DST-FIST Grant of Rs 1.4 Crores for Mechanical Engineering Department

SRM University-AP shares a momentous achievement as the Mechanical Engineering department has been awarded a financial grant of Rs 1.4 crores under the prestigious FIST (Fund for Improvement of S&T Infrastructure) by DST (Department of Science and Technology) Government of India.
The equipment proposed under the FIST grant is High-Resolution X-ray Micro Computed Tomographic Scanner that will help Materials Scientists, Engineers, Manufacturers and Researchers investigate internal structures, pore flaws of metallic, polymer and ceramic samples/ components non-destructively. This state-of-the-art facility will promote R&D activities in new and emerging areas of Materials Science Engineering and Manufacturing. Additionally, it seeks to attract fresh talents to the university, fostering an environment of innovation and scientific excellence. The established facility will be available to internal and external users (from academic institutions, research labs, manufacturing Industries, MSMEs and Startups.
The grant, awarded for a duration of 5 years, is a testament to the unwavering commitment of SRM University-AP to providing cutting-edge resources for the advancement of scientific studies. This achievement results from the exceptional efforts put forth by the faculty members of the Department of Mechanical Engineering of the university. Their dedication, expertise, and commitment to academics and research played a pivotal role in securing this grant amidst tough competition.
Prof. Manoj K Arora, Vice Chancellor, SRM University-AP proudly remarked, “This grant will not only enhance our research capabilities but also provide a platform for our students and faculty members to explore new avenues in the field.” Prof. G S Vinod Kumar, Head of the Mechanical Department, expressed his delight that the grant will be utilised for advanced characterisation and diagnostic research in the area of Materials and Manufacturing. It will also be used to strengthen the postgraduate and doctoral research facilities in the mechanical engineering department.
The Institute applauds the Mechanical Engineering department for proving their mettle and emerging success among departments from various universities/institutes, both government-funded and private, in the national level competition for the DST-FIST grant. SRM University-AP is confident that this financial support will propel the Mechanical Engineering department to new heights of success and enable them to contribute significantly to the scientific community. The institution remains committed to fostering an environment that encourages research, innovation, and knowledge creation.
- Published in Departmental News, Mechanical Engineering NEWS, News, Research News
Best Paper Award: Accorded to Dr Supen Kumar at MRAE 2023

The Department of Mechanical Engineering is delighted to share that Dr Supen Kumar Sah, Assistant Professor, Department of Mechanical Engineering, has received the best paper award for his paper titled “Free Vibration Analysis of Functionally Graded Material Sandwich Plate Using Refined Shear Deformation Theory” in the 2nd International Conference on Modern Research in Aerospace Engineering (MRAE 2023). Dr Supen collaborated with Saloni Malviya of VIT, Bhopal, for the research paper. The paper explores the intricate dynamics of functionally graded material sandwich plates, employing a refined deformation theory. Dr Sah’s exceptional work has not only contributed to the scientific community but has also demonstrated his dedication and passion for advancing knowledge in the field of materials science and engineering.
Abstract
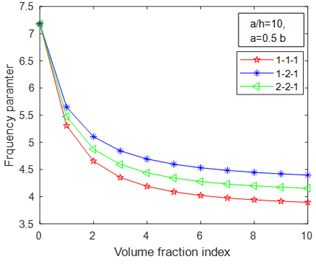
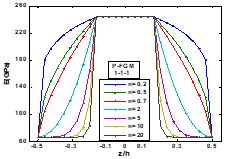
In the present study, free vibration analysis of a functionally graded material sandwich plate has been carried out using refined shear deformation theory. The shear correction factor is not needed since the parabolic variation of shear strain through the thickness is in such a way that shear stresses vanish on the plate surfaces. Hamilton’s principle is used for the derivation of the equation of motion for the theory. Additionally, Navier’s solution is used to obtain the eigenvalue equation for the sandwich plate. The three variants of sandwich plate are chosen for the analysis. To carry out the free vibration analysis three different types of FGM sandwich plate models namely 1-1-1, 1-2-1, and 2-2-1 have been considered. A power law defines the volume fraction index and the material properties of the individual layers of the sandwich plate. Lastly, the impact of parameters such as volume fraction, aspect ratio, and length-to-width ratio on frequency parameters is investigated.
Future Research Plans
• Modelling and Analysis of porous uni and multi-directional Functionally Graded Material (FGM) plates to obtain the impact of porosity distributions over structural responses.
• Analytical and finite Element Solutions for static and dynamic response of FGM sandwich plates employing non-polynomial shear deformation theories under elastic foundation.
- Published in Departmental News, Faculty Achievements, Mechanical Engineering NEWS, News, Research News
ICSSR Sanction for Research Project on PM Krishi Sinchai Yojana

SRM University-AP takes pride in the achievements of its students and faculty. Dr Ghanshyam Pandey, Assistant Professor, Department of Economics and Dr Deep Raj, Assistant Professor, Department of Environmental Science and Engineering were sanctioned a project by the Indian Council of Social Science Research, New Delhi (ICSSR). The research project titled, “PM Krishi Sinchai Yojana- A Step Ahead to Achieve Sustainable Development Goal: A Study of Select Areas of AP, Tamil Nadu and Maharashtra” was sanctioned a total outlay of 16.5 Lakhs for a period of 6 months.
Abstract
Agriculture in India is dominated by smallholders. Yet only about 55% of India’s agricultural land is irrigated. The frequent occurrence of extreme climate events such as drought and heat are some of the main reasons for low agricultural productivity, food insecurity, and persistent poverty in developing nations. In this respect, irrigation plays a significant role in addressing climate change. However, irrigation costs are also very high for small-scale farmers because of their low incomes. Therefore, they do not have the resources to irrigate 100% of their land. In this context, PMKSY is a step towards resolving this problem in India and was introduced by the NDA government in 2015 by Har Khet Ko Pani. Therefore, the present study will examine the coverage, impact, adaptation and constraints of PMKSY in the Indian states of Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu and Maharashtra.
Congratulations on this remarkable achievement!
- Published in Departmental News, Economics News, ENVS News, News, Research News
Faculty Duo Publish a Critical Analysis and Research on Cyberbullying

In the digital era, where technology dominates over communication, connection and social relationships, the staggering rise of cyberbullying proves to be detrimental to the social and mental psyche of people. The limited research present regarding the crisis fails to provide sufficient data to critically analyse and initiate policies to combat the same. In this regard, Dr Dhamodharan M and Dr Sunaina K, faculty from the Department of Psychology have conducted insightful research into cyberbullying, the role of technology and the challenges in tackling the act. The faculty duo has published a book chapter titled “Cyberbullying – A Disturbed Psyche and Digital Abuse in 21st Century” in the book In Analyzing New Forms of Social Disorders in Modern Virtual Environments in IGI Global Publishers (US).
Abstract
Cyberbullying is ‘a violent, planned act carried out by a group or specific, using electronic forms of communication, frequently and over time in contradiction of a victim who cannot easily protect him or herself.’ (Smith et al., 2008). According to the UNICEF and Broadband search survey 2023, around 36.5 out of a hundred people feel they were cyberbullied at least once in life, and seventeen percent of people experienced cyberbullying in the last month. 60 out of 100 adolescents experienced cyberbullying. Seventy percent of youths have reported perpetrators. Sixteen percent of women have been stalked at least once in life. 1 in 19 men have been stalked at some point. Fifty percent of LGBTQ people experience cyberbullying. Girls face cyberbullying more than boys. Around 36 percent of girls experience cyberbullying, whereas 24 percent of boys experience cyberbullying. Eighty-three percent of the victims who experienced online bullying also experienced physical bullying. Around 42 percent of the people experience cyberbullying on Instagram, followed by Facebook at 37%, Snapchat at 31%, WhatsApp at 12%, YouTube at 10%, and Twitter at 9%. Cyberbullying refers to using digital technologies such as cyberspace, societal broadcasting platforms, direct messaging, and email to bother, intimidate, or harm others.
This chapter provides an indication of cyberbullying, including its definition, incidence, and impact on individuals and society. Firstly, the chapter reviews the existing research on cyberbullying, exploring its different forms and characteristics and the psychological and social consequences for both victims and perpetrators. Secondly, the role of technology in facilitating and exacerbating cyberbullying is also examined, focusing on the anonymity and distance that online platforms provide. Thirdly, legal and ethical considerations surrounding cyberbullying including the challenges of enforcing laws and policies online are explored. Finally, the chapter highlights the importance of a comprehensive and collaborative approach involving parents, educators, policymakers, and online platforms to address cyberbullying.
Implications
Cyberbullying is a pervasive problem with significant and long-lasting consequences for people, their families, and society. It is essential to address cyberbullying thoroughly and implement effective prevention measures to create a more secure and respectful online environment. Cyberbullying can have detrimental effects on its victims, leading to feelings of helplessness, mental health issues, trouble with schoolwork, and even self-harm or suicide. In addition, cyberbullying affects the social fabric of groups, and trust, and impedes the proper growth of individuals, especially children and adolescents. Cyberbullying has a shocking prevalence worldwide, and it is spreading over to people silently. Traditional bullying differs from cyberbullying; it occurs to the victims in various forms and levels.
- Published in Departmental News, News, Psychology News, Research News
Research on Tribal Communities Receives Green Flag from ICSSR

SRM University-AP proudly announces that Dr Bikku R, Assistant Professor at The Department of Liberal Arts has been sanctioned a major research project by the Indian Council of Social Science Research (ICSSR). The research project titled “Religious Deities and Saints/Legends/Heroes Changing Geographic Belongingness and Cultural Economy among the Four Tribal Communities (Chenchus, Kondareddis, Koyas and Lambadi’s) of Telangana and Andhra Pradesh” will receive an outlay of Rs. 10.00 Lakhs.
Congratulations, Dr Bikku on this outstanding achievement!
Research Abstract
India is one of the most diverse countries in the world, where around 705 scheduled tribes are notified with their distinct culture, and as per the 2011 census, they constitute 8.6% of the total population. Out of these, 75 communities belong to Particular Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs), having declining or stagnant populations, low literacy rates, pre-agricultural technologies and economic backwardness. For tribal communities, culture, economic, political and geographical belongingness are distinct from non-tribals in India. Studying their religious beliefs and practices and changing cultural economies and landscapes is crucial to preserving India’s diverse cultures. The existing studies by social scientists have not emphasised much on tribal saints/ heroes, changing cultural economies and landscapes in India, particularly in the newly bifurcated southern states, Telangana and Andhra Pradesh. The study focuses on religious deities and Saints/Legends/Heroes, changing geographic belongingness and cultural economies among the four tribal communities (Chenchus, Kondareddis, Koyas and Lambadis) of Telangana and AP states of India. Qualitative (ethnographic) and quantitative methods will be used to map their deities and saints/legends/heroes, cultural economy and traditions and record memories of past and contemporary relationships with the belonging to their landscapes and natural resources.
- Published in Departmental News, Liberal Arts News, News, Research News
Teacher-Student Duo Author a Chapter on Graph Neural Networks

Dr Ravi Kant Kumar, Assistant Professor at the Department of Computer Science and Engineering at SRM University-AP and his research scholar, Ms Gayathri Dhara have recently made a significant contribution to the field of Graph Neural Networks. The teacher-student duo have offered relevant analysis of visual saliency applications using Graph Neural Networks (GNN) in their book chapter titled “Study and Analysis of Visual Saliency Applications Using Graph Neural Networks” in the book, Concepts and Techniques of Graph Neural Networks. The topic of their study will prove to be a key source of reference for industry professionals, researchers, scholars, academicians, practitioners, instructors, and students.
Description and Significance of the Chapter
The chapter covers the practical applications of GNN in the field of visual saliency. Various applications of computer vision problems implemented using graph neural networks (GNNs) have been studied and analysed in this chapter. It also includes the design approach of GNN, the various computational models used in GNN, its challenges and recommendations. The social significance of GNN in visual saliency extends to various domains like Human attention modelling, Advertising and marketing, Visual content understanding, and so on.
Significance of GNNs
Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) have gained significance in the field of visual saliency due to their ability to model complex relationships and dependencies within visual data. Visual saliency refers to the process of predicting the most visually prominent regions or areas in an image or video that attract human attention. It plays a crucial role in various computer vision applications, such as image understanding, object recognition, and scene understanding. GNNs can learn spatial dependencies and feature representations from visual data. There are many methodologies that address the detection of the salient object using GNN. GNNs can handle multi-modal data, combining visual information with other modalities such as textual or semantic features. This integration allows GNNs to leverage additional cues and contextual information to improve visual saliency prediction. So, studying these different salient object detection methods using GNN and knowing the challenges of GNN will help in meeting our research objectives.
- Published in CSE NEWS, Departmental News, News, Research News
Biological Science Researcher bags DST INSPIRE Fellowship

Barath Sivaraj, a research scholar from the Department of Biological Sciences at SRM University-AP has achieved an outstanding feat by receiving the DST INSPIRE Fellowship, a highly regarded programme sponsored and overseen by the Department of Science & Technology.
Sivaraj’s research focuses on exploring how bacteriophages, a type of virus that infects and reproduces inside bacteria, utilises the bacterial system. This research has earned Sivaraj the Fellowship, which runs for a duration of 5 years. The researcher also gets to carry out his research at any national or international laboratories other than their host institute for a period of 18 months.
Barath expresses his immense delight and pride in receiving this fellowship and considers it a significant milestone in his academic journey. Sivaraj explains that applicants must meet several criteria, such as being a top-ranked student in a full-time postgraduate science programme or a related field at the university level. Sivaraj credits his research supervisor, Dr Sutharsan Govindarajan, for guiding him through the application process. As a future prospect, Sivaraj plans to pursue his post-doctoral studies abroad and eventually wishes to offer his professional services at a reputable university.
We wish him all success!
- Published in Biology News, Departmental News, News, Research News
SRM AP Professor Swaminathan in joint observational study on US Medicaid effect on Renal Disease patients.
For a study published in JAMA (Journal of the American Medical Association – Impact factor – 47.661), SRM AP Associate Dean of SLABS, Professor Shailender Swaminathan, and US based colleagues (Benjamin D. Sommers, Rebecca Thorsness, Rajnish Mehrotra, Yoojin Lee, and Amal N. Trivedi) used a U.S.national registry to identify patients 19-64 with newly developed end stage renal disease who had initiated dialysis in a 6 year period 2011-2017.
- Published in Research News
“Research is a culture, adopted through practice.” Professor Prasant Mohapatra
“Problems in the world are not discipline specific. Universities need a wider scope in research,” was one of the points raised by Prasant Mohapatra, member of SRM AP Board of Governors, in his symposium on research methodologies. “Research responds to societal needs. To remain contemporary and dynamic it is necessary to reinforce it regularly with current best practices.”
- Published in Research News
SRM AP Pro Vice Chancellor Dr. D. Narayana Rao and BOSCH to establish Bosch-SRM Research Centre for Artificial Intelligence in health care
The Robert Bosch Engineering and Business Solutions Pv.t Ltd in Bangalore along with SRM AP will set up a centre at SRM Amaravati to carry out research in Artificial Intelligence for health care. SRM AP Pro Vice Chancellor Dr. D. Narayana Rao and BOSCH Bangalore have been in discussions on this initiative that will bring together researchers from SRM AP’s engineering program and Bosch, a leading supplier of technology and services in mobility solutions, industrial technology and energy.
- Published in News, Research News




