Research News
- Reimagining Island Poetics: Seminal Research on N S Madhavan’s Novel April 12, 2024

Dr Soni Wadhwa, Assistant Professor at the Department of Literature and Languages and her research scholar, Ms Jintu Alias, from the Easwari School of Liberal Arts at SRM University-AP, have published their seminal research paper titled “Provincialising Island Poetics: The Personal as the Spatial in N S Madhavan’s Litanies of Dutch Battery.”
Their research delves into the intricate relationship between personal experiences and spatial representations, challenging traditional island narratives. Focusing on the island city of Kochi and its rich history of cosmopolitanism, they aim to draw attention to alternative island spaces in India and Asia. Furthermore, they are convinced that their work will inspire further studies and creative writing on cultural traditions in smaller Indian island cities, highlighting the diverse themes and settings that are yet to be explored in Indian literature.Abstract
Affect towards islands is a unique approach to engage with in discussions of the phenomenology of fictional islands. This affect complements the already identified tropes within island poetics: those of sensorial exploration, spatial practices, and textural detailing of islands. This article turns to a work of fiction about a fictional island based on the island city of Kochi in south India to unpack an alternative aesthetic of spatiality, the kind that changes the personal/political relationship to personal/spatial one. We argue that the novel, Litanies of Dutch Battery (the novel in question) by N.S. Madhavan, expands inquiries into phenomenology of fictional islands by making space for corporeal memory and collective memory in storytelling. These memory-oriented narrative devices, we suggest, “provincialize” island poetics to add a hermeneutic of postcolonial angst to the repertoire of formal features of literary islandness.
Link to the Article
https://doi.org/10.24043/001c.94614
We wish the pair continued success in their future endeavours!
Continue reading → - Inauguration of NMR Spectrometer Marks a Milestone in SRM University-AP’s Research Capabilities April 10, 2024
 In a significant leap forward for scientific research, SRM University-AP proudly inaugurated the 400 MHz NMR (Nuclear Magnetic Resonance) Spectrometer, procured through the DST-FIST program. This acquisition is a vital component of the broader DST FIST project, which has been awarded to the Department of Chemistry at SRM University- AP with a budget of 2.20 crores.
In a significant leap forward for scientific research, SRM University-AP proudly inaugurated the 400 MHz NMR (Nuclear Magnetic Resonance) Spectrometer, procured through the DST-FIST program. This acquisition is a vital component of the broader DST FIST project, which has been awarded to the Department of Chemistry at SRM University- AP with a budget of 2.20 crores.As part of the project, the Department of Chemistry was recommended a 400 MHz NMR spectrometer by DST, which will play a crucial role in enhancing our expertise and aiding in achieving the proposed objectives. This state-of-the-art equipment is capable of characterising organic, inorganic, and biomolecules, enabling us to conduct comprehensive analyses and advance our understanding of complex chemical systems.
The ceremony, graced by esteemed guests, university dignitaries, faculties, and students, heralded a new era of scientific exploration and innovation. Prof. Lakshmi Kantam Mannepalli, Dr B P Godrej Distinguished Professor, ICT Mumbai, Chief Guest at the event, expressed, ” The inauguration of the 400 MHz NMR Spectrometer heralds a new era of precision and insight in scientific exploration. This instrument will unravel the mysteries of molecular structures and catalyse groundbreaking discoveries in the realm of chemistry and beyond.”
Dr S Mannathan, Associate Professor, Department of Chemistry, extended a warm welcome to the esteemed gathering and offered an insightful demonstration of the equipment’s operation, highlighting its advanced features and functionalities.
Prof. Manoj K Arora, Vice Chancellor, conveyed heartfelt congratulations to the team for this remarkable accomplishment, emphasising the transformative impact the new NMR Spectrometer will have on research and academic pursuits within the Department of Chemistry and beyond.”
Prof D Narayana Rao, Executive Director – Research, SRM Group of Institutions, emphasised, “The addition of this advanced equipment will significantly enhance the research capabilities, opening new avenues for exploration and discovery.”
V S Rao, Advisor, lauded the team for their achievement, stating, “This state-of-the-art equipment embodies our commitment to providing cutting-edge resources for our researchers and fostering a culture of innovation and discovery.”
Dr Pardha Saradhi Maram, Head of the Department of Chemistry, expressed his gratitude to all present and extended heartfelt thanks for their support and encouragement.
The acquisition of the 400 MHz NMR Spectrometer represents a significant advancement in scientific instrumentation, enabling researchers to delve deeper into molecular structures, chemical compositions, and dynamic processes. The Equipment will not only benefit the Department of Chemistry and Physics but also serve as a valuable resource for faculties and students across various disciplines.
The university has already trained 70 to 80 individuals in the operation of this equipment and is planning to organise a workshop for students and faculties from different universities, offering them the opportunity to leverage this advanced technology for their research and academic pursuits.
Continue reading → - Shining Bright: PhD Scholar Wins 2nd Prize at National Symposium March 20, 2024
 SRM University-AP is proud to congratulate Harsha, a brilliant PhD scholar from the Department of Physics, for her exceptional achievement at the National Symposium of Research Scholars on Metallurgy and Materials held at IIT Kanpur. Harsha secured the prestigious 2nd prize for her remarkable presentation titled “Tarnish Resistance Mechanism in Ag-4Cu-2.5Zn-1Ge Novel Alloy: A Comprehensive Experimental and Computational Analysis”.
SRM University-AP is proud to congratulate Harsha, a brilliant PhD scholar from the Department of Physics, for her exceptional achievement at the National Symposium of Research Scholars on Metallurgy and Materials held at IIT Kanpur. Harsha secured the prestigious 2nd prize for her remarkable presentation titled “Tarnish Resistance Mechanism in Ag-4Cu-2.5Zn-1Ge Novel Alloy: A Comprehensive Experimental and Computational Analysis”.The symposium, organised at IIT Kanpur, brought together some of the brightest minds in the field of metallurgy and materials research. Harsha’s presentation stood out among the impressive array of research papers, showcasing her expertise and dedication to pushing the boundaries of scientific exploration.
Her presentation focused on the intricate mechanism of tarnish resistance in the Ag-4Cu-2.5Zn-1Ge novel alloy. Through a comprehensive analysis that combined experimental and computational approaches, Harsha shed light on the factors influencing tarnish resistance in this unique alloy composition. Her findings have significant implications for the development of advanced materials with enhanced durability and longevity.
The symposium, which congregates the brightest minds in the field, was the perfect platform for Harsha to showcase her extensive research. Her work, which provides significant insights into the tarnish resistance mechanisms of novel silver alloys, has been recognised for its depth and scientific rigour.
The recognition received by Harsha at this prestigious national symposium is a testament to her exceptional research capabilities and the quality of education and mentorship provided at SRM University-AP. It highlights the university’s commitment to nurturing talent and fostering an environment conducive to groundbreaking research.
SRM University-AP extends its warmest congratulations to Harsha for this remarkable achievement. Her success serves as an inspiration to fellow students and researchers, encouraging them to pursue excellence in their respective fields of study.
Continue reading → - Unleashing the Power of Neuroscience: Paper on Person Identification March 19, 2024
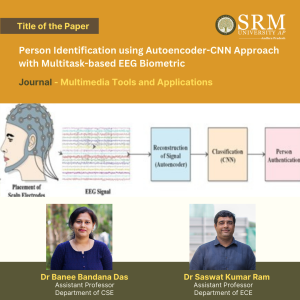 In a remarkable academic achievement, Dr Banee Bandana Das, Assistant Professor in Department of Computer Science and Engineering and Dr. Saswat Kumar Ram, Assistant Professor in Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, have made significant contributions to the field of biometric security. Their paper, titled “Person Identification using Autoencoder-CNN Approach with Multitask-based EEG Biometric,” has been published in the esteemed ‘Multimedia Tools and Applications journal, which is recognised as a Q1 journal with an impressive impact factor of 3.6.
In a remarkable academic achievement, Dr Banee Bandana Das, Assistant Professor in Department of Computer Science and Engineering and Dr. Saswat Kumar Ram, Assistant Professor in Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, have made significant contributions to the field of biometric security. Their paper, titled “Person Identification using Autoencoder-CNN Approach with Multitask-based EEG Biometric,” has been published in the esteemed ‘Multimedia Tools and Applications journal, which is recognised as a Q1 journal with an impressive impact factor of 3.6.This pioneering work showcases a novel approach to person identification using electroencephalogram (EEG) data. The research leverages the power of Autoencoder-CNN models combined with multitask learning techniques to enhance the accuracy and reliability of EEG-based biometric systems.
The publication of this paper not only underscores the high-quality research conducted at SRM University-AP but also places the institution at the forefront of innovative developments in biometric technology. It is a testament to the university’s commitment to advancing scientific knowledge and providing its faculty with a platform to impact the global research community positively.
Abstract
In this research paper, we propose an unsupervised framework for feature learning based on an autoencoder to learn sparse feature representations for EEG-based person identification. Autoencoder and CNN do the person identification task for signal reconstruction and recognition. Electroencephalography (EEG) based biometric system is vesting humans to recognise, identify and communicate with the outer world using brain signals for interactions. EEG-based biometrics are putting forward solutions because of their high-safety capabilities and handy transportable instruments. Motor imagery EEG (MI-EEG) is a maximum broadly centered EEG signal that exhibits a subject’s motion intentions without real actions. The Proposed framework proved to be a practical approach to managing the massive volume of EEG data and identifying the person based on their different task with resting states.
The title of Research Paper in the Citation Format
Person identification using autoencoder-CNN approach with multitask-based EEG biometric. Multimedia Tools Appl (2024).
Practical implementation/social implications of the research
- To develop a personal identification system using MI-EEG data.
- This work is about an Autoencoder-CNN-based biometric system with EEG motor imagery inputs for dimensionality reduction and denoising (extracting original input from noisy data).
- The designed Autoencoder-CNN-based biometric architecture to model MI-EEG signals is efficient for cybersecurity applications.
Collaborations
- IIITDM, Kurnool, India
- National Institute of Technology, Rourkela, India
- University of North Texas, Denton, USA
Future Research Plan
In the future, different deep learning and machine learning methods can be merged to explore better performance in this EEG-based security field and other signal processing areas. We will investigate the robustness deep learning architectures to design a multi-session EEG biometric system.
- Breakthrough in Lead-Free Brass Manufacturing: Patent Granted to Prof. G. S. Vinod Kumar March 19, 2024

The Department of Mechanical Engineering are excited to share a significant milestone achieved in the field of material science and metallurgy. Prof. G S Vinod Kumar, Professor and Head of the Department, has been granted a patent jointly with Titan Company, Bangalore, for the invention “METHOD OF MANUFACTURING LEAD-FREE BRASS” (Patent Grant Number: 452003). This industrial patent was created through a collaboration between SRM University-AP and Titan Company Limited.
This groundbreaking discovery not only transforms the manufacturing of lead-free brass, but it also highlights the collaborative spirit that drives advances in materials engineering.
Abstract
The present disclosure relates to a field of material science and metallurgy. In particular, the present disclosure discloses a method for manufacturing lead-free brass alloy. The method includes preparation of first master alloy by melting copper and a transition element, and a second master alloy by mixing molten zinc and molten copper. The lead-free brass is obtained by meting a predetermined proportion of the first master alloy and second master alloy along with elemental copper in a furnace under an argon atmosphere. The lead-free brass alloy is then subjected to a precipitation hardening process to improve hardness. The lead-free hard brass alloy containing titanium exhibits improved hardness in comparison to bare lead-free brass mainly due to the presence of intermetallic nanoscale precipitates, which are distributed throughout the lead-free brass matrix.
SRM University-AP continues pushing the limits of scientific discovery and industrial innovation.
Continue reading → - Metallurgical Study on Fusion Welding of Aluminium and Magnesium March 14, 2024
 In a significant scientific endeavour, Dr Maheshwar Dwivedy, Associate Professor in the Department of Mechanical Engineering, and Dr B Prasanna Nagasai, Post-Doctoral Researcher have jointly authored a research paper titled “Metallurgical Characteristics of AA6061 Aluminium and AZ31B Magnesium Dissimilar Joints by Fusion Welding Technique”. Their work delves into the metallurgical properties of dissimilar joints formed by fusion welding between AA6061 aluminium and AZ31B magnesium.
In a significant scientific endeavour, Dr Maheshwar Dwivedy, Associate Professor in the Department of Mechanical Engineering, and Dr B Prasanna Nagasai, Post-Doctoral Researcher have jointly authored a research paper titled “Metallurgical Characteristics of AA6061 Aluminium and AZ31B Magnesium Dissimilar Joints by Fusion Welding Technique”. Their work delves into the metallurgical properties of dissimilar joints formed by fusion welding between AA6061 aluminium and AZ31B magnesium.The study, published in the esteemed Q1 journal “Microscopy Research and Technique”, sheds light on the intricate interactions between these two dissimilar materials. By employing advanced microscopy techniques, the researchers meticulously examined the weld interfaces, grain structures, and elemental compositions. Their findings contribute to our understanding of the joining behaviour and intermetallic formation in such hybrid joints.
This collaborative effort exemplifies SRM University – AP’s commitment to cutting-edge research and interdisciplinary exploration. As the scientific community continues to unravel the mysteries of material behaviour, Dr Dwivedy and Dr Nagasai’s work stands as a beacon of knowledge and innovation.
Stay tuned for more updates on this groundbreaking research!
Abstract
Aluminium (Al) and magnesium (Mg) alloys are extensively used in the automobile sector because of their high strength-to-weight ratio, excellent castability, low density and simplicity of recycling. Al-Mg structures that automotive uses have a big chance of lowering their weight. Although there is a significant opportunity for substantial cost reduction, the use of magnesium in aluminium structures remains restricted. This study aims to weld 3 mm-thick rolled sheets of AA6061 Al and AZ31B Mg alloy using the cold metal transfer (CMT) arc welding process. Three different filler wires (ER1100, ER4043, and ER5356) were used in the experiment. In this article, the mechanical and microstructure characteristics of Al/Mg dissimilar joints manufactured by CMT are evaluated and discussed in depth. Optical microscope (OM), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX), and X-ray diffraction were all used to analyse the CMT-welded Al/Mg dissimilar joints. Of the three filler wires used, ER4043 (Al-5%Si) filler wire yielded defect-free sound joints due to the presence of Si, which improves the flow ability of molten filler during welding. The Al/Mg dissimilar weld still produced the Mg-rich intermetallic (IM) Al12Mg17 and the Al-rich IM Al3Mg2. The surfaces of the fractured area of the CMT-welded Al/Mg dissimilar joints revealed the presence of the Mg-rich intermetallics (Al12Mg17), which is responsible for the decrease in tensile strength. The reduction of intermetallics, particularly of Mg-rich intermetallics (Al12Mg17) is important for improving joint strength.
Highlights
- Cold metal transfer (CMT) arc welding was used to control the Al-Mg-rich intermetallics in the Al/Mg dissimilar joints.
- The microstructure, morphology and phase composition of the welded joints were studied by OM, SEM, TEM, EDS and XRD.
- The weld metal and AL substrate are joined with a strong interface, while the weld metal and Mg substrate are joined with an epitaxial solidification area where the intermetallic compounds of Mg2Al3, Mg17Al12 and Mg2Si are generated.
- The weld metal on the Mg side experienced a brittle fracture, with a continuous distribution of Mg2Al3, Mg17Al12 and Mg2Si.
Explanation of Research in Layperson’s Terms
Al and Mg alloys are extensively used as light metals in engineering due to their advantageous characteristics, including high strength-to-weight ratio, cheap casting costs, low density, excellent machinability, and simple recyclability. Often, each of these materials fails to meet the criteria for lightweight buildings. Consequently, there is a high need for a significant quantity of Al/Mg hybrid structures in many industrial sectors with a particular emphasis on the automotive industry. Choosing the appropriate filler material for joining Al and Mg is crucial for creating robust weldments. The main difficulty in welding dissimilar metals like aluminium and magnesium lies in the formation of inflexible and brittle intermetallic compounds (IMCs) like Mg2Al3 and Mg17Al12, which severely affect the joint’s strength. When it comes to melting points, magnesium is at 650°C and aluminium is at 660°C. Based on the Mg-Al binary phase diagram, the compounds Mg2Al3 and Mg17Al12 can be produced at 450 and 437°C by eutectic reaction. Hence, the primary challenge in Al/Mg dissimilar welding is effectively suppressing the growing number of IMCs. Similarly, minimising energy input and utilising the appropriate chemistry of wire are the primary methods for decreasing the formation of IMCs and improving joint strength.
CMT is an advanced arc welding process which comes under controlled short circuiting transfer mode. The CMT welding cycle consists of two phases, i.e. the arcing phase and short circuit phase. In arcing phase, the filler wire gets melted and it forms as a droplet at the tip of the filler wire. In short circuiting phase, the droplet bridges the gap between the electrode and the weld pool. Once the short circuiting takes place, the filler wire gets retracted backward due to the retraction force and the droplet is detached from the filler wire. In conventional short circuiting transfer mode, the electromagnetic pinch force assists in detaching the droplet from the filler wire and thereby high heat input is produced by means of the short current. Where as in CMT short circuit transfer mode, the welding current is decreased to a lower value whenever a short circuit signal is sensed by the power source and the droplet gets separated from the filler wire with the help of the retraction force that is generated during the backward movement of the filler wire. Finally, the heat input is reduced to a lower value with this metal transfer mode. So, the CMT arc welding process was used to join the 3 mm-thick rolled sheets of AA6061 Al and AZ31B Mg alloy dissimilar materials. This article details the microstructural characteristics of an Al/Mg dissimilar joint. The CMT process controlled IMCs in the Al/Mg dissimilar joint and increased weld metal hardness compared to base metal.
The title of Research Paper in the Citation Format
aAddanki Ramaswamy, *aBellamkonda Prasanna Nagasai, aMaheshwar Dwivedy, Sudersanan Malarvizhi, Visvalingam Balasubramanian, Metallurgical Characteristics of AA6061 Aluminium and AZ31B Magnesium Dissimilar Joints by Fusion Welding Technique, Microscopy research and technique, 2024. DOI: 10.1002/JEMT.24510.
Corresponding Author: Bellamkonda Prasanna NagasaiCollaborations
Dr. V. Balasubramanian, Professor & Director, Centre for Materials Joining & Research (CEMAJOR) Annamalai University, Annamalai Nagar-608002, Tamilnadu
Future Research Plans:
Planning to work on Fusion Welding (CMT, MIG, TIG, LASER, PLASMA and EBW) and Solid State Welding Processes (FSW, Rotary Friction Welding, Resistance Spot Welding, Magnetic Pulse Welding). Working on Additive Manufacturing (Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing on Metals, 3D Printing on Plastics), Cladding and Machinability. Characterisation, Tribology, and Corrosion. Steels and alloys, Aluminum, Nickel and Titanium Alloys.
Continue reading → - Tracing a Translator’s Journey: An Interview with V Ramaswamy March 13, 2024

A translated work must retain the essence and flavour of regional culture and locales. A good translator tries to reproduce the particularities that are ingrained within the texts. On this note, Dr Bidisha Pal, Assistant Professor from the Department of Literature and Languages, has published a paper, “Delving into a Translator’s Journey of Translating Marginalised Voices of Bengal: An Insightful Discussion with V Ramaswamy” in Meta Journal des traducteurs Translators’ Journal. This research revolves around a discussion with the well-known translator V Ramaswamy, a noted name in Bengali Dalit literature and translation. Ramaswamy shares his thoughts on working on the translation projects that he enjoys doing and that establish the cause of the marginalised people of Bengal.
Abstract
In this interview discussion with Bidisha Pal and Md. Mojibur Rahman, translator V Ramaswamy focuses on the journey of his translation and tryst with the marginalised Dalit voice(s) in Bengal. He speaks about the writings that propel him to choose translating and to carry voice(s) beyond the Bengal arena, thus dissolving language barriers. The deliberate choice to translate various pieces representing various periods acts as a witness to his existence as an independent translator. According to him, translation is also a source of healing to deal with a tragic past and the complicacies that life often presents to him. He shares his experience translating Subimal Mishra, the powerful poet who speaks for marginalised people. Ramaswamy, as he states in the interview, makes a vow to translate Mishra’s whole writing career. He talks about translating Manoranjan Byapari, a Bengali Dalit prize-winning author and political persona who has also championed the Dalit cause in Bengal, Adhir Biswas, the story-writer and publisher of a publishing house in Kolkata Gangchil that publishes writings by those literary personas who do not fall, as such, into the category of the mainstream, Bangladeshi writer Shahidul Zahir whose revolutionary voice and zeal reverberate in the literary world of Bangladesh, as well as Ansaruddin, a writer and farmer by profession whose works Ramaswamy is currently translating. Despite not being a part of the literary world, Ramaswamy has built an intense connection with literature and has gradually become part of the world. For him, translation is something that has to remain faithful to the source text, especially if people are doing literary translation.
Practical implementation/social implications of the research
The research contains elements that are connected with the values of the society. It discusses the nuances of translation of the writings of marginalised people, which contain many unforeseen truths of society, and depicts the struggles for the existence of the people. The translator is doing a commendable job compiling the writing thorough translation that will act as a bridge to the unfamiliar audience who could feel connected with the marginalised people.
Dr Bidisha aims to publish many more articles in the diverse interdisciplinary fields of literature, edit books, and attend conferences.
Continue reading → - Promoting Well-Being in Children and Adolescents: A Holistic Guide to Mindfulness Strategies and Effects March 12, 2024

Mindfulness has emerged as a pivotal aspect in the domain of mental health, especially in the context of children and adolescents’ well-being. It refers to an inherent ability to be fully present in the moment, enabling an individual to gain an acute sense of awareness without any biases. Such a state of mindfulness empowers individuals to navigate the ups and downs of life with clarity and composure. Dr M Dhamodharan, an Assistant Professor in the Department of Psychology, has published a book chapter titled “Mindfulness for Child and Adolescent Well-Being: A Comprehensive Exploration of Strategies and Outcomes,” where he has comprehensively explored the intricacies of mindfulness and its impact on children and adolescents.
Here’s an abstract of the chapter published in the book, “Promoting Mindfulness and Well-Being with Indian Psychology.”
About the book chapter
The chapter examines the significant impact of mindfulness on children and adolescents. Mindfulness is the mental state defined by greater concentration, consciousness, and focus on the here and now, free from judgment. This chapter starts with the theoretical background of mindfulness and the current developments of mindfulness related to children’s and adolescents’ wellbeing. There are three main domains focused on mindfulness. Begin with emotional domains—that explains how mindfulness helps to regulate emotions. Secondly, cognitive domains explain how mindfulness practices help cognitive development and academic performance in educational settings. Thirdly, social and interpersonal domains explain the uses of mindfulness to improve social skills and interpersonal relationships with peer groups, family, and society. The chapter concludes with the role of parental and educational institutions in promoting mindfulness among children and adolescents to create a positive impact on their lives.
Dr Dhamodharan’s book chapter is targeted at Educators, parents, counsellors, and mental health specialists who stand to gain invaluable insights from the exploration of mindfulness within these pages.
Continue reading → - Revolutionising LED Lighting: Paper Published in IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications March 12, 2024
 In a significant academic accomplishment, Dr Ramanjaneya Reddy, Assistant Professor in the Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, along with UG students Ms Mehataj Syed and Mr Busam Gopichand, have recently published a groundbreaking paper titled “A Three Leg Asymmetrical Voltage Resonant Converter with Independent Dimming Control for Multiple Load LED Lighting Applications” in the esteemed Q1 journal IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications. The journal boasts an impressive impact factor of 4.4, further underscoring the importance of this research contribution.
In a significant academic accomplishment, Dr Ramanjaneya Reddy, Assistant Professor in the Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, along with UG students Ms Mehataj Syed and Mr Busam Gopichand, have recently published a groundbreaking paper titled “A Three Leg Asymmetrical Voltage Resonant Converter with Independent Dimming Control for Multiple Load LED Lighting Applications” in the esteemed Q1 journal IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications. The journal boasts an impressive impact factor of 4.4, further underscoring the importance of this research contribution.The paper delves into the development of a novel Three Leg Asymmetrical Voltage Resonant Converter that offers independent dimming control for multiple load LED lighting applications. This innovation holds great promise for enhancing the efficiency and versatility of LED lighting systems, paving the way for more sustainable and adaptable lighting solutions in various industrial applications.
Dr Ramanjaneya Reddy’s leadership and the collaborative efforts of Ms Mehataj Syed and Mr Busam Gopichand have culminated in this significant publication, which not only adds to the body of knowledge in the field but also showcases the talent and dedication of the researchers at the department.
This achievement highlights the commitment to excellence and innovation within the Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, positioning it as a hub for cutting-edge research and academic prowess. The impact of this research is expected to reverberate across the industry, contributing to advancements in LED lighting technology and its applications.
The publication of this paper underscores the quality and rigour of the research solidifying their reputation as leaders in the field. This accomplishment is a testament to the department’s commitment to pushing boundaries and making meaningful contributions to the field of electrical engineering.
Congratulations to Dr Ramanjaneya Reddy, Ms Mehataj Syed, and Mr Busam Gopichand on this remarkable achievement, and we look forward to seeing the continued impact of their research in the field.
Abstract
This work proposes a three-leg asymmetrical voltage resonant converter for multiple load Light Emitting Diode (LED) lighting applications. The proposed converter is developed with a common leg-1 for both load-1 and load-2. The load-1 is powered from asymmetrical voltage between leg-1 and leg-2. Similarly, load-2 is powered from asymmetrical voltage between leg-1 and leg-3. The proposed circuit provides the following major contributions: (1) Independent dimming control of LED loads; (2) Zero Voltage Switching (ZVS) of all power switches; (3) High efficiency; and (4) Asymmetrical voltage regulation. To achieve independent dimming control, the voltages between legs are made zero by dimming leg-2 and leg-3 independently. Two resonant circuits are connected in the proposed circuit. Owing to this all the power switches operate with ZVS, which reduces the switching losses. Further, two LED lamps are connected in series with battery sources to supply the threshold voltage to lamps which in turn results in a lower power processing of the converter.
Explanation of Research in Layperson’s Terms
This work proposes a three-leg asymmetrical voltage resonant converter with independent dimming control for multiple load LED lighting applications. The proposed converter drives multiple loads independently with a dimming feature. The converter is developed with leg-1 is common for both LED loads. The major contributions of the proposed LED driver are independent dimming control, asymmetrical voltage regulation, zero voltage switching of all the power switches, and high efficiency. The threshold voltage of LED loads is supplied by batteries connected in series with LED loads, which will help in lower power processing of the proposed converter. Further, due to soft switching technology implemented in this converter, it reduces the losses in the system considerably increasing efficiency.
Title of Research Paper in the Citation Format
A Three Leg Asymmetrical Voltage Resonant Converter with Independent Dimming Control for Multiple Load LED Lighting Applications.
Citation: Ramanjaneya Reddy Udumula, et. al, “A Three Leg Asymmetrical Voltage Resonant Converter with Independent Dimming Control for Multiple Load LED Lighting Applications,” IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, Feb 2024. doi: 10.1109/TIA.2024.3363676
Practical and Social Implementation of Research
To achieve effective and efficient use of energy resources under the sustainable development goals, Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs) have emerged as a global lighting industry solution. Over the conventional lighting sources such as incandescent lamps, fluorescent lamps, and high intensity discharge lamps, LEDs are i) more efficient, ii) eco-friendly due to absence of toxic gases, iii) have longer life span up to one lakh year, iv) high luminous intensity and v) good colour rendering index. LED’s requires low voltage direct current supply and the V-I characteristics of LEDs which is like Shockley diode represents the exponential growth of current over a small voltage variation which may damage the LED or effects the illumination. Hence, an LED driver is necessary in an LED system to supply LEDs with constant current. DC fed LED drivers are more reliable due to absence of AC-DC conversion stage and power factor correction stage which are crucial in AC fed LED drivers. Therefore, DC fed LED drivers are paid more attention in recent times in the majority of battery-powered/solar-powered applications. Given its features of high power, exceptional efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and flicker-free operation, this innovation is well-suited for streetlight/stadium lighting applications.
Collaborations
Dr. Kasi Ramakrishna Reddy, Assistant Professor
Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, Vasavi College of Engineering, HyderabadFuture Research Plans
The future work is on PV/battery fed LED driver topologies suitable for streetlighting/stadium lighting applications with low component count, high efficiency, reduced device stress, and flicker free lighting system
Continue reading → - Advances in Electric Vehicle Technology: A Study on Bi-Directional Converters March 12, 2024
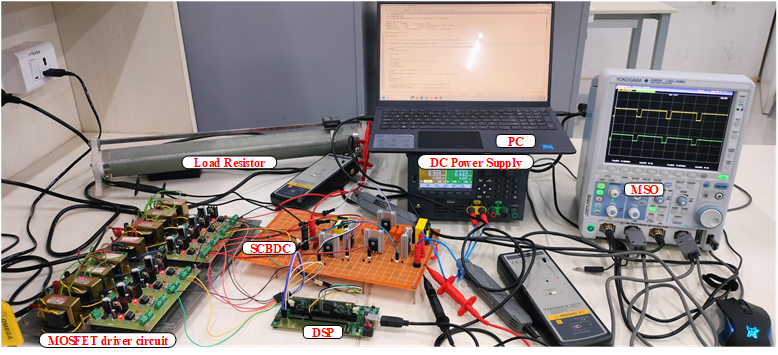
Electric Vehicles are in vogue today, thanks to the heightened environmental concerns, greater availability of models, increased cost competitiveness and improved vehicle ranges. To contribute to the growing field of electric vehicle technology, Assistant Professors, Dr Tarkeshwar Mahto, Dr Somesh Vinayak Tewari and Dr Ramanjaneya Reddy from the Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering at SRM University-AP along with the research scholar, Ms K Mounika Nagabushanam, conducted a study and published a research paper titled “Development of High-Gain Switched-Capacitor Based Bi-Directional Converter for Electric Vehicle Applications.” The team’s research focuses on creating a bi-directional DC-DC converter that enables power flow from the battery to the motor and vice versa while maintaining necessary voltage gains and ensuring improved efficiency and low cost.
Abstract
High efficiency, high voltage transfer ratio (VTR), and low input ripple current are required in any bidirectional DC-DC converter (BDC) that plays a major role in interfacing batteries in applications like DC microgrids and electric vehicles (EVs). To meet these requirements, a switched capacitor-based BDC is proposed to interface the battery with a propulsion system via a DC Link. It has a simple circuit with only a set of switching operations, High VTR, and lesser ripple current on the low voltage (LV) side, which are advantages of the proposed High Gain Switched-Capacitor Bi-directional DC-DC Converter (SC-BDC), making it appropriate for use in EVs. The steady-state analysis, design consideration of passive components, loss and efficiency analysis are presented. Finally, the proposed High Gain SC-BDC is compared with a few of the existing BDCs in the literature. The feasibility of the converter was demonstrated by simulating a 200 W converter and validating results produced in a MATLAB environment.
Practical implementation of your research or the social implications associated with it.
The developed converter can be used in Electric Vehicle for integration of battery to traction motor.
Collaborations.
1. Majed A. Alotaibi, Department of Electrical Engineering, College of Engineering, King Saud University, 11421, Saudi Arabia.
2. Hasmat Malik, Department of Electrical Power Engineering, Faculty of Electrical Engineering, University Technology Malaysia (UTM), Johor Bahru 81310, Malaysia.
3. Fausto Pedro García Márquez, Ingenium Research Group, Universidad Castilla-La Mancha, 13071 Ciudad Real, Spain.
As part of their future research plans the team plans of working on noise reduction methods that are brought on by regeneration action and to incorporate various control techniques to keep the DC link voltage of the propulsion system constant.
We wish the team all success in their future endevours!
Continue reading →