Innovative Study on Microplastics in Groundwater Published
 Dr Kousik Das and Dr Deep Raj, Assistant Professors in the Department of Environmental Science and Engineering (EVSE) at SRM University AP, along with Dr Uttiya Dey (Post-doc) and PhD Scholar Mr. Mijanur Mondal, have achieved a significant milestone with the publication of their research paper, “Microplastics in groundwater: An overview of source, distribution, mobility constraints and potential health impacts during the Anthropocene.
Dr Kousik Das and Dr Deep Raj, Assistant Professors in the Department of Environmental Science and Engineering (EVSE) at SRM University AP, along with Dr Uttiya Dey (Post-doc) and PhD Scholar Mr. Mijanur Mondal, have achieved a significant milestone with the publication of their research paper, “Microplastics in groundwater: An overview of source, distribution, mobility constraints and potential health impacts during the Anthropocene.
This pioneering work has been published in the esteemed journal “Groundwater for Sustainable Development,” a Q1 journal with an impressive Impact Factor of 5.9. The paper offers a comprehensive overview of the sources, distribution, mobility constraints, and potential health impacts of microplastics in groundwater, contributing valuable insights to the scientific community.The research team’s dedication to advancing environmental science and addressing crucial issues such as microplastic pollution underscores SRM University AP’s commitment to impactful research and innovation.
Abstract
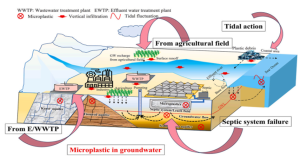
Microplastics (MPs) are the tiny particles of plastic of > 5 mm in diameter that have already been detected in various environmental matrices like soil, sediment, and surface water, and recently in groundwater also. The occurrence of MPs in groundwater depends up on the transportation through recharge and may controlled by source and local hydrogeology, and partly on the process of surface water-groundwater interaction (SW-GW). Groundwater recharge from agricultural stagnant water, losing streams near dumping sites and agricultural fields, effluents from wastewater treatment plants, septic system failure, etc., are the potential sources of MPs in groundwater. The factors like sea level rise and tidal pumping are among the major factors that may control the migration of MPs in coastal aquifers, along with the physical and chemical properties of the aquifer media. These MPs have another ecological concern as they can adsorb persistent organic pollutants as well as heavy metals and transfer them to animal tissues through the food chain. No such study has been done on the existence, profusion, or environmental factors that contribute to MP pollution in the groundwater in relation to the present climate change scenario. Understanding the extent of MP contamination in groundwater systems is necessary for developing effective management strategies and minimizing their impact on the environment and human health. This study focuses on the source along with the controlling factors of the migration of MPs towards groundwater, including the effect of climate change.
Citation
Dey, U.,Raj, D., Mondal, M., Roy, P., Mukherjee, A., Mondal, N.K. and Das, K. (2023). Microplastics in groundwater: An overview of source, distribution, mobility constraints and potential health impacts during the Anthropocene. Groundwater for Sustainable Development. 23: 101036
Practical implementation and social implications of the research
Microplastic pollution is among the recent emerging pollutants which is still understudied. n. Studies are being conducted mainly focusing the MP contamination in surface water, marine environment and soil, and very limited studies are available to address the source of MPs in groundwater. Even there is lack of standard methods for the effective detection, both qualitatively and quantitatively, of MPs. However, no such study has been done on the existence, profusion, or environmental factors that contribute to MP pollution in the groundwater in relation to the present climate change scenario. As groundwater is a major source of drinking water worldwide, it is of immense importance to enquire more about the source, transport pathways, controlling factors and human health effects of MPs for the safeguard of this valuable resource. Understanding the extent of MP contamination in groundwater systems is necessary for developing effective management strategies and minimizing their impact on the environment and human health. Our study was conducted to mainly focus on the source along with the controlling factors of the migration of MPs towards groundwater including the effect of climate change. The findings of our study would provide valuable insights into the characteristics of MPs in the environment and suggest efforts to mitigate their impact on ecosystems as well as on human health.
Collaborations
The collaborators in this present study are:
- Prof. Abhijit Mukherjee, Department of Geology and Geophysics & School of Environmental Science and Engineering, IIT Kharagpur, West Bengal
- Prof. Naba Kumar Mondal, Department of Environmental Science, The University of Burdwan, West Bengal
Future research plans
Microplastic is one of the recent emerging pollutants which is still understudied. The research has just started to detect MPs in different environmental media as well as to establish effective removal technologies. Our future plans with MP research are as follows:
- To measure the MPs concentration in different coastal areas in India, as the oceans are the major sink for any pollutants, to obtain baseline information about the contamination load
- To detect how much amount of MPs are coming through the major rivers by linking the land use and land cover pattern so that the major sources can be detected
- Detection of MPs in the freshwater aquifer to adopt effective management strategies to safeguard the groundwater
- Development of effective and environment-friendly MP removal technologies
- Published in Departmental News, ENVS News, News, Research News
Leadership Talk by Mr Satakarni Makkapati

On October 12, 2023, Paari School of Business hosted a Leadership Talk by Mr Satakarni Makkapati, highlighting the critical role of effective leadership in navigating challenges and driving success. Mr Satakarni shared insights on mentorship, change management, the power of teamwork, exercising authority with care, and leading with proactivity, providing invaluable guidance for personal and professional growth.
- Published in Departmental News, News, Paari Current Happenings
Seven Mantras of Entrepreneurship: A Talk by Mr Siddharth Tripathi

The Paari School of Business invited Mr Siddharth Tripathi, Founder and CEO of Skillizen Learning, for a Guest Talk on the “Seven Mantras of Entrepreneurship”. In the talk held on November 14, 2023, Mr Tripathi extensively discussed the key strategies and skills required to gain entrepreneurial success. He enlightened that the term ‘Entrepreneurship’ originates from the French language but derives its innermost inspiration from the Sanskrit word ‘Antah Prerna’. He enlightened the students that an entrepreneur should always have original and innovative ideas and sound domain knowledge.
During his session, Mr Tripathi stated, “The world belongs to the change agent” emphasising that young entrepreneurs must always focus on becoming change agents who can change the norms of the world. He also highlighted that there is no right strategy for successful entrepreneurship. The key to success in entrepreneurship is financial capital as well as social capital, as networking is crucial for the development of the company and critical to entrepreneurial success. Mr Tripathi encouraged budding ventures claiming that in the tortoise and rabbit race in entrepreneurship, the rabbit always wins, but the tortoise comes back with a solid stay, sharing that the fastest launcher will always be the first.
- Published in Departmental News, News, Paari Current Happenings
MSc Environmental Science Students Shines at 7th University Challenge

In a remarkable display of talent and dedication, three MSc Environmental Science students from the Department of Environmental Science and Engineering showcased their expertise at the 7th University Challenge, India, held on 18-19 October 2023 at the Bombay Exhibition Centre, Goregaon, Mumbai. Mr Om Banerjee, Ms Sejal Sudhir Kulkarni, and Ms Manaswini Mirthipati Subrahmanya exhibited exceptional knowledge and passion for environmental science at the event organised by the German Water and Waste Association (DWA) as a part of IFAT India 2023. IFAT- India is India’s acclaimed trade fair that showcases environmental technologies for sustainable solutions to problems in the subcontinent. The students interacted with professionals from diverse sectors, such as water, sewage, solid waste, and recycling, and explored their innovative solutions and services.
Their participation not only reflects their commitment to academic excellence but also underscores the Department’s dedication to nurturing top-tier talent in the field of environmental science. We extend our heartfelt congratulations to these students and anticipate their continued success in their academic and professional endeavors.
- Published in Departmental News, ENVS News, News







