Research News
- Naga Sravanthi Explores the Role of Blockchain in Food Marketing August 23, 2024
 In a significant contribution to the field of food marketing and consumption, Ms P Naga Sravanthi, an Assistant Professor Ad hoc in the Department of Computer Science and Engineering, has recently published a book chapter titled “Blockchain-Based Food Influencer Verification.” The chapter is part of the book “Innovative Trends Shaping Food Marketing and Consumption,” shedding light on the emerging use of blockchain technology in authenticating food influencers.
In a significant contribution to the field of food marketing and consumption, Ms P Naga Sravanthi, an Assistant Professor Ad hoc in the Department of Computer Science and Engineering, has recently published a book chapter titled “Blockchain-Based Food Influencer Verification.” The chapter is part of the book “Innovative Trends Shaping Food Marketing and Consumption,” shedding light on the emerging use of blockchain technology in authenticating food influencers.In the rapidly evolving world of food marketing, trust and authenticity have become more critical than ever. The book chapter delves into how blockchain technology can revolutionise the way food influencers are verified and trusted by their audiences. Blockchain technology, known for its transparency and security features, has been making waves across various industries, and its application in the food sector is no exception.
Ms Naga Sravanthi’s work focuses on utilising blockchain to verify the credibility and authenticity of food influencers, a vital aspect in today’s digital era, where influencer marketing plays a significant role in consumer decision-making. The book chapter explores how blockchain can address issues of trust and reliability in food marketing by providing a secure and immutable record of influencers’ endorsements and partnerships. This innovative approach not only benefits consumers by ensuring they receive genuine recommendations but also helps food brands collaborate with legitimate and reputable influencers.
The publication of this book chapter underscores SRM University-AP’s commitment to fostering cutting-edge research and innovation in diverse fields, positioning its faculty members as thought leaders in their respective domains. Ms Naga Sravanthi’s work serves as a testament to the university’s dedication to academic excellence and pushing the boundaries of knowledge in emerging technologies.
Brief Description of the Book Chapter:
This chapter explores the integration of blockchain technology into the verification process of food influencers, providing a transparent and tamper-proof method to authenticate their influence and endorsements. By leveraging blockchain, the chapter outlines how the food industry can ensure that influencers are genuine, their endorsements are credible, and their impact is accurately measured. The chapter also delves into case studies and practical applications, demonstrating how this technology can reshape the landscape of influencer marketing in the food sector.Significance of the Book Chapter
The significance of this chapter lies in its exploration of a cutting-edge application of blockchain technology in a field that deeply influences consumer behaviour in food marketing. As the digital space becomes more saturated with influencers, the need for a reliable verification system becomes paramount. This chapter is particularly meaningful because it addresses the growing concern of authenticity in influencer marketing, a crucial factor in maintaining consumer trust and brand integrity. For those passionate about the intersection of technology, marketing, and food, this chapter offers insights into how blockchain can be a game-changer in ensuring that the voices consumers trust is, indeed, trustworthy.Target Audience
The book is primarily targeted at professionals in the food industry, including marketers, brand managers, and digital strategists, who are keen on understanding the latest trends shaping consumer behaviour and marketing practices. Additionally, this chapter will be valuable to academics and students in the fields of marketing, food science, and technology, as well as tech enthusiasts interested in the practical applications of blockchain.
Startups and entrepreneurs looking to innovate within the food sector will also find this book to be a vital resource, providing both theoretical insights and practical examples of how technology can redefine industry standards.In essence, “Innovative Trends Shaping Food Marketing and Consumption” and its chapter on blockchain-based influencer verification is an essential read for anyone looking to stay ahead of the curve in the dynamic world of food marketing.
Continue reading → - Dr Vineeth Thomas Analyses Challenges Ahead for Modi’s Third Term August 22, 2024
 Dr Vineeth Thomas, an Assistant Professor in the Department of Political Science, has recently published a thought-provoking paper titled “Why Modi’s Third Term as India’s Prime Minister Will Be Tough” in the distinguished journal Asian Affairs. In his comprehensive analysis, Dr Vineeth delves into the political landscape of India and the various challenges Prime Minister Narendra Modi may face if he seeks re-election for a third consecutive term in 2024. Drawing on an array of political theories and current socio-economic indicators, the paper examines the underlying factors shaping Indian politics and public sentiment.
Dr Vineeth Thomas, an Assistant Professor in the Department of Political Science, has recently published a thought-provoking paper titled “Why Modi’s Third Term as India’s Prime Minister Will Be Tough” in the distinguished journal Asian Affairs. In his comprehensive analysis, Dr Vineeth delves into the political landscape of India and the various challenges Prime Minister Narendra Modi may face if he seeks re-election for a third consecutive term in 2024. Drawing on an array of political theories and current socio-economic indicators, the paper examines the underlying factors shaping Indian politics and public sentiment.Dr Thomas argues that while Modi’s leadership has been marked by significant economic reforms and a robust foreign policy, the landscape is shifting in a manner that could complicate his re-election bid. Key issues explored in the paper include rising economic disparities, increasing urban unrest, and the challenge of maintaining communal harmony in a diversely populated nation.
The findings of this research are particularly pertinent in light of ongoing debates surrounding economic policy, agrarian distress, and the role of civil liberties – a backdrop that could significantly influence electoral dynamics heading into 2024.
The publication of this paper not only highlights Dr Thomas’s expertise in political science but also underscores the vital role academic discourse plays in contemporary political analysis. His insights contribute to a deeper understanding of India’s complex interplay between governance and public perception.
Abstract of the Research
On 9 June 2024, Narendra Modi became India’s Prime Minister for a third consecutive term, a feat previously accomplished only by Jawaharlal Nehru. However, this historic victory also began one of the most uncertain periods of his prime ministership. The fractured outcome of India’s 18th general election has created a fundamentally different political landscape. Modi’s Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) secured just 240 seats, a significant drop from its 2019 tally, and was therefore short of an absolute majority. Although the BJP-led National Democratic Alliance (NDA) did win a majority, Modi will now be dependent upon coalition partners, necessitating a shift towards a more collaborative governance style.
Research in Layperson’s Terms
In the recent election, Modi’s party, the BJP, won only 240 seats, much fewer than in the last election and not enough for a clear majority. Although the broader alliance led by the BJP still has a majority, Modi now needs to rely more on other parties in the alliance to govern. This means he will have to work more closely with his coalition partners and be more collaborative in his leadership style.
Research Paper in the Citation Format
Vineeth Thomas, Agney GK & Arsha V Sathyan (2024), Why Modi’s Third Term As India’s Prime Minister Will Be Tough, Asian Affairs, ISSN: 0306-8374
(Routledge, SCOPUS/WoS Indexed)Practical implementation or the social implications associated with Research
The practical implementation of my research lies in shaping policies that promote gender equality in political representation. By identifying barriers and proposing solutions, it aims to enhance women’s participation in politics, leading to more inclusive governance. The social implications include fostering a more equitable society with diverse perspectives in decision-making.
Your collaborations
Electoral Politics
Your Future Research Plans
Indian govt and politics
Continue reading → - A Pathway to Sustainable Active Food Packaging August 20, 2024

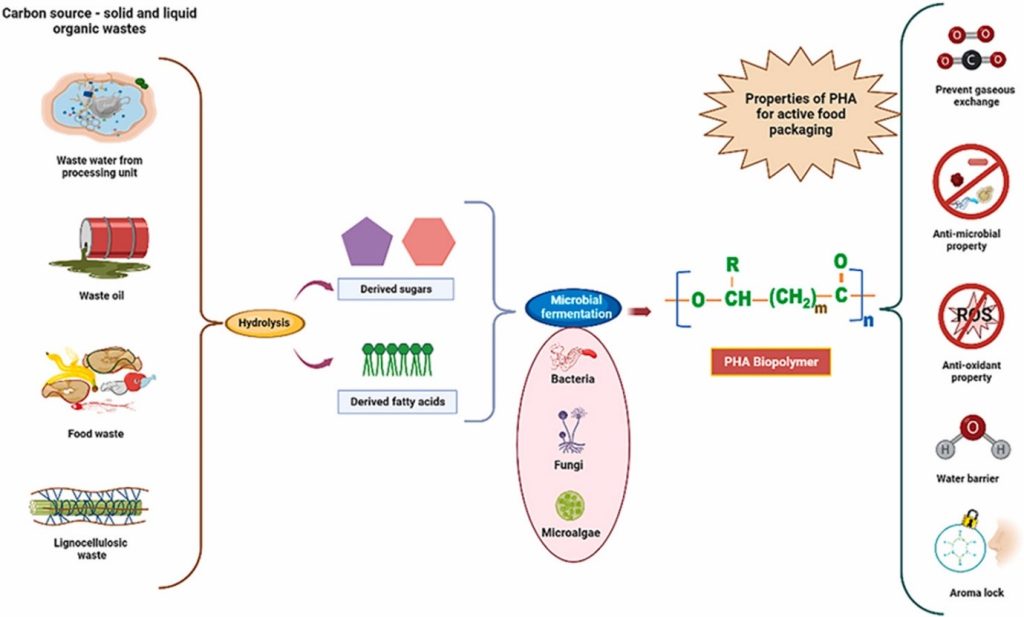
Dr Debajyoti Kundu, Assistant Professor, Department of Environmental Science and Engineering, has conducted an impactful study on developing polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA), an eco-friendly solution that can help reduce plastic waste and make food packaging more sustainable. His recent paper “Advancements in microbial production of polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA) from wastes for sustainable active food packaging: An eclectic review”, published in the Q1 journal Biocatalysis and Agricultural Biotechnology, Dr Debajyoti investigates how microorganisms can convert waste into a special type of plastic called PHA, which can be used for food packaging.
Unlike regular plastics, PHA is biodegradable and safe for both the environment and human health. The study reviews recent innovations in making PHA stronger and more effective for packaging, including its ability to prevent food spoilage and improve food safety.
Abstract
This study explores advancements in microbial production of polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA) from waste resources for sustainable active food packaging. It highlights the eco-friendly nature of PHAs as bioplastics and their potential to replace synthetic plastics in food packaging. The paper discusses recent technological improvements in PHA production and formulations, focusing on enhancing material properties to make PHA a viable alternative. It also examines trends in active packaging, including antimicrobial, antioxidant properties, and spoilage indicators, which can significantly improve food safety and quality.
Practical Implementation/ Social Implications of the Research
The practical implementation of this research involves using PHA-based materials for food packaging to replace conventional plastics. This can lead to reduced environmental pollution due to PHA’s biodegradability and lower reliance on fossil fuels. Social implications include improved food safety through active packaging features like antimicrobial and antioxidant properties, potentially reducing foodborne illnesses and extending shelf life. Additionally, using waste to produce PHA promotes waste recycling and resource efficiency.
Collaborations
This research is a collaborative effort among various prestigious institutions including St. Joseph’s University, SRM Institute of Science and Technology, Gurudas College, and SRM University-AP.
Moving forward, Dr Debajyoti will continue to work on improving the production processes and formulations of PHA to enhance its mechanical properties and cost-effectiveness. Additionally, he will explore new waste sources for PHA production and develop advanced active packaging technologies, such as smart packaging with sensors for real-time monitoring of food quality. Collaborations with industry partners to scale up production and test real-world applications of PHA-based packaging are another key focus.
Continue reading → - Algae Biochar: A Promising Solution to Water Pollution August 9, 2024

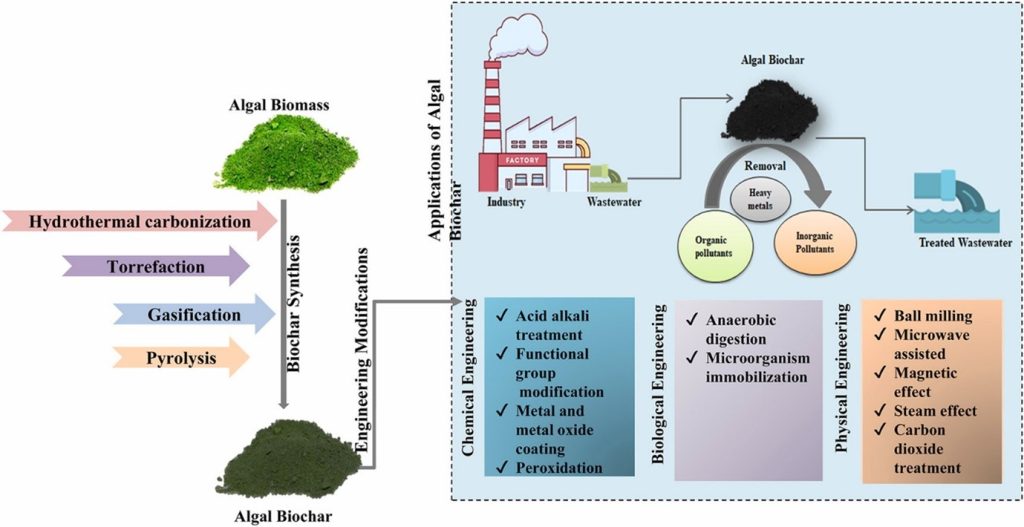
Dr Debajyoti Kundu, Assistant Professor in the Department of Environmental Science and Engineering, has published a research paper titled “Synthesis, delineation and technological advancements of algae biochar for sustainable remediation of the emerging pollutants from wastewater – A Review” in the esteemed Q1 journal “Environmental Research”, which has an impact factor of 8.3.
Dr Debajyoti’s research focuses on using algae biochar, which is particularly effective at cleaning polluted water. The study reviews how this biochar is made and improved and how it can effectively remove harmful substances from wastewater. This process is sustainable and environmentally friendly, offering a promising solution to water pollution.
Abstract
The study examines the synthesis, technological advancements, and applications of algae biochar for the sustainable remediation of emerging pollutants from wastewater. It highlights the unique properties of algae biochar, including its high surface area, pore volume, and adsorption capacity, which make it an effective medium for removing inorganic and organic contaminants from wastewater. The paper discusses various methods for producing algae biochar, such as pyrolysis, gasification, and torrefaction, and explores chemical and structural modifications to enhance its pollutant removal efficiency.
Practical Implementation /Social Implications of the Research
The practical implementation of this research involves using algae-derived biochar in wastewater treatment plants to remove harmful pollutants. This can lead to cleaner water, reduced environmental pollution, and improved public health. The process is also sustainable and cost-effective, contributing to environmental conservation and resource efficiency.
Collaborations
This research is a collaborative effort among various experts from institutions such as the University of Calcutta, Babasaheb Bhimrao Ambedkar University, Koneru Lakshmaiah Education Foundation, Graphic Era Deemed to be University, Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur, Ranchi University, King Abdulaziz University, Incheon National University, Korea Aerospace University, and B.S. Abdur Rahman Crescent Institute of Science and Technology.
Future Research Plans
Dr Debajyoti’s future research projects include exploring advanced modification techniques for algae biochar to further enhance its pollutant removal capabilities, investigating its application in different types of wastewater, and developing large-scale production methods. Additionally, there is an interest in studying the long-term environmental impacts and economic viability of using algae biochar in wastewater treatment.
Continue reading → - AI-Based Remote Fetal Heart Rate Monitoring Published in Leading Journal August 9, 2024
 Dr Sibendu Samanta, Assistant Professor in the Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, and Ms Radha Abburi, a PhD Scholar, have made significant strides in the field of fetal health monitoring. Their paper, titled “Adopting Artificial Intelligence Algorithms for Remote Fetal Heart Rate Monitoring and Classification using Wearable Fetal Phonocardiography,” has been published in the prestigious Q1 Journal, Applied Soft Computing, which boasts an impressive impact factor of 7.2.
Dr Sibendu Samanta, Assistant Professor in the Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, and Ms Radha Abburi, a PhD Scholar, have made significant strides in the field of fetal health monitoring. Their paper, titled “Adopting Artificial Intelligence Algorithms for Remote Fetal Heart Rate Monitoring and Classification using Wearable Fetal Phonocardiography,” has been published in the prestigious Q1 Journal, Applied Soft Computing, which boasts an impressive impact factor of 7.2.This pioneering study addresses the critical gaps in the analysis of Fetal Heart Rate (FHR) recordings by leveraging wearable Phonocardiography (PCG) signals and advanced AI algorithms. The primary goal of the research is to achieve accurate classification results through the remote monitoring of fetal heartbeats. Additionally, the study tackles complex issues related to data quantity and the inherent complexity of FHR analysis. Dr Samanta and Ms Abburi’s work represents a significant advancement in the field, promising to enhance the accuracy and reliability of fetal health monitoring, ultimately contributing to better prenatal care.
Abstract of the Research:
Fetal phonocardiography (FPCG) is a non-invasive Fetal Heart Rate (FHR) monitoring technique that can detect vibrations and murmurs in heart sounds. However, acquiring fetal heart sounds from a wearable FPCG device is challenging due to noise and artefacts. This research contributes a resilient solution to overcome the conventional issues by adopting Artificial Intelligence (AI) with FPCG for automated FHR monitoring in an end-to-end manner, named (AI-FHR). Four sequential methodologies were used to ensure reliable and accurate FHR monitoring. The proposed method removes low-frequency noises and high-frequency noises by using Chebyshev II high-pass filters and Enhanced Complete Ensemble Empirical Mode Decomposition with Adaptive Noise (ECEEMDAN) in combination with Phase Shifted Maximal Overlap Discrete Wavelet Transform (PS-MODWT) filters, respectively.
The denoised signals are segmented to reduce complexity, and the segmentation is performed using multi-agent deep Q-learning (MA-DQL). The segmented signal is provided to reduce the redundancies in cardiac cycles using the Artificial Hummingbird Optimization (AHBO) algorithm. The segmented and non-redundant signals are converted into 3D spectrograms using a machine learning algorithm called variational auto-encoder-general adversarial networks (VAE-GAN). The feature extraction and classification are carried out by adopting a hybrid of the bidirectional gated recurrent unit (BiGRU) and the multi-boosted capsule network (MBCapsNet). The proposed method was implemented and simulated using MATLAB R2020a and validated by adopting effective validation metrics.
The results demonstrate that the proposed method performed better than the current method with accuracy (81.34%), sensitivity (72%), F1-score (83%), Energy (0.808 J), and complexity index (13.34). Like other optimization methods, AHO needs precise parameter adjustment in order to function well. Its performance may be greatly impacted by the selection of parameters, including population size, exploration rate, and learning rate.
The title of the Research Paper in the Citation Format:
R. Abburi, I. Hatai, R. Jaros, R. Martinek, T. A. Babu, S. A. Babu, S. Samanta, “Adopting artificial intelligence algorithms for remote fetal heart rate monitoring and classification using wearable fetal phonocardiography”, Applied Soft Computing, vol. 165, pp. 112049, 2024, ISSN 1568-4946.Practical Implementation or the Social Implications Associated with the Research
- Chebyshev filter and EC2EMDAN-PS-MODWT reduce low and high frequency noises.
- MA-DRL and optimization algorithms reduce complexity during classification.
- Machine learning spectrogram conversion to capture time, frequency, and spectral variations.
- Hybrid deep learning algorithms can be used to reduce positive rates.
Collaborations:
- Dr. Indranil Hatai (Signal Processing and FPGA, Mathworks, Bangalore, India)
- Dr. T. Arun Babu (HoD, Dept. of Pediatrics, All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS), Andhra Pradesh, India)
- Dr. Sharmila Arun Babu, MBBS, MS (HoD, Dept. of Obstetrics and Gynecology, All India Institute of Medical Sciences (AIIMS), Andhra Pradesh, India)
- Dr. Rene Jaros (Dept. of Cybernetics and Biomedical Engineering, Faculty of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, VSB–Technical University of Ostrava, 708 00, Ostrava, Czechia)
- Prof. Radek Martinek (Dept. of Cybernetics and Biomedical Engineering, Faculty of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, VSB–Technical University of Ostrava, 708 00, Ostrava, Czechia)
Future Research Plans:
- Design a low cost for continuous fetal heart rate (FHR) monitoring system
- Develop a proper deep learning algorithm to get a proper understanding of fetal’s abnormality.
- Scaling Heights: Nilesh Bags an Internship at RBI August 9, 2024

The Department of Economics proudly announces that Mr Nilesh A, a third-year B.Sc. Economics (Hons.) student, has secured a highly coveted one-month research-based internship at the Reserve Bank of India, Mumbai. This internship is under the Department of Economic and Policy Research (DEPR).
“I am thrilled to share my experience of securing an internship at the Reserve Bank of India, a journey that was significantly supported by the resources and guidance provided by my university. I am grateful to all my professors at Easwari School of Liberal Arts at SRM University-AP for their unwavering support and encouragement. This internship is a pivotal step in my career, and I am excited about the future and eager to continue building on this incredible foundation,” stated Nilesh while expressing his gratitude for this once-in-a-lifetime opportunity.
Internships are remarkable opportunities to gain experience and exposure, build a strong network, and hone the skills you already possess. The Easwari School of Liberal Arts of SRM University-AP provides academic and research internships prioritising experiential and industry-based learning to help students cultivate a refined practical skillset.
Continue reading → - A Novel Breakthrough on Developing Heterogeneous Small-World LPWANs August 9, 2024

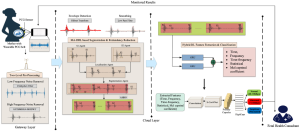
The Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering is delighted to announce that Assistant Professor Dr Anirban Ghosh, PhD scholars Mr Naga Srinivasarao and Ms Manasa Santhi, and BTech student Mr Sk Abdul Hakeem have filed and published their patent, “A System and a Method for Low Transmission Delay and Energy Efficiency,” with Application No: 202441045389. The research cohort has demonstrated groundbreaking research on integrating Small-World Characteristics (SWC) into Low-Power Wide-Area Networks (LPWANs) through Reinforcement Learning.
Abstract
To support the rapid growth of Internet of Things (IoT) applications, networking technologies like Low-Power Wide-Area Networks (LPWANs) are evolving to provide extended network lifespan and broader coverage for Internet of Things Devices (IoDs). These technologies are highly effective when devices remain stationary under static conditions. However, practical IoT applications, ranging from smart cities to mobile health monitoring systems, involve heterogeneous IoDs that move dynamically, leading to changing network topologies. Typically, dynamic networks use multi-hop data transmission schemes for communication, but this method presents challenges such as increased data latency and energy imbalances. To address these issues, this patent introduces a novel approach that integrates recent advancements in social networks, specifically Small-World Characteristics (SWC), into LPWANs using Reinforcement Learning. Specifically, the SWCs are embedded into heterogeneous LPWANs through the Q-learning technique. The performance of the developed heterogeneous Small-World LPWANs is then evaluated in terms of energy efficiency (including the number of alive and dead IoDs, as well as network residual energy) and data transmission delay within the network.
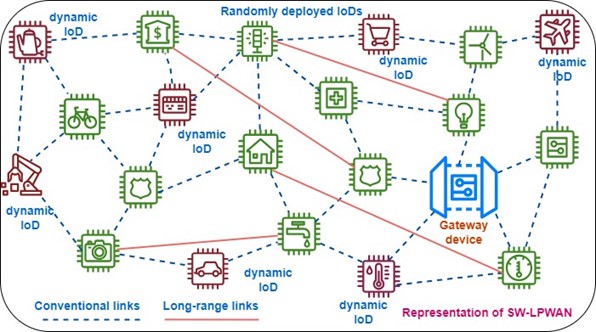
Explanation of Research in Layperson’s Terms
The existing or the present technology moves around the applications that are either static or dynamic in nature, but the current invention considers a realistic IoT application that contains both static and dynamic nodes in the network. However, maintaining low data transmission delay and high network longevity over such a heterogeneous network is a challenge. By integrating SWCs over the developed heterogeneous networks using Q-learning technique helps in minimizing the data transmission delay and improves the network lifetime (energy efficient data transmission).
Practical Implementation of the Research
Applications that contain both static and dynamic nodes, such as smart health care systems, smart environmental monitoring systems, real-time traffic monitoring systems, and smart cities and homes, require less data transmission delay and high network longevity.
Collaborations
- Dr Om Jee Pandey – Assistant Professor, Department of Electronics Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology (BHU) Varanasi
- Dr Satish Kumar Tiwari – Assistant Professor, IIITDM Jabalpur, India
In the next phase of research, the reserach team will work towards investigating how the energy efficiency and other quality of service of smart devices in an IoT setting can be improved if they are completely mobile.
Continue reading → - Exploring Inventive Methods to Detect Microplastics in Contaminated Products August 7, 2024

The Department of Chemistry is glad to announce that Dr Rajapandiyan Panneerselvam, Associate Professor, Ms Jayasree K, Research Scholar, and Ms Mounika Renduchintala, BSc student, have had their breakthrough research published as a patent titled “A Method for Detecting Microplastics from Contaminated Products” with Application Number: 202441045388. Various research has been undertaken by scientists in developing improved methods for sample preparation and data analysis, aiming to reliably detect pollutants like microplastics in complex samples such as sea salt, soil, and water. In line with these efforts, this patent introduces a rapid and easy method to detect microplastics in contaminated products and water bodies using a filter paper-based substrate.
Abstract
Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) has emerged as one of the most promising analytical tools in recent years due to its advantageous features, such as high sensitivity, specificity, ease of operation, and rapid analysis. These attributes make SERS particularly well-suited for environmental and food analysis. However, detecting target analytes in real samples using SERS faces several challenges, including matrix interference, low analyte concentrations, sample preparation complexity, and reproducibility issues. Additionally, the chemical complexity of pollutants and environmental factors can impact SERS measurements. Overcoming these hurdles demands optimized experimental conditions, refined sample preparation methods, and advanced data analysis techniques, often necessitating interdisciplinary collaborations for effective analysis. Therefore, our focus lies in the development of various methods for fabricating SERS substrates, pretreating analytes, and devising sample preparation strategies. These efforts aim to enable the detection of analytes like microplastics within complex real samples, including sea salts, soil samples, lake water, and various food products.
Practical Implementation/ Social Implications of the Research
SERS Community: Introducing a facile fabrication method for developing filter paper-based substrates, utilizing evaporation-induced self-assembly methods with the aid of 96-well plates. These substrates boast exceptional sensitivity and uniformity, exhibiting a relative standard deviation (RSD) of 8.2%. They offer easy fabrication and serve as effective SERS substrates for various applications.
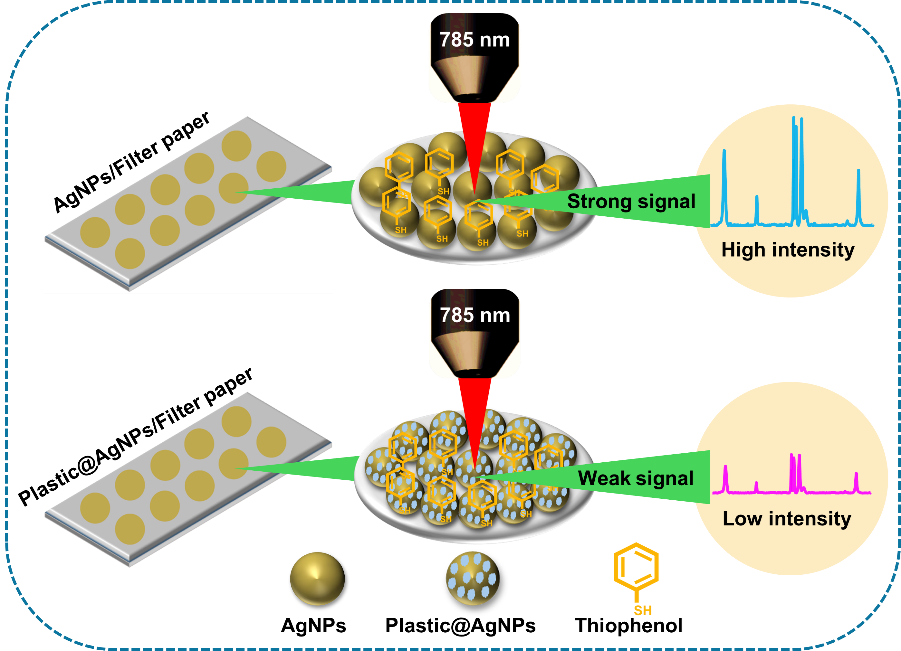
Industry and Government Bodies: This invention plays a pivotal role in assessing contamination in food and water bodies, serving as a crucial tool in monitoring environmental contamination through on-site analysis with portable instruments. It ensures adherence to regulatory standards and safeguards public health.
Research: Beyond its practical applications, the invention supports scientific research endeavors focused on identifying microplastic contaminants in real-world samples using portable Raman spectrometers. This not only aids ongoing research but also paves the way for future studies in this critical field.
Collaborations
- Dr Hemanth Noothalapati – Raman Project Center for Medical and Biological Applications, Shimane University, Japan
- Dr Murali Krishna C – Advanced Centre for Treatment, Research and Education in Cancer, Tata Memorial Centre, Navi Mumbai, India
- Dr Soma Venugopal – University of Hyderabad, India
The research team hopes to develop a novel SERS substrate for the detection of environmental pollutants in real-world samples.
Continue reading → - Dr Vineeth Publishes Paper on Policy Responses to Caste Violence in Tamil Nadu August 6, 2024
 Dr Vineeth Thomas, Assistant Professor in the Department of Political Science, has recently published a paper titled “Policy Responses to Caste Violence in Tamil Nadu” in the esteemed journal Economic and Political Weekly (EPW). In the paper, Dr. Thomas offers valuable insights into the crucial issue of caste violence in Tamil Nadu and examines various policy responses aimed at addressing this complex societal challenge.
Dr Vineeth Thomas, Assistant Professor in the Department of Political Science, has recently published a paper titled “Policy Responses to Caste Violence in Tamil Nadu” in the esteemed journal Economic and Political Weekly (EPW). In the paper, Dr. Thomas offers valuable insights into the crucial issue of caste violence in Tamil Nadu and examines various policy responses aimed at addressing this complex societal challenge.
Dr Thomas’s research illuminates the dynamics of caste violence and provides a comprehensive analysis of the policy measures adopted to tackle this pressing issue. His work in the EPW is expected to significantly contribute to the discourse on caste-based conflicts and policy formulation in the region. The publication of this paper not only exemplifies Dr. Vineeth Thomas’s scholarly prowess but also underscores SRM University—AP’s commitment to fostering impactful research in the realm of social and political sciences. It is anticipated that this publication will stimulate further academic dialogue and influence policy considerations in the domain of caste relations and violence in Tamil Nadu.Abstract of the Research
This study examines the policy response to caste violence in schools in Tamil Nadu, particularly through the recommendations of a committee led by retired Justice K. Chandru. The committee’s report highlights pervasive caste discrimination in schools and proposes various measures, including teacher transfers, banning caste markers, and implementing orientation programs on caste-related issues. The report also suggests the establishment of School Welfare Officers and Social Justice Student Forces, along with a robust grievance redressal mechanism. Despite opposition and criticism, these recommendations represent a significant step toward addressing caste discrimination in Tamil Nadu’s educational institutions.Research in Layperson’s Terms
This research focuses on the problem of caste discrimination in schools in Tamil Nadu, India. Despite the state’s reputation for promoting social justice, caste-based violence still occurs, even among students. A committee led by retired Justice K. Chandru made several recommendations to address this issue, such as banning caste markers like wristbands and educating students and teachers about discrimination. The report also suggests having specific officers to ensure these measures are followed. While these recommendations aim to create a fairer school environment, their success depends on proper implementation and support from the community.
Practical Implementation and the Social Implications Associated
Implementing this research can lead to more inclusive and equitable school environments by eliminating caste-based discrimination. By enforcing bans on caste markers, educating students and teachers, and establishing grievance mechanisms, schools can foster a culture of equality, reducing social tensions and promoting a just society for future generations.
Collaborations
Electoral Politics
Future Research Plans
Indian govt and politics
Continue reading → - A Novel SERS Substrate to Detect Food Contamination August 6, 2024

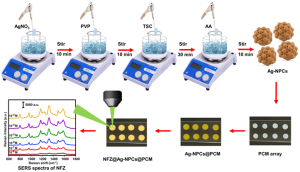
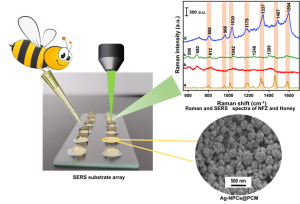
Dr Rajapandiyan P, Associate Professor, Department of Chemistry, and his PhD scholar, Ms Arunima Jinachandran, recently filed and published a patent, “A Substrate for Contaminant Detection and a Process for its Synthesis,” with Application Number: 202441043642 in the Patent Office Journal. The research duo has developed a novel SERS (Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy) substrate by synthesising silver nanopopcorn and depositing it on a polycarbonate membrane.
This novel substrate demonstrates excellent uniformity, reproducibility, and mechanical stability. It is used for the sensitive detection of toxic antibiotic nitrofurazone on fish surfaces and in honey. This breakthrough could significantly enhance food safety monitoring by providing a reliable and efficient method for detecting harmful substances.
Abstract
Detecting nitrofurazone (NFZ) in aquaculture and livestock is crucial due to its carcinogenic properties. This study presents a flexible polycarbonate membrane (PCM) with three-dimensional silver nanopopcorns (Ag NPCs) for NFZ detection on fish surfaces using surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS). The Ag-NPCs/PCM substrate demonstrates a significant Raman signal enhancement (EF = 2.36 × 106) due to hotspots from nanoscale protrusions and crevices. It achieves a low limit of detection (LOD) of 3.7 × 10−9 M, with uniform and reproducible signals (RSD < 8.34%) and retains 70% efficacy after 10 days. The practical detection LODs for NFZ in tap water, honey water, and on fish surfaces are 1.35 × 10−8 M, 5.76 × 10−7 M, and 3.61 × 10−8 M, respectively, demonstrating its effectiveness for various samples. This Ag-NPCs/PCM substrate offers a promising approach for sensitive SERS detection of toxic substances in real-world applications.
Practical Implementation/ Social Implications of the Research
The practical applicability of the proposed Ag-NPCs/PCM SERS substrate is validated by successfully detecting NFZ in various actual samples, such as tap water, honey water, and irregular fish surfaces.
Collaborations – Prof. Tzyy-Jiann Wang – National Taipei University of Technology, Taiwan
Dr Rajapandiyan and Ms Arunima will continue to work towards the development of novel flexible SERS substrates for detecting toxic pollutants in food.
Continue reading →