Budget Panel Discussion 2022-23
 The Department of Economics of SRM University-AP, Andhra Pradesh, conducted a Panel Discussion on February 09, 2022, for the much needed and relevant in-depth analysis of the Union Budget proposed by the Finance Minister in the parliament on February 01, 2022.
The Department of Economics of SRM University-AP, Andhra Pradesh, conducted a Panel Discussion on February 09, 2022, for the much needed and relevant in-depth analysis of the Union Budget proposed by the Finance Minister in the parliament on February 01, 2022.
Professor Bandi Kamaiah was the moderator of the event, and Dr Anandarao Suvvari, the faculty coordinator of the Department of Economics in the University, organised this discussion, inviting four eminent public finance economists of India, Prof N R Bhanu Murthy, Vice-Chancellor, BASE University, Bengaluru; Prof K R Shanmugam, Director, Madras School of Economics, Chennai; Prof K Gayathri, Professor, Institute for Social and Economic Change (ISEC), Bengaluru; Dr Shri Hari Naidu, Economist, National Institute of Public Finance and Policy (NIPFP), New Delhi. The co-convenors of the event were Dr Ghanshyam Pandey, Dr Manzoor Hassan Malik, Dr Kamal Sai Erra, Dr Hari Venkatesh from the Department of Economics SRM-AP.
The discussion started with a brief overview and essence of the Union budget by Dr Anandarao Suvvari, followed by Prof Bandi Kamaiah. Then first panellist Prof N R Bhanu Murthy, who our Indian Finance Minister also quoted, spoke about how the current budget is a continuation of the previous budget and emphasised more on the capital expenditure, which is the route to growth. He highlighted that the government should bring efficiency in public expenditure and expressed that the public policymakers side-lined the public debt number to GDP ratio at both central and state levels. An issue identified by Prof Murthy was bringing in many commodities under the customs tariff line and how doing this will have a negative impact on the exports. Further, he mentioned the ignorance towards the health and education sectors by a reduction in the allocation of expenditure for the same.
The second panellist Prof K R Shanmugam, gave a very detailed look at the budget, sector by sector, pointing out the benefits and the concerns related to each of them. He gave us a brief look at how the Indian economy has been doing for the past few years and gave an analysis taking this into consideration and stated that the budget had provided necessary fiscal stimuli through an increase in capital expenditure for the revival of the economy.
The third panellist Prof K Gayathri highlighted the philosophy of policy implications of budget and the need for a continuous process for analysing it. She also focused on the need for scientificity for estimates and the need for a sustainable approach for the budget. She pointed out that the current budget was future-looking in line with the vision for India 100 and that it put thorough emphasis on capacity building inclusive development by involving all stakeholders and modern infrastructure while expressing concern over effective implementation of policies.
The final panellist, Dr Shri Hari Naidu, discussed the revenue side of the budget thoroughly while focusing on the new taxation regime, other and legitimising crypto assets and digital Indian currency. In addition to this, Dr Naidu commented on the budget that the tax GDP ratio has been stagnant for the past two decades also, it has not been addressed in the budget, and despite the fact that there were a lot of tax reforms, the tax bases needed to be expanded.
After individual reviews by the panellists, questions posed by the students and the co-convenors were answered, followed by an interactive and engaging discussion among panellists, moderator, convenor and co-convenors on various issues spanning from the way of analysing the budget, trade-offs between debt and capital expenditure, debt sustainability, control mechanisms, the process of allocation, outcome evaluation or impact of the budget and the need for reality and effectiveness of planned budget on the ground level.
The session, after a thorough discussion on the union budget, was concluded by a vote of thanks proposed by Asst. Prof. Dr Hari Venkatesh to the esteemed panellists, moderator, convenor, co-convenors and all the people who made this session successful for contributing their precious time and valued efforts.
- Published in Departmental News, Economics Current Happenings, Economics News, News
SRM University-AP publishes as the lead author among 21 co-authors from 13 countries
 “Progress in Alternative Strategies to Combat Antimicrobial Resistance: Focus on Antibiotics” is a paper authored by Prof Jayaseelan Murugaiyan, Professor & Head, Department of Biological Sciences at SRM University-AP and his research scholar Ms Saranya Adukkadukkam, in Antibiotics Journal, having an impact factor of 4.639. It is a remarkable achievement that our university served as the first and the corresponding authors of this paper published in association with “Global AMR Insights Ambassadors Network”. A total of 21 co-authors from 13 countries (India, UK, France, The Netherlands, Switzerland, Italy, Spain, Ukraine, Lebanon, Egypt, Uganda, Bangladesh, and Nigeria) and six Indian universities (including SRM AP) participated in this work.
“Progress in Alternative Strategies to Combat Antimicrobial Resistance: Focus on Antibiotics” is a paper authored by Prof Jayaseelan Murugaiyan, Professor & Head, Department of Biological Sciences at SRM University-AP and his research scholar Ms Saranya Adukkadukkam, in Antibiotics Journal, having an impact factor of 4.639. It is a remarkable achievement that our university served as the first and the corresponding authors of this paper published in association with “Global AMR Insights Ambassadors Network”. A total of 21 co-authors from 13 countries (India, UK, France, The Netherlands, Switzerland, Italy, Spain, Ukraine, Lebanon, Egypt, Uganda, Bangladesh, and Nigeria) and six Indian universities (including SRM AP) participated in this work.
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) – the ability of microorganisms to survive antimicrobials – is a global healthcare concern. AMR contributes to 1.27 million deaths among the 4.95 million deaths associated with bacterial AMR. If no control measures are taken, it is estimated that by 2050, it will claim the lives of 300 million people. The rise of these “superbug bacteria’s” – means that trivial medical interventions will soon become once again high-risk since no efficient antimicrobial chemotherapy is available. It is, therefore, crucial to understand the current situation and identify alternatives to combat the emergence and spread of antimicrobial resistance. This paper comprehensively discusses the alternative approaches that can be effectively utilised to combat AMR and, at the same time, without inducing further resistance among the pathogens. The paper has great social implications in making society aware of the scenario and encouraging the researchers to focus on alternative strategies to combat AMR.
Abstract of the paper: Antibiotic resistance, and, in a broader perspective, antimicrobial resistance (AMR), continues to evolve and spread beyond all boundaries. As a result, infectious diseases have become more challenging or even impossible to treat, leading to an increase in morbidity and mortality. Despite the failure of conventional, traditional antimicrobial therapy, in the past two decades, no novel class of antibiotics has been introduced. Consequently, several novel alternative strategies to combat these (multi-) drug-resistant infectious microorganisms have been identified. The purpose of this review is to gather and consider the strategies that are being applied or proposed as potential alternatives to traditional antibiotics. These strategies include combination therapy, techniques that target the enzymes or proteins responsible for antimicrobial resistance, resistant bacteria, drug delivery systems, physicochemical methods, and unconventional techniques, including the CRISPR-Cas system. These alternative strategies may have the potential to change the treatment of multi-drug-resistant pathogens in human clinical settings.
Global AMR Insight Ambassador Network: AMR Insights, an international network-based organisation interacting with professionals around the globe: in Human and Veterinary Health, Agri-food and Environment, was set up in 2017 following an in-depth feasibility study towards a new information platform on AMR. It mainly focuses on informing, educating and connecting people with the aim to curb antimicrobial resistance. Prof Jayaseelan Murugaiyan and Ms Saranya Adukkadukkam are members of the Global AMR Insights Ambassador Network.
Ms Saranya Adukkadukkam, the co-author from SRM AP says:
The guidance of Prof Jayaseelan Murugaiyan is the pillar of my research. His support and passion for research always encourage me. He gives importance to translational research and motivates me to stand unique in the field. He shows me a path where I can serve the people through research. Foreseeing my future as a scientist, he guides me to more opportunities to collaborate with international scientists. I feel proud of my mentor Prof Jayaseelan Murugaiyan for letting me fly. Also, I thank SRM University-AP for providing generous fellowship, excellent research facilities and ambience to carry out the research.
- Published in Biology News, Departmental News, News, Research News
Vision-based fall detection AI
Human-like care is difficult to replicate. Due to the lack of a reliable vision-based fall detection AI, it is often more effective to assign a lot of manpower towards vision-based detections that have not been efficiently implemented.
Ms Inturi Anita Rani, Research Scholar in the Department of Computer Science Engineering, working with her supervisor, Dr V. M. Manikandan, has worked on a paper titled, “A Novel Vision-Based Fall Detection Scheme using Keypoints of Human-Skeleton with Long Short-term Memory Network” in the Arabian Journal for Science and Engineering published by Springer with an Impact Factor of 2.33.
Abstract of the research:
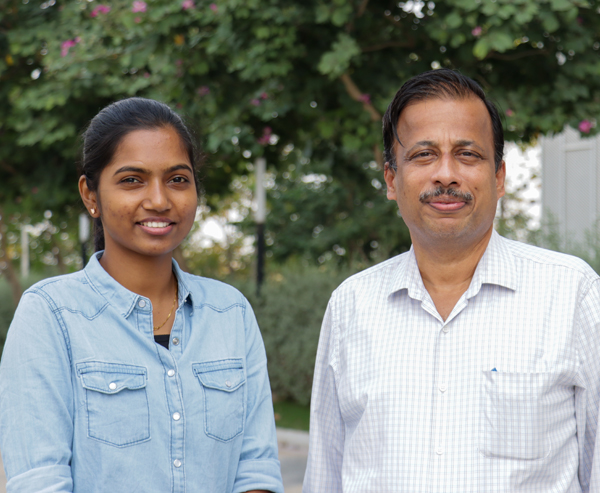
Humans are skilled at visually recognizing and classifying actions in videos, but it’s tough to automate this process. Human action detection in videos is useful in applications like automated surveillance, assisted living, human-computer interaction, content-based video retrieval, and video summarization. The ability to recognize atomic actions like “walking,” “bending,” and “falling” is critical for activity analysis when monitoring elderly people’s daily activities. Our paper presents a new promising solution for fall detection using vision-based approaches. In this approach, we analyse the human joint points which are the prime motion indicators. A set of keypoints of the subject are acquired by applying the AlphaPose pre-trained network. These keypoints are inferred to be the joint points of the subject. The acquired keypoints are processed through a framework of convolutional neural network (CNN) layers. Here, the spatial correlation of the keypoints is analysed. The long-term dependencies are then preserved with the help of long short-term memory (LSTM) architecture. Our system detects five types of falls and six types of daily living activities. We used the UP-FALL detection dataset for validating our fall detection system and achieved commendable results when compared to the state-of-the-art approaches. For comparison, we employed the OpenPose network for keypoint detection. It is inferred from the results that the AlphaPose network is more precise in keypoint detection.
About the research paper:
In this paper, the author proposes a vision-based system that is capable of detecting various types of falls accurately through video processing with the help of a machine learning approach.
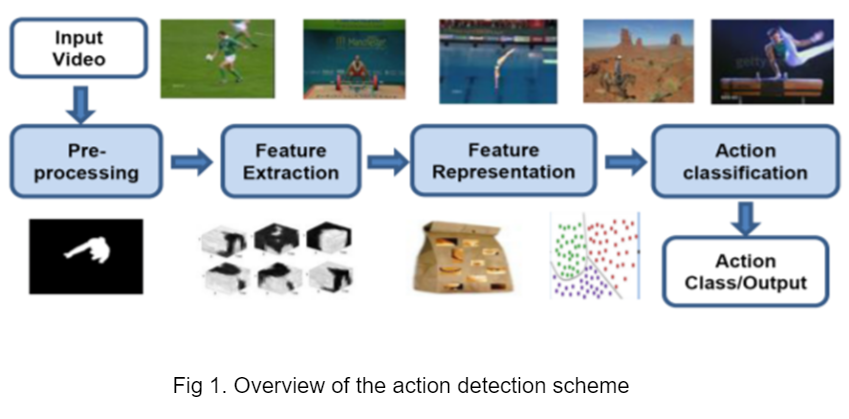
Implementation of the research:
The proposed scheme can be used to monitor the activity of elderly people and if any unusual falls happen, the information can be shared with caretakers to ensure emergency services.
- Published in CSE NEWS, Departmental News, News, Research News
Tenancy and Credit: Exploring Facts below the Crust in AP
 SRM University-AP is proud to announce that Dr Ghanshyam Kumar Pandey, Department of Economics, has received the prestigious NABARD (National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development) grant of Rs 14.85 lacs for a duration of 10 months of active research on “Tenancy and Credit: Exploring Facts below the Crust in AP”.
SRM University-AP is proud to announce that Dr Ghanshyam Kumar Pandey, Department of Economics, has received the prestigious NABARD (National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development) grant of Rs 14.85 lacs for a duration of 10 months of active research on “Tenancy and Credit: Exploring Facts below the Crust in AP”.
About the Research
The study will attempt to identify different possible sources of credit of agriculture households in the Guntur district of AP and then an analysis of the impact at the macro level will be carried out. The role of self-help groups and microfinance on agriculture and livelihood will be one important component of this analysis. Transaction cost, cascading effect, and loan waiver impact will be estimated across tenant and owner cultivators, and social groups.
The study will help to understand the improvement in the life of tenants due to the adoption of the ‘Model Tenancy Act’ and provide feedback on the Tenancy Certificate introduced in AP for enabling farmers to access bank/formal credit and whether the formation of JLGs has led to increase in the credit availability to tenants or not.
The project will help understand the sociological impact of economic decisions by the governance and help direct policies to more beneficial outcomes especially in terms of Tenancy and Credit.
- Published in Departmental News, Economics Current Happenings, Economics News, News
Molybdenum as the next-generation catalyst
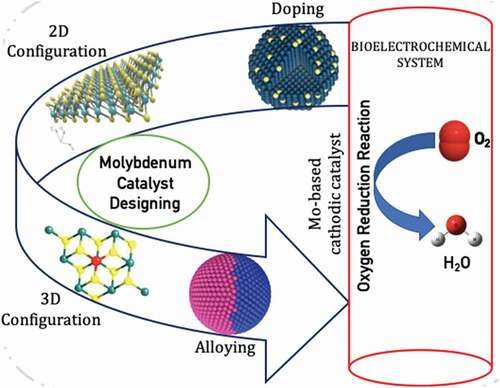 The Department of Environmental Science is proud to announce that Dr Lakhveer Singh has published his paper titled, “Progressions in cathodic catalysts for oxygen reduction and hydrogen evolution in bioelectrochemical systems: Molybdenum as the next-generation catalyst” in a prestigious journal Catalysis Review with a high Impact Factor of 20.21.
The Department of Environmental Science is proud to announce that Dr Lakhveer Singh has published his paper titled, “Progressions in cathodic catalysts for oxygen reduction and hydrogen evolution in bioelectrochemical systems: Molybdenum as the next-generation catalyst” in a prestigious journal Catalysis Review with a high Impact Factor of 20.21.
The article is published in collaboration with NCL Pune, Hong Kong Baptist University, and VITO-Flemish Institute for Technological Research, Belgium.
Abstract of the Research
Oxygen reduction reactions (ORR) are unanimously a key factor of system performances in bioelectrochemical systems (BESs), low-temperature fuel cells, and generally in several electro-chemical platforms. Platinum (Pt)-based catalyst is the finest electrocatalyst for ORR in BESs; however, it is constrained by its low abundance, high price, and poor catalytic durability in an electrochemical setup for cathodic reaction kinetics. Molybdenum (Mo) with its multi-dimensional form as 2D and 3D layers and synergistic combination with other non-metals offers prospects of extraordinary performance as a low-cost metal-based ORR catalyst over the Pt in delivering enhanced ORR potential.
About the Research
This article throws light on the current requirements of sturdier catalyst material and thus provides a comprehensive review of the continuing efforts in exploring the possibility of Mo as a low-cost metal-based ORR catalyst for sustainable energy production.
Mo-based catalysts have been now widely used for their applications in environmental and energy-based catalysis due to the low cost of Mo, high stability, and excellent activity.
In the future, Dr Lakhveer Singh and his collaborators are working on overcoming limitations to fabricate durable, stable, and catalytically active micro/nanoscale two-dimensional MoS2-based cathodes at an industrial scale, commercial bioelectrochemical devices can be obtainable in future.
- Published in Departmental News, ENVS News, News, Research News
Security Framework using Blockchain Technology
The Department of Computer Science Engineering is proud to announce that Dr Sriramulu Bojjagani has published a paper titled “Blockchain-Based Security Framework for Sharing Digital Images using Reversible Data Hiding and Encryption” in the journal Multimedia Tools and Applications (MTAP) having an impact factor of 2.757.
The paper is published in collaboration with D.R Denslin Brabin from the Department of Computer Science and Engineering, DMI College of Engineering, Tamil Nadu and Christo Ananth from the Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, St. Mother Theresa Engineering College, Tamil Nadu.
Abstract of the Research
Security is an important issue in current and next-generation networks. Blockchain will be an appropriate technology for securely sharing information in next-generation networks. Digital images are the prime medium attacked by cyber attackers. In this paper, a blockchain-based security framework is proposed for sharing digital images in a multi-user environment. The proposed framework uses reversible data hiding and encryption as component techniques. A novel high-capacity reversible data hiding scheme is also proposed to protect digital images. Reversible data hiding in combination with encryption protects the confidentiality, integrity and authentication of digital images. In the proposed technique, the digital image is compressed first to create room for data hiding, then the user signature is embedded; afterwards, the whole image is encrypted. For compression, JPEG lossy compression is used to create high capacity. For encryption, any symmetric block cipher or stream cipher can be used. Experimental results show that the proposed blockchain-based framework provides high security and the proposed reversible data hiding scheme provides high capacity and image quality.
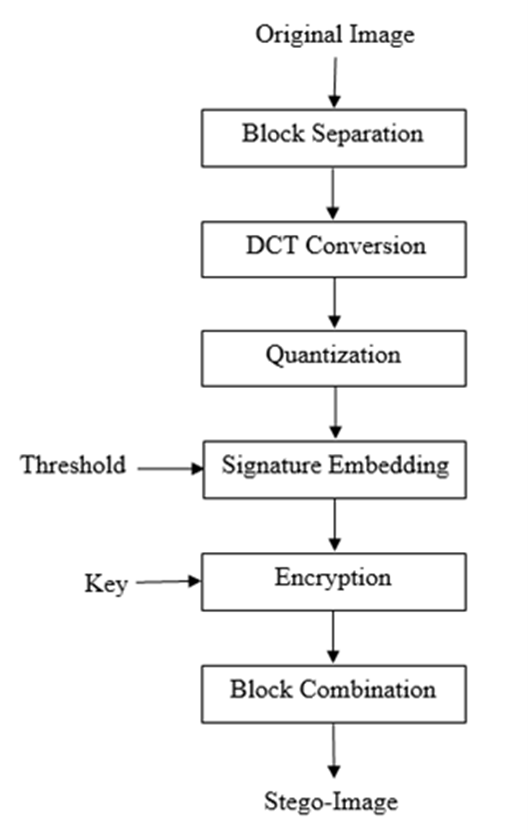
Fig 1: The process of encoding during reversible data hiding
Dr Sriramulu Bojjagani also intends to work on the development of block-chain based solutions to intelligent transport systems and on addressing the challenges of security issues involved in connected and autonomous vehicles.
- Published in CSE NEWS, Departmental News, News, Research News
Pursue Your Dream of Overseas Education with SRMAP
 Pursuing higher education in universities of international repute is perhaps a long-cherished dream of every student. SRM University-AP has always been at the forefront in providing the right avenues for students to explore their inherent talents and in equipping them with the right skillset through educational practices and research programmes of global standard.
Pursuing higher education in universities of international repute is perhaps a long-cherished dream of every student. SRM University-AP has always been at the forefront in providing the right avenues for students to explore their inherent talents and in equipping them with the right skillset through educational practices and research programmes of global standard.
It is an honour for SRM University-AP to announce that three of our students; Varanasi Koundinya, Sai Nived Chandanam and Jayanth Devarajugattu of the Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering have secured admission in the University of Texas at Dallas to the Master of Science in Computer Engineering programme for the Fall 2022 semester.
Exposure to state-of-the-art technological facilities and involvement in research-oriented pedagogical practices enable students to outperform in a world where technology is evolving at a rapid pace. Courses anchored in a multi-stream framework empower students to specialize across disciplines, thereby expanding their choice of higher studies in and outside the country.
In the words of Jayanth Devarajugattu, a strong collaboration of the university with international universities and industries across the globe have been of immense help to seize an opportunity for overseas education. He also marked his gratitude to the faculty members who have provided him with effective guidance throughout the research. “I am extremely grateful to Ramesh Vaddi sir, Siva Sankar sir, Anirban sir, Gangi Reddy sir for guiding us throughout the process by helping us choose the right university and issuing a letter of recommendation”, he said.
Associating with faculty members on various research projects will always offer new insights to students to think differently. “Dr Ranjit Thapa sir with his teaching and research work inspired me the most in pursuing my masters, I look up to him”, said Sai Nived.
All of them expressed their gratefulness to the university for endowing them with appropriate training which helped them maintain good grades, conduct research and publish papers. “Your CGPA and paper publications play a crucial role in making into an international university of your choice”, they mentioned.
The Inter-Disciplinary Experiential Active Learning (IDEAL) pioneered by SRM offers flexibility in course curriculum, thereby giving students the freedom of curating syllabus with respect to their interests and aspirations. Fostering an environment of academic freedom and prioritizing the interests of students in line with the demands of present times distinguish SRM University-AP as an emerging university of world-class standard. Working towards the dreams of students has always been the driving force behind the advancement of SRM University-AP.
- Published in Departmental News, ECE NEWS, International Relations, IR-News, News, Students Achievements
French Delegation in SRM University-AP discusses prospects of academic collaboration
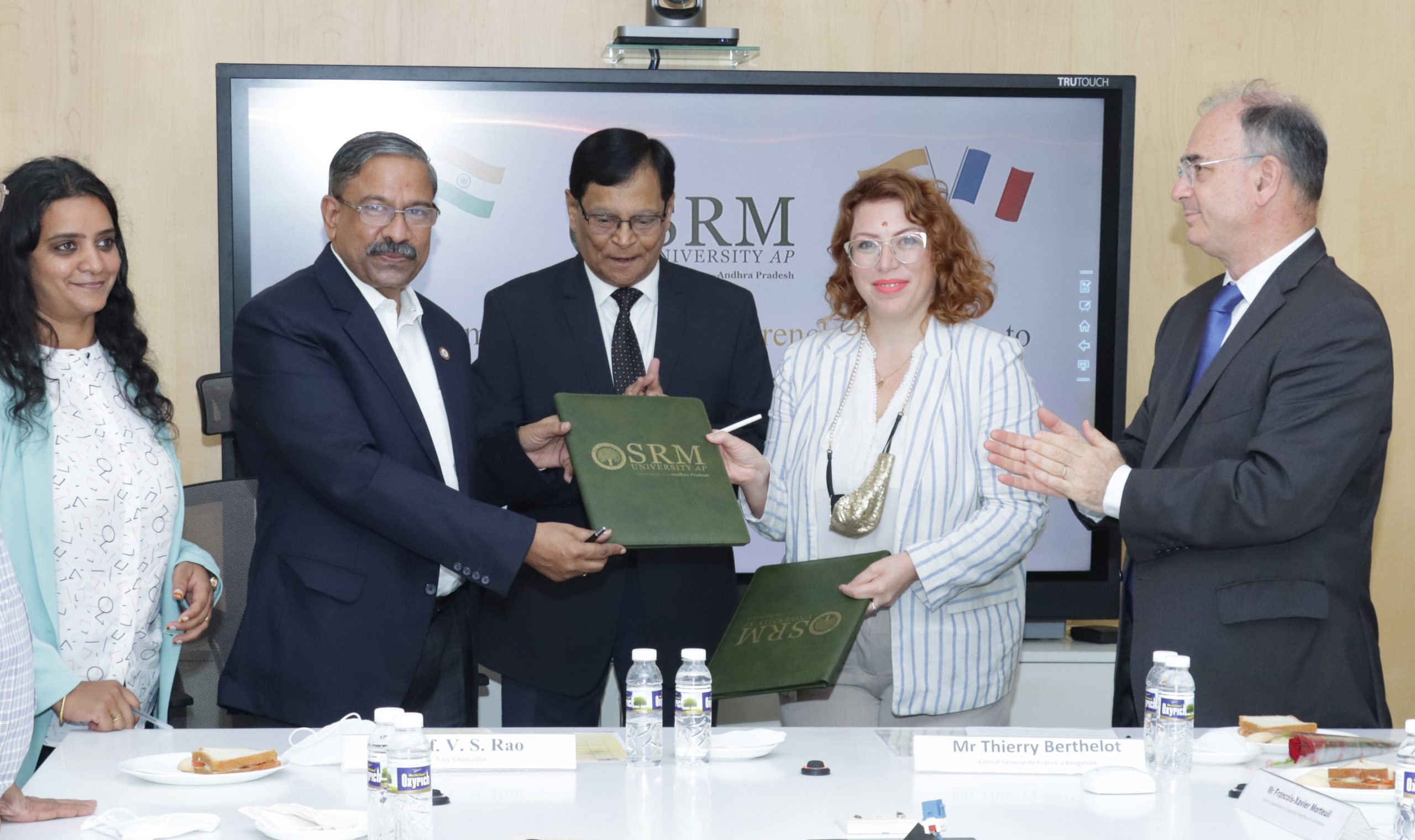 MoU inked with Rennes School of Business
MoU inked with Rennes School of Business
As part of an official visit to Andhra Pradesh, members of the French Delegation visited the SRM University-AP campus on Friday, 25 February 2022. An MoU has been signed between Rennes School of Business, France and SRM University-AP on student exchange, curriculum development, and articulation programmes. University Vice-Chancellor Prof V S Rao called the MoU “an important milestone for SRM AP” and welcomed students from France to India.
Mr Thierry Berthelot, Consul General de France a Bangalore, reaffirmed the MoU between India and France in the number and quality of student exchanges. “We have reached the aim of 10,000 Indian students by 2020; now, we look forward to increasing the number of Indian students in France significantly to 20,000 by 2025”, he added. The signing of the agreement for the mutual recognition of degrees will facilitate the pursuit of higher education by Indian students in France and French students in India and enhance their employability. The delegation emphasised that the collaboration with Rennes School of Business will further equip students of SRM University-AP to gain professional experience and job opportunities around the world. Mrs Maud LE BARS, South Asia Area Manager Rennes School of Business and Conseillere du Commerce Exterieur de la France, highlighted the student and faculty diversity in France that surpasses language barriers.
Consequently, Dr Naga Swetha Pasupuleti, Associate Director – International Relations and Higher Studies, talked about the strong partnerships SRM AP holds with QS ranked global universities and especially EFREI, France. The delegation interacted with the students and faculty members of SRM University-AP and discussed various possibilities of international internships and study abroad opportunities.
Mr Francois-Xavier Morteuil, Attache Consulaire pour la Coopération Scientifique et Universitaire; Mrs Ambika Anilkumar, Deputy to Attache Consulaire; Mrs Vasudha Murlikrishna, Campus France Manager Hyderabad; Mrs Vidya Suresh, Country Manager ESIGELEC (engineering school in France); and Mr Samuel Berthet, Director of Alliance Francaise of Hyderabad were part of the delegation and explored the university campus.
Pro-Vice-Chancellor Prof D Narayana Rao, Registrar Dr R Premkumar, Deans and Associate Deans of all schools were present in the discussion pertaining to the future scope of collaborations with French academic institutions.
- Published in Departmental News, International Relations, IR-News, News, Paari Current Happenings
SRM University-AP launches Aadigyan: To promote India’s cultural knowledge tradition
 Special invitees shower wishes to the initiative
Special invitees shower wishes to the initiative
Aadigyan, the flagship initiative of the International Relations and Higher Studies office at SRM University-AP, has been launched in a grand ceremony held at the auditorium in hybrid mode on February 26, 2022. Chief guest Shri G Kishan Reddy, Minister of Tourism, Culture, and Development of the North Eastern Region of India, shared the message that it is heartening to launch Aadigyan, which embarks the beginning of sharing Indian values, culture, heritage and art to a global level. “I wish Aadigyan a grand success and congratulate SRM University-AP for providing this wonderful opportunity to the world”, he added.
Prof V S Rao, the Vice-Chancellor, launched the promo video of Aadigyan and remarked that Aadigyan aims to integrate education with the art and culture of India. Dr Naga Swetha Pasupuleti, Associate Director – International Relations and Higher Studies, introduced the partnering institutions- ISKCON; The Art of Living; The Temple Dance; Nrityanjali; Isha Foundation; Rajyoga Education & Research Foundation, Brahma Kumaris; and Vivekananda Institute of Human Excellence, Ramakrishna Math, Hyderabad.
Introducing the Project Samskriti to the students of SRM AP, Smt Radhe Jaggi from Isha Foundation highlighted the need to nurture, conserve, and expose the majesty of traditional Indian arts when these art forms are being practised as hobbies.
As an alumnus of SRM, Shri Radheshyam Das, Founding Director of VOICE (Vedic Oasis for Inspiration Culture and Education), and President of ISKCON, Pune, appreciated the efforts of SRM AP to gear education towards human-making rather than money-making.
“Dance goes beyond the realm of physical reality. Indian dance forms are widely used for therapeutic purposes” highlighted Prateeksha Kashi, Indian Kuchipudi Dancer & Actress. Smt. Himansee Katragadda, Founder – The Temple Dance, further shared her happiness to offer Kuchipudi dance courses to the students of SRM AP.
Smt. BK Shivani, renowned Motivational Speaker & Spiritual Teacher from Brahma Kumaris elucidated the need for living in the fundamental equations of life. Brahma Kumaris will be offering courses on value education and holistic health as a part of Aadigyan.
“Let us not forget the identity and dignity of our own culture and traditions”, said Dr Tushar Guha, Founder & Chairman, Nrityanjali Group, while expressing his pleasure to partner with SRM AP. “Diversity is the basis of existence, and India celebrates diversity”, added Shri. Rajeev Nambiar, Director – Institutional Programs/National Teachers Coordination, The Art of Living.
Other special invitees who graced the virtual ceremony with their inspiring words include Dr Rewant Vikram Singh, Diplomat – High Commission of India, Srilanka; Ms Goli Gabby, Health and Wellness Coach and Educator; Swami Bodhamayananda, R K Math; and Ms Jennifer Mawulolo Ami Ametewee First Secretary – Trade, Tourism & Culture Officer High Commission of India, Ghana.
The event witnessed several cultural performances by the students of SRM University-AP. Ms Revathi Balakrishnan, Assistant Director- Student Affairs, thanked all the distinguished invitees and audience who joined the virtual inaugural ceremony of Aadigyan.
- Published in Departmental News, International Relations, IR-News, News
AI to boost up the performance of bioelectrochemical systems
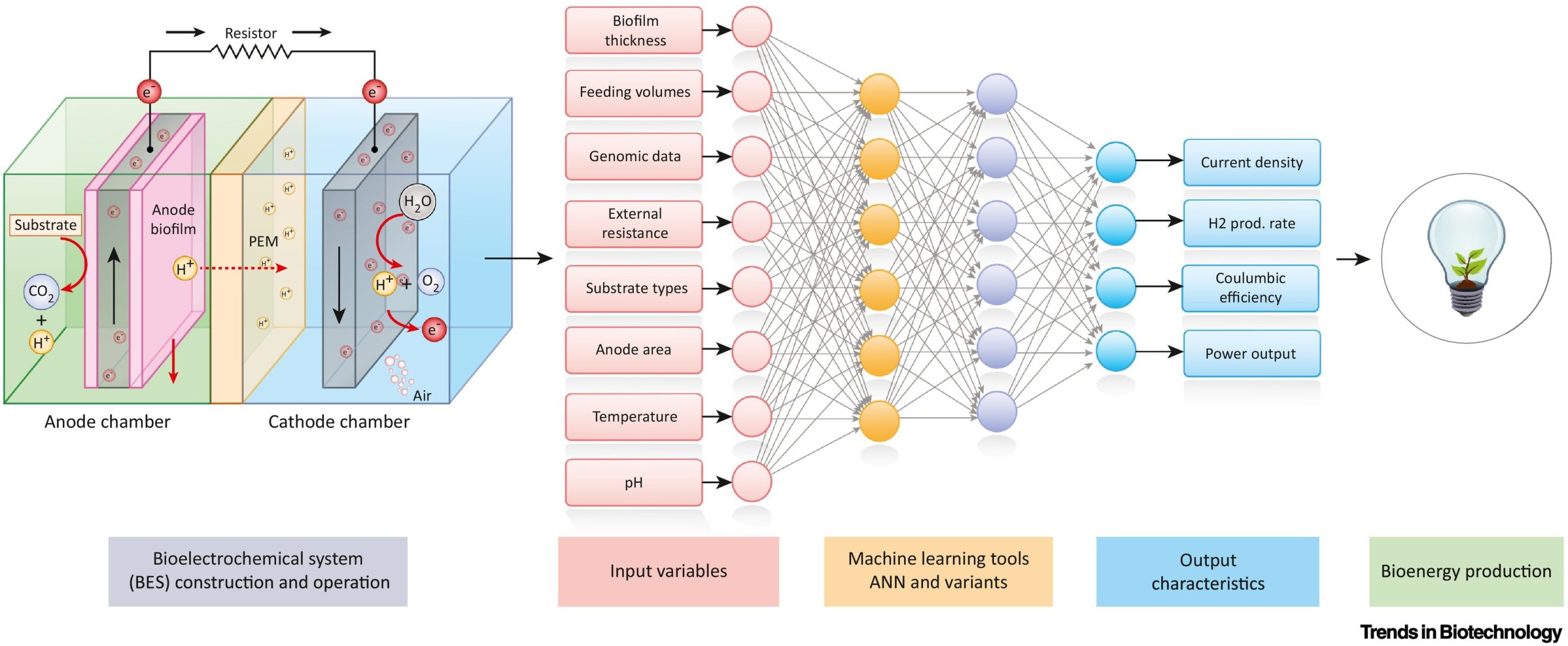
The Department of Environmental Science is glad to announce that Dr Lakhveer Singh has published his paper titled, “Leveraging artificial intelligence in bioelectrochemical systems” in a prestigious journal Trends in Biotechnology with a high Impact Factor of 19.53.
The paper was published in collaboration with Baptist University, Hong Kong and Oregon State University, USA.
Abstract of the Research
Bioelectrochemical systems (BESs) are highly evolved and sophisticated systems that produce bioenergy via exoelectrogenic microbes. Artificial intelligence (AI) helps to understand, relate, model, and predict both process parameters and microbial diversity, resulting in higher performance. This approach has revolutionised BESs through highly advanced computational algorithms that best suit the systems’ architecture for suitable fuel production.
About the Research
The performance of the microbial reactors primarily depends on the activity of the biocatalysts, indirectly governed by the microbial community structure and function. In this context, microbial dynamics are crucial for performance consistency and are sensitive to both biotic and abiotic stress in the reactor. To address this, a comprehensive, mechanistic understanding of the community dynamics is essential. Understanding the metabolic and electrochemical potentials would provide a basis for the selection and control of efficient communities with ramped metabolic flux and boosted electrogenic activity. The research will help in the development of an improved system for green fuel production.
According to Dr Lakhveer Singh and his collaborators, Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs) and Adaptive Neuro-fuzzy Systems (ANFISs), backed with iterative and backpropagation abilities, can be applied to Microbial Fuel Cells (MFCs) with improved computational models. This will eventually provide a breakthrough in operational and translational research predicting newer parameters, such as predictions of the emergence of substrate-specific microbial communities in biosensors or bioreactors. They intend to work on this in future.
- Published in Departmental News, ENVS News, News, Research News

