Exploring the Impact of Welding Processes on Duplex Stainless Steel Parts in Additive Manufacturing
 In a recent publication in the prestigious Journal Metals and Materials International, Dr Maheshwar Dwivedy, Associate Professor in the Department of Mechanical Engineering and Dr B Prasanna Nagasai, Post-Doctoral Researcher, delve into the intricate relationship between welding processes and the resulting microstructure and mechanical properties of Duplex Stainless-Steel parts fabricated through Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing.
In a recent publication in the prestigious Journal Metals and Materials International, Dr Maheshwar Dwivedy, Associate Professor in the Department of Mechanical Engineering and Dr B Prasanna Nagasai, Post-Doctoral Researcher, delve into the intricate relationship between welding processes and the resulting microstructure and mechanical properties of Duplex Stainless-Steel parts fabricated through Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing.
The research paper, aptly titled “Influence of Welding Processes on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Duplex Stainless-Steel Parts Fabricated by Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing,” illuminates the crucial factors that influence the quality and performance of components produced using this innovative manufacturing technique.
This collaborative effort not only enriches the academic community but also holds promising implications for the advancement of additive manufacturing technologies, particularly in the realm of Duplex Stainless-Steel fabrication. By unravelling the impact of different welding processes on the microstructural characteristics and mechanical behaviour of such components, the researchers offer valuable insights that can potentially enhance the efficiency and reliability of the manufacturing process.
The publication of this paper signifies a significant milestone in the ongoing exploration of material science and additive manufacturing techniques, highlighting the dedication and expertise of Dr Maheshwar Dwivedy and Dr B Prasanna Nagasai in pushing the boundaries of knowledge and innovation in the field.
Abstract
Direct energy deposition (DED) is an advanced additive manufacturing (AM) technique for producing large metal components in structural engineering. Its cost-effectiveness and high deposition rates make it suitable for creating substantial and complex parts. However, the mechanical and microstructural properties of these components can be influenced by the varying heat input and repeated thermal treatments associated with different welding procedures used during the deposition process. This study employed gas metal arc welding (GMAW) and cold metal transfer (CMT) arc welding techniques to fabricate cylindrical components from 2209 duplex stainless steel (DSS).
The research investigated the impact of these welding methods on the microstructure and mechanical properties of the 2209 DSS cylinders. The intricate thermal cycles and cooling rates inherent in the DED process significantly influenced the primary phase balance, ideally comprising 50% austenite and 50% ferrite. In components processed using GMAW, σ-phase formation was noted at the grain boundaries. Additionally, a slower cooling rate and extended time for solid-state phase transformations led to an increase in austenite content from the bottom to the top of the component. The cylinder fabricated using the CMT process exhibited fine austenite morphologies and a higher ferrite content compared to the GMW-processed cylinder.
Furthermore, the cylinder produced using the CMT process showed consistent properties across the building direction, unlike the components manufactured with the GMW process. In terms of tensile properties, hardness, and impact toughness, the cylinder produced using the CMT technique outperformed the one made with the GMW process.
Research in Layperson’s Terms
Over the last ten years, a new way of making things called additive manufacturing (AM) has become really popular, especially in industries like aerospace, oil, and gas. This technology builds parts layer by layer, which is a big change from traditional methods that often involve cutting away material to shape a part. One specific method of AM, called Directed Energy Deposition (DED), is particularly good at creating complex metal parts quickly and efficiently. A special kind of stainless steel called duplex stainless steel (DSS) is made of two types of microstructures, ferrite and austenite, which give it great strength and resistance to corrosion. This makes it ideal for use in demanding environments like the oil and gas industry.
A technique within DED called Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing (WAAM) is becoming a popular way to make large, strong metal parts like pipes and storage tanks. WAAM uses the same equipment as welding and can build parts by melting wire with an electric arc. It’s faster and cheaper than other AM methods. However, the process can change the structure of the metal, which affects its properties. For example, too much heat can reduce the amount of ferrite in the metal, making it less strong.
Researchers have been studying how different methods of WAAM, including ones that use less heat, affect the metal’s structure and properties. They’ve found that controlling the heat can lead to better mechanical properties, like higher strength and toughness. They’ve also looked at new technologies like digital twins (virtual models of the manufacturing process) to improve the stability and consistency of the process. In this study, researchers focused on making cylindrical parts from 2209 DSS using two different welding processes within WAAM: Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW) and Cold Metal Transfer (CMT).
They studied how these processes affected the metal’s structure and properties, like tensile strength, hardness, and toughness. The goal was to understand which process produces the best quality parts for industrial use. In summary, the research aims to improve the manufacturing of strong, corrosion-resistant metal parts using advanced AM techniques, making them more efficient and cost-effective for industries that need durable components.
Practical Implementation or the Social Implications Associated
The practical implementation of this research can revolutionise industrial manufacturing, especially in sectors like aerospace, oil and gas, automotive, and marine applications. Using WAAM with DSS, industries can produce lightweight, high-strength parts that withstand extreme environments, significantly improving efficiency and cost-effectiveness. WAAM’s ability to quickly produce customized and high-quality components also makes it ideal for rapid prototyping and repair, reducing lead times and overall production costs. Furthermore, WAAM is a more sustainable manufacturing method, generating less waste and utilizing recycled materials, contributing to eco-friendly production practices. The social implications are substantial, including the creation of new job opportunities and the need for specialized training programs to equip workers with advanced skills.
The economic impact is also notable, as WAAM enhances the competitiveness of companies, driving economic growth in high-tech industries. Innovation is fostered through advancements in manufacturing processes and materials science, leading to improved product performance and longevity, particularly in safety-critical applications. Additionally, the environmental benefits of reduced waste and potential use of recycled materials align with global sustainability goals. Overall, the adoption of WAAM can democratize the manufacturing landscape, making advanced technologies more accessible and affordable for smaller companies and startups, thereby fostering a more inclusive and innovative industrial environment.
Future Research Plans:
The upcoming work will focus on creating Functionally Graded Materials (FGMs) using Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing (WAAM) by merging various metals, including nickel, stainless steel, mild steel, Inconel 718, and AISI 410 MSS. The goal is to optimise material interfaces, refine deposition processes, and ensure structural integrity for high-performance applications.
- Published in Departmental News, Mechanical Engineering NEWS, News, Research News
Unraveling Chaos Dynamics in Cancer: Dr Koyel Chakravarty’s Breakthrough Research
 Dr Koyel Chakravarty, Assistant Professor in the Department of Mathematics, has made a significant contribution to the field of cancer research with her paper “Analysis and Regulation of Chaos Dynamics in a Cancer Model through Chemotherapeutic Intervention and Immune System Augmentation,” which was recently published in the International Journal of Dynamics and Control. In her paper, Dr Chakravarty delves into the intricate world of chaos dynamics within a cancer model and explores the potential for regulating these dynamics through the combined approach of chemotherapeutic intervention and immune system augmentation.
Dr Koyel Chakravarty, Assistant Professor in the Department of Mathematics, has made a significant contribution to the field of cancer research with her paper “Analysis and Regulation of Chaos Dynamics in a Cancer Model through Chemotherapeutic Intervention and Immune System Augmentation,” which was recently published in the International Journal of Dynamics and Control. In her paper, Dr Chakravarty delves into the intricate world of chaos dynamics within a cancer model and explores the potential for regulating these dynamics through the combined approach of chemotherapeutic intervention and immune system augmentation.
Her research offers insights into understanding the complex behaviour of cancer cells and how such insights can be leveraged to develop more effective treatment strategies. Dr Chakravarty’s work marks a crucial step forward in the ongoing efforts to combat cancer, shedding light on the dynamic interplay between therapeutic interventions and the body’s immune response.
The publication of this paper not only underscores Dr Koyel’s expertise in the field of mathematical analysis in cancer research but also signifies a promising advancement in the collective pursuit of understanding and addressing the challenges posed by cancer.
Abstract
The focus of the current investigation lies in the formulation and analysis of a dynamic model depicting cancer growth, incorporating the joint influences of chemotherapy and immune system augmentation. The primary emphasis of this study revolves around the analysis of the dynamic behaviour within a living-cell closed carcinoma system, specifically one devoid of external vitamin support, with a particular exploration of chaos dynamics. Subsequently, the authors aim to scrutinise the pivotal impact of infused vitamins in attaining stable system dynamics through the application of chaos control techniques.
The formulated model exhibits fundamental mathematical properties, revealing a spectrum of co-dimension one and co-dimension two bifurcations. The identification of specific bifurcation types relies on algebraic criteria techniques, where conditions necessary and sufficient for bifurcation types are developed. Notably, these criteria are distinct from traditional approaches based on the characteristics of the eigenvalues of the Jacobian matrix, instead relying on coefficients derived from characteristic equations. The accuracy of the analytical conclusions is validated through numerical findings, elucidating diverse bifurcation structures. The article enriches its contribution by delving into the control of chaos through the reinforcement of the internal immune system and the maintenance of the biological system’s stability. This work culminates in proposing future directions aimed at advancing a more realistic approach to eradicating cancer.
Research in Layperson’s Terms
This study focuses on developing and analysing a model that simulates how cancer grows, considering both chemotherapy and the immune system’s response. The main goal is to understand how cancer behaves over time in a system that doesn’t have external vitamin support, especially looking at how chaotic or unpredictable the growth can become. The researchers also investigate how adding vitamins might help stabilise this chaotic system using specific control techniques. The model they created has certain mathematical features that show different types of changes, called bifurcations, which can occur under specific conditions.
Additionally, the study explores how strengthening the immune system might help control this chaos and stabilise the biological system. The paper concludes by suggesting future research directions that could lead to more effective cancer treatment strategies.
Practical implementation
The practical implementation and social implications of analysing and regulating chaos dynamics in a cancer model through chemotherapeutic intervention and immune system augmentation can be profound. Insights gained from this research could be applied to optimize cancer treatment protocols, potentially leading to more effective therapies with reduced side effects. By understanding and controlling the chaotic behaviour in cancer systems, patient outcomes could be improved through personalized treatment strategies.
Socially, the adoption of these findings may lead to increased public confidence in advanced cancer treatments, as well as a broader acceptance of integrating immune system support with traditional therapies. The potential for more stable and predictable treatment outcomes may also reduce the emotional and financial burden on patients and healthcare systems. Additionally, this approach may encourage further interdisciplinary research, bridging gaps between Mathematics, Biology, and Medicine, thus fostering innovation in cancer therapy development.
Collaborations
Dr Lakshmi Narayan Guin, Associate Professor, Department of Mathematics, Siksha Bhavana, Visva-Bharati
Future research plans
Potential areas for further exploration include:
- Personalised Medicine: Developing patient-specific models that consider individual biological variations could lead to more tailored and effective cancer treatments, minimising side effects and improving outcomes.
- Integration with Advanced Therapies: Combining the insights from chaos dynamics with emerging therapies such as immunotherapy, targeted therapy, and gene editing could enhance the precision and efficacy of cancer treatments.
- Published in Departmental News, Math News, News, Research News
A Look into Sequential Art: Exploring Sean Michael Wilson’s Graphic Creations

Graphic novels, a subgenre of comics, have witnessed stellar growth in popularity, encouraging readers to decipher meaning from the text and the images. The combination of visual and textual storytelling aids readers in decoding complex narratives. Dr Abhilasha Gusain, Assistant Professor from the Department of Literature and Languages, has published a paper titled “From Ideas to Ink: The Craft of Graphic Novel Creation with Sean Michael Wilson” in the Journal of Graphic Novels and Comics.
The current research advances the field of comics studies, highlighting aspects related to the industry like readership, publication, and distribution of graphic narratives across the globe. It emphasises the process of creation of a graphic novel, with reference to author Sean Michael Wilson’s works.
Abstract
In this interview, Sean Michael Wilson delves into his multifaceted career as a graphic novel writer, revealing the intricacies of his creative process, the challenges of adapting complex subjects into visual narratives, and the evolving role of graphic novels in cultural discourse. With over 40 projects under his belt, Wilson shares his approach to beginning new works, whether they stem from original ideas or/are adaptations of historical events and existing literature. He discusses the balance between authenticity and readability, the importance of research, and the collaborative dynamic between writer and artist in bringing graphic novels to life. Wilson also touches on the broader implications of graphic novels in education and social commentary, the economic realities of the industry, and the impact of digital platforms on publishing. His experiences across different cultures, particularly between the West and Japan, provide insight into the global reception of his work. Throughout the interview, Wilson emphasises the power of graphic novels as a medium for storytelling, education, and political engagement.
- Published in Departmental News, English Current Happenings, English news, News, Research News
Dr Sunil Publishes Paper on Ethereum Blockchain Framework in IEEE Access
 We are thrilled to announce that Dr Sunil Chinnadurai, Associate Professor in the Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering has published a significant research paper titled “Ethereum Blockchain Framework Enabling Banks to Know Their Customers” in the esteemed journal IEEE Access. In his paper, Dr Chinnadurai explores the innovative applications of Ethereum blockchain technology in enhancing customer verification processes within the banking sector. His research addresses the growing need for robust and secure methods for banks to comply with Know Your Customer (KYC) regulations while ensuring customer privacy and data integrity.
We are thrilled to announce that Dr Sunil Chinnadurai, Associate Professor in the Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering has published a significant research paper titled “Ethereum Blockchain Framework Enabling Banks to Know Their Customers” in the esteemed journal IEEE Access. In his paper, Dr Chinnadurai explores the innovative applications of Ethereum blockchain technology in enhancing customer verification processes within the banking sector. His research addresses the growing need for robust and secure methods for banks to comply with Know Your Customer (KYC) regulations while ensuring customer privacy and data integrity.
This pioneering work contributes to the ongoing discourse on digital transformation in the banking industry and presents a framework that could potentially revolutionise customer onboarding and identity verification practices.
We extend our congratulations to Dr Chinnadurai for this remarkable achievement and look forward to his continued contributions to the field of electrical and electronics engineering. His research not only enhances the academic reputation of SRM University-AP but also paves the way for innovative solutions in the financial sector.
Abstract of the Research
This paper looks at how blockchain technology can improve the Know Your Customer (KYC) process. It aims to make things more open, secure, and unchangeable. Banks can use the Ethereum blockchain to get and keep customer information, which saves time and money. The solution tries to solve problems with KYC procedures making sure banks follow the rules and stop fraud. The central bank will keep a list of all banks and check if they’re doing KYC right. This spread-out approach gives banks a good long-lasting way to bring in new customers.
Explanation of the Research in Layperson’s Terms
Our study seeks to cause a revolution in the Know Your Customer (KYC) process for banks using Ethereum blockchain technology. Current KYC methods take too long, cost too much, and leave room for cheating. Blockchain offers a clear, safe, and unchangeable platform to store customer data letting banks check and confirm identities. This spread-out approach means customers only need to complete the KYC process one time, which saves a lot of time and money for both banks and customers. Also, blockchain’s safety features make sure that private data stays unchanged and safe from people who shouldn’t see it. Our planned system involves the central bank keeping a full list of all banks and watching to make sure they follow KYC rules. In the future, we plan to put our solution on the real Ethereum network and build a working decentralized app. This system promises to make KYC processes faster, safer, and cheaper, giving a strong answer for banks all over the world.
Practical Implementation or the Social Implications associated
Our research puts blockchain tech to work to improve how banks verify customers. This decentralized system gives everyone access to the same current info through a shared record. This cuts down on middlemen and their costs. Smart contracts that run on their own speed up checks with less human involvement. This lowers the chance of data getting out. It makes transactions faster and keeps data safe from changes it shouldn’t have. This new way of checking customers can save money, make customers happier, and follow rules better. It can make people trust banks more by keeping data safer and being more open. It also means banks don’t have to do the same checks over and over, which is better for them and their customers. In the end, our blockchain answer for customer checks aims to make banking safer, smoother, and cheaper. It should also help build more trust in banks overall.
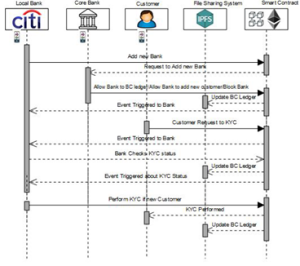
FIGURE 1. Implementation of a blockchain-based KYC process
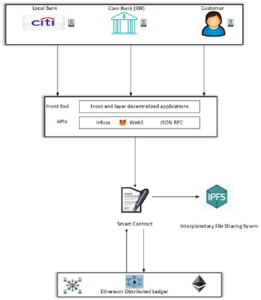
FIGURE 2. Sequential flow diagram illustrating the proposed KYC process using blockchain technology
Future Research Plans
We’re planning to test our idea a lot on the Ethereum network to make sure it works well. We want to build a working DApp that shows our KYC system is doable. We’ll check if people might use it and look at how safe and private it is. By doing this, we hope to make a strong and reliable DApp that’s easy to use, open, safe, and quick. In the end, we want to create something that makes KYC better and sets a new bar for money stuff making banking safer and faster for everyone. Our main goal is to make a system that does not improve how KYC works but also changes how money moves around, making sure banks are safer and work better for people.
- Published in Departmental News, ECE NEWS, News, Research News

