
The water crisis in India, especially in the coastal regions, has worsened alarmingly, coercing environmentalists and researchers to critically study the reason behind this phenomenon. The Sundarbans region faces a scarcity of drinking water in terms of quality and quantity due to various reasons. Dr Kousik Das, Asst. Professor, Department of Environmental Science and Engineering, Dr Harish Puppala, Asst Professor, Department of Civil Engineering and Mr Mijanur Mondal, Research Scholar from the Department of Environmental Science and Engineering has conducted a groundbreaking study on the increased salinization of water due to human activities. The research trio has published a paper titled “Understanding the susceptibility of groundwater of Sundarbans with hydroclimatic variability and anthropogenic influences” in the prestigious Q1 journal Groundwater for Sustainable Development, which has an impact factor of 5.9, critically analysing the numerous factors that affect the quality of drinking water in the Sundarbans region.
Abstract
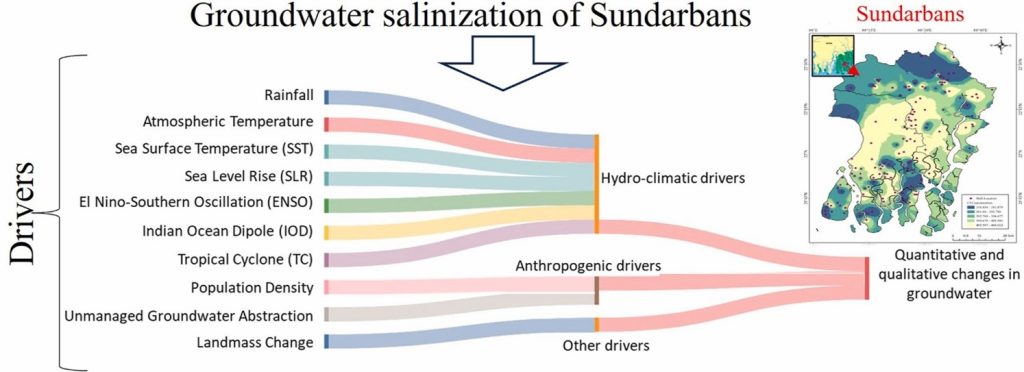
Coastal aquifers worldwide are experiencing increased salinisation due to climate change and human activities. Sundarbans, in India, is one such area where this phenomenon is noticed at an unprecedented rate, making drinking water unpotable for consumption. Existing studies lack a comprehensive analysis of the underlying causes. This study conducts a systematic literature review to identify drivers of groundwater salinisation, examining climate change parameters such as rainfall patterns, sea level rise, El Niño-Southern Oscillation, and tropical cyclones. Significant groundwater level declines from 1996 to 2017 are primarily attributed to variations in the Indian Ocean Dipole and El Niño Southern Oscillation, affecting rainfall and recharge rates. During tropical cyclones, groundwater levels rise rapidly, and quality is sensitive to El Niño Southern Oscillation. Rising sea levels, changing rainfall, and increasing population density worsen salinisation. Shallow aquifers have high salinity, whereas deep aquifers exceed permissible limits. This underscores the urgent need to address drinking water scarcity and potential migration resulting from complex interactions between climate, population, and groundwater management.
Social Implications of the Research
- Water Quality Monitoring: Implementing regular monitoring of salinity levels in groundwater to ensure compliance with safety standards.
- Community Awareness Programmes: Conducting educational campaigns to inform local communities about the risks of high salinity levels in drinking water and promoting the judicious use of water sources so that unscientific abstraction can be reduced.
- Policy Development: Formulating policies at the local and national levels to regulate salinity levels in drinking water and ensure public health protection.
- Infrastructure Improvement: Investing in water treatment facilities or technologies to remove high salt levels from groundwater sources. Alternative sources and rainwater harvesting can be taken into consideration.
Collaborations – IIT Kharagpur, India
The research team plans to work on Groundwater vulnerability modelling using AI/ML in Sundarbans, India next. The team has begun collecting primary data using questionnaire surveys and interviews to throw light on socio-economic conditions and to understand the core reasons for the water crisis and health and psychological issues due to water unavailability, especially during extreme events like cyclones.
Link to the article

