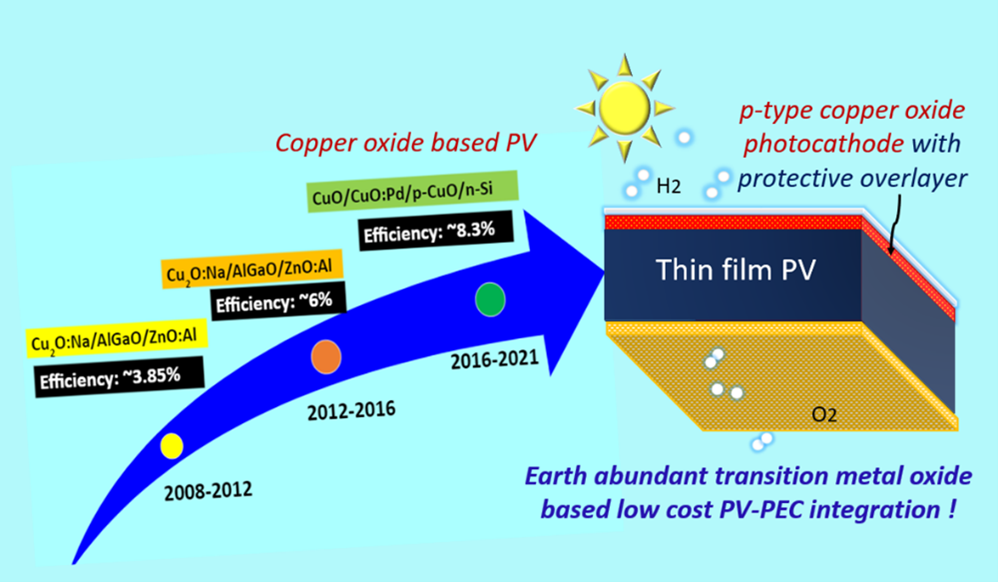 Solar light-driven hydrogen generation via water splitting is essential to combat global warming and CO2 emission. The production of hydrogen from fossil fuels produces massive amounts of CO2. Developing a sustainable and eco-friendly approach to hydrogen production is the need of the hour. Photoelectrochemical water splitting is a clean way to produce hydrogen by using water. The hydrogen generated through water splitting is referred to as Green Hydrogen. Photoelectrochemical water splitting uses metal oxides as photocathode/anode. The challenges that occur here are stability, low efficiency, and large-scale development (reusable electrodes are essential). Hence, the primary goal is to demonstrate photoelectrodes using different metal oxides by in-situ doping of different metals to detect the challenges.
Solar light-driven hydrogen generation via water splitting is essential to combat global warming and CO2 emission. The production of hydrogen from fossil fuels produces massive amounts of CO2. Developing a sustainable and eco-friendly approach to hydrogen production is the need of the hour. Photoelectrochemical water splitting is a clean way to produce hydrogen by using water. The hydrogen generated through water splitting is referred to as Green Hydrogen. Photoelectrochemical water splitting uses metal oxides as photocathode/anode. The challenges that occur here are stability, low efficiency, and large-scale development (reusable electrodes are essential). Hence, the primary goal is to demonstrate photoelectrodes using different metal oxides by in-situ doping of different metals to detect the challenges.
- Published in Chemistry-news, Departmental News, News, Research News
Evaluating workplace well-being

Employee wellbeing and productivity of the organisation are closely interlinked concepts mutually impacting each other in the long run. The idea of workspace wellness and health promotion has been making rounds in recent times, and the outset of the coronavirus pandemic has given added importance to the topic. Having conducted intense study in this regard, Prof AVS Kamesh and his PhD scholar Ms Ashrafunnisa Mohammed from the Department of Management have authored a chapter titled ‘’Evaluating the Role of Workplace Well-Being in Enhancing Employee Productivity in the 21st Century’’, in book Transforming Lives through Mindfulness published by IIM Bodh Gaya AND Excel India Publishers.
Their study tries to evaluate the unique role of workplace well-being in enhancing employee productivity in the 21st century. The contemporary business world is characterised by organisations competing against each other. In a dynamic and complex business environment, the main aim of modern corporate organisations is to retain talented employees by ensuring mindfulness and workplace well-being because these employees are the main sources of competitive advantage from a strategic point of view. Thus, an enhanced level of workplace wellbeing is an effort to create happy and productive workers so that they work optimally and happily. Work is a key social determinant of population health and well-being.
Workplace well-being in India is often focused on changing individual health behaviours through employer wellness programs. The Covid-19 health crisis brought into focus, some of the limitations of present approaches revealing structural conditions that intensify the physical and psychosocial problems of employees and their family members. The onset of the Covid-19 pandemic augured the new dimension of workplace well-being by converting home into a happy place to work. This perspective leads management experts and human resource managers to think about a combined model of work and home as a place of well-being.
This chapter is significant in the times of Post Covid-19 with new perspectives evolving to discuss work-life balance and well-being at workplace which are significantly related to the productivity of the employees. The article mainly targets management educators, corporate managers and personnel managers from public sector companies in India, calling for a comprehensive renovation in the workplace environment.
- Published in Departmental News, News, Paari Current Happenings, Research News
Co-edited and authored in the world’s longest-running science journal
Dr Soumyajyoti Biswas, Assistant Professor, Department of Physics, had two lucky breaks as he got his article “Kinetic Exchange Models of Societies and Economies” featured in the prestigious journal Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A, the theme issue co-edited by Dr Biswas himself, along with Dr Guiseppe Toscani from the University of Pavia, and Dr Parongama Sen from the University of Calcutta. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society has the prestige of being the world’s longest-running science journal launched in 1665. Publishing high-quality theme issues on topics of current importance and general interest within the physical, mathematical, and engineering sciences, the journal continues its history of influential scientific publishing.
A kinetic model of binary interaction, with conserving or non-conserving exchange, has been an elegant and powerful tool to explain collective phenomena in myriad human interaction-based problems, where an energy consideration for dynamics is generally inaccessible. Nonetheless, in this age of Big Data, seeking empirical regularities emerging out of collective responses is a prominent and essential approach, much like the empirical thermodynamic principles preceding quantitative foundations of statistical mechanics.
Through this theme issue, the authors intend to bring together the current progress in the applications of kinetic exchange models in various applications of societies (opinion formations, rating, social networks, fake news, etc.) and economies (inequality measures, taxation, trade models, behavioral economics, etc.) using numerical simulations, machine learning techniques, analytical methods, and data analysis, reported by physicists, social scientists, mathematicians and economists through some of the original and reviewed articles.
In human interactions, such as a trade (exchange of money) or, discussions or debates (exchange of opinions), following simple dynamical rules, a collection of agents (a society) shows emergent properties that are widely seen in real data (distributions of wealth, formation of consensus, etc.). Without knowing the complexities that are involved at the individual levels, it is, therefore, possible to understand the average properties of the society as a whole. This is reminiscent of simple elastic collisions of ideal gas molecules that give average thermodynamic properties, such as temperature, pressure, etc. without knowing the complexities of the individual atoms. This has been a widely followed route to formulate statistical physical models of societies and economies.
The kinetic exchange models have been a very successful set of tools to understand the socio-economic emergent properties from simple models. Among other things, these models helped understand the growth of economic inequalities, the effects of taxes as well as the spread of opinions. A close quantitative resemblance with real data from various countries of the world demonstrates its usefulness.
The future prospects of the kinetic exchange models for societies and economies include possible predictions of extreme fluctuations in average measurable quantities by looking at the inequality of time series data. The models can help us in identifying the features of the real data that can mirror the underlying extreme fluctuations.
- Published in Departmental News, News, Physics News, Research News
Department of ECE publish paper on Fourier holography

A paper titled “Sparse reconstruction for integral Fourier holography using Dictionary Learning method” has been published by Dr Inbarasan Muniraj, Dr Karthikeyan Elumalai and Dr Sunil Chinnadurai – Assistant Professors of Electronics and Communications Engineering at SRM University-AP, along with PhD students Lakshmi Kuruguntla and Vineela Chandra Dodda.
The paper proposes reconstructing holograms from fewer data, thereby reducing the need for processing the complete hologram data, which is otherwise computationally expensive.
Abstract: A simplified method was demonstrated to generate a hologram from multiple two-dimensional (2D) images. Sparse reconstruction was shown using the Sequential Generalised K-means (SGK) algorithm. It is shown that the proposed sparse reconstruction method provides a good hologram quality, in terms of peak signal-to-noise ratio, even under ~90% sparsity.
The paper is written in collaboration with Professor John T Sheridan, Vice-Principal for Research & Innovation – College of Engineering & Architecture, Head of School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, University College Dublin, Ireland.
Holography has been shown useful for biomedical imaging, cryptography, data storage, and entertainment. The future plans of the research group include extending this approach to other holographic systems such as digital holography and holographic microscopy.
- Published in Departmental News, ECE NEWS, News, Research News
Network resource allocation for emergency management
The focus of the network keeps changing with every generation of communication technology. The 5G era is waiting for the next generation to bring a remarkable revolution in communication technologies. Applying various changes and modifying the drawbacks of 5G technology can help us to improve the features of the upcoming 6G. The Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering is delighted to inform you that the paper, “Network Resource Allocation for Emergency Management based on Closed Loop Analysis” has been published by Dr Udaya Sankar, Assistant Professor, and BTech students; Sai Jnaneswar J and VMVS Aditya, in “ ITU Journal on Future and Evolving Technologies – 2nd special issue on AI and machine learning solutions in 5G and future networks”.
Abstract of the research
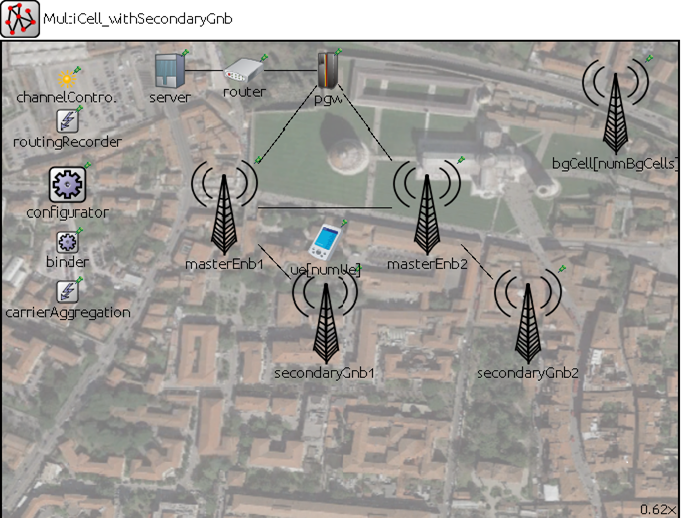 Telecommunication systems being a critical pillar of emergency management, intelligent deployment, and management of slices in an affected area, will help emergency responders. Techniques such as automated management of ML (machine learning) pipelines across the edge and emergency responder devices, usage of hierarchical closed-loops, and offloading inference tasks closer to the edge, can reduce latencies for first responders in case of emergencies. This paper describes the major findings of building a Proof of Concept (PoC) for network resource allocation for emergency management using a hierarchical autonomous artificial intelligence (AI)/ML-based closed-loops in the mobile network, which was organized by the Internal Telecommunication Union Focus Group on Autonomous Network (ITU FGAN). The background scenario for this PoC included the interaction between a higher closed-loop in the Operations Support System (OSS) and a lower closed-loop in RAN (Radio Access Network) to intelligently share RAN resources between the public and emergency responder slice. Representation of closed-loop “controllers” in a declarative fashion (Intent), triggering “imperative actions” in the “underlay” based on the intent, setup of a data pipeline between various components, and methods of “influencing” lower layer loops using specific logic/models, were some of the important aspects investigated by various teams. The main conclusions are summarised in this work, along with the significant observations and limitations from the PoC as well as future directions.
Telecommunication systems being a critical pillar of emergency management, intelligent deployment, and management of slices in an affected area, will help emergency responders. Techniques such as automated management of ML (machine learning) pipelines across the edge and emergency responder devices, usage of hierarchical closed-loops, and offloading inference tasks closer to the edge, can reduce latencies for first responders in case of emergencies. This paper describes the major findings of building a Proof of Concept (PoC) for network resource allocation for emergency management using a hierarchical autonomous artificial intelligence (AI)/ML-based closed-loops in the mobile network, which was organized by the Internal Telecommunication Union Focus Group on Autonomous Network (ITU FGAN). The background scenario for this PoC included the interaction between a higher closed-loop in the Operations Support System (OSS) and a lower closed-loop in RAN (Radio Access Network) to intelligently share RAN resources between the public and emergency responder slice. Representation of closed-loop “controllers” in a declarative fashion (Intent), triggering “imperative actions” in the “underlay” based on the intent, setup of a data pipeline between various components, and methods of “influencing” lower layer loops using specific logic/models, were some of the important aspects investigated by various teams. The main conclusions are summarised in this work, along with the significant observations and limitations from the PoC as well as future directions.
Explanation of the research
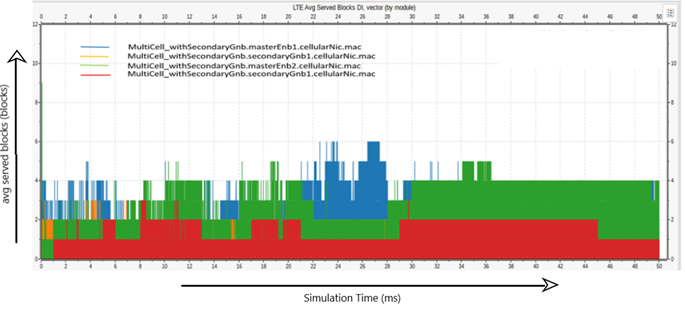 This is a collaborative study where the researchers have developed and implemented a hierarchical closed-loop that autonomously handles an emergency case. This project contains several groups working on separate functions such as monitoring, computing, ML selection, and resource allocation. Some presented how the AI agents and the network can be adapted to assist mobile network users in Search, Diagnostic, and Rescue (SDAR) missions. Some integrated the implementation of the closed loops in O-RAN based software. The researcher’s role in this project is to generate the data which will be used for analysis and this gets integrated with another team. Rather than putting dummy data and analysing or creating and training a machine learning model, we use the Simu5g simulator which is library-based on OMNET++ framework to generate data, mainly resource allocation data. In Simu5g they configure the required network, set all the input parameters such as and simulate it for a specific duration of time. After simulation, the various results are obtained like SINR, throughput, resource block allocation, and many more. This data of the selected parameter results is converted into CSV files and handed over to the required for ML. This project blends all the chunks of work like monitoring, computing, ML selection, and resource combination, to facilitate network resource allocation for emergency management.
This is a collaborative study where the researchers have developed and implemented a hierarchical closed-loop that autonomously handles an emergency case. This project contains several groups working on separate functions such as monitoring, computing, ML selection, and resource allocation. Some presented how the AI agents and the network can be adapted to assist mobile network users in Search, Diagnostic, and Rescue (SDAR) missions. Some integrated the implementation of the closed loops in O-RAN based software. The researcher’s role in this project is to generate the data which will be used for analysis and this gets integrated with another team. Rather than putting dummy data and analysing or creating and training a machine learning model, we use the Simu5g simulator which is library-based on OMNET++ framework to generate data, mainly resource allocation data. In Simu5g they configure the required network, set all the input parameters such as and simulate it for a specific duration of time. After simulation, the various results are obtained like SINR, throughput, resource block allocation, and many more. This data of the selected parameter results is converted into CSV files and handed over to the required for ML. This project blends all the chunks of work like monitoring, computing, ML selection, and resource combination, to facilitate network resource allocation for emergency management.
Practical implementations of the research
In this project, the researchers have gathered the simulated data and want to analyse it and apply machine learning algorithms to improve the condition of existing 5G networks. AI/ML model will help to analyse the data which helps in optimizing resource allocation. Optimization algorithms for resource allocation like Interference minimization, Throughput maximization, and many more. Optimising such parameters would be really helpful for the development of new generation networks.
Collaborations
The paper was developed as part of a build-a-thon track, “ITU AI/ML in 5G Challenge: applying machine learning in communication networks” challenge. The researchers worked under the problem statement “ITU-ML5G-PS-014: Build-a-thon (PoC) Network resource allocation for emergency management based on closed-loop analysis”. This project is guided by Dr. V Udaya Sankar under AI-Designed Wireless (AIDW) Project Simulated network scenarios using simu5g for measuring resource allocation. This build-a-thon challenge was started on June 7, 2021 and ended on November 5, 2021. The research team was placed fifth among 12 teams who participated across the world in the “build a thon” track of the global challenge. While the overall challenge saw over 600 participants across more than 80 countries, the “build a thon” track was a unique coding challenge from ITU FG AN. The team worked on the simulation of the 5G system and corresponding analysis using Simu5G from ITU global partners. After the build-a-thon, the teams that have participated in the build-a-thon under the problem statement “ITU-ML5G-PS-014: Build-a-thon (PoC) Network resource allocation for emergency management based on closed-loop analysis” were collaboratively developed the journal from the observations and results that were made during this build-a-thon.
The current research work focuses on the Implementation of a simulation environment to generate data for model training and testing purposes, and serve as a simulation underlay for testing. The simulations allow us to study various configurations and analyse them to optimize the allocations. For the later stages, various machine learning techniques can be applied for the data that was generated through simulation, and further, the comparison can be done for various machine learning techniques.
- Published in Departmental News, ECE NEWS, News, Research News
Communication revolution and data security
The structure of human society is always profoundly affected by the developments happening in the domain of communication. Data security and privacy have always been a concern in the ongoing communication revolution. The Department of Computer Science and Engineering is glad to inform you that the paper, “An Efficient Spatial Transformation-based Entropy Retained Reversible Data Hiding Scheme in Encrypted Images,” has been published by Dr V M Manikandan, Assistant Professor, and his PhD student Mr Shaiju Panchikkil in “Optik Journal” with an impact factor of 2.443.
Abstract of the research
A critical issue with the current communication revolution is data security and privacy, which is an inevitable part of trustworthiness in the communication system. Hence, the applicability of the Reversible Data Hiding schemes (RDH) in this scenario is encouraging and critical, like medical image communication, satellite image transmission, etc. Earlier, we explored Arnold transform in one of our previous works to hide the secret data that uses the Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) model to design a complete RDH scheme. The proposed scheme follows a statistical approach to support recovering the cover image and the embedded information. This approach proves advantageous over the previous work following its computational capability. The scheme designed can retain the entropy of the encrypted images even after embedding the additional information, complementing the security of the encryption algorithm.
Explanation of the research
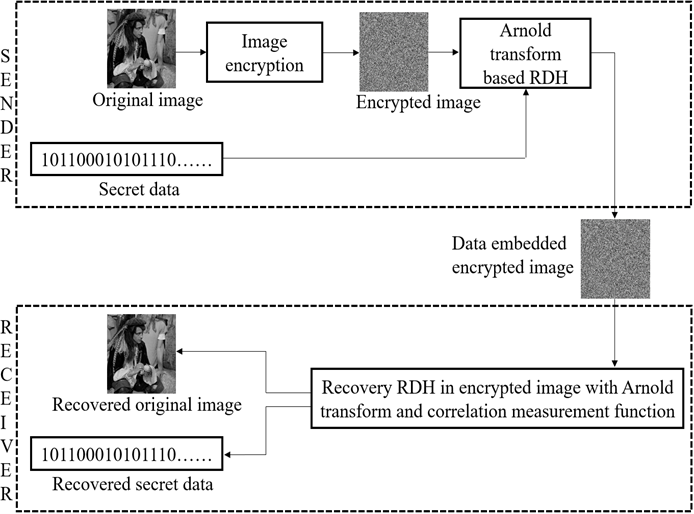 The research focuses on hiding information in an encrypted image and transmitting it to the receiver. Earlier, the researchers used the Arnold transform-based image scrambling algorithm to facilitate the data hiding. But at the receiver end, they have used a convolutional neural network model, which acts as a binary classifier to recover the image properly after extracting the hidden information. The researchers had a few overheads over there, like training the model and then sharing the same with the receiver to recover the original image efficiently. To overcome these overheads, they analysed the correlation of neighboring pixels and introduced a statistical measure at the receiver end to recover the exact image.
The research focuses on hiding information in an encrypted image and transmitting it to the receiver. Earlier, the researchers used the Arnold transform-based image scrambling algorithm to facilitate the data hiding. But at the receiver end, they have used a convolutional neural network model, which acts as a binary classifier to recover the image properly after extracting the hidden information. The researchers had a few overheads over there, like training the model and then sharing the same with the receiver to recover the original image efficiently. To overcome these overheads, they analysed the correlation of neighboring pixels and introduced a statistical measure at the receiver end to recover the exact image.
Social implications of the research
One of the various social implications of the research is an application concerning patient treatment. In a general scenario, during the covid 19 pandemic, people make an online consultation with the doctor by uploading their medical images. If the doctor wants to take a specialist’s opinion, he should send this image and the diagnosis report via a communication medium. The research team’s approach is meaningful in this aspect. The original image is initially encrypted, which makes it unreadable. The diagnosis report information is hidden over the encrypted image. Hence the doctor needs to send only a single file to the specialist. It is also difficult for an external agent or an unauthorized party to decode the report and the image as it is encrypted. Now it is essential to regain the original quality of the recovered image, as any degradation in the quality of the recovered image can lead to a wrong diagnosis. Hence, they have designed the recovery module carefully to extract all the hidden information and recover the original image without compromising its quality.
The researchers are in constant collaboration with Professor Yu-Dong Zhang from the University of Leicester, University Road, Leicester, LE1 7RH, UK, to introduce new strategies to elevate the embedding capacity from the current level without negotiating the quality of the recovered image.
- Published in CSE NEWS, Departmental News, News, Research News
Interdisciplinary research and the integration of perspectives
Assistant professors Dr Sabyasachi Mukhopadhyay and Dr Imran Pancha from the Department of Physics and the Department of Biological Sciences, respectively, along with Ms Ashwini Nawade, a PhD student of the Department of Physics, have developed a method to integrate plant proteins in the solid-state electronic circuits and utilize the biological functionality to produce a thin film, cost-effective photodetector. Their paper entitled Electron Transport across Phycobiliproteins Films and its’ Optoelectronic Properties has been published in the ECS Journal of Solid State Science and Technology with an Impact Factor of 2.07. It is an interdisciplinary research project between the Department of Biotechnology and Physics.
Explanation of the research
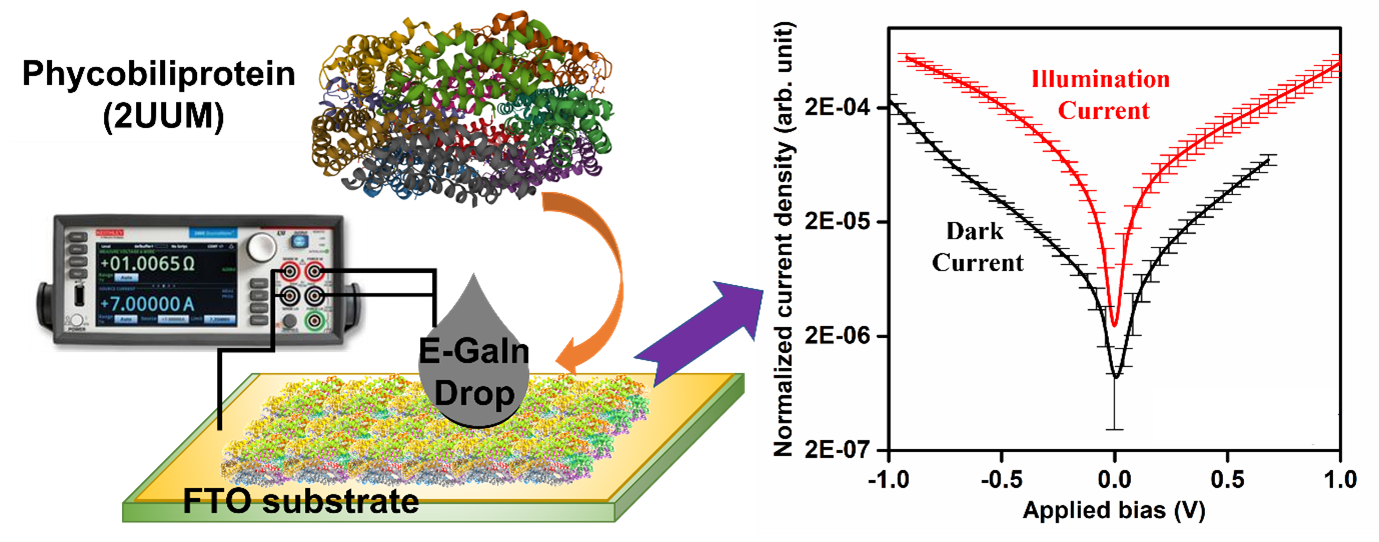 Biomolecules such as proteins, peptides being the most crucial life-forms, have an intimate relationship with various life activities for biological functions. The contemporary work with biomolecules mainly focuses on its evolving potential associated with nanoscale electronics where proteins and peptides are integrated as sensing materials. The researchers explored the optoelectronics functionality of combined proteins known as phycobiliproteins. They investigated electron transport behavior across the phycobiliproteins films under dark and white light illumination. The research affirms that the photochemical activity of the protein is more stable in a solid-state/ thin-film with tightly bonded water molecules than its presence in a buffer solution. Furthermore, the studies demonstrate that phycobiliproteins films modulate their electrical conductivity within their different conformation states. Researchers speculate that the electrical conductance variation could originate from the chemical alteration of cysteine-conjugated bilin chromophores to protein and the electrostatic environment around the chromophores.
Biomolecules such as proteins, peptides being the most crucial life-forms, have an intimate relationship with various life activities for biological functions. The contemporary work with biomolecules mainly focuses on its evolving potential associated with nanoscale electronics where proteins and peptides are integrated as sensing materials. The researchers explored the optoelectronics functionality of combined proteins known as phycobiliproteins. They investigated electron transport behavior across the phycobiliproteins films under dark and white light illumination. The research affirms that the photochemical activity of the protein is more stable in a solid-state/ thin-film with tightly bonded water molecules than its presence in a buffer solution. Furthermore, the studies demonstrate that phycobiliproteins films modulate their electrical conductivity within their different conformation states. Researchers speculate that the electrical conductance variation could originate from the chemical alteration of cysteine-conjugated bilin chromophores to protein and the electrostatic environment around the chromophores.
The research explores the photochemical properties and electrical transport efficiency of phycobiliproteins (PBPs) films. In addition, it investigates the optoelectronics functionality of PBPs films by studying electron transport behavior across the protein films under a dark state and white light illumination. The researchers proposed to develop a photodetector with the protein film in the future.
- Published in Biology News, Departmental News, News, Physics News, Research News
Metaheuristics attribute selection model for efficient diagnosis of chronic disorders
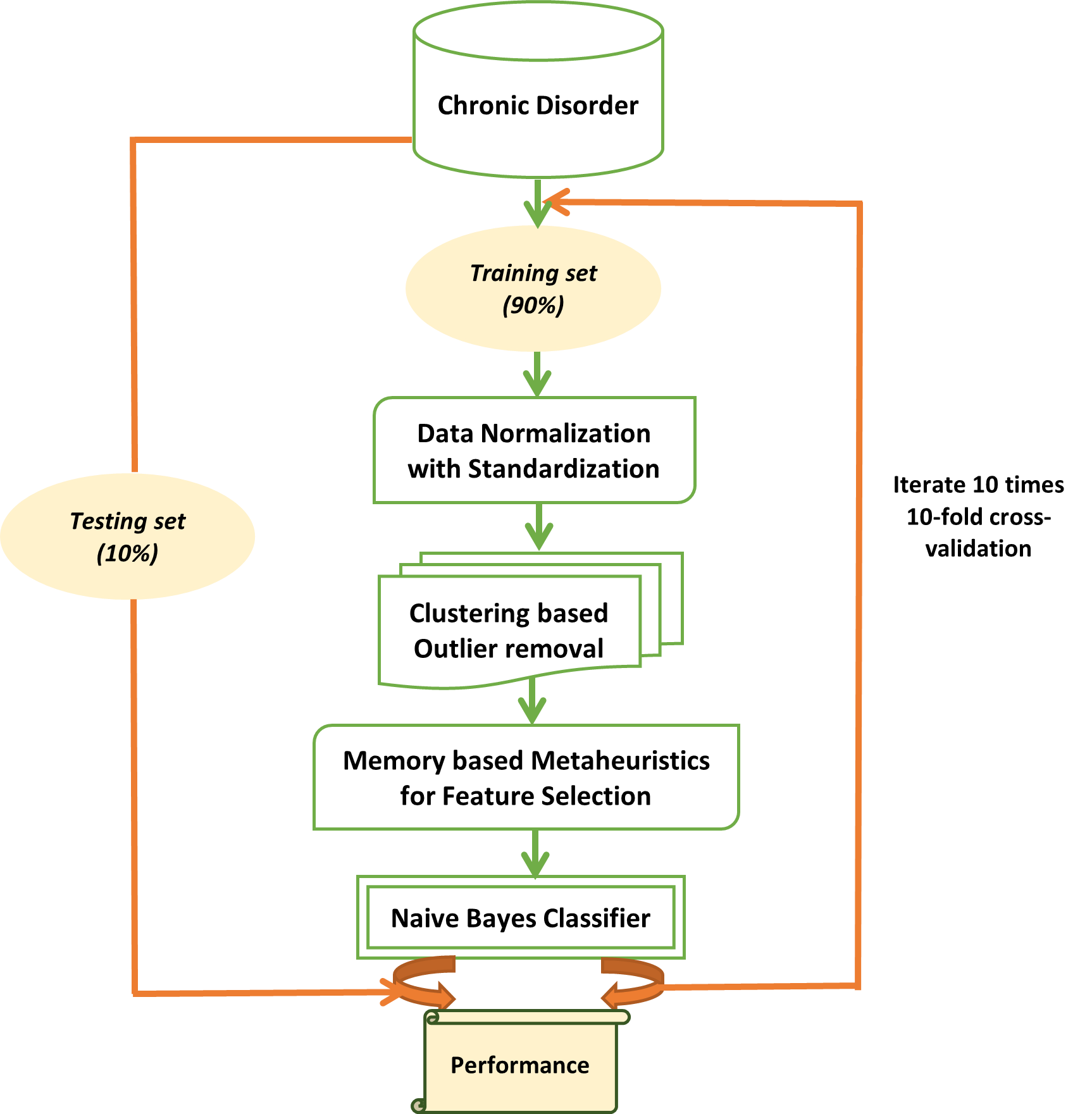 The technological advancements in the medical domain have aided in the effective collection of data such as personal information, clinical history, and disease symptoms of patients. However, the accumulation of massive quantity of data may cause errors in the diagnosis of the disease. A chronic disease dataset may be comprised of numerous symptoms and attributes where not all of them are of equal importance in disease diagnosis. A few of those attributes may be less relevant or redundant.
The technological advancements in the medical domain have aided in the effective collection of data such as personal information, clinical history, and disease symptoms of patients. However, the accumulation of massive quantity of data may cause errors in the diagnosis of the disease. A chronic disease dataset may be comprised of numerous symptoms and attributes where not all of them are of equal importance in disease diagnosis. A few of those attributes may be less relevant or redundant.
Through her research, Dr Priyanka from the Department of Computer Science and Engineering proposes metaheuristics driven attribute optimization techniques that can be implemented in optimizing chronic disease datasets to achieve optimal efficiency in disease risk prediction which can help in proper medical diagnosis. Her paper titled “A Decisive Metaheuristics Attribute Selector Enabled Combined Unsupervised-Supervised Model for Chronic Disease Risks Assessment” was published in the Q1 journal Computational Intelligence and Neuroscience.
 This research can be used to develop a decision support system to assist medical experts in the effective analysis of chronic diseases in a cost-effective manner. The system model may be used to assist medical experts in the efficient diagnosis of chronic disease risks. In future, the research study can be further enhanced to validate the model on more complex heterogeneous datasets with varying sizes and structures. Also, deep learning methods can be employed using image-based real-time datasets.
This research can be used to develop a decision support system to assist medical experts in the effective analysis of chronic diseases in a cost-effective manner. The system model may be used to assist medical experts in the efficient diagnosis of chronic disease risks. In future, the research study can be further enhanced to validate the model on more complex heterogeneous datasets with varying sizes and structures. Also, deep learning methods can be employed using image-based real-time datasets.
Abstract of the Research
Advanced predictive analytics coupled with an effective attribute selection method plays a pivotal role in precise assessment of chronic disorders risks in patients. In this paper, a novel buffer enabled heuristic a Memory based Metaheuristics Attribute Selection (MMAS) model is proposed, which performs local neighbourhood search for optimizing chronic disorders data. Heart disease, breast cancer, diabetes and hepatitis are the datasets used in the research. Upon implementation of the model, a mean accuracy of 94.5% using MMAS was recorded and it dropped to 93.5% if clustering was not used. The average precision, recall and f-score metric computed were 96.05%, 94.07% and 95.06% respectively. The model also has a least latency of 0.8 sec. Thus it is demonstrated that chronic disease diagnosis can be significantly improved by heuristics based attribute selection coupled with clustering followed by classification.
Figure 1: The proposed Metaheuristics attribute selector based classification model for chronic disorders detection
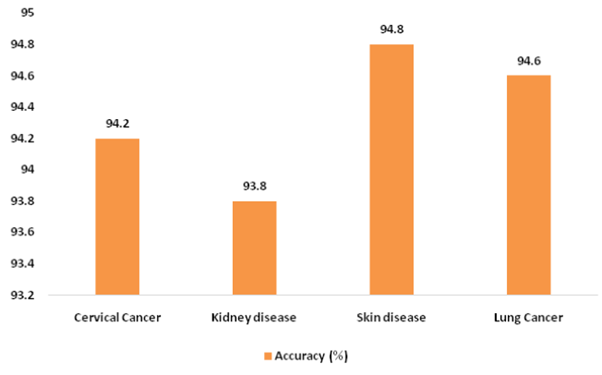
Figure 2: Accuracy analysis of MMAS method on different disease datasets
- Published in Computer Science News, Departmental News, News, Research News
Ultra-stable perovskite nanocrystals for light-emitting applications
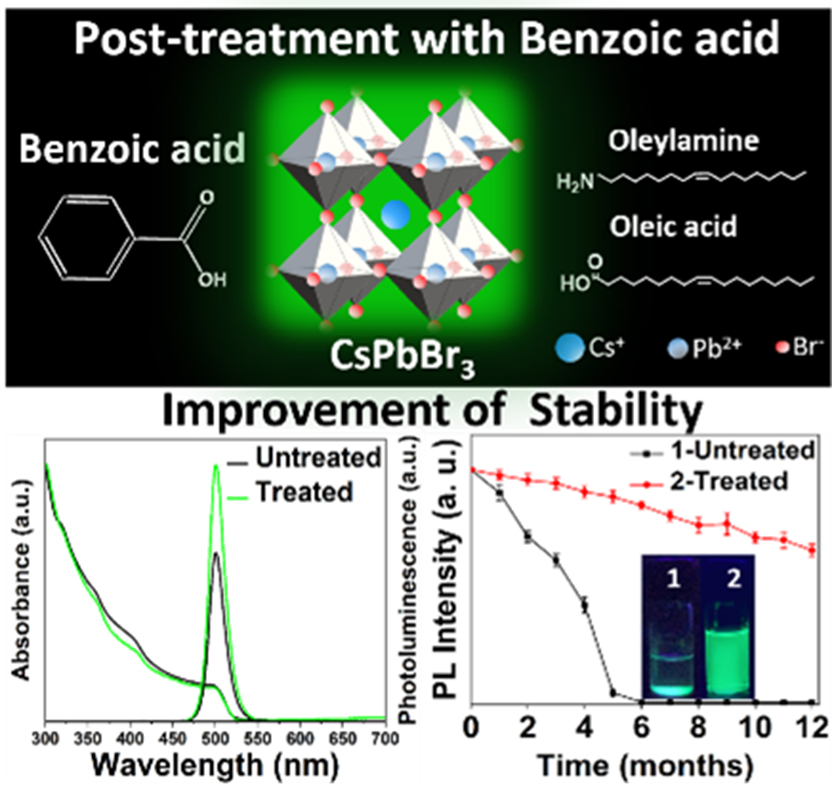
Cesium lead halide perovskite nanocrystals (PNCs) belong to the flourishing research area in the field of photovoltaic and optoelectronic applications because of their excellent optical and electronic properties. Mainly, Cesium lead bromide (CsPbBr3) NCs with bright green photoluminescence (PL) and narrow full-width at half-maximum (FWHM) of <25 nm are the most desirable for television displays and green-emitting LEDs. However, challenges with respect to CsPbBr3 PNCs‘ stability, limit their usage in practical applications. The recent findings of Dr Nimai Mishra and his research team assert that surface passivation with an additional ligand could be an excellent, easy, and facile approach to enhancing the photoluminescence and stability of PNCs.
Dr Nimai Mishra, Assistant Professor, Department of Chemistry, along with his research group comprising of students pursuing PhD under him, Dr V G Vasavi Dutt, Mr Syed Akhil, Mr Rahul Singh, and Mr Manoj Palabathuni have published their research article titled “Year-Long Stability and Near-Unity Photoluminescence Quantum Yield of CsPbBr3 Perovskite Nanocrystals by Benzoic Acid Post-treatment“ in The Journal of Physical Chemistry C (A Q1 journal published by ‘The American Chemical Society’) having an impact factor of ~4.2.
In this article, the research group addresses the stability issues of green-emitting CsPbBr3 PNCs with simple post-treatment using benzoic acid (BA). A remarkable improvement in PLQY from 69.8% to 97% (near unity) was observed in benzoic acid-treated CsPbBr3 PNCs. The effective surface passivation by benzoic acid is also apparent from PL decay profiles of BA-CsPbBr3 PNCs. The long-term ambient stability and stability against ethanol of BA-CsPbBr3 PNCs are also well presented in the research. The PL intensity of untreated CsPbBr3 PNCs is completely lost within five months since the synthesis date, while ̴ 65% of initial PL intensity is preserved for BA-CsPbBr3 PNCs even after one year.
Furthermore, BA-CsPbBr3 PNCs exhibits excellent photo-stability where 36% of PL is retained while PL is completely quenched when the PNCs are exposed to 24 hours of continuous UV irradiation. Importantly, BA-CsPbBr3 PNCs show excellent stability against ethanol treatment as well. Finally, green, emitting diodes using BA-CsPbBr3 PNCs are fabricated by drop-casting NCs onto blue-emitting LED lights. Thus a simple benzoic acid posttreatment further presents the scope of use of these materials display technologies.
- Published in Chemistry-news, Departmental News, News, Research News

