Research News
- Empowering Innovation at the 2nd Research Scholars’ Summit December 23, 2024
 The varsity concluded the second edition of its distinguished Research Scholars’ Summit. This two-day summit witnessed the participation of 27 universities from the states of Andhra Pradesh and Telangana, resulting in a total of 243 abstract submissions.
The varsity concluded the second edition of its distinguished Research Scholars’ Summit. This two-day summit witnessed the participation of 27 universities from the states of Andhra Pradesh and Telangana, resulting in a total of 243 abstract submissions.The summit delved into four major thematic areas namely: Engineering and Technology; Medicine, Life Sciences, Agriculture and Fisheries; Management, Social Sciences, Humanities, and Applied Sciences, including Computational Physics. Each thematic area encompassed a variety of subtopics.
The academic colloquium featured the esteemed presence of Shri Mannava Mohan Krishna, Honourable Chairman of Andhra Pradesh Technology Services, who graced the occasion as the chief guest. He expressed his vision for collaborative efforts with the researchers, stating, “We want to work with you, partner with you to serve the people better.” Shri Mohan Krishna also highlighted the Chief Minister, Shri N Chadraababu Naidu’s ambition to transform Andhra Pradesh into a technological hub, asserting that summits of this nature represent a commendable starting point. He also referred to the 153 services set to be launched under the WhatsApp Governance initiative by the government of Andhra Pradesh, stating that ideas such as these demonstrate how technological advancements benefit governance and thereby the society.
Prof. Manoj K. Arora, Vice Chancellor, SRM University-AP in his address, reminded the students that this summit serves as a platform for the exchange of ideas and offers a significant opportunity to the researchers for career progression. He emphasised SRM AP’s impressive research trajectory, stating, “in just seven and a half years since its inception, the university has established its presence on the scientific landscape.” While acknowledging the rise in research fervour, he urged attendees to prioritise the societal impact of their work stating that their PhD should symbolise Passion, Hard Work, and Dedication rather than a simple Doctor of Philosophy.
He encouraged students to meticulously frame their professional futures, he said “During your five years at the university, you should aspire to discern the path you wish to pursue—whether as educators, researchers, or entrepreneurs and the university will facilitate all the necessary resources to support your professional journey.” He also extended invitation to the scholars from other universities to come forward and use the infrastructure and facilities that SRMAP has invested in for Research.
The summit showcased a myriad of multidisciplinary research presentations from scholars culminating in the awarding of 18 gold medals, 14 silver medals and several special mention awards across various categories for their exemplary contribution. The success of the summit was further supported by the efforts of the convenors, Dr Sibendu Samanta, Dr Jatis Kumar Dash, and Mr Manikanta Bandlamudi, whose guidance and organisation were instrumental in creating a platform for scholarly exchange and collaboration.
Prof. Ranjit Thapa, Dean – Research, delivered the vote of thanks, expressing gratitude to all participants, organisers, and attendees. The summit culminated in a fruitful and awe-inspiring work showcasing dedication and perseverance and a promise to keep inspiring, igniting and innovating.
Continue reading →









- A Blockchain and IoT-Driven Solution for Farmers December 19, 2024
 Farming is often regarded as an occupation that is challenging and has become a sobriquet for hardship and unpredictability, leaving farmers financially vulnerable and many a times at the brink of poverty. Insuring crops can, however, minimise the risk of loss, making it a viable option as long as the process doesn’t get bogged down by excessive bureaucracy and cumbersome paperwork. Dr Naga Sravanthi Puppala, Assistant Professor at the Department of Computer Science and Engineering has come up with a game-changing solution of utilising blockchain technology and real time IoT data for automatic and quick coverage of crops by simplifying the insurance process thereby helping reshaping the future of agriculture, just when it’s needed most.
Farming is often regarded as an occupation that is challenging and has become a sobriquet for hardship and unpredictability, leaving farmers financially vulnerable and many a times at the brink of poverty. Insuring crops can, however, minimise the risk of loss, making it a viable option as long as the process doesn’t get bogged down by excessive bureaucracy and cumbersome paperwork. Dr Naga Sravanthi Puppala, Assistant Professor at the Department of Computer Science and Engineering has come up with a game-changing solution of utilising blockchain technology and real time IoT data for automatic and quick coverage of crops by simplifying the insurance process thereby helping reshaping the future of agriculture, just when it’s needed most.Abstract
The invention is a groundbreaking design patent that employs a single, sophisticated smart contract policy to autonomously manage the entire crop insurance process. This system innovatively combines blockchain technology with real-time IoT data collection to create an efficient, transparent, and reliable insurance solution for farmers. Central to this invention is a singular smart contract policy designed to oversee every stage of the insurance lifecycle, from policy issuance and dynamic risk assessment to claims processing and payout disbursement. This smart contract policy is meticulously programmed with specific conditions and thresholds, including weather patterns, soil moisture levels, and crop health indicators, all monitored by IoT devices in the field. As these conditions are tracked in real-time, the smart contract policy autonomously adjusts coverage and triggers payouts when necessary, eliminating the need for human intervention. This system not only enhances efficiency by reducing administrative costs but also ensures prompt and accurate payouts. By relying on tamper-proof data and predefined conditions, the invention offers a secure and transparent approach to crop insurance, providing farmers with a dependable safety net against crop losses.
In short, this invention makes crop insurance smarter, simpler, and fairer, giving farmers the support they need when they need it most.Practical Implementation and Social Implications of the Research
Practical Implementation
- Blockchain: Secure platform for immutable records.
- Smart Contracts: Automate insurance claims based on predefined triggers.
- IoT Devices: Monitor crop and environmental data in real-time.
- Oracles: Fetch external data (e.g., weather reports).
- Workflow: Farmers enroll, pay premiums digitally, and receive automatic payouts if crop damage is detected.
Social Implications
- Transparency: Eliminates fraud and delays in claims.
- Inclusivity: Provides insurance access to small-scale farmers.
- Economic Stability: Reduces financial strain on farmers after disasters.
- Sustainability: Encourages data-driven, risk-resilient agriculture.
Future Research Plans:
Building upon the foundation of this invention, my future research will focus on advancing and expanding its applications to maximize impact in agriculture and beyond. Key areas of exploration include:
1. Enhancing IoT Integration for Precision Agriculture
Aimed to develop more advanced IoT devices and sensors that can collect highly specific data on soil quality, weather patterns, and crop health. This data will improve the system’s ability to predict risks and tailor insurance policies to individual farms. Research will also involve optimizing sensor networks for affordability and accessibility to smallholder farmers.
2. Developing Dynamic Risk Assessment Models
By incorporating machine learning and predictive analytics, I plan to create dynamic risk assessment models. These models will continuously learn from real-time data and historical trends, allowing the system to provide proactive alerts to farmers about potential risks and automatically adjust insurance terms to reflect current conditions.
3. Expanding Blockchain Applications Beyond Crop Insurance
While the current focus is on crop insurance, blockchain’s secure and transparent nature offers opportunities for broader agricultural applications. I intend to explore its use for supply chain traceability, ensuring that crops reach markets efficiently and without tampering, and for facilitating peer-to-peer lending among farmers.
4. Testing and Scaling in Diverse Agricultural Environments
Field trials will be conducted in various regions and farming contexts to test the system’s adaptability and scalability. This includes:
- Testing in regions prone to extreme weather conditions.
- Evaluating the system’s performance in specialized farming industries, such as vineyards or organic farming.
- Collaborating with agricultural cooperatives to implement the system across multiple farms simultaneously.
5. Social and Economic Impact Assessment
A critical part of my research will involve studying the socioeconomic impact of this invention on farmers, particularly smallholder farmers. I aim to assess how it influences their livelihoods, productivity, and financial security. This will guide future improvements to make the system more inclusive and equitable.
6. Exploring Policy and Regulatory Frameworks
For widespread adoption, I plan to engage with policymakers to align the system with existing agricultural and insurance regulations. The research will focus on creating policy frameworks that encourage adoption, particularly in developing regions and addressing potential legal challenges related to blockchain and data privacy.
7. Collaborating for Multi-Sectoral Impact
Partnerships with financial institutions, agritech companies, and government agencies to co-develop solutions that integrate blockchain-based insurance with other agricultural services, such as microloans, subsidies, and educational programs.
By addressing these areas, my research will contribute to creating a more resilient and sustainable agricultural ecosystem, empowering farmers with cutting-edge technology while enhancing food security and economic stability globally.
Continue reading → - Student-Teacher Collaboration Culminates in IEEE Transactions December 10, 2024
 The increasing demand for sustainable energy solutions has led to the development of hybrid energy systems that integrate renewable sources like solar photovoltaic (PV) systems and fuel cells (FC). The practical applications of the research in sectors such as electric vehicles and residential power systems, contribute to a more reliable and sustainable energy future contributing to a more reliable and sustainable future.
The increasing demand for sustainable energy solutions has led to the development of hybrid energy systems that integrate renewable sources like solar photovoltaic (PV) systems and fuel cells (FC). The practical applications of the research in sectors such as electric vehicles and residential power systems, contribute to a more reliable and sustainable energy future contributing to a more reliable and sustainable future.Abstract of the research.
This paper introduces novel high-gain tertiary port boost converter (HGTPBC) designed for hybrid energy sources such as solar photovoltaic (PV) and fuel cells (FC). The converter is employed with dual input sources by facilitating modular converters and accomplishes a high step-up voltage gain by virtue of a voltage multiplier in a DC microgrid, where the prosumers can have an islanded operation. The proposed topology allows home appliances to be powered by multiple energy source without the need for a large storage unit. Key features include continuous input current, reduced normalized voltage stress on switches, expandability for multiple input sources and independent source control. The independent control facilitates the standalone operation with single source during source failure or absence. To evaluate the converter performance, a thorough steady-state analysis, both with and without consideration of nonidealities is carried out. Detailed comparisons with existing converter topologies highlight the advantages of the proposed converter. Moreover, the loss distribution and efficiency analysis of proposed converter are presented and found to be 91.59% efficiency at rated power. Theoretical aspects are validated through hardware testing on a 100W laboratory prototype.
Explanation of the Research in layperson’s terms.
The proposed converter is a 100W DC-DC converter topology used in hybrid energy systems applications and electric vehicular applications in DC microgrid. The converter can accept two sources like fuel cell and solar PV system to supply the load and even can be extended for a greater number of sources. Thus, it is suitable for various applications of traction vehicles, household electrifications etc. It exhibits a lower switch stress and higher step-up conversion gain.
Practical Implementation and Social implications
The features include high step-up conversion gain, independent control possible, reduced normalised switch voltage stress. And flexible operation based on PV availability. It is most suitable for electric vehicles, Unmanned ariel vehicles, and hybrid energy systems etc. It improves the reliability of the renewable energy source by the incorporation of the second fixed source, fuel cell. It can be used in various on-grid and off-grid applications like home, hospitals, offices, and educational institutions, especially where source reliability is necessary. The major advantage is the reduction in the size of the source due to higher step-up gain and ease of control between the sources.
Future Research Plans
We are working towards the development of efficient and ultra-high gain bidirectional converters for various applications on DC microgrids. That should be able of reducing the source ratings and to integrate multiple sources to improve the grid reliability. Design and implementation of bidirectional multi-port converters for various applications of DC microgrids, such as renewable and hybrid storage integration are the scope of our research.
The link to the article- https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10772206
Continue reading →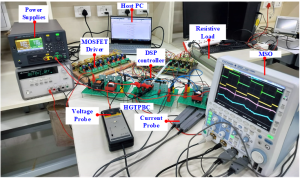
- Research on Vehicle Density Detection Granted a Patent December 3, 2024
 Research Scholars Chetan Mylapilli, Jethin Sai Chilukuri, Rohith Kumar Akula, Sana Fathima, and Assistant Professor Dr Anirban Ghosh from the Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering at SRM University-AP have co-authored an innovative paper titled “A System and Method for Detecting Density-Based Intelligent Parallel Traffic.” This pioneering research delves into the development of an intelligent traffic control system that dynamically adjusts traffic signals based on real-time vehicle density analysis, their research with the patent no- 202241044904 represents a significant step in integrating technology with transportation efficiency.
Research Scholars Chetan Mylapilli, Jethin Sai Chilukuri, Rohith Kumar Akula, Sana Fathima, and Assistant Professor Dr Anirban Ghosh from the Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering at SRM University-AP have co-authored an innovative paper titled “A System and Method for Detecting Density-Based Intelligent Parallel Traffic.” This pioneering research delves into the development of an intelligent traffic control system that dynamically adjusts traffic signals based on real-time vehicle density analysis, their research with the patent no- 202241044904 represents a significant step in integrating technology with transportation efficiency.Abstract
This work presents an intelligent traffic control system that addresses the gaps in the current state-of-the-art by using a novel hardware-software integration. The system evaluates traffic density in each lane direction and dynamically adjusts traffic lights using a computational algorithm to significantly reduce waiting times at junctions. It also ensures safe pedestrian movement and enables parallel traffic flows. A Raspberry Pi serves as the system’s control unit, utilizing video processing to determine traffic density, while LEDs simulate the traffic lights. The system integrates various hardware and software components, including Raspberry Pi, LEDs, relay modules, VNC software, and sample traffic videos, to provide an efficient solution to the traffic management problem.
Explanation of Research in Layperson’s Terms
The current system uses a Raspberry Pi to control traffic lights based on real-time video of cars at intersections. It detects how many vehicles are in each lane and adjusts the lights to reduce waiting time. Pedestrian safety is managed by ensuring safe crossing times. LED lights simulate the traffic signals, and the system allows smoother traffic flow by handling vehicles moving in parallel. However, it can’t yet control turning vehicles or prioritize emergency vehicles.
Practical Implementation of the Research
The intelligent traffic control system significantly reduces congestion by dynamically adjusting traffic signals, leading to shorter wait times and smoother commutes. It helps lower pollution and fuel consumption by minimizing idle time at junctions, contributing to better air quality and conservation of resources. Pedestrian safety is improved through designated crossing times, reducing accidents. The system also supports economic growth by cutting time wasted in traffic, enhancing productivity.
Future Research Plans
Future research will focus on adding control for turning traffic and distinguishing between different vehicle types to enable emergency vehicle priority. To improve real-time video processing, the system will transition from Raspberry Pi to more efficient hardware like FPGAs or GPUs. Machine learning will be explored for better vehicle detection and traffic signal optimization. Integration with V2X communication will enhance traffic management, and real-world scalability will be tested for deployment in smart city environments.
The prototype:
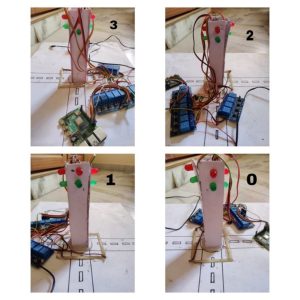

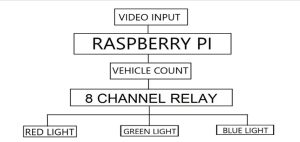
Figure 1. Image of the prototype
Figure 2. Working prototype
Figure 3. Block Diagram of the prototype
Continue reading → - Faculty Collaborate on Interdisciplinary Innovation December 3, 2024
 In an inspiring collaboration, Prof. G S Vinod Kumar and Prof. Sheela Singh from the Department of Mechanical Engineering, Prof. Ranjit Thapa from the Department of Physics, and Dr Rajapandiyan Panneerselvam from the Department of Chemistry at SRM University – AP, along with PhD scholars Ms Harsha K and Ms Arunima J, have co-authored a compelling paper titled “Innovative Approaches to Enhancing the Tarnish Resistance of Silver Alloys.” This groundbreaking research focuses on developing new silver alloys that resist tarnishing, enhancing durability and aesthetic appeal for applications in the jewellery industry. Together, they are paving the way for innovative solutions that blend science with artistry.
In an inspiring collaboration, Prof. G S Vinod Kumar and Prof. Sheela Singh from the Department of Mechanical Engineering, Prof. Ranjit Thapa from the Department of Physics, and Dr Rajapandiyan Panneerselvam from the Department of Chemistry at SRM University – AP, along with PhD scholars Ms Harsha K and Ms Arunima J, have co-authored a compelling paper titled “Innovative Approaches to Enhancing the Tarnish Resistance of Silver Alloys.” This groundbreaking research focuses on developing new silver alloys that resist tarnishing, enhancing durability and aesthetic appeal for applications in the jewellery industry. Together, they are paving the way for innovative solutions that blend science with artistry.Abstract
Silver and its alloys undergo tarnishing with time, which is a black stain on the surface due to the formation of Ag2S. Developing a tarnish resistant Ag alloy was attempted by alloying Ag with elements that form a passive oxide layer on the surface. Germanium is proven to provide better tarnish resistance to sterling silver alloy (92.5wt.% pure) which is available under the trade name of Argentium©. The present work investigates the tarnish resistance behaviour of sterling silver alloy (92.5wt.% pure) containing various additions of Copper, Zinc, Germanium, Aluminium, Beryllium, Titanium, Zirconium, and Magnesium. The alloys were prepared by melting and casting route, followed by Passivation Heat Treatment (PHT) to create a stable and continuous oxide layer. The temperature for PHT was optimized using thermogravimetry analysis (TGA) of the alloys prepared. An accelerated tarnish test was carried out to investigate the tarnishing behaviour of alloy samples obtained before and after PHT. The samples were characterized using XRD, SEM-EDX, TG-DSC, micro-Raman Spectroscopy, and XPS. The change in reflectance of the samples after the tarnish test is determined using UV-visible reflectance spectroscopy. The mechanism behind the tarnish resistance was derived using Density Functional Theory (DFT) by comparing sulphur (S2) and Oxygen (O2) adsorption energies (BE) of the alloying elements.
Explanation of the Research in layperson’s terms
Age-old silver pieces are found in different colours ranging from light yellow(silver Jewellery pieces after a few weeks of usage) to black(archaeological silver pieces). They look different in terms of the metallic white colour and lustrous appearance from fresh silver. This demeans silver and thus affects its market. The major cause of the staining of silver is the interaction of individual silver particles with some elements found common in the atmosphere. We work on the prevention of this staining of silver. For the study, silver is incorporated with other elements which makes silver less interacting with staining elements in the atmosphere. These additional elements create a layer over silver so that it is protected. The appropriate elements are identified by using modelling using computer software. After obtaining appropriate elements, the experimental trials are also done with the same elements until stainless silver is obtained. Then, what happens to the added elements inside silver is also studied by using modern microscopic technics.
Practical/Social Implications of the Research
The major application of the invention is in the jewellery industry. The problem of tarnishing is an age-old threat in jewellery making. The alloys we proposed could be used to make quality silver jewellery/articles that can sustain the colour and lustre for a longer period. This will stop the hesitation from jewellery designers and industries to try intricate designs in silver and find a better market for them. The alloys based on the proposed composition show good grain refinement and thus high hardness. This strengthens the soft silver and improves the range of its applications from low hardness articles to high. The alloys based on the proposed composition have high tensile strength. They deform plastically for a wide range of stress values and will not break easily.
Collaborations:
Waman Hari Pethe & Sons Jewellery
Future Research Plans:
1. Corrosion studies of silver alloys to understand the behaviour in solutions having compositions similar to that of sweat.
2. Study of mechanical properties of silver alloys to develop workable alloys of sterling silver which could be used for jewellery manufacturing
3. Identification of elements having better oxide layer formation when alloyed with silver, by using computational techniques and experimental studies of their properties.
Link to the article:
Continue reading →
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2238785424024633 - Patent Published on Segmentation of Kidney Abnormalities November 29, 2024
 Prompt and timely disease detection forms an essential part of any treatment, Dr Pradyut Kumar Sanki, Dr Swagata Samanta, and research scholar Ms Pushpavathi Kothapalli from the Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering have worked towards a timely and accurate disease detection when it comes to kidney disease diagnosis through medical images. Their innovative research titled, “A System and a Method for Automated Segmentation of Kidney Abnormalities in Medical Images” has been published in the patent journal with Application No. 202441074765 and has significant potential for clinical adoption, improving patient care in kidney disease detection and treatment.
Prompt and timely disease detection forms an essential part of any treatment, Dr Pradyut Kumar Sanki, Dr Swagata Samanta, and research scholar Ms Pushpavathi Kothapalli from the Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering have worked towards a timely and accurate disease detection when it comes to kidney disease diagnosis through medical images. Their innovative research titled, “A System and a Method for Automated Segmentation of Kidney Abnormalities in Medical Images” has been published in the patent journal with Application No. 202441074765 and has significant potential for clinical adoption, improving patient care in kidney disease detection and treatment.Abstract:
This research work aimed to develop an effective method for segmenting kidney diseases, including kidney stones, cysts, and tumours. The method achieved high accuracy in segmenting kidney diseases, with a good mean precision, and recall. The study employed techniques to efficiently select the most relevant features for kidney disease segmentation, identifying key features related to imaging and patient health. The method outperformed other approaches in terms of accuracy, precision, and recall. The study utilized a comprehensive dataset of kidney disease patients to train and test the segmentation method effectively. The results suggest that this method has the potential to be widely adopted in clinical settings, contributing to more accurate and efficient diagnostic tools for kidney disease segmentation and improving patient care in an effective manner.
Practical Implementation:
The practical implementation of the research involves deploying a system for real-time segmentation of kidney diseases, including kidney stones, cysts, and tumours. The method achieved high accuracy in segmenting kidney diseases using deep learning techniques. The model can quickly identify and delineate diseased areas within the kidney. The study employed techniques to select the most relevant features for kidney disease segmentation, focusing on key imaging and health-related characteristics. The method outperformed other approaches in terms of accuracy, precision, and recall. The study utilized a comprehensive dataset of kidney disease patients to train and test the segmentation method. The results suggest that the method has the potential to be widely adopted in clinical settings, contributing to more accurate and efficient diagnostic tools for kidney disease segmentation and improving patient care.
Future Research Plans:
The future plans for the work on chronic kidney disease (CKD) detection and segmentation involve several key areas:
Expanding Disease Coverage: Future research could involve adapting and expanding the segmentation model to detect and segment other kidney-related abnormalities and diseases, such as renal infections or congenital disorders, thereby increasing the versatility and applicability of the tool.
Improving Model Accuracy and Robustness: To further improve accuracy, additional deep learning techniques, such as ensemble learning or advanced attention mechanisms, could be explored. Testing on larger and more diverse datasets could help make the model more robust and generalizable across various patient demographics and imaging devices.
Integration with Multi-modal Data: Incorporating other data types, such as blood test results, genetic markers, or electronic health records, could be an exciting avenue to explore. This would create a multi-modal approach, combining imaging data with clinical information, potentially improving diagnostic accuracy and providing more comprehensive insights into kidney health.
Real-world Clinical Trials: Conducting clinical trials in real-world settings to validate the effectiveness of the segmentation tool with healthcare professionals. Gathering feedback from these trials would provide valuable insights into user experience and model performance, facilitating further refinement.
Developing a User-friendly Interface: Future work could involve creating an easy-to-use interface that seamlessly integrates with hospital systems. This interface would allow healthcare providers to interact with the segmentation results, adjust parameters, and view comprehensive diagnostic reports.
Exploring Semi-supervised and Unsupervised Learning Approaches: To reduce the reliance on labeled data, which can be time-consuming to obtain, exploring semi-supervised or unsupervised learning techniques could be beneficial. These approaches might help in training the model on large datasets without extensive labeling, thereby improving scalability.
Longitudinal Studies for Prognostic Analysis: Research could also focus on tracking patients over time to understand how kidney disease progresses and how segmentation results correlate with long-term health outcomes. This could help in creating predictive models for disease prognosis.
Continue reading →
- Patent on IoT System for Sensor Data Monitoring and Geo-Storage November 29, 2024

Prof. Rupesh Kumar from the Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering and his research cohort, Mr Venkata Naga Sai Kiran Damarla, Mr Prasannakumar Seelam, Ms V L S Tanmay P, and Mr Venkata Ramana Murthy Pondala (BTech ECE students), has published a patent titled “An Integrated Iot System for Sensing, Monitoring, and Geo-Information Storage of Sensor Data” with Application No: 202441065318 for their breakthrough research on developing an intelligent IoT system that can detect environmental changes.
Abstract
This research presents an integrated IoT system designed to monitor environmental conditions and store the corresponding data along with geo-information. The system autonomously collects data from its surroundings, processes it, and stores the information for future retrieval. The system is designed for use in remote monitoring applications where consistent tracking of environmental variables and location data is essential.
Explanation of the Research in Layperson’s Terms
The project aims to create a smart system that can sense changes in its environment—like temperature or humidity—and record those changes alongside its current location and time stamp. The collected data is stored so that it can be retrieved later for analysis, making the system useful in situations like monitoring climate conditions in farming or tracking environmental changes in various locations.
Practical Implementation/Social Implications of Research
The practical implementation of this system spans various fields such as agriculture, environmental management, and logistics. For example, in agriculture, the system can help farmers track environmental changes, allowing them to optimize crop management. Similarly, it can monitor environmental conditions in remote areas, ensuring timely interventions when necessary. The system could also aid in asset tracking, providing both environmental data and the location of critical resources. Its broader social impact lies in its ability to automate data collection, improve accuracy, and reduce human intervention in critical monitoring tasks.

Collaboration
This project was completed with the support and guidance of the Wireless Sensing & Imaging (WSI) Lab. The research team worked closely within the lab to develop the system, utilising the lab’s resources and expertise to achieve the research goals. There were no external collaborations involved in this project.
Prof. Rupesh and his team plan to explore radar design and focus on working with radar technology in their future research. By developing and integrating radar systems, the team aims to enhance IoT applications with advanced sensing capabilities, such as distance measurement, object detection, and environmental monitoring. Their goal is to contribute to more accurate and reliable solutions through the implementation of IoT Integrated Radar technology.
Continue reading → - Research on Real-Time Detection and Classification of Defects in PCBAs November 28, 2024
 In today’s fast-paced technological world, ensuring the quality and reliability of electronic devices is essential. Associate Professor Dr Ramesh Vaddi and his research Scholar Mr Vinod Kumar Ancha from the Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering introduce an innovative system for real-time detection and classification of defects in PCBAs, leveraging advanced machine learning techniques. Their research titled, “System And Method For Real-Time Detection And Classification of Defects in Assembled Printed Circuit Boards (PCBA)” was published in the Patent Journal with Application number 202441045761.
In today’s fast-paced technological world, ensuring the quality and reliability of electronic devices is essential. Associate Professor Dr Ramesh Vaddi and his research Scholar Mr Vinod Kumar Ancha from the Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering introduce an innovative system for real-time detection and classification of defects in PCBAs, leveraging advanced machine learning techniques. Their research titled, “System And Method For Real-Time Detection And Classification of Defects in Assembled Printed Circuit Boards (PCBA)” was published in the Patent Journal with Application number 202441045761.Abstract:
This study presents a new system for real-time detection and classification of defects in Assembled Printed Circuit Boards (PCBAs), which are critical in electronic products and systems. It employs an efficient model with pretrained weights to detect defects for enhanced quality control. The model is initially trained and fine-tuned on a computer, then deployed on a compact computing board. For real-time imaging, a high-definition USB camera is connected to the system, allowing direct defect identification without the need for external devices. The output is shown on a monitor, with the PCBA image featuring clearly labeled boxes to indicate the type and location of defects. This method offers a streamlined approach to defect classification, helping to improve the quality control process in electronics manufacturing.
Explanation of the Research in layperson’s terms:
This research focuses on finding defects or flaws in Assembled Printed Circuit Boards (PCBAs). Which are the “backbone” of most electronic devices, like computers and phones. This system uses a powerful computer model to “look” at these boards and quickly identify any defects, like missing holes, mouse byte, open circuit, short circuit, spur and spurious copper in real-time. The research starts by training this model using a deep learning object detection model on a regular computer, teaching it to recognize what a normal PCBA looks like and what various defects might look like. Once it’s ready, we transfer the model to a small, efficient computer edge board, which does all the processing. A camera is used to capture images of the PCBAs, and the system analyzes these images to find respective defects. The results are displayed on a screen, where it clearly marks where the defects are and what kind of defects they are. Overall, this system helps companies detect defects in their electronics manufacturing process quickly and accurately, which can save time, reduce waste, and improve the quality of their products.
Practical Implementation:
The practical implementation of our research involves deploying a system for real-time detection and classification of defects in Assembled Printed Circuit Boards (PCBAs) a crucial component in nearly all electronic devices. By using advanced Deep learning techniques, our system can quickly identify manufacturing defects, allowing electronics manufacturers to detect the defect early in the production process. This can lead to significant improvements in quality control, reduced waste, and lower production costs. By improving quality control in electronics manufacturing, the system can help reduce electronic waste, which is a significant environmental concern. Early detection of defects also reduces the chances of faulty electronic products reaching consumers, thereby improving safety and reducing the need for product recalls. Additionally, the efficiency and accuracy of our system could lead to more reliable electronics, contributing to greater consumer trust in electronic products. This, in turn, could encourage companies to invest in higher-quality manufacturing processes, ultimately leading to a more sustainable and responsible electronics industry.
Collaborations:
To develop our system, we first trained a computer model to recognize defects in Assembled Printed Circuit Boards (PCBAs). This training process involved feeding the model a large dataset of PCBA images, some with defects and some without. By analyzing these examples, the model learned to identify common defects, like Missing hole, mouse byte, open circuit, short circuit, Spur and Spurious copper. Once the model was trained, we implemented it in a real-time setting. This meant integrating it with equipment that could inspect PCBAs as they were being produced. The system used a camera to capture images of each PCBA and then applied the trained model to analyze those images, checking for any defects. With the model running in real-time, the system could immediately detect issues and alert the manufacturing team, allowing them to correct problems on the spot. This approach helped improve the quality of the final product and reduced the chances of defective electronics reaching consumers. It also sped up the quality control process and reduced waste, making the entire manufacturing process more efficient.
Future Research Plans:
Our future research plans focus on enhancing and expanding our system for defect detection in Assembled Printed Circuit Boards (PCBAs):
Model Optimization: We aim to further refine our machine learning model to improve accuracy and speed. This includes experimenting with different architectures and training techniques to boost performance.
Expanded Defect Library: We plan to gather a more extensive dataset of PCBA defects, allowing our model to identify a wider range of issues. This will make the system more versatile and capable of handling various manufacturing environments.
Real-World Testing: We intend to test our system in a broader range of manufacturing settings to ensure its robustness and adaptability. This will help us understand how it performs in diverse real-world scenarios and how we can fine-tune it for optimal results.
Integration with Manufacturing Systems: Our goal is to integrate our system with other manufacturing processes and technologies. This will allow for seamless communication between defect detection and other quality control systems, enhancing the overall manufacturing workflow.
Automation and Robotics: We’re interested in exploring the use of automation and robotics to streamline the defect detection process. This could lead to a more automated manufacturing line, reducing human intervention and potential errors.
Collaboration and Partnerships: We plan to collaborate with more industry partners and academic institutions to accelerate our research and development. These partnerships will provide valuable insights and resources for advancing our system.
Continue reading → - Advancing Next-Gen Networks with MIMO Channel Capacity at 300 GHz November 28, 2024

The Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering is pleased to announce the publication of a significant research paper by Dr Anirbhan Ghosh, Assistant Professor, exploring MIMO channel capacity at high frequencies (300 GHz), which holds great potential for beyond 5G and 6G networks. The paper “MIMO Channel Capacity Measurement in Open Square Hot Spot Access Scenarios at 300 GHz” published in the Q1 journal IEEE Wireless Communication Letters, investigates data transmission in three different line-of-sight (LoS) scenarios and contributes to building the next generation of communication networks, which will have a significant positive impact on society by improving connectivity, supporting technological advancements, and promoting economic development.
Abstract
This letter explores the possibility and effectiveness of using multiple communication paths for futuristic outdoor networks, focusing on three scenarios: clear line-of-sight (LoS), partially obstructed line-of-sight (OLoS), and completely blocked line-of-sight (NLoS). A study was conducted at a high frequency of 300 GHz to measure how many useful communication paths are available for transmitting data simultaneously. Based on the results, the average data transmission capacity for these paths was calculated, both with and without the help of passive reflecting surfaces (PRS). The findings show that using multiple antennas significantly boosts the average data capacity, and PRS further enhances this improvement.
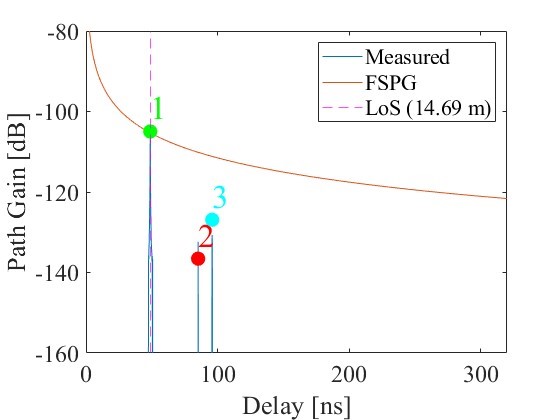
Practical Implementation of the Research
The results align with the design of high-frequency, ultra-high-speed, low-latency, reliable communication envisioned for several futuristic applications beyond 5G and 6G Networks.
Collaborations
Prof. Minseok Kim, Professor, Faculty of Engineering, Course of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, Niigata University, Japan.
Dr Ghosh plans to extend his efforts to other communication scenarios for a similar study. He opines that generating appropriate channel models, coverage design, etc., for the explored scenario would also be an exciting study.
Continue reading → - Dr Rangabhasiyam on Tackling the Issue of Microplastic Pollution November 28, 2024
 Microplastic pollution is an urgent environmental crisis that threatens ecosystems on land and in water. Addressing this critical issue, Associate Professor and HoD, Dr Rangabhashiyam Selvasembian from the Department of Environmental Science and Engineering has published a groundbreaking book titled Microplastics, Environmental Pollution and Degradation Process with Springer. This book examines the perilous effects of microplastics, their characterisation, and innovative treatment strategies. By integrating the latest research and insights, Dr Selvasembiyan’s work serves as a vital guide for students, researchers, and policymakers committed to combating microplastics and protecting our environment.
Microplastic pollution is an urgent environmental crisis that threatens ecosystems on land and in water. Addressing this critical issue, Associate Professor and HoD, Dr Rangabhashiyam Selvasembian from the Department of Environmental Science and Engineering has published a groundbreaking book titled Microplastics, Environmental Pollution and Degradation Process with Springer. This book examines the perilous effects of microplastics, their characterisation, and innovative treatment strategies. By integrating the latest research and insights, Dr Selvasembiyan’s work serves as a vital guide for students, researchers, and policymakers committed to combating microplastics and protecting our environment.About this Book
This book presents microplastics pollution in land and water bodies, their hazardous effects, characterization approaches, and suitable means of utilizing advanced treatment options to solve the problem. It is mainly understood that microplastic pollutants are associated with water bodies, however there also exists soil contamination and their interaction with the food web. The discussions related to strategies and policies for the management of microplastics are very limited. This book not only narrows microplastic pollution in marine or fresh water bodies, but also takes into account the terrestrial environment, including the toxicity effects, characterization aspects and treatment approaches. The main feature of the book includes latest research related to microplastics pollution, examining the different health effects including environmental (related) issues and highlights the advances in treatment approaches. The book serves as a guide with an up-to-date information on microplastics related problems useful for students, researchers, professionals/environmentalists and also as a reference for policy makers.
Collaborations:
- Professor Ajay Kumar Mishra, Professor – Durban University of Technology, South Africa.
- Dr. Pankaj Raizada, Professor -School of Advanced Chemical Sciences, Shoolini University, Solan (H.P) India.
- Dr Elsayed T Helmy, Researcher – National Institute of Oceanography and Fisheries, Egypt
- Prof. Santhiagu Arockiasamy Professor- National Institute of Technology Calicut, India.
Link to the article: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-97-6461-7
Continue reading →

