Dr Goutam Kumar Dalapati develops high-performance photodetectors with improved electrical parameters
 Dr Goutam Kumar Dalapati, Associate Professor, Department of Physics, SRM University-AP, Andhra Pradesh, published a research paper “Improvement on Photoresponse Properties of Self-Powered ITO/InP Schottky Junction Photodetector by Interfacial ZnO Passivation” in the reputed Journal of Electronic Materials, Springer. Photodetection has emerged as the key technology in contemporary science because of their wide range of applications in daily life and in industry, including astronomy, surveillance, environmental monitoring, machine vision, and cameras in smart phones. Commercial photodiodes should meet the criteria of high charge carrier mobility, small exciton binding energy, and higher stability. This intrigued Dr Goutam to indulge in the study of photodetector which is essential to improve several electrical parameters such as low power consumption, and higher sensitivity.
Dr Goutam Kumar Dalapati, Associate Professor, Department of Physics, SRM University-AP, Andhra Pradesh, published a research paper “Improvement on Photoresponse Properties of Self-Powered ITO/InP Schottky Junction Photodetector by Interfacial ZnO Passivation” in the reputed Journal of Electronic Materials, Springer. Photodetection has emerged as the key technology in contemporary science because of their wide range of applications in daily life and in industry, including astronomy, surveillance, environmental monitoring, machine vision, and cameras in smart phones. Commercial photodiodes should meet the criteria of high charge carrier mobility, small exciton binding energy, and higher stability. This intrigued Dr Goutam to indulge in the study of photodetector which is essential to improve several electrical parameters such as low power consumption, and higher sensitivity.
 In this research, Dr Goutam developed a high-performance photodetector using Indium phosphide/indium tin oxide (InP/ITO) semiconductor metal junction. He explains, “Photodetection in semiconductors follows the principle of generating electron-hole pairs under incident light higher than or equal to its bandgap. In Schottky type photodiode, at thermal equilibrium, the Fermi levels of the metal and the semiconductor are equalized, and a transfer of electronic charge occurs from the semiconductor to the metal. Moreover, these charge transport properties can be simply tailored by compositional engineering, which provides plenty of space to modulate the performance metrics of the photodetectors. During my research, the atomic layer deposition of zinc oxide (ZnO) on the InP surface was found to increase the valence band offset for current conduction in the photodiode. Photoresponse properties were believed to improve through effective hole blocking by the ZnO interface layer which further prevents the surface recombination of photo-induced generated electron-hole pair. Through my research, I deciphered that the ITO/ZnO/InP photodiode exhibited a maximum photoresponsivity of 44.2 mAW−1 under a 520 nm laser irradiation with an illumination power of 1 μW at the zero bias voltage.”
In this research, Dr Goutam developed a high-performance photodetector using Indium phosphide/indium tin oxide (InP/ITO) semiconductor metal junction. He explains, “Photodetection in semiconductors follows the principle of generating electron-hole pairs under incident light higher than or equal to its bandgap. In Schottky type photodiode, at thermal equilibrium, the Fermi levels of the metal and the semiconductor are equalized, and a transfer of electronic charge occurs from the semiconductor to the metal. Moreover, these charge transport properties can be simply tailored by compositional engineering, which provides plenty of space to modulate the performance metrics of the photodetectors. During my research, the atomic layer deposition of zinc oxide (ZnO) on the InP surface was found to increase the valence band offset for current conduction in the photodiode. Photoresponse properties were believed to improve through effective hole blocking by the ZnO interface layer which further prevents the surface recombination of photo-induced generated electron-hole pair. Through my research, I deciphered that the ITO/ZnO/InP photodiode exhibited a maximum photoresponsivity of 44.2 mAW−1 under a 520 nm laser irradiation with an illumination power of 1 μW at the zero bias voltage.”
For the successful implementation of the proposed ITO/ZnO/InP photodiode in the manufacturing levels, significant efforts are essential. Dr Goutam acknowledges that device to device variability must be addressed which arise from the deposition condition of the ZnO layer by atomic layer deposition. Surface defects reduction and selection of charge collecting electrodes must be optimized to improve the performance of the photodetector. Thus, Dr Goutam will dedicate his future research work to study patterned 2D graphene-based electrode to improve the performance. Also, n-type 2D MoS2 and hexagonal boron nitride (hBN) passivation will be studied by him on the III-V semiconductor surface for better photoresponsivity.
- Published in News, Research News
SRMAP faculty recognised by Stanford University among the top Biotechnologists
Dr Imran Pancha from the Department of Biological Sciences, SRM university – AP is recognised in Biotechnology among the top 2% scientists/researchers across the world By Stanford University Researchers. Recently an article has been published in PLOS Biology by Stanford University Researchers on the highly cited researchers in 22 different fields and their subfields. In the Biotechnology field, 1,074 scientists/faculty members were identified, and Dr Imran Pancha is one amongst them. From India, only 77 scientists/faculty members could achieve this honour, and Dr Imran Pancha is one among them. This is an admirable achievement for a young faculty from a nascent University to be in the top 2% scientists of the world. Dr P Sathyanarayanan, the President of SRM University-AP honoured Dr Pancha for bringing this scientific laurel to the university.
Overall, of the top 160,000 scientists from different fields of Science & Technology, India hosts 2,313 scientists/faculty members. This list comprises of the prominent and illustrious scientists from India.

Dr Imran Pancha is a young researcher working as an Assistant Professor in the Department of Biological Sciences in SRM University-AP, Andhra Pradesh. He has obtained his doctoral degree from CSIR-Central Salt and Marine Chemicals Research Institute-Bhavnagar after graduating from Bhavnagar University. He has also worked as a post-doctoral fellow at Japanese Society for Promotion of Science, Japan before joining SRM University-AP.
Dr Pancha’s primary research focus is to produce renewable energy from microalgae. His team is trying to develop integrated microalgal bio-refinery to produce high-value compounds like phycobiliproteins, carotenoids along with biofuel and bio-fertilisers from microalgae. Apart from this, he is also interested to understand algal-bacterial interaction, particularly isolate and characterise the microalgae associated bacteria and finding their role in growth enhancement and inhibition in microalgae.
- Published in Biology News, News, Research News
Minister of Education-AP applauds the Research Focus of SRMAP
SRM University-AP has been honoured with the gracious presence of the Hon’ble Minister of Education Dr Adimulapu Suresh on November 17, 2020, when he came to inaugurate the sub Post Office at the SRM University-AP, Andhra Pradesh Campus. He visited the campus and, witnessed its infrastructure, and discussed the future plans and goals of SRMAP with Prof V S Rao, Vice-Chancellor. In his welcome address, Prof V S Rao, Vice-Chancellor expressed his gratitude to the Minister for finding some time to visit SRMAP. With a well-documented presentation, he narrated how SRMAP has embarked upon the vessel of excellence and innovation within a meagre span of just two years. The three-year-old university has already published almost 300 papers in reputed journals, has 27 projects with an outlay of 14 crores and 17 patents.
 Minister of Education with SRM FacultyIn his message, the august guest of the day, Dr Suresh expressed his joy to see a university achieving such great heights within two years in the realms of research and education. While presenting the offer letters to the placed students, he was enraptured to see that SRMAP provides such quality education that not only students from engineering, but also the students from other general degree courses were able to bag desired packages from reputed companies like Deloitte etc. According to Dr Suresh, Hon’ble Minister, the greatest predicament of the country is not unemployment but unemployability as most educational institutions fail to deliver a proper and complete education that can satisfy the demands of the present world and make the students job-ready. He was delighted to know that SRMAP, since its inception, always strived to make curriculums industry-oriented, put particular emphasis on the placement training to make students interview-ready, encouraged the students for research since their undergraduate studies, helped them to grow and know the world with the Semester Abroad Programme. Among the maiden batch of SRM University-AP, 40% of students have bagged job offers with packages of 10 lakhs per annum or higher, with the highest offered salary of 29.5 lakhs per annum. The Minister of Education was greatly satisfied with SRM University’s vision and progress so far and wished for further marvels to be created.
Minister of Education with SRM FacultyIn his message, the august guest of the day, Dr Suresh expressed his joy to see a university achieving such great heights within two years in the realms of research and education. While presenting the offer letters to the placed students, he was enraptured to see that SRMAP provides such quality education that not only students from engineering, but also the students from other general degree courses were able to bag desired packages from reputed companies like Deloitte etc. According to Dr Suresh, Hon’ble Minister, the greatest predicament of the country is not unemployment but unemployability as most educational institutions fail to deliver a proper and complete education that can satisfy the demands of the present world and make the students job-ready. He was delighted to know that SRMAP, since its inception, always strived to make curriculums industry-oriented, put particular emphasis on the placement training to make students interview-ready, encouraged the students for research since their undergraduate studies, helped them to grow and know the world with the Semester Abroad Programme. Among the maiden batch of SRM University-AP, 40% of students have bagged job offers with packages of 10 lakhs per annum or higher, with the highest offered salary of 29.5 lakhs per annum. The Minister of Education was greatly satisfied with SRM University’s vision and progress so far and wished for further marvels to be created.
 Dr Suresh inaugurating the sub post-officeThe Minister later met with the DEANS and HODs and the reputed Ramalingaswami Fellow, DST-Inspire Fellow and faculty members who are rigorously working on several projects. The Minister was pleased to see the focus on research. He said, “The Govt of Andhra Pradesh is against of commercialization of education, but we are not against private educational institutes. It is very encouraging to see how SRM University, following the footsteps of the government, has embedded complete and inclusive education that supports equity, equality, and affordability. Industry-Academia interaction is a weak point in our pedagogical system, but it is good to see that SRM University is moulding students in a proper way to make them market-ready. The advancement of the Education sector is the dream of our Chief Minister, and many pedagogical and educational reforms are being done in order to the standardization of the Education Sector. The Management of SRM University-AP has opted for a student-centric education that follows the mandates of National Education Policy-2020.”
Dr Suresh inaugurating the sub post-officeThe Minister later met with the DEANS and HODs and the reputed Ramalingaswami Fellow, DST-Inspire Fellow and faculty members who are rigorously working on several projects. The Minister was pleased to see the focus on research. He said, “The Govt of Andhra Pradesh is against of commercialization of education, but we are not against private educational institutes. It is very encouraging to see how SRM University, following the footsteps of the government, has embedded complete and inclusive education that supports equity, equality, and affordability. Industry-Academia interaction is a weak point in our pedagogical system, but it is good to see that SRM University is moulding students in a proper way to make them market-ready. The advancement of the Education sector is the dream of our Chief Minister, and many pedagogical and educational reforms are being done in order to the standardization of the Education Sector. The Management of SRM University-AP has opted for a student-centric education that follows the mandates of National Education Policy-2020.”
- Published in News, Research News
Dr Satya Pramod Jammy develops open-source SBLI framework for computing high-resolution fluid flow simulations
 Dr Satya Pramod Jammy, Associate Professor, Mechanical Engineering, SRM University AP, Andhra Pradesh developed the open-source SBLI framework dedicated to enable computing high-resolution fluid flow simulations in the supersonic regime using high-end desktop systems with GPUs. It enables users to set up the problem to be solved at a high-level with the details similar to what one sees in any textbook and the tool will automatically generate a low-level code that can run on CPUs and GPUs using the OPS library.
Dr Satya Pramod Jammy, Associate Professor, Mechanical Engineering, SRM University AP, Andhra Pradesh developed the open-source SBLI framework dedicated to enable computing high-resolution fluid flow simulations in the supersonic regime using high-end desktop systems with GPUs. It enables users to set up the problem to be solved at a high-level with the details similar to what one sees in any textbook and the tool will automatically generate a low-level code that can run on CPUs and GPUs using the OPS library.
Dr Satya Pramod Jammy explains, “It is hosted on GitHub and is available to download free of charge under GNU GPL license (https://opensbli.github.io). I lead the development of OpenSBLI over the last four years as a part of my research. The basic organization of the classes and architecture of the tool is designed along with the automatic code generation. The tool has been transformed over the years starting with a basic version to demonstrate its ability to its current version (V2.0), that is capable of generating codes for around 27 different numerical schemes by changing one line of the setup script. A new version of the framework is under testing and a release is planned in March 2021.”
Advancing the framework, Dr Satya Pramod Jammy informed that the capabilities of the tool are being upgraded constantly. Among other renowned scientists, Dr Gary Coleman, Senior Research Scientist, Computational AeroSciences Branch, NASA Langley Research Center has been using the tool for his scientific research pursuits. Appreciating Dr Satya Pramod Jammy, Dr Coleman said, “I have found the OpenSBLI framework to be an extremely valuable tool in my recent research into the physics and modelling of high-speed wall-bounded turbulent flows. Its combination of efficiency, fidelity, and flexibility has allowed me to perform a thorough case study using local computational resources to produce a vast amount of high-quality data, which I expect will be of great utility to the research community. I am grateful to you for your role in developing this excellent resource.”
- Published in News, Research News
Research Day Celebration 2021
“Startups and Government bodies must be complementing one another to steer space industry towards excellence”- Sri S Somanath, Director, VSSC
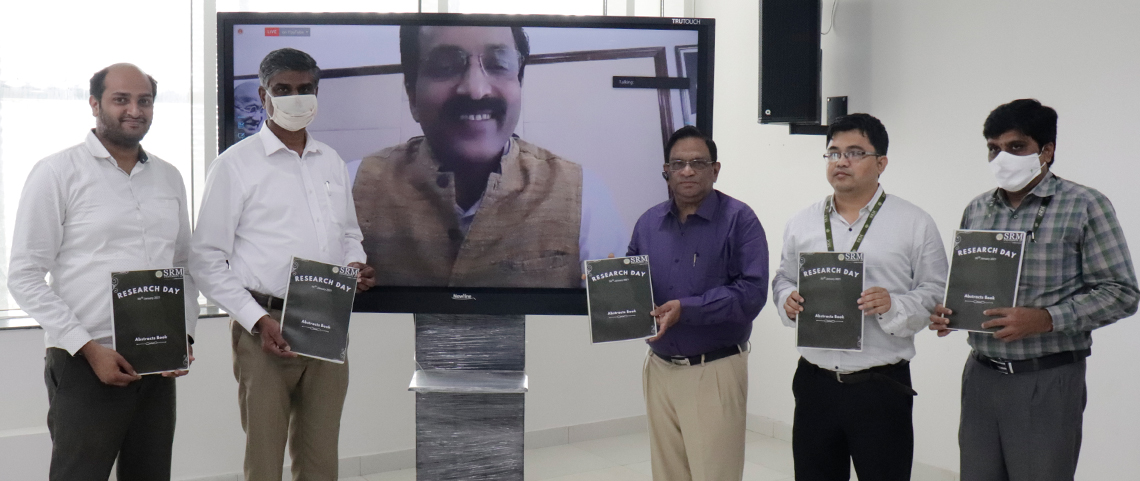 Research Day 2021 ceremony at SRM University-AP, Andhra Pradesh encompasses various endeavors aimed at appreciating and encouraging scholars to carry out extensive research works to enrich the society. Applauding the initiative, Dr P Sathyanarayanan, President, SRM AP stated “Research Day is when SRM University-AP commemorate the faculty and students for their outstanding research contributions. This university, though just a three-year-old one, has grown leaps and bounds in research and is now clearly the front runner among all the universities in the region.”
Research Day 2021 ceremony at SRM University-AP, Andhra Pradesh encompasses various endeavors aimed at appreciating and encouraging scholars to carry out extensive research works to enrich the society. Applauding the initiative, Dr P Sathyanarayanan, President, SRM AP stated “Research Day is when SRM University-AP commemorate the faculty and students for their outstanding research contributions. This university, though just a three-year-old one, has grown leaps and bounds in research and is now clearly the front runner among all the universities in the region.”
Prof V S Rao, Vice-Chancellor, SRM AP welcomed the Chief Guest Sri S Somanath, Director, Vikram Sarabhai Space Center (VSSC), Thiruvananthapuram, and other revered audience. Prof V S Rao highlighted, “Research day brings an excellent opportunity for the scientific community to showcase their accomplishments and impactful research works.”
Advancing the celebration, Prof D Narayana Rao, Pro Vice-Chancellor, SRM AP took the virtual podium to comment “Science and Technology is the driving force for the economic development of India. We need to encourage young scholars by providing a vibrant and conducive research environment. Expanding the frontiers of knowledge by triggering interest among students must be the priority of the institutions. Also, focus should be on translational research with societal applications through collaborative research to make our nation a global leader.”
During his motivating speech on “The Indian Space Enterprise Achievements & New Directions”, Dr S Somanath interpreted the complexities of Space Engineering by describing details pertaining to space infrastructure, and technology elements in rocket production involving the development of space vehicles capable of operating for years unattended in the space. He further informs, “The high cost and low volume production remains the challenge associated with Space Engineering.” He also stated that there are increasing demand and scope for satellite startups and the export potential is on the higher side for satellites in India.
Dr S Somanath proceeded to illuminate the audience on the changing horizons of the space industry, contributed by the emerging technologies such as integrating satellites, drones, and terrestrial imagery. In addition, he addressed the disruptive technologies that led to reusable rockets, space technology-driven drones, etc., enhancing the market substantially for the satellite production and reducing the market for the launching vehicles.
Consequently, Dr S Somanath accentuated that the government bodies such as ISRO, IN-SPAC, and NSIL should remodel its direction of operation. He suggests, “Government of India should be opening the space sector and assist the new participants by sharing technological expertise. Startups and government bodies must be complementing one another to steer this industry towards excellence.”
Progressing with the celebration, eminent scientific works and contributions of various faculty, research scholars, and undergraduate students were rewarded. As part of the research day programme, the students and faculty were urged to submit abstracts of their research. Among 176 submissions from students and 40 from the faculty community of SRM AP, 20 were awarded with gold medals while 6 were presented with silver medals. Further, a special issue of abstracts was unveiled during the Research Day celebration that comprised of all the submitted abstracts for public consumption.
Media Panorama
- Published in News, Research News, Research Webinars, Webinars
DST- SERB grant awarded to Dr Sutharsan Govindarajan
Alleviating healthcare challenges by augmenting efficacy of antibiotics
 Dr Sutharsan Govindarajan, Assistant Professor, Department of Biological Sciences, SRM University – AP, Andhra Pradesh received an outlay of Rs 55 lakhs by the Department of Science and Technology (DST)- Science and Engineering Research Board (SERB), Government of India to advance the project “Mechanistic understanding of bacterial cytoskeleton inhibition by antibiotics and novel bacteriophage proteins”. The research grant is provided to support active researchers in undertaking research and development in the frontiers of Science and Engineering. Dr Sutharsan exclaims, “It is thrilling to see that my proposal has been accepted for funding. This is a huge recognition for the science that we do at SRM University – AP. Through this funding, I will be able to establish an independent molecular microbiology lab at the university.”
Dr Sutharsan Govindarajan, Assistant Professor, Department of Biological Sciences, SRM University – AP, Andhra Pradesh received an outlay of Rs 55 lakhs by the Department of Science and Technology (DST)- Science and Engineering Research Board (SERB), Government of India to advance the project “Mechanistic understanding of bacterial cytoskeleton inhibition by antibiotics and novel bacteriophage proteins”. The research grant is provided to support active researchers in undertaking research and development in the frontiers of Science and Engineering. Dr Sutharsan exclaims, “It is thrilling to see that my proposal has been accepted for funding. This is a huge recognition for the science that we do at SRM University – AP. Through this funding, I will be able to establish an independent molecular microbiology lab at the university.”
While the entire world is aggressively working to end the menace of COVID19, antimicrobial resistance has been a long-standing unsolved threat. This project is dedicated to interpreting the mechanism of inhibition of bacterial cytoskeleton by antibiotics, which has an immediate impact on the society as it strives to unravel the mystery of ‘how bacteria are able to outsmart antibiotics and survive’. In this project, Dr Sutharsan will be probing antibiotics to comprehend the response of bacteria to them. The scholar says, “Currently, antibiotic resistance is one of the greatest health care challenges of this century leading to serious clinical manifestations. In countries like India, the situation is alarming since nearly 58 thousand new-born babies are dying every year due to bacteria escaping the antibiotics.”
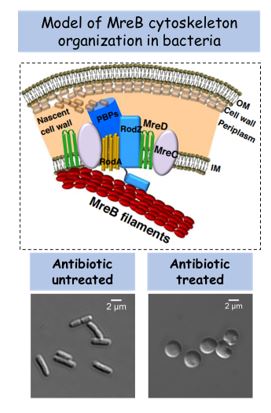 Dr Sutharsan informs, “Largely, solutions to antibiotic resistance problem is directed towards discovering new antibiotics and therapies. However, there are hundreds of existing antibiotics that could be made more effective to kill bacteria. But these antibiotics are not considered as compelling options in the market due to their poor efficiency or lack of understanding. In this project, we will investigate one such antibiotic and attempt to assess its response to the killing agent. By understanding how bacteria escape the antibiotic action, we hope to find effective strategies to combat them.”
Dr Sutharsan informs, “Largely, solutions to antibiotic resistance problem is directed towards discovering new antibiotics and therapies. However, there are hundreds of existing antibiotics that could be made more effective to kill bacteria. But these antibiotics are not considered as compelling options in the market due to their poor efficiency or lack of understanding. In this project, we will investigate one such antibiotic and attempt to assess its response to the killing agent. By understanding how bacteria escape the antibiotic action, we hope to find effective strategies to combat them.”
The laboratory of phage-bacteria interaction will be established and led by Dr Sutharsan at SRM University-AP, where he will be relentlessly working on various aspects of bacteriology including antibiotic resistance, bacteriophage engineering, and therapy. Sharing his plans of advancing the work, Dr Sutharsan says “In the near future, we are planning to connect with the clinicians and explore the possibility of taking our research findings to actual patients – a bench to bedside model of research.”
- Published in News, Research News
Prof Siva Sankar Y’s remarkable research paces up wireless data transmission
 Prof Siva Sankar Y, Professor & Head, Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, SRM University-AP, Andhra Pradesh published a research paper titled “60 GHz common gate single stage current reuse cascode LNA topology for high data rate applications” in the Journal of Electronic Materials. In the recent era, wireless communication has become essential in the lives of mankind. The data transfer rate of wireless systems varies from a few kilobits per second (kbps) to gigabits per second (Gbps), and the distance of communication supported by these technologies fluctuate from a few meters to kilometers.
Prof Siva Sankar Y, Professor & Head, Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, SRM University-AP, Andhra Pradesh published a research paper titled “60 GHz common gate single stage current reuse cascode LNA topology for high data rate applications” in the Journal of Electronic Materials. In the recent era, wireless communication has become essential in the lives of mankind. The data transfer rate of wireless systems varies from a few kilobits per second (kbps) to gigabits per second (Gbps), and the distance of communication supported by these technologies fluctuate from a few meters to kilometers.
Gbps transmission entails the transfer of huge data between different devices such as high-definition (HD) video cameras, smartphones, HD set-top boxes, HD DVD players, and high-definition printers. Realizing Gpbs transmission requires operating frequency of several tens of GHz to hundreds of GHz. To meet the escalating demand for high data transfer rates, wireless technologies are penetrating the millimeter wave technology domain, which supports transmission data rates up to Gbps within small distances.
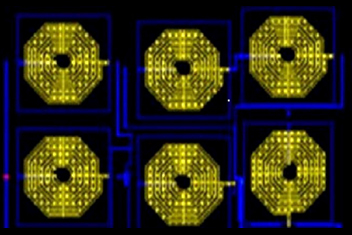 Layout of the proposed circuitMillimeter (mm) wave spectrum can be used for such high-speed wireless communication. Dr Siva Sankar informs, “One of the major challenges in realizing mm wave based transceivers is the design of the CMOS analog RF components. In the design of CMOS RF components, power dissipation, and speed are the two important and conflicting factors that lay stringent requirements on RF design. In our work, RF component design has been used in mmWave transceivers.”
Layout of the proposed circuitMillimeter (mm) wave spectrum can be used for such high-speed wireless communication. Dr Siva Sankar informs, “One of the major challenges in realizing mm wave based transceivers is the design of the CMOS analog RF components. In the design of CMOS RF components, power dissipation, and speed are the two important and conflicting factors that lay stringent requirements on RF design. In our work, RF component design has been used in mmWave transceivers.”
Dr Siva Sankar and his research group developed a high frequency, low noise LNA that can be used in mmWave transceivers to facilitate high data transfer rates. The professor explains, “The designed LNA can be used in mm wave transceivers. The speed (operating frequency) of these components is chosen to be 60GHz because the spectrum around 60GHz is available for unlicensed operation in many regulatory domains including the USA, Japan, Canada and Australia.”. Advancing the research, Dr Siva Sankar and his research group will focus on high speed RF components such as mixers, PLL, and others to realize 60 GHz.
- Published in News, Research News
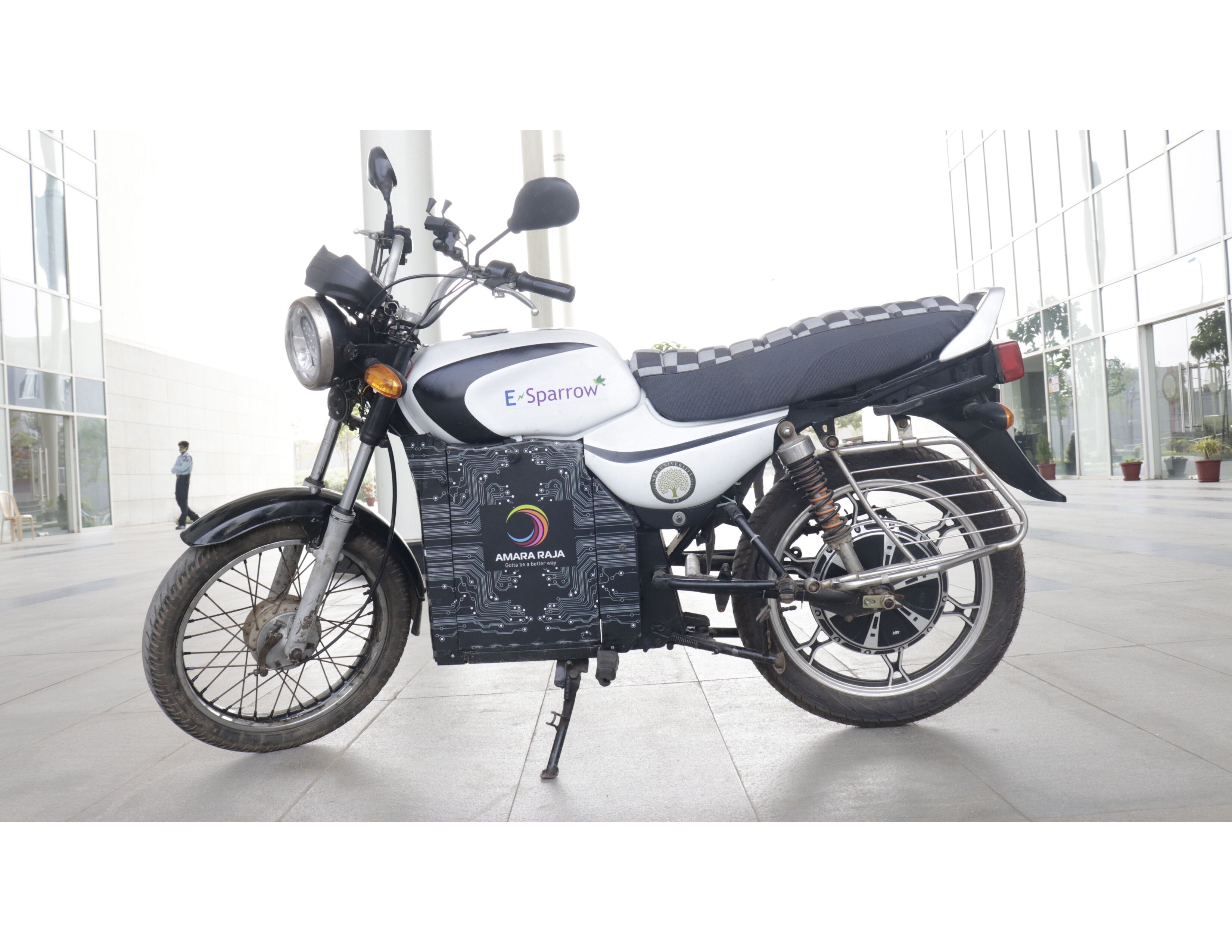
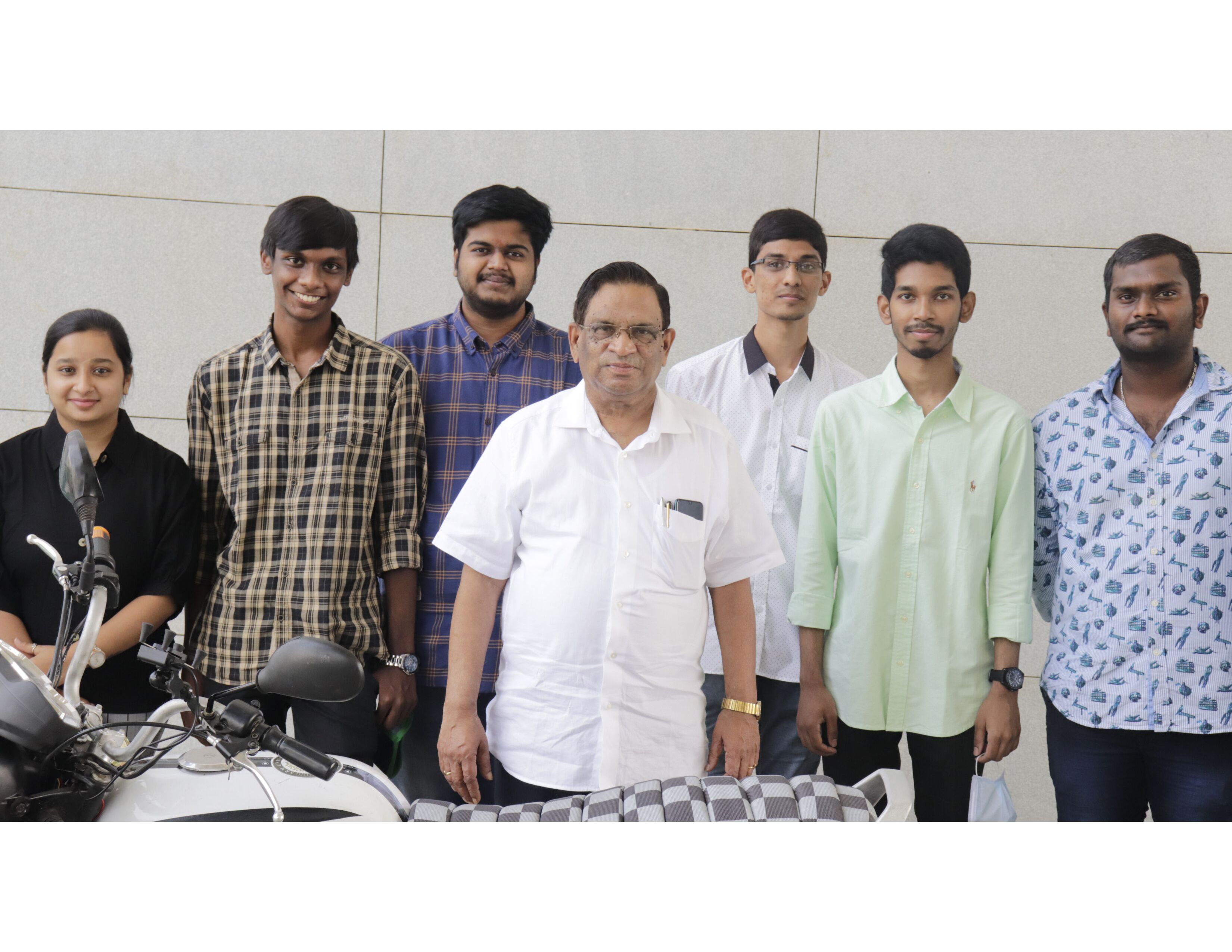
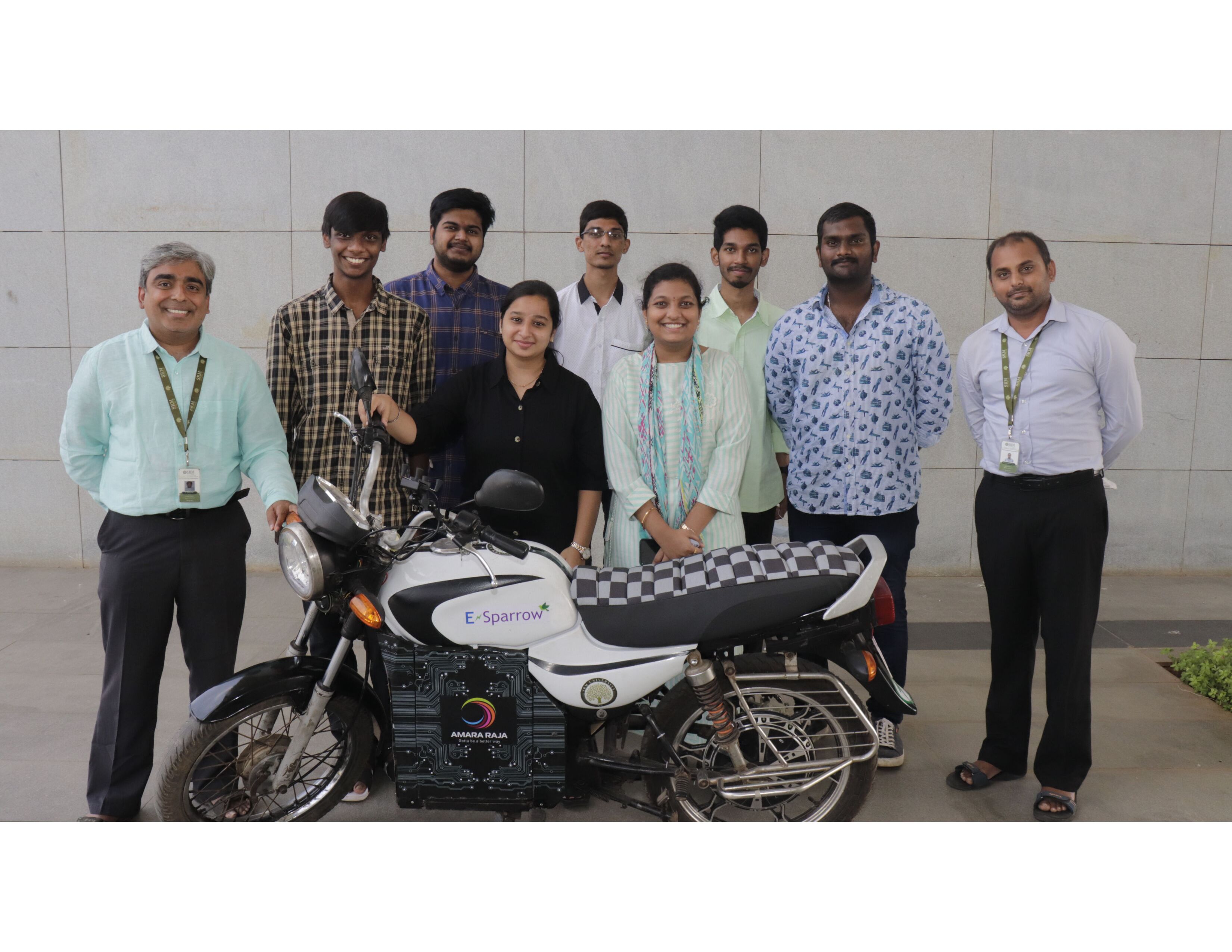
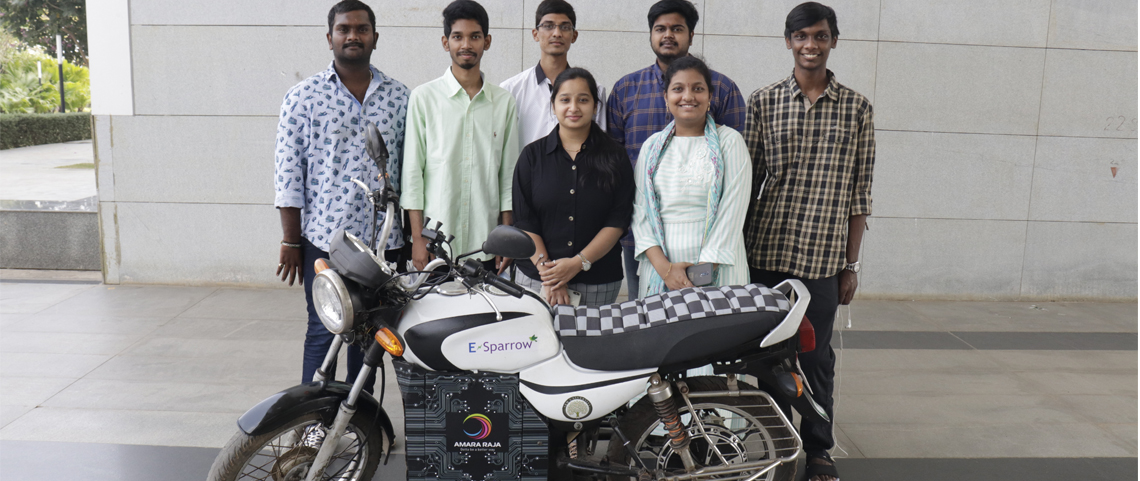
Undergraduate students design e-bike for sustainable environment

Advancing the celebration, Prof D Narayana Rao, Pro Vice-Chancellor, SRM AP took the virtual podium to comment “Science and Technology is the driving force for the economic development of India. We need to encourage young scholars by providing a vibrant and conducive research environment. Expanding the frontiers of knowledge by triggering interest among students must be the priority of the institutions. Also, focus should be on translational research with societal applications through collaborative research to make our nation a global leader.”
The team comprises of undergraduate students – Mr Raviteja Reddy, Mr A Chaitanya, Mr P M Aditya, Mr K Praveen, K Yeshashwini, A Sravya, K Vasu, and G Priyanka along with faculty members – Dr Venkata N Nori, Associate Professor, and Dr Panchagnula Jayaprakash Sharma, Assistant Professor, Department of Mechanical Engineering. Aditya reveals, “We endured several challenges in various aspects of retrofitting the conventional petrol motorcycle. Also, designing a portable battery system, enhancing the performance of the Hub motor, Chassis improvements, etc. enriched our understanding of electric vehicles and manufacturing techniques.”
Conversion of IC engine bike to an e-bike is considered to be a potential business venture by the team. Sharing their forthcoming plans, Aditya informs, “We are working on additional designs and ideas to incorporate the best possible features to make the e-bike more reliable. We heartily thank Prof D Narayana Rao, Pro Vice-Chancellor, for his continuous support. Also, Dr Venkata Nori and Dr Jayaprakash propelled us to create a steadfast model by relentlessly helping us in improving our design to make our model more cost-effective.”
- Published in Mechanical Engineering NEWS, News, Research News
“Jumbo Catalyst” to resolve real-time catalytic challenges: SRMAP conceded the patent
 Dr Anil K Suresh is a renowned scientist in the area of Bio-Nanotechnology . The prestigious Ramalingaswami Fellow is now an Associate Professor at the Department of Biological Sciences, SRM University-AP. He recently developed an innovative catalyst that he named “Jumbo Catalyst” to address the demanding challenges in heterogeneous catalysis. This 3D-megacatalyst generated using “intact eggshell” food-waste is hand-removable with an overall surface area of ~ 78 cm2, featuring wide catalytic support and is highly stable in polar and non-polar solvents for ultra-efficient heterogeneous catalysis. This megacatalyst can overcome the existing limitations such as cost, time, labour, sustainability, mechanical stability, diverse-reactions, large-volumes, aggregation, recyclability and precursor recovery. Dr Anil K Suresh owns the copyrights for this pathbreaking invention through a published patent.
Dr Anil K Suresh is a renowned scientist in the area of Bio-Nanotechnology . The prestigious Ramalingaswami Fellow is now an Associate Professor at the Department of Biological Sciences, SRM University-AP. He recently developed an innovative catalyst that he named “Jumbo Catalyst” to address the demanding challenges in heterogeneous catalysis. This 3D-megacatalyst generated using “intact eggshell” food-waste is hand-removable with an overall surface area of ~ 78 cm2, featuring wide catalytic support and is highly stable in polar and non-polar solvents for ultra-efficient heterogeneous catalysis. This megacatalyst can overcome the existing limitations such as cost, time, labour, sustainability, mechanical stability, diverse-reactions, large-volumes, aggregation, recyclability and precursor recovery. Dr Anil K Suresh owns the copyrights for this pathbreaking invention through a published patent.
Catalysis is widely used in various industrial processes to produce desired end products. Research in this area substantially evolved from using organic reagents and metals to the adaptation of metal-based nanoparticles. Supported catalysis is a fast-emerging class of catalysis using inert and supportive frameworks with a potential for efficient reuse and recovery of the catalyst. Synthesis of metal-organic frameworks, fibres, polymers and hydrogel-based catalytic nanoparticle loadings are being reported. However, these are associated with intrinsic complexities and are produced using toxic ingredients, ecologically unbenign and are expensive.
The megacatalyst, generated by Dr Anil and his team using eggshell food-waste in the process, is autogenic, facile, cost-efficient and entirely biodegradable. Dr Anil strongly believes that theirs is the biggest catalyst developed so far. The intact eggshell provides an extensive support area for ultra-efficient catalysis. Applicability of this megacatalyst is so simple that even a layman can use it with ease. Moreover, this supported megacatalyst can be effortlessly removed from the reaction mixture post application as it can be recovered by hand. Catalytic reactions using the megacatalyst can be controlled as the tuff, and uniform coating protects the shedding of nanoparticles. Dr Anil Says, “We presume that the mega-size of the catalyst could be instrumental in several challenging applications. As a proof of concept, we selected three eclectic applications including- 1. Large volume sewage dye degradations, 2. Gram-scale hydrogenation of nitroarenes and 3. Transesterification of used oil to biodiesel- which are all difficult to achieve, highly challenging but are now practically feasible using our megacatalyst.”
“Keeping in mind the ultra-catalytic proficiency of our catalyst that can be simply resourced from continuously available eggshell waste, with minimal maintenance for the large scale practical implementation, we welcome interested beneficiaries from diverse heterogeneous catalysis sectors for bringing this innovation to execution,” Dr Anil asserted.
 The team is currently investigating to design and fabricate other species of megacatalyst using other significant metal precursors and earth-abundant metals to expand the applicability in allowance of diverse reactions such as oxidation of CO, Methane, Mono/Polyhydric alcohols, hydrogenation of alkynes, Nitroaromatics and CO2.
The team is currently investigating to design and fabricate other species of megacatalyst using other significant metal precursors and earth-abundant metals to expand the applicability in allowance of diverse reactions such as oxidation of CO, Methane, Mono/Polyhydric alcohols, hydrogenation of alkynes, Nitroaromatics and CO2.
Dr Anil K. Suresh concluded that this breakthrough conception would not have been possible without the rigorous efforts of his team and the continuous support from the university management. Dr Anil Suresh thanked his PhD students Chandra Bhatt, Divya Parimi, Tharun Bollu and Madhura. Dr Anil especially thanked Professor D Narayana Rao, Pro-Vice-Chancellor, SRM University-AP for his extensive support in all his scientific endeavours since his association with the university.
- Published in News, Research News
A book by Dr Lakhveer Singh featured in the list of Best Waste Management books
Converting waste to fuel: way forward to a resilient planet
 Dr Lakhveer Singh, Assistant Professor, Department of Environmental Science published a book titled “Waste to Sustainable Energy: MFCs – Prospects through Prognosis”. This book has been featured in the list of Best Waste Management books of all time by CNN, Forbes, and Inc-Book Authority. The book has been awarded this stature by venerated reviewers of the International Expert Committee, as well as global leaders of the discipline.
Dr Lakhveer Singh, Assistant Professor, Department of Environmental Science published a book titled “Waste to Sustainable Energy: MFCs – Prospects through Prognosis”. This book has been featured in the list of Best Waste Management books of all time by CNN, Forbes, and Inc-Book Authority. The book has been awarded this stature by venerated reviewers of the International Expert Committee, as well as global leaders of the discipline.
A Microbial Fuel Cells (MFC) bio-refinery treat water using microorganisms and converts waste products and byproducts into fuel. This entails efficient waste management along with contributing to the generation of renewable fuel, and products that foster sustainable development. Addressing the present challenges in waste management, bioenergy, bioproduct recovery, and commercial sustainability, this book on MFCs emphasize on an array of mechanisms, routes, and reaction engineering approaches for extensive transformation of waste to wealth.
Extensive use of fossil fuels for energy emits carbon dioxide and other harmful gases adversely affecting the environment and leading to soaring global warming. Subsequently, domestic, agricultural waste products from animal facilities, refineries, and industries cause a tremendous environmental burden. Energy systems from MFCs enable the treatment and recycling of wastes, preventing environmental problems, and offsetting the pollution loads. Dr Lakhveer informs, “We are aiming at ensuring a sustainable and resilient environment that eliminates any potential odds of future climate change. Though globalization has preceded the escalation in production processes, a significant quantum of the waste materials generated through these practices can be transformed into fuels with the help of MFCs. Efficacies of this mechanism would ensure a paradigm shift built on the principles of sustainability.”
This book focuses on the MFCs with various combinations of substrates generating bioelectricity with valued co-products. Essentially, the book provides fundamental ideas on MFC technologies, entailing various design and modeling aspects with examples. Further, the book illustrates distinctive aspects of basic sciences, reactor configuration, application, and market feasibility of MFCs. Critically assessing the feasibility of waste-powered MFCs for sustainable bioenergy production, the book highlights the tradeoff between resource needs and energy production. The extensive research and details in the book will help academicians, entrepreneurs, and industrialists to understand the scope and challenges empowering them to select unique, and specific integrated approaches in unit processes.
Advancing his research to mitigate environmental issues, Dr Lakhveer will continue to explore bioenergy, water treatment, bioelectrochemical systems, and nanomaterial synthesis for energy and water applications, and bioreactors development. Also, he is presently editing two books that address several environmental challenges.
- Published in News, Research News













