The Anxiety of Indianness in the Making of Sindhi Literature

Very often, it is assumed that the “vernacular” language texts in India do not undergo any anxiety of proving themselves Indian while works written in English do. In her research paper, “A Literature of Frustration and Failure”: The Anxiety of Indianness in the Making of Sindhi Literature as an Indian Literature”, published in the esteemed Q2 journal Journal of Sindhi Studies, Dr Soni Wadhwa, Assistant Professor, Department of Literature and Languages, focuses on Sindhi post literary activity that unfolded in the first 20 years after independence to show that Sindhi has a history of going through anxiety of belonging in India.
Abstract
Studies of Partition frequently turn to literature to understand how displacement processes, among other things, impact aesthetics and representation. The article takes a broader view of aesthetics as representation: it demonstrates how turning to the literary archive of a moment and a community gives rise to questions about the politics of individual texts and literary historiography. Centred on Sindhi literature produced in India after Partition, it shows that examining the literary productivity of the community needs to involve questions of literature as political survival. It focuses on the earliest essays from the Sindhi literary scene in India (published in the Sahitya Akademi journal Indian Literature). The article argues that these essays register anxiety about the survival of a language trying to come into being in an already existing and complicated language-nation relationship. It unpacks three registers of anxiety visible in the literary archive to broaden the scope of the conversations around the Sindhi language and its literature.
This research has been conducted to advance interest in and conversations around Sindhi literature in India. Since Sindhi does not have a state in India, most people are not aware that it exists as a language and that it has a rich literary tradition.
After this article, Dr Soni Wadhwa intends to explore different writers, themes, and movements in Sindhi literature.
Collaborations
The research has been funded by George Mason University.
- Published in Departmental News, English Current Happenings, English news, News, Research News
Dr Bidisha on Translating Dalit Voices
 Translation often serves as a vital bridge between languages and cultures and Translators are often poised as “gatekeepers” who preserve the authenticity and richness of a text. Dr Bidisha Pal, Assistant Professor at the Department of Literature and Languages in her research paper, “From Transregional to Global Space: Translating Dalit Autobiography and Bridging the Boundaries” speaks of the power of translation in safeguarding and raising awareness of caste. Her work also illustrates how translation smoothens the divide between language and enables the voice of the marginalised to be heard.
Translation often serves as a vital bridge between languages and cultures and Translators are often poised as “gatekeepers” who preserve the authenticity and richness of a text. Dr Bidisha Pal, Assistant Professor at the Department of Literature and Languages in her research paper, “From Transregional to Global Space: Translating Dalit Autobiography and Bridging the Boundaries” speaks of the power of translation in safeguarding and raising awareness of caste. Her work also illustrates how translation smoothens the divide between language and enables the voice of the marginalised to be heard.
Abstract:
The present research brings forward some standpoints. First, the translation of Dalit autobiographies creates transnational solidarity. Second, the translators play the role of gatekeepers to show that translation sustains the literary and cultural essence ingrained within the texts and initiates and engages dialogic discussions among the audience and readers on the global platform. Third, the translation of Dalit autobiographies arrests the attention of those global readers who barely nurture any idea on caste, class, and casteist politics and deep-rooted issues like untouchability in India and constructs a distinct literary geography.
Explanation in layperson’s terms:
The research deals with the idea of literary translation and its necessity. These two autobiographies are written in regional Bengal. When translated, the boundary of regions gets dissolved, and the essence of the texts reach the global arena. Besides, translation also acts as the bridge to the outer world. However, oftentimes the act of translation is not an innocent act anymore; rather it interferes with the original meaning to transcreate.
Practical/ Social Implications:
The research talks about translation and its necessity to bridge boundaries. The texts that the article focuses on are from the people of the marginalized communities of Bengal who write to voice their concerns and who feature in a considerable period of history that should be known to people. Since, linguistic regionalism is the main constraint for the literary texts, translation provides the desired space and opportunity to help them reach the global platforms and their history and literature become part of the larger repertoire of World Literature.
The link to the article:
- Published in Departmental News, English Current Happenings, English news, News, Research News
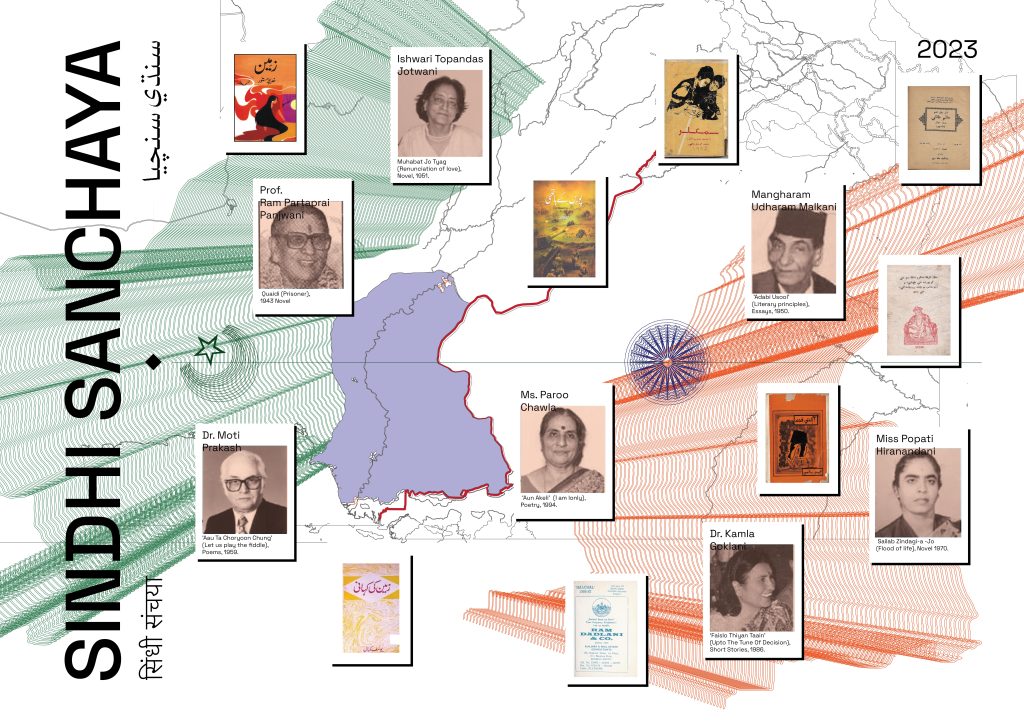
Where Technology Meets Literature: Reviving Sindhi Libraries with a Digitised Five-point Framework

Minor languages face many challenges in India and elsewhere. With most of these languages on the verge of extinction, preservation efforts using technology need to develop a different vision for helping these languages and their communities. Dr Soni Wadhwa, Assistant Professor from the Department of Literature and Languages, has published her research in the article “Digital Technology for Literature Revitalisation: A Framework for Sindhi Libraries in India” in the Q1 journal Preservation, Digital Technology and Culture, highlighting on overcoming these challenges. Her research emphasises a five-point framework to revive Sindhi literature.
Abstract
Linguistic diversity does not find adequate space in LIS discourses around libraries in India and other regions with similar kinds of linguistic heritage. This study focuses on the state of Sindhi literature in India through a look at the libraries that house the works of Sindhi literary activity in post-Partition India. The objective is to highlight the role of libraries within language revitalization efforts. This study puts forth a five-point framework for digital transformation of Sindhi libraries in India which can help broaden the digital transformation efforts elsewhere in the Global South especially with minor languages and dialects. While the five-point framework is customized to the specific challenges faced by Sindhi regarding its script (and includes designing solutions for OCR, transliteration, and text to speech interaction), its principles could be applied to several other linguistic contexts, especially in the Global South. It, thus, seeks to bring LIS into sharp focus within the social imagination of communities of readers and as speakers of a language, and not just as academic institutions alone.
Practical Implementation/Social Implications of the Research
- Using this five-point framework, scholars from various fields (history, partition studies, language, literature, digital humanities, digital archiving, etc) can identify different ways of preserving the Sindhi language.
- The use of technology for this purpose can lead to technological innovation, which in turn can accelerate preservation efforts.
- Similar models and frameworks can be developed for other minor languages.
Collaboration
The project is funded by IIT Indore.
- Published in Departmental News, English Current Happenings, English news, News, Research News
Decolonial Insights on Partition in Indian Comics

Dr Partha Bhattacharjee, Assistant Professor from the Department of Literature and Languages, along with his scholar Mr Rounak Gupta has published their paper titled “Fractured Identities and Wounded Memories in Indian Comics on Partition: A Decolonial Reading of Frame and Panel” in the esteemed Q1 journal Journal of Graphic Novels and Comics. This paper explains comics as a medium whose panels, frames, and stylistic aspects can be interpreted in the Indian context. This interpretation has been read as a decolonial intervention into the medium’s history and the established aesthetic theories.
Abstract
Within the liaison of decoloniality studies and comics studies, this paper investigates how the decolonial visual style in the comics anthology This Side That Side (2013) has been used to locate the traumatised past and violation of human rights due to the “b/ordering” practices of partition of India (Rifkind 2017; Bhattacharjee and Tripathi 2022). “The Taboo” by Malini Gupta and Dyuti Mittal, “An Afterlife” by Sanjoy Chakraborty, and “Making Faces” by Orijit Sen cultivate the stories of the inhumane condition of the migrants and victims during and after the Indo-Pakistan and Indo-Bangladesh-Pakistan partition. These narratives exemplify decolonised counter comics narratives on collective and personal memories (Chute 2016; Mickwitz 2016; Ahmed and Crucifix 2018) inflicted upon and against the dominant partition discourse. They help churn out the human stories of the interminable psychological violence of partition and post-partitioned reality.
The paradigm established in this research can later be used to interpret different formations within comics, especially pertaining to decolonial aesthetics, dialogue, and attitude.
Collaborations
This paper has been published as a part of a continuing study that began with the preceding paper – Bhattacharjee, Partha, and Priyanka Tripathi. 2022. “Penning the Pain of Partition: Refugee Camp Narratives in Indian Comics.” Studies in Comics 12(2): 179-200. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1386/stic_00062_1.
- Published in Departmental News, English Current Happenings, English news, News, Research News
The Vision of ‘Moner Manush’ through the Lens of Dr Sayantan’s Research

Today, we approach the topics of caste and religion with great sensitivity, aware of the deep-rooted complexities they carry. Yet, here was a character who transcended these societal boundaries, evolving into the embodiment of ‘Moner Manush’—a figure who rose above the constraints of identity to embrace a higher sense of spiritual unity and inclusiveness. Dr Sayantan Thakur, Assistant Professor at the Department of Literature and Languages closely reads into the intricacies of Lalon’s conceptualisation of man and the caste barriers in his research paper.
Abstract:
The paper entitled ‘Beyond ‘Jaat’ and Dharma: Exploring the Evolution of Lalon’s Idea of ‘Moner Manush’ delves into an in-depth exploration of Lalon’s conceptualization of ‘Moner Manush,’ transcending the conventional confines of ‘Jaat’ (caste) and Dharma (religion). Through a nuanced analysis of Lalon’s evolving perspectives, the study traces the transformative journey of the idea of ‘Moner Manush.’ By dissecting the lyrical and philosophical aspects, the paper illuminates how Lalon’s spiritual musings challenge societal norms, promoting a universal ethos that goes beyond distinctions. This inquiry aims to unravel the evolving nature of Lalon’s concept of ‘Moner Manush’ and its enduring significance in fostering inclusivity and spiritual interconnectedness, surpassing the limitations of caste and religion.
Practical Implementation and Social Implications:
The practical implementation of my research on “Beyond ‘Jaat’ and Dharma: Exploring the Evolution of Lalon’s Idea of ‘Moner Manush'” has profound social implications, particularly in fostering inclusivity and breaking down societal barriers. By promoting Lalon’s vision of transcending caste (jaat) and religious (dharma) divisions, this research advocates for a more egalitarian society where people are valued for their inner virtues, not external identities. In practical terms, this philosophy can be integrated into education, community-building, and social reform initiatives to encourage tolerance, empathy, and unity among diverse groups.
In multicultural societies, teaching Lalon’s ideas in schools and community programs can help dismantle deep-seated prejudices and promote cross-cultural understanding. Socially, the emphasis on the Moner Manush—the ideal human being—can encourage individuals to focus on self-reflection, moral development, and compassion, creating a more harmonious coexistence. Additionally, his philosophy can inform contemporary debates on identity politics, helping people prioritize human connections over rigid societal structures.
Future Research Plans
Regional Literature in Translation
Tantric Tradition and Eastern Indian Literature
Folk Music of Bengal
Indian Philosophy, Aesthetics & Literature
- Published in Departmental News, English Current Happenings, English news, News, Research News
Revisiting Clément Baloup’s Comics through Dr Gusain’s Research

SRM University-AP is proud to announce that Dr Abhilasha Gusain, Assistant Professor in the Department of Literature and Languages has made an outstanding contribution to the academic world with her recent publication. Her research paper, “Illustrating Memory: Clément Baloup’s Vietnamese Memories and the Visual Representation of the Past,” featured in 3L: The Southeast Asian Journal of English Language Studies, a Q1-ranked journal known for its high impact in the field.
Abstract
The present study aims to highlight the role that Clément Baloup’s comics, Vietnamese Memories: Leaving Saigon (Volume 1) and Vietnamese Memories: Little Saigon (Volume 2), play in the creation of an alternate archive that validates the forgotten tales and the memories of a neglected past. These texts provide an alternate form of remembrance by materialising the past in the form of images. The two volumes present the unheard experiences of the Vietnamese diaspora that Baloup recorded during his travels to the different parts of France and the U.S. Such experiences bring to the forefront memories that are otherwise kept at the margins or suppressed by the dominant discourse. If not recorded, they will be lost forever. The counter-memory, thus, calls for a reassessment of the idea of a singular past that denies the marginalised memories. It claims representation and restoration in the cultural memory. As works of postmemory, these texts form a link between the past and the present through mediation and give memorability to unremembered accounts. The memories are illustrated, and hence, visual representation becomes important to the task of postmemory here.
Explanation of the Research:
This study emphasises the significance of visual representation in postmemory, showing how the two graphic narratives create a space for counter-memory and contribute to a reassessment of cultural memory by including marginalised experiences. Postmemory is a term used to describe how the memories of one generation are shaped by the stories and experiences of the previous generation. It often relates to events that people haven’t directly experienced, like wars or significant historical events, but feel a strong connection to through family stories, photographs, or cultural narratives. The paper illustrates how Baloup’s works serve as an alternate archival repository, creating a dynamic and inclusive cultural memory that reflects the complex, polyphonic nature of human experience; thus contributing significantly to the fields of comics studies and memory studies.
- Published in Departmental News, English Current Happenings, English news, News, Research News
Language Lab to Boost Student Communication Skills
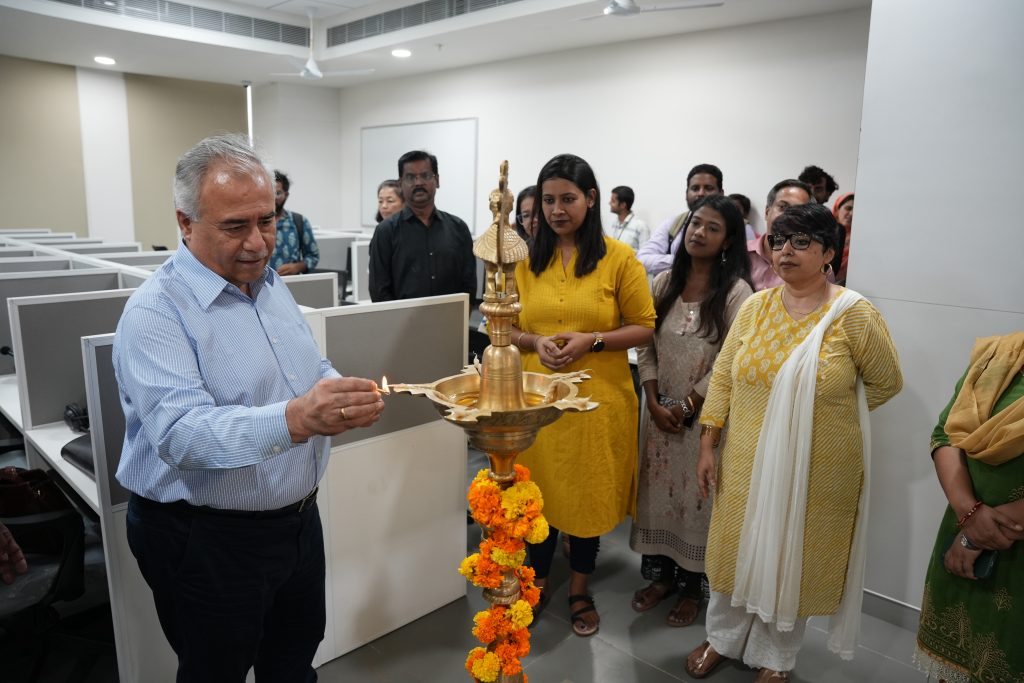 The Department of Literature and Languages at SRM University-AP celebrated the launch of its Language Lab, a state-of-the-art, 70-seater facility designed to enhance the Listening, Speaking, Reading, and Writing (LSRW) skills of its students.
The Department of Literature and Languages at SRM University-AP celebrated the launch of its Language Lab, a state-of-the-art, 70-seater facility designed to enhance the Listening, Speaking, Reading, and Writing (LSRW) skills of its students.
The inauguration was witnessed and officiated by the honourable Vice Chancellor, Prof. Manoj K Arora, along with Prof. Vishnupad, Dean- ESLA; Prof. C V Tomy, Dean-SEAS, Dr Vinayak Kalluri, Dean-Academic Affairs, Ms Suma N, CFAO; Dr Sayantan Thakur, Assistant Professor and Head; Dr Karthik Rajendran; Dr Srabani Basu, other faculty members, research scholars and students.
The laboratory, valued at 10 million rupees, is equipped with Sanako and Lanquill software, providing students with access to advanced resources. During the event, Vice Chancellor Prof. Manoj K Arora emphasised the value of communication he stated “Communication is an essential skill. With this lab, our students have a real opportunity to build those skills and contribute meaningfully to society.” he also voiced that, In future, the varsity will also be looking forward to opening this facility to the wider community so that more people can benefit from this resource.
Dr Thakur and Dr Amlan Baisya, Assistant Professors at the university, provided insights into the laboratory’s cutting-edge software and technology. They explained how these tools can significantly enhance the learning experience, making language acquisition more interactive and engaging. The faculty expressed their excitement about the opportunities this facility will create for both students and instructors alike.
Prof. Arora took a moment to commend the Department of Literature and Languages and the Directorate of Information Technology and Knowledge Management (ITKM) for their commitment to advancing education through innovative resources. He underscored the bright future ahead, not only for students but for the entire university community, as they leverage this new laboratory to improve communication skills that are vital in both academic and professional settings.
- Published in Departmental News, English Current Happenings, English news, News
Dr Sayantan’s Research Paper on Overcoming the Digital Divide

In the context of online English education in India, the “digital divide” has emerged as a significant obstacle, especially for students from rural or underprivileged areas. Dr Sayantan Thakur, Assistant Professor at the Department of Literature and Languages in his article introduces a research study titled “Navigating the Digital Divide: Challenges and Strategies in Teaching Communicative English Online in Indian Classrooms,” which aims to address the unequal access to online learning tools.
Abstract
The advent of online learning platforms is providing new opportunities for English language learning (ELL) in India. However, there is a significant challenge posed by the digital divide – the gap in accessing technology. This study investigates what causes the digital divide in internet ELL classrooms such as infrastructure limitations, device ownership and usage, and digital literacy skills; and how they affect student engagement, development of communication skills, and overall learning experiences. It suggests ways to bridge this gap which include government policies on infrastructure development; affordable tech solutions like mobile apps; teaching programs that enhance digital literacy among learners; support for teachers involved in web-based pedagogy. Through these recommendations, education stakeholders can create an inclusive cyberspace for all students where their communication abilities will be nurtured throughout different parts of India.
The Practical Implementation
The practical implementation of your research on “Navigating the Digital Divide: Challenges and Strategies in Teaching Communicative English Online in Indian Classrooms” has far-reaching social implications. By addressing the digital divide, your work can help level the playing field in education, especially for students from underprivileged backgrounds.
Improved Access to Education: Implementing strategies like infrastructure development, affordable mobile-based learning tools, and digital literacy programmes can provide more students, especially in rural and low-income areas, access to online English learning resources. This improves their chances of acquiring essential communication skills, opening doors to better job opportunities.
Empowering Teachers: Equipping teachers with digital tools and training enables them to deliver more effective online lessons, increasing student engagement and success rates.
Reducing Inequality: Bridging the technology gap can reduce educational disparities between urban and rural areas, promoting social mobility and reducing the long-term impacts of inequality.
Building a Digitally Literate Society: Enhancing digital literacy among students and teachers fosters a society better prepared for the demands of the modern workforce, ultimately contributing to economic growth and social inclusion.
Future Research Plans
- Regional Literature in Translation
- Tantric Tradition and Eastern Indian Literature
- Folk Music of Bengal
- Indian Philosophy, Aesthetics & Literature
- Published in Departmental News, English Current Happenings, English news, News, Research News
A Look into Sequential Art: Exploring Sean Michael Wilson’s Graphic Creations

Graphic novels, a subgenre of comics, have witnessed stellar growth in popularity, encouraging readers to decipher meaning from the text and the images. The combination of visual and textual storytelling aids readers in decoding complex narratives. Dr Abhilasha Gusain, Assistant Professor from the Department of Literature and Languages, has published a paper titled “From Ideas to Ink: The Craft of Graphic Novel Creation with Sean Michael Wilson” in the Journal of Graphic Novels and Comics.
The current research advances the field of comics studies, highlighting aspects related to the industry like readership, publication, and distribution of graphic narratives across the globe. It emphasises the process of creation of a graphic novel, with reference to author Sean Michael Wilson’s works.
Abstract
In this interview, Sean Michael Wilson delves into his multifaceted career as a graphic novel writer, revealing the intricacies of his creative process, the challenges of adapting complex subjects into visual narratives, and the evolving role of graphic novels in cultural discourse. With over 40 projects under his belt, Wilson shares his approach to beginning new works, whether they stem from original ideas or/are adaptations of historical events and existing literature. He discusses the balance between authenticity and readability, the importance of research, and the collaborative dynamic between writer and artist in bringing graphic novels to life. Wilson also touches on the broader implications of graphic novels in education and social commentary, the economic realities of the industry, and the impact of digital platforms on publishing. His experiences across different cultures, particularly between the West and Japan, provide insight into the global reception of his work. Throughout the interview, Wilson emphasises the power of graphic novels as a medium for storytelling, education, and political engagement.
- Published in Departmental News, English Current Happenings, English news, News, Research News
Dr Soni Wadhwa Publishes Paper on Digital Libraries for Minor Languages in India
 In a significant academic achievement, Dr Soni Wadhwa, Assistant Professor in the Department of Literature and Languages, has recently published a paper titled “Digital Libraries for Minor Languages in India: Frameworks for Addressing Absences in Policy and Governance.” The paper was published in the esteemed Journal Digital Library Perspectives. Dr Wadhwa’s research illuminates the importance of establishing digital libraries for minor languages in India and proposes frameworks to address existing gaps in policy and governance. This pioneering work not only explores the significance of preserving linguistic diversity but also advocates for inclusive and accessible digital resources for all.
In a significant academic achievement, Dr Soni Wadhwa, Assistant Professor in the Department of Literature and Languages, has recently published a paper titled “Digital Libraries for Minor Languages in India: Frameworks for Addressing Absences in Policy and Governance.” The paper was published in the esteemed Journal Digital Library Perspectives. Dr Wadhwa’s research illuminates the importance of establishing digital libraries for minor languages in India and proposes frameworks to address existing gaps in policy and governance. This pioneering work not only explores the significance of preserving linguistic diversity but also advocates for inclusive and accessible digital resources for all.
The publication of this paper not only adds to Dr Wadhwa’s scholarly contributions but also highlights the commitment of SRM University-AP faculty members to engaging in research that can have a positive impact on society.
Abstract
This study aims to deliberate on strategies for enlisting community support for gathering diverse learning resources in different languages and for enlisting participation in activities such as crowdsourcing in initiatives such as annotations and transliteration. This paper calls for interventions that imagine and create infrastructure for the flourishing of smaller libraries that can draw from and feed into large-scale national and international libraries. Offering a conceptual framework to rethink the country’s approach toward minor languages, it first offers an overview of policies and initiatives relevant to the concerns of minor languages in digital libraries in India. Based on the policy analysis, it then goes on to suggest starting points for policy designers and custodians of libraries to help them work toward better representation of languages in their resources.
The existing frameworks analyzed here for the greater or representation of minor Indian languages reveal a culture of silence toward the issue of language. With some advocacy, these frameworks can be mined to craft different ways that are critical not just for enriching libraries but also for preservation of cultural heritage of the communities concerned, thus adding a larger social dimension to the question of access.
Explanation of the Research in Layperson’s terms
Given that Indian languages in general are under-represented on the internet and that languages of minority linguistic groups find very little space on digital platforms, it is imperative for institutions such as libraries to cater to smaller communities and their educational needs while also reaching out to them in their own languages. While a lot of socio-political discourse on minority languages in India exists, this study pushes for their bearing on digital libraries, educational frameworks and cultural heritage. It offers five suggestions for strengthening the presence of minor languages in digital libraries in India.
Details in citation format
Wadhwa, S. (2024), “Digital libraries for minor languages in India: frameworks for addressing absences in policy and governance”, Digital Library Perspectives, Vol. ahead-of-print No. ahead-of-print. https://doi.org/10.1108/DLP-01-2024-0002
Practical Implications
This viewpoint paper can be used to enhance policy and governance around libraries. With National Education Policy 2020, which emphasises the importance of learning in regional/mother/Indian languages, Indian educational system as well as social institutions need stronger platforms to make resources in Indian languages available to students as well as lifelong learners. With more of such research, it will be possible to come up better digital infrastructure for Indian languages.
Social Implications
Indian languages are not widely represented on the Internet and in the knowledge set up. Making existing resources and knowledge available in digital libraries will stimulate further research on generating further research and knowledge production in Indian languages. It is hoped that more research in the domain of Indian languages works towards the digital divide and knowledge divide in India.
Collaborations
This research came out of the researcher’s previous archival work. Her digital archive PG Sindhi Library is dedicated to post-partition Sindhi writing in India. This article is based on an invited talk delivered at the international symposium titled “Digital Libraries: Sustainable Development in Education” held at IIT Kharagpur in India in November 2023. The author is grateful to the organisers and fellow participants for their feedback.
Future Research Plans
The researcher is involved in a sanctioned project titled “Sindhi Sanchaya: Building a Comprehensive and Interactive Database of a Partitioned Literature” funded by IIT Indore. She hopes to build on this work produced in this article as she makes progress in the project.
- Published in Departmental News, English Current Happenings, News, Research News












