Research News
- Groundbreaking Research on Advanced Technology Nodes May 2, 2024

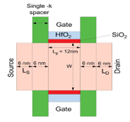
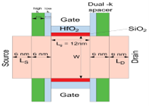
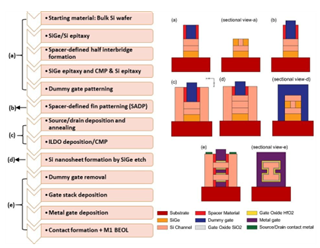
Dr M Durga Prakash, Assistant Professor in the Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, and his PhD scholar, Ms U Gowthami, have published a research paper titled “Performance Improvement of Spacer-engineered N-type Tree Shaped NSFET towards Advanced Technology nodes” in the Q1 journal, IEEE Access. The paper has an impact factor of 3.9 and will pave the way for significant advancements in the field.
Here’s an abstract of their research paper
Abstract:
Scaling gate lengths deep is most reliable with tree-shaped Nanosheet FETS (NSFET). This paper uses TCAD simulations to study the 12nm gate length (LG) n-type Tree-shaped NSFET with a stack of high-k dielectric (HfO2) and (SiO2) spacers. The Tree-shaped NFET device features high on-current (ION) and low off-current (IOFF) with T(NS) = 5 nm, W(NS) = 25 nm, WIB=5nm, and HIB = 25 nm. Comparison of single- and dual-k spacer 3D devices and DC properties are shown. Because fringing fields with spacer dielectric prolong the effective gate length, the dual-k device has the highest ION / IOFF ratio, 109, compared to 107. This research also examines where work function, inter bridge height, breadth, gate lengths, temperature, and analog/RF and DC metrics affect the device. The suggested device has good electrical properties at 12 nm LG, with DIBL = 23 mV/V, SS = 62 mV/dec, and switching ratio (ION / IOFF) = 109. The device’s performance proves Moore’s law applies to lower technological nodes, enabling scalability.
The link to the article- https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10499264 DOI: 10.1109/ACCESS.2024.3388504
Continue reading →
- Critical Analysis of the Influence of Hydroclimatic Variability and Anthropocene on the Groundwater of the Sundarbans May 2, 2024

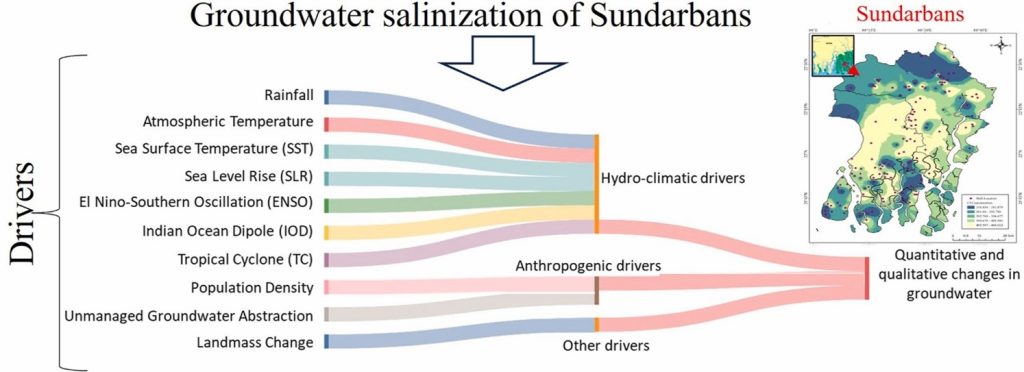
The water crisis in India, especially in the coastal regions, has worsened alarmingly, coercing environmentalists and researchers to critically study the reason behind this phenomenon. The Sundarbans region faces a scarcity of drinking water in terms of quality and quantity due to various reasons. Dr Kousik Das, Asst. Professor, Department of Environmental Science and Engineering, Dr Harish Puppala, Asst Professor, Department of Civil Engineering and Mr Mijanur Mondal, Research Scholar from the Department of Environmental Science and Engineering has conducted a groundbreaking study on the increased salinization of water due to human activities. The research trio has published a paper titled “Understanding the susceptibility of groundwater of Sundarbans with hydroclimatic variability and anthropogenic influences” in the prestigious Q1 journal Groundwater for Sustainable Development, which has an impact factor of 5.9, critically analysing the numerous factors that affect the quality of drinking water in the Sundarbans region.
Abstract
Coastal aquifers worldwide are experiencing increased salinisation due to climate change and human activities. Sundarbans, in India, is one such area where this phenomenon is noticed at an unprecedented rate, making drinking water unpotable for consumption. Existing studies lack a comprehensive analysis of the underlying causes. This study conducts a systematic literature review to identify drivers of groundwater salinisation, examining climate change parameters such as rainfall patterns, sea level rise, El Niño-Southern Oscillation, and tropical cyclones. Significant groundwater level declines from 1996 to 2017 are primarily attributed to variations in the Indian Ocean Dipole and El Niño Southern Oscillation, affecting rainfall and recharge rates. During tropical cyclones, groundwater levels rise rapidly, and quality is sensitive to El Niño Southern Oscillation. Rising sea levels, changing rainfall, and increasing population density worsen salinisation. Shallow aquifers have high salinity, whereas deep aquifers exceed permissible limits. This underscores the urgent need to address drinking water scarcity and potential migration resulting from complex interactions between climate, population, and groundwater management.
Social Implications of the Research
- Water Quality Monitoring: Implementing regular monitoring of salinity levels in groundwater to ensure compliance with safety standards.
- Community Awareness Programmes: Conducting educational campaigns to inform local communities about the risks of high salinity levels in drinking water and promoting the judicious use of water sources so that unscientific abstraction can be reduced.
- Policy Development: Formulating policies at the local and national levels to regulate salinity levels in drinking water and ensure public health protection.
- Infrastructure Improvement: Investing in water treatment facilities or technologies to remove high salt levels from groundwater sources. Alternative sources and rainwater harvesting can be taken into consideration.
Collaborations – IIT Kharagpur, India
The research team plans to work on Groundwater vulnerability modelling using AI/ML in Sundarbans, India next. The team has begun collecting primary data using questionnaire surveys and interviews to throw light on socio-economic conditions and to understand the core reasons for the water crisis and health and psychological issues due to water unavailability, especially during extreme events like cyclones.
Link to the article
Continue reading → - Uncovering the Factors Influencing Income Inequality in Rural Indian Households: A Comprehensive Study May 1, 2024

The Department of Economics takes immense pride in announcing the publication of the research paper, “Determinants of Rural Households’ Income Inequality in India” authored by Dr Ghanshyam Pandey, Assistant Professor. The paper has been published in the Journal of Agricultural Economics Research Review (ABDC-C), and has an impact factor of 0.19. Dr Pandey’s paper examines the factors that determine income inequality among rural farm households in India and discusses the implications of the findings for policymakers, practitioners, and researchers. The study highlights how addressing the identified factors could potentially reduce income inequality among rural farm households and improve the overall well-being of the rural population.
Abstract
This study has identified the drivers of income inequality in rural India using IHDS 2011–12 national-level survey. The inequality decomposition methodology developed by Fields (2003) based on a two-way regression methodology has been used. The study has modified the previous regression based inequality decomposition technique by accounting for diverse income sources and regimes as well as by effectively correcting for selectivity in the various income regimes. The CLAD model has been used to distinguish the determinants of income inequality in rural India. The study has indicated that income inequality in farm households can be attributed to the level of education, family size, caste/social group composition, and composition in land ownership and that family size and land ownership are instrumental primarily due to off-farm labour income. The study has shown that education is a significant factor in income inequality due to its impact on off-farm work income. The study has suggested that a continued increase in variability in land distribution may exacerbate income inequality in households in rural India.
Link to the Article
Pandey G and Devi B (2023). Determinants of rural households’ income inequality in India. (2024). Agricultural Economics Research Review, 36(2), 213-225. https://epubs.icar.org.in/index.php/AERR/article/view/150669
Continue reading →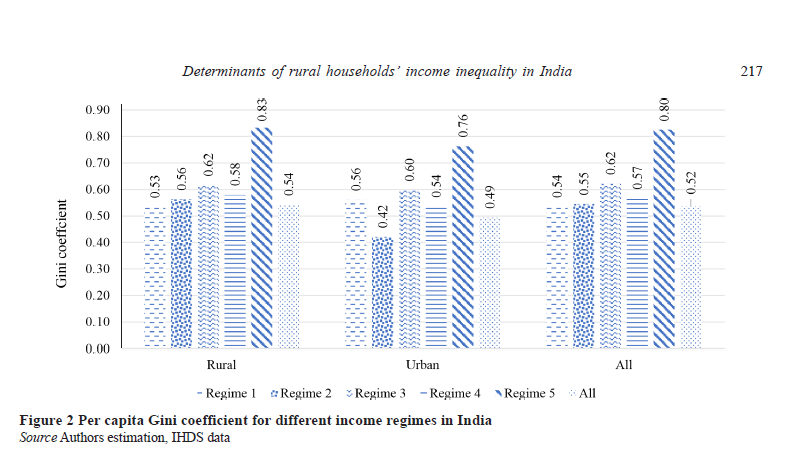
- Dr Chimoy Das’ Research Makes Latest Breakthrough in Material Science May 1, 2024

The Department of Chemistry is thrilled to announce the paper “Mechanochemically-induced glass formation from two-dimensional hybrid organic-inorganic perovskites”, published by Dr Chinmoy Das, Assistant Professor in the reputed Q1 Journal Chemical Science with an 8.4 Impact Factor. This groundbreaking research introduces a novel method for transforming crystalline phases into glasses through mechanochemical processes. This environmentally friendly and efficient method opens new doors for manufacturing glasses, revolutionising traditional processes. This remarkable research celebrates this extraordinary blend of chemistry, physics, and innovation!
Abstract
The first mechanochemically-induced hybrid organic-inorganic perovskites (HOIPs) crystal-to-glass transformation was reported as a quick, environmentally friendly, and productive method of making glasses. Within ten minutes of mechanical ball milling, the crystalline phase transformed into the amorphous phase, demonstrating glass transition behaviour as shown by thermal analysis methods. The microstructural evolution of amorphization was studied using time-resolved in situ ball-milling with synchrotron powder diffraction. The results indicated that energy may accumulate as crystal defects because the crystallite size reaches a comminution limit before the amorphization process is finished. The limited short-range order of amorphous HOIPs was discovered through total scattering experiments, and photoluminescence (PL) and ultraviolet-visible (UV-vis) spectroscopy were used to examine their optical characteristics.
Explanation of the research in layperson’s terms
Crystalline inorganic perovskites (general chemical formula is ABX3, where A and B are cations, and X is anion) are generally known for their unique optoelectronic applications, such as solar cells, photodetectors, and LEDs (light emitting diodes). In this research, Dr Das revealed hybrid materials comprised of organic linkers and inorganic nodes, which constitute hybrid organic-inorganic perovskites (HOIPs). The research demonstrated a rapid and environment-friendly (mechanochemically ball milling assisted) synthetic approach to transform the crystalline phase to its non-crystalline/amorphous phase. Interestingly, the amorphous phase of HOIPs showed temperature-dependent glass transition temperature (Tg) at very low temperatures, ~50 C. The structure of the HOIP glasses has been characterised through total-X-ray diffraction studies and pair-distribution functions. The crystalline and glassy HOIPs showed optical properties, which were studied by photoluminescence (PL) and ultraviolet-visible (UV-vis) spectroscopy.
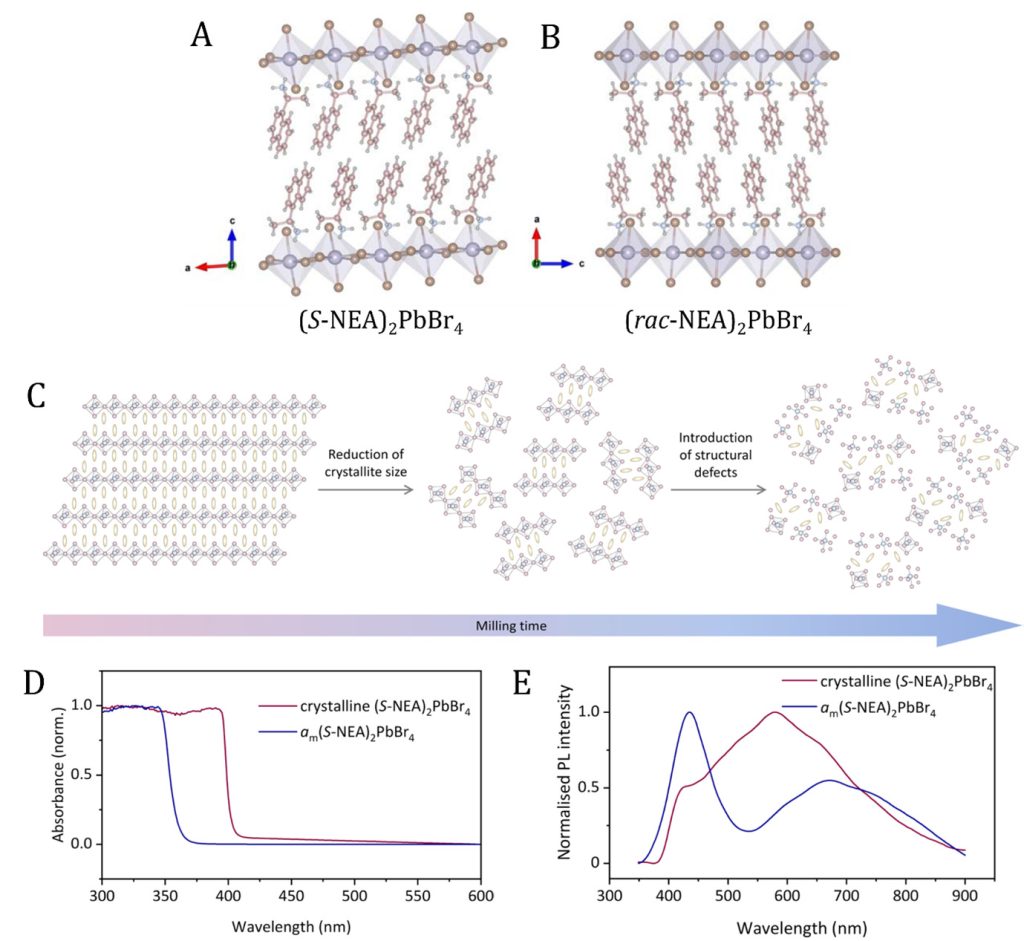
Figure 1. Single crystal structures of (A) (S-NEA)2PbBr4 and (B) (rac-NEA)2PbBr4. Pb, Br, C, N and H atoms are represented by purple, brown, pink, blue, and grey colours, respectively. (C) Schematic illustration of the microstructural evolution on 2D HOIPs upon ball-milling. (D) UV-Vis and (E) photoluminescent properties of crystalline (S-NEA)2PbBr4 (purple) and glassy (S-NEA)2PbBr4 (blue) HOIPs.
Practical implementation/ social implications of your research
Through the mechanochemical approach, we prepared novel hybrid organic-inorganic perovskite (HOIP) glasses within ten minutes, showing the greater feasibility of processing the glass material for industrial implication. On the other hand, we also demonstrated that the HOIP glasses showed photoluminescence properties, which would enable us to fabricate the device for solar cells, photodetectors, LEDs and many more.
Collaborations
- Department of Materials Science and Metallurgy, University of Cambridge, United Kingdom.
The Department of Chemistry has established a research group at SRM University-AP, and the group has started to explore an emergent research area of crystal-glass composite materials towards the applications of atmospheric water harvesting, solid-state electrolytes, photovoltaics, and conversion of gaseous Carbon-dioxide molecules to industrially relevant liquids, such as methanol or ethanol.
Any interested candidate can reach out to Dr Chinmoy for exciting projects.
Continue reading → - GPEMC Sanctions Consultancy Project Worth 48.9 Lakhs April 30, 2024
 Green Pearl Education and Management Corporation (GPEMC) has recently sanctioned a significant consultancy project to SRM University-AP, titled “Multilingual Minutes of the Meeting Generation.” This project aims to develop innovative solutions for generating multilingual minutes of meetings, ensuring effective communication, and understanding across language barriers.
Green Pearl Education and Management Corporation (GPEMC) has recently sanctioned a significant consultancy project to SRM University-AP, titled “Multilingual Minutes of the Meeting Generation.” This project aims to develop innovative solutions for generating multilingual minutes of meetings, ensuring effective communication, and understanding across language barriers.The Consultancy Project has been assigned to Dr. Ashu Abdul and Dr. Dinesh Reddy Vemula, Assistant Professors for a period of 7 months from the Department of Computer Science and Engineering (CSE). Their expertise in language processing and computational linguistics will play a crucial role in the successful execution of this project.
Joining them in this endeavour is Mr Phanindra Kumar, a dedicated PhD scholar, and a team of talented B.Tech. students, including Mr Shivansh Goel, Mr Md Ahmad Raza Khan, Ms Subrabala Dash, Mr Nithish Sri Ram, Mr Hadi Mahmood, and Mr Phanidra Kumar. Their combined skills and enthusiasm will contribute to the development of innovative solutions for multilingual meeting documentation.
The Consultancy Project has been sanctioned with an outlay of Rs 48,91,786/- as consultancy charges for a period of 7 months. This funding will support the research and development efforts required to deliver efficient and accurate multilingual minutes of meetings.
The objective of this project is to create an automated system that can generate minutes of meetings in multiple languages, ensuring accurate and comprehensive documentation. By overcoming language barriers, this project aims to facilitate effective communication and collaboration in diverse organizational settings.
The collaboration between SRM University-AP and GPEMC highlights the commitment of both institutions to research and innovation. This consultancy project presents an exciting opportunity for the faculty members and students to contribute to real-world problem-solving and make a substantial impact in the field of language processing.
Abstract
The project ‘Multilingual Minutes of the Meeting Generation’ aims to develop an innovative application that automates the creation of meeting minutes, action plans, and summaries in multiple languages. Leveraging advanced research in natural language processing and speech recognition technologies, our application seeks to streamline the tedious and time-consuming task of minute-taking. It will do so by accurately identifying, associating, and documenting statements with their respective speakers during meetings using speech diarization techniques.
The primary objective is to enhance the efficiency and accuracy of meeting minutes while supporting diverse linguistic needs and eliminating human error, thereby catering to global business environments. The system will improve the meeting outcomes for all participants by identifying the action items from the meeting. This project intends to deliver an effective solution for enterprises by combining the latest technological advances with a user-centric design.
Explanation of the Research in Layperson’s Terms
The project called “Multilingual Minutes of the Meeting Generation” is about creating a new tool that automatically writes down what happens in meetings—like the minutes, action items, and summaries—and can do this in several languages. This tool uses the latest technology in understanding and processing human speech, which helps make the task of recording meeting details much faster and easier.
The special feature of this tool is its ability to figure out who is speaking and accurately attach their words to them in the meeting notes. This makes sure the meeting records are both correct and detailed. The main goal here is to make creating and keeping track of meeting records more efficient and accurate, help people who speak different languages, and reduce mistakes that can happen when humans take down notes.
This system is especially useful in today’s global business setting, where people from different parts of the world need to work together smoothly. It aims to lessen the work involved in manually writing meeting notes and make the results easier for everyone to use and understand. Overall, the project promises to blend cutting-edge technology with designs that focus on the needs of the users to provide a practical tool for businesses.
Practical Implementation or the Social Implications Associated with the Research
The practical implementation of this project is particularly beneficial for enterprises, institutions, and professional settings where meetings are frequent. By automating minute-taking, it allows participants to focus more on discussion and decision-making, rather than note-taking. This leads to more productive meetings and ensures that important details are not lost or misinterpreted. Ultimately, this technology enhances communication and documentation accuracy across diverse linguistic and cultural landscapes in business and professional environments.
Collaborations
This project is being developed in collaboration with the members of the Next Tech Lab AP at SRM University-AP
Future Research Plans
The future plans for this project involve integrating the application with widely used platforms such as Zoom, Google Meet, and others that support video/audio conferencing. This integration aims to seamlessly incorporate the automated minute-taking functionality into these platforms, enhancing accessibility and usability for users across various companies and institutions. By expanding compatibility with popular conferencing tools, the project seeks to further streamline meeting documentation processes and cater to a broader user base in diverse professional settings.
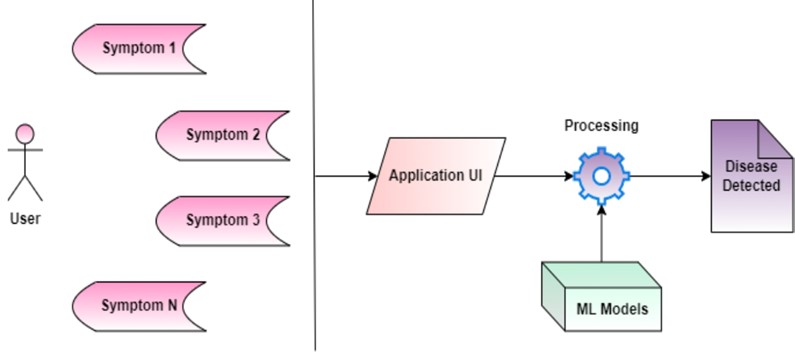
Continue reading → - Dr Pradyut and Students Revolutionise Disease Detection April 29, 2024

In the groundbreaking research paper titled “Innovative Web Application Revolutionizing Disease Detection: Empowering Users and Ensuring Accurate Diagnoses,” Dr Pradyut Sanki, Associate Professor at the Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, along with doctoral scholars Mr P N S B S V Prasad, and Mr Syed Ali Hussain and BTech students Ms Pragya Gupta and Ms Swikriti Khadke introduce a cutting-edge web application that aims to revolutionise disease detection and empower users to understand their health conditions.Their research paper published in the Journal of Electronic Materials has an impact factor of 2.1.
Abstract:
This paper presents an innovative enhancement aimed at revolutionizing disease detection and providing users with a reliable source of information for accurate diagnoses of their symptoms. Our open-source initiative combines a user-friendly interface design with advanced machine learning models, establishing a new benchmark for accuracy and enabling integration with even higher-performing models. We address the pervasive challenges of misinformation and misdiagnosis associated with online symptom searches, presenting a significant advancement in disease detection. Leveraging cutting-edge machine learning techniques.
Practical and Social Implications:
The practical implementation of our research means that people can use our smart tool to get better advice about their symptoms. This could lead to quicker and more accurate diagnoses, helping people get the right treatment sooner. Socially, our research could reduce the spread of false information online about health issues, leading to better-informed decisions and potentially improving overall public health.
Future Research Plans:
As a future research plan the students and faculty together plan to refine and expand their smart tool to make it even more accurate and helpful. They aim to incorporate feedback from users and collaborate with other experts to continually improve the technology. Additionally, they plan to explore ways to make the tool more accessible to a wider range of people and to address any potential biases in the data or algorithms. Overall, they are committed to advancing healthcare technology for the benefit of society.
Continue reading →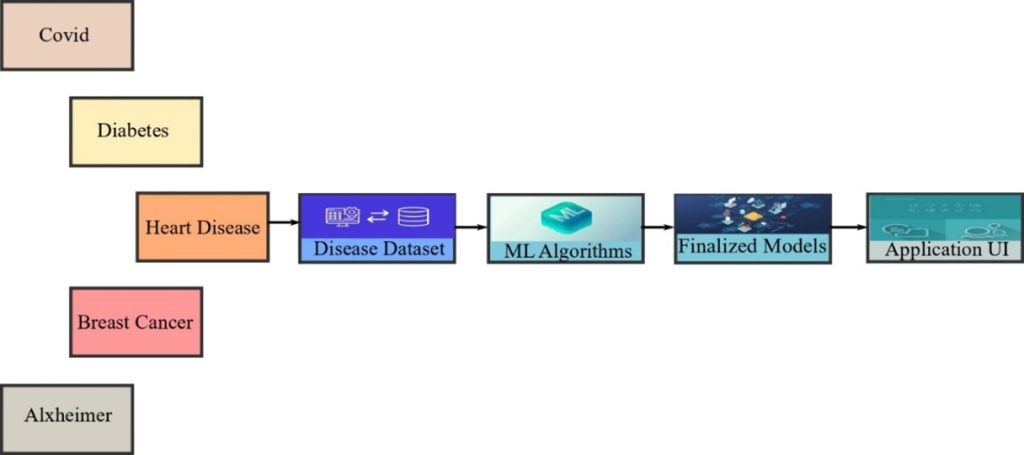
- SRM AP Researchers Publish Groundbreaking Paper on DC Microgrid Integration April 29, 2024
 In a significant stride towards sustainable energy solutions, a team of researchers from the Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering has unveiled a groundbreaking innovation. Their paper titled “A Novel Multi-Port High-Gain Bidirectional DC–DC Converter for Energy Storage System Integration with DC Microgrids” has been accepted in the prestigious Q1 Journal of Energy Storage, boasting an impressive impact factor of 9.4. The study focuses on addressing the critical challenges associated with energy storage systems (ESS) in direct current (DC) microgrids. Dr Ramanjaneya Reddy, Assistant Professor, Dr Tarkeshwar Mahto, Assistant Professor, and Mrs Maya Vijayan, a dedicated PhD Scholar, collaborated to design a multi-port high-gain bidirectional DC-DC converter. This innovative converter facilitates seamless integration of energy storage systems with DC microgrids, enhancing overall system efficiency and reliability.
In a significant stride towards sustainable energy solutions, a team of researchers from the Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering has unveiled a groundbreaking innovation. Their paper titled “A Novel Multi-Port High-Gain Bidirectional DC–DC Converter for Energy Storage System Integration with DC Microgrids” has been accepted in the prestigious Q1 Journal of Energy Storage, boasting an impressive impact factor of 9.4. The study focuses on addressing the critical challenges associated with energy storage systems (ESS) in direct current (DC) microgrids. Dr Ramanjaneya Reddy, Assistant Professor, Dr Tarkeshwar Mahto, Assistant Professor, and Mrs Maya Vijayan, a dedicated PhD Scholar, collaborated to design a multi-port high-gain bidirectional DC-DC converter. This innovative converter facilitates seamless integration of energy storage systems with DC microgrids, enhancing overall system efficiency and reliability.Abstract
Bidirectional converters have often been used in numerous applications like DC microgrids, renewable energy, hybrid energy storage systems, electric vehicles, etc. The paper proposes a novel multi-port high-gain (NMPHG) bidirectional DC-DC converter that supports DC microgrid (DC-MG) applications. The main contributions of the proposed converter are high step-up/step-down conversion gain, multiple input ports, lower switch voltage stress, and lower component count owing to the single converter with multiple input ports for DC microgrid applications.
The detailed operational principle, analysis, and design considerations of proposed NMPHG bidirectional DC-DC converters are discussed. Furthermore, the loss analysis, detailed comparison with similar works, and efficiency analysis with non-modalities during forward power flow (LV to HV) and reverse power flow (HV to LV) modes are presented. The efficiency of the proposed converter is found to be 93.8% in forward power flow and 92.9% in reverse power flow modes at rated power. Finally, a hardware prototype of the proposed NMPHG bidirectional DC-DC converter is implemented with 100 W in FPF mode and 200 W in RPF mode with a TMS320F28335 processor and validated with theoretical counterparts.
Explanation of Research in Layperson’s Terms
The proposed converter is a 200W bidirectional topology used in DC microgrid applications such as renewable energy, hybrid energy storage systems, and electric vehicles. The converter can accept two or more sources to supply the load. Thus, it is suitable for various applications of traction vehicles. It exhibits a lower switch stress and reduces the component ratings to lower values.
Title of Research Paper in the Citation Format
A NOVEL MULTI-PORT HIGH-GAIN BIDIRECTIONAL DC-DC CONVERTER FOR ENERGY STORAGE SYSTEM INTEGRATION WITH DC MICROGRIDS
Vijayan, Maya, Ramanjaneya Reddy Udumula, Tarkeshwar Mahto, and Ravi Eswar KM. “A novel multi-port high-gain bidirectional DC-DC converter for energy storage system integration with DC microgrids.” Journal of Energy Storage 87 (2024): 111431.
Practical Implementation or the Social Implications Associated with it
The features include port expandability on the source side, lower switch voltage stress, bidirectional property, and fewer components. It is most suitable for electric vehicles, Unmanned ariel vehicles, and energy storage systems at renewable power plants, etc. It improves the reliability of the grid system whereas hybrid energy storage systems with battery or supercapacitor will improve system stability.
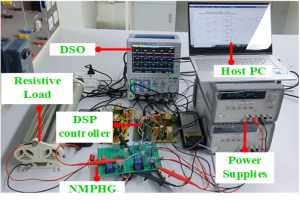
It can be used in various on-grid and off-grid applications like hospitals, offices, and educational institutions, especially where energy backup is very important. These types of converters are more specific for use in fast power transition required such as EVs, drones, aircraft, space vehicles, etc. The major advantage is the reduction in the size of the converter due to multiple source capability and ease of control.
Future Research Plans
We plan to work on a bidirectional converter with better efficiency and ultra-high gain. That should be able to reduce the size of the converter and the source ratings too. Design and implement bidirectional multi-port converters for various applications of DC microgrids, such as renewable and hybrid storage integration.
Continue reading → - 8th Research Day: A Pathway to Research and Innovation April 29, 2024
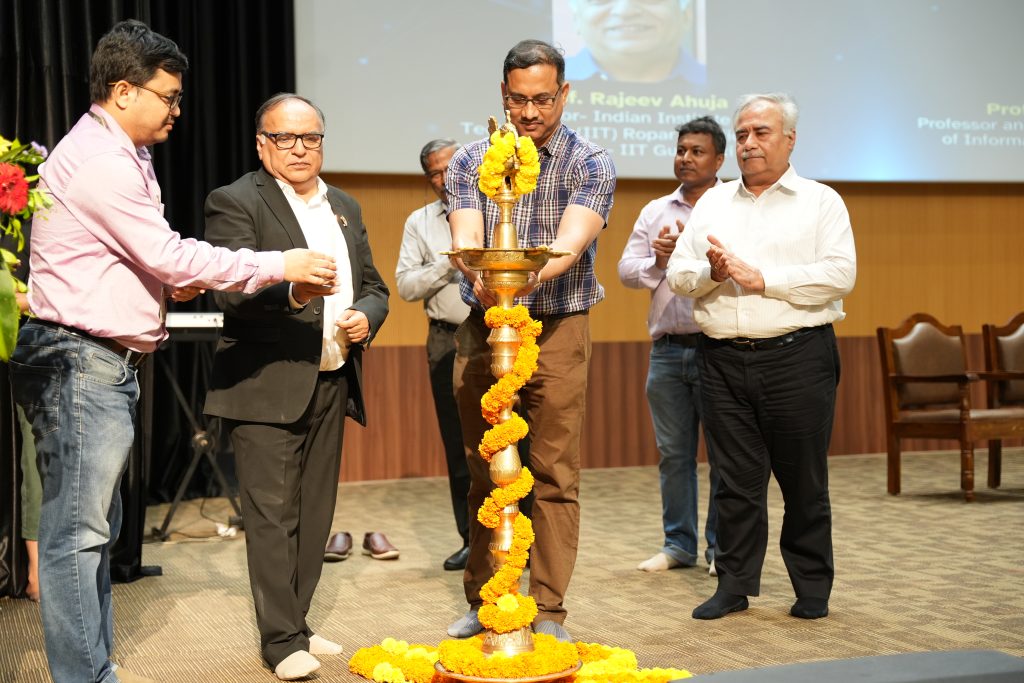

“Research is a passion. We must lay a strong foundation of basic research to further develop, grow and produce a high-quality research output. Focus on translational research as it is the way forward for an innovative world,” said Prof. Rajeev Ahuja, Chief Guest of the 8th Research Day, while addressing the research community of SRM University-AP.
The university hosted the 8th Research Day on April 26, 2024, in the august presence of Chief Guest Prof. Rajeev Ahuja, Director-IIT Ropar and Officiating Director-IIT Guwahati, Guest of Honour Prof. Amlan Chakrabarti, Director–A. K. Choudhury School of Information Technology, University of Calcutta; Vice Chancellor Prof. Manoj K Arora, Registrar Dr R Premkumar, Dean-Research Prof. Ranjit Thapa, Deans of all schools, faculty, research scholars and students. “Research Day at SRM AP is the celebration of our students’ innovative thought and applauding them in their developing research acumen”, remarked Prof. Arora in his welcome address. He encouraged students to take their research to the next level and become entrepreneurs who will transform the Indian market and economy.
Prof. Amlan Chakrabarti, the designated guest of honour for the day, tremendously appreciated the efforts put forth by the SRM AP in propelling a research-centric education. He remarked that research is the pursuit of thought and the product of innovation. Prof. Chakrabarti also delivered distinguished lectures on the intriguing realm of quantum machine learning and exploring generative AI, shedding light on the latest advancements and potential applications in both fields.
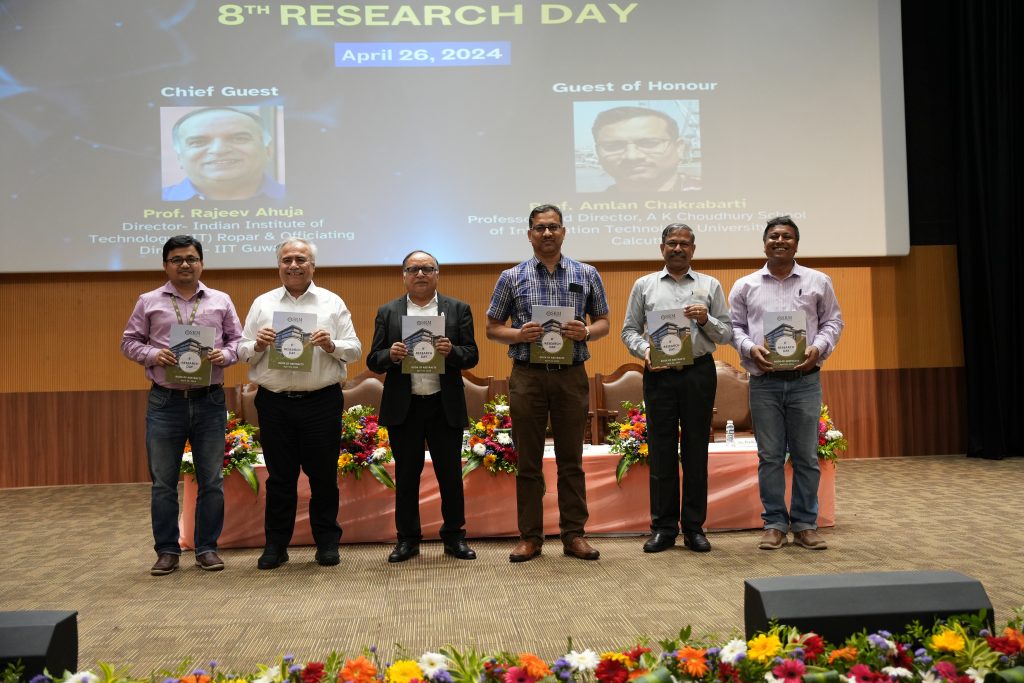

The 8th Research Day was commemorated to celebrate research and innovation in the emerging fields of science, technology, humanities, social sciences, management and commerce. 350+ research abstracts were submitted by undergraduate/postgraduate students and research scholars from across the country, which were culminated and unveiled as an Abstract Book. Selected papers were presented, and medals were awarded to the winners. The paper presentation witnessed 27 participants bagging gold medals and 7 participants securing silver medals. Five esteemed faculty of the university, Dr K M Divya Chaturvedi, Dr Mahesh Kumar Ravva, Prof. G S Vinod Kumar, Dr Ghanshyam Pandey and Dr Ramanjeya Reddy Udumula, were awarded prestigious awards for their stellar contributions and ingenious inventions in their respective domains.
The dignified guests of the events were presented with mementos as a token of gratitude by the university leaders, Dean-Research Prof. Ranjit Thapa and Convenor of the 8th Research Day, Dr Pradyut Kumar Sanki, Associate Professor, Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering. Dr R Premkumar delivered the Vote of Thanks, concluding the spectacular event.
Ranked Third among all private universities in India for two consecutive years according to Nature Index Ranking, SRM University-AP has a total of 2040+ research publications, 200 published patents, 24 granted patents, 43 Nature Index publications and a total outlay of Rs. 37+ crores in projects. The research environment is anchored by Eight Interdisciplinary Research Centres of Excellence. Research Day is a testament to the varsity’s commitment to building a strong research culture and research capacity among the faculty and students across different domains.
Continue reading → - Unveiling Findings on Thermo-Mechanical Behaviour of FGM Sandwich Plates April 26, 2024
 In a significant advancement in the field of material engineering, Dr Supen Kumar Sah, an esteemed Assistant Professor from the Department of Mechanical Engineering, has published a groundbreaking research paper.
In a significant advancement in the field of material engineering, Dr Supen Kumar Sah, an esteemed Assistant Professor from the Department of Mechanical Engineering, has published a groundbreaking research paper.The study, titled “Effect of Bi-Directional Material Gradation on Thermo-Mechanical Bending Response of Metal Ceramic FGM Sandwich Plates Using Inverse Trigonometric Shear Deformation Theory,” appears in the prestigious International Journal of Structural Integrity.
Dr Sah’s research provides new insights into the behaviour of Functionally Graded Materials (FGMs) under thermal and mechanical loads, which is crucial for the design of advanced engineering structures. His work employs an innovative inverse trigonometric shear deformation theory to analyse the bending response of metal-ceramic FGM sandwich plates, offering a more accurate prediction of their performance in real-world applications.
This publication not only highlights the cutting-edge research being conducted at SRM University but also positions Dr Sah as a leading figure in the application of FGMs in structural engineering. The findings from this paper have the potential to influence the design and optimization of materials used in various industries, from aerospace to automotive.
Abstract
The purpose of this study is to investigate the bending analysis of metal (Ti-6Al-4V) ceramic (ZrO_2) functionally graded material (FGM) sandwich plate having material property gradation along length and thickness direction under thermo-mechanical loading using inverse trigonometric shear deformation theory (ITSDT). Mechanical and thermal properties of BDFGM sandwich plates are considered temperature-dependent in the present study. Analytical solution for bending analysis of FGM plate has been carried out using Hamilton’s principle and Navier’s solution.
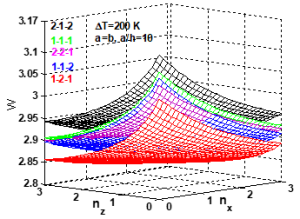
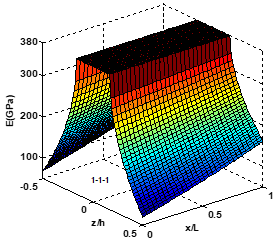
The present study shows that centre deflection, normal stress, and shear stress are significantly influenced by temperature-dependent material properties, bi-directional gradation exponents’ geometrical parameters, sandwich plate layer thickness, etc.
Title of the Research Paper in the Citation Format
Sah, S. K., Ghosh, A. (2024). Effect of Bi-Directional Material Gradation on Thermo-Mechanical Bending Response of Metal Ceramic FGM Sandwich Plates Using Inverse Trigonometric Shear Deformation Theory. International Journal Structural Integrity. DOI: 10.1108/IJSI-02-2024-0016
Collaborations
Prof Anup Ghosh, Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur, India
Future Research Plans
Modelling and Analysis of porous uni and multi-directional Functionally Graded Material (FGM) plates to obtain the impact of porosity distributions over structural responses.
Analytical & Finite Element Solution for static and dynamic response of FGM sandwich plates employing non-polynomial shear deformation theories under elastic foundation.
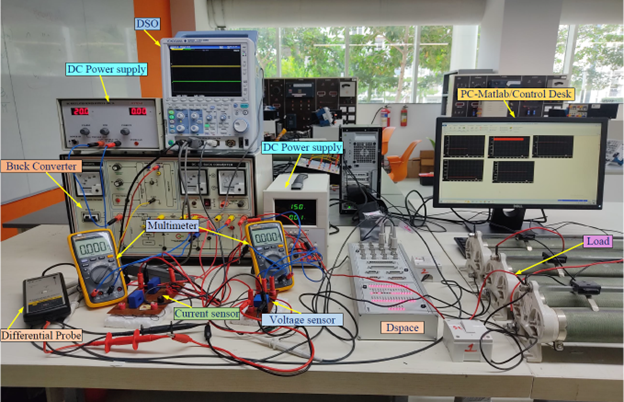
Continue reading → - A Study on Self-Learning Controller Design for DC-DC Power Converters April 26, 2024
It is with great pleasure that we announce the publication of a research paper titled “Self-Learning Controller Design for DC-DC Power Converters with Enhanced Dynamic Performance,” jointly authored by Dr Tousif Khan N, Associate Professor, Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, and Dr Ramanjaneya Reddy & Dr Arghya Chakravarty, Assistant Professors, Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering. The research paper introduces a novel self-learning control for precise output voltage tracking in DC-DC buck power converters.
Abstract:
This article introduces a self-learning robust control approach for accurate output voltage tracking in DC-DC buck power converters, focusing on scenarios with high precision requirements and significant load uncertainties. The method employs a simple online neural network to swiftly estimate unexpected load changes and disturbances across a wide range. Operating within a backstepping framework, the controller utilises neural network-learned uncertainties to enhance stability and improve dynamic and steady-state performance of both output voltage and inductor current. Extensive numerical simulations and practical experiments on a laboratory prototype demonstrate substantial enhancements in dynamic performance with a 94% reduction in settling time and precise steady-state tracking. The reliability of the proposed controller is further supported by the consistency between computational and experimental outcomes, showcasing its potential for real-world applications.
Practical implementations:
The proposed controller can be implemented/used for robotics applications, industrial processes, and medical equipment where precise control is needed.
Future research plans:
The following are the potential future directions of the proposed work;
(i) Design and development of the proposed self-learning neural network-based control for DC-DC buck converter systems with real-time DC sources, such as solar PV and fuel cells, experiencing highly intermittent input voltage changes.
(ii) Incorporating inductor current constraints and output voltage limitations into the proposed controller would also be an avenue worth exploring.
We congratulate the professors for their valuable contribution and look forward to future breakthroughs in this area.
Continue reading →