The Department of Environmental Science is glad to announce that Dr Lakhveer Singh has published his paper titled, “Leveraging artificial intelligence in bioelectrochemical systems” in a prestigious journal Trends in Biotechnology with a high Impact Factor of 19.53.
The paper was published in collaboration with Baptist University, Hong Kong and Oregon State University, USA.
Abstract of the Research
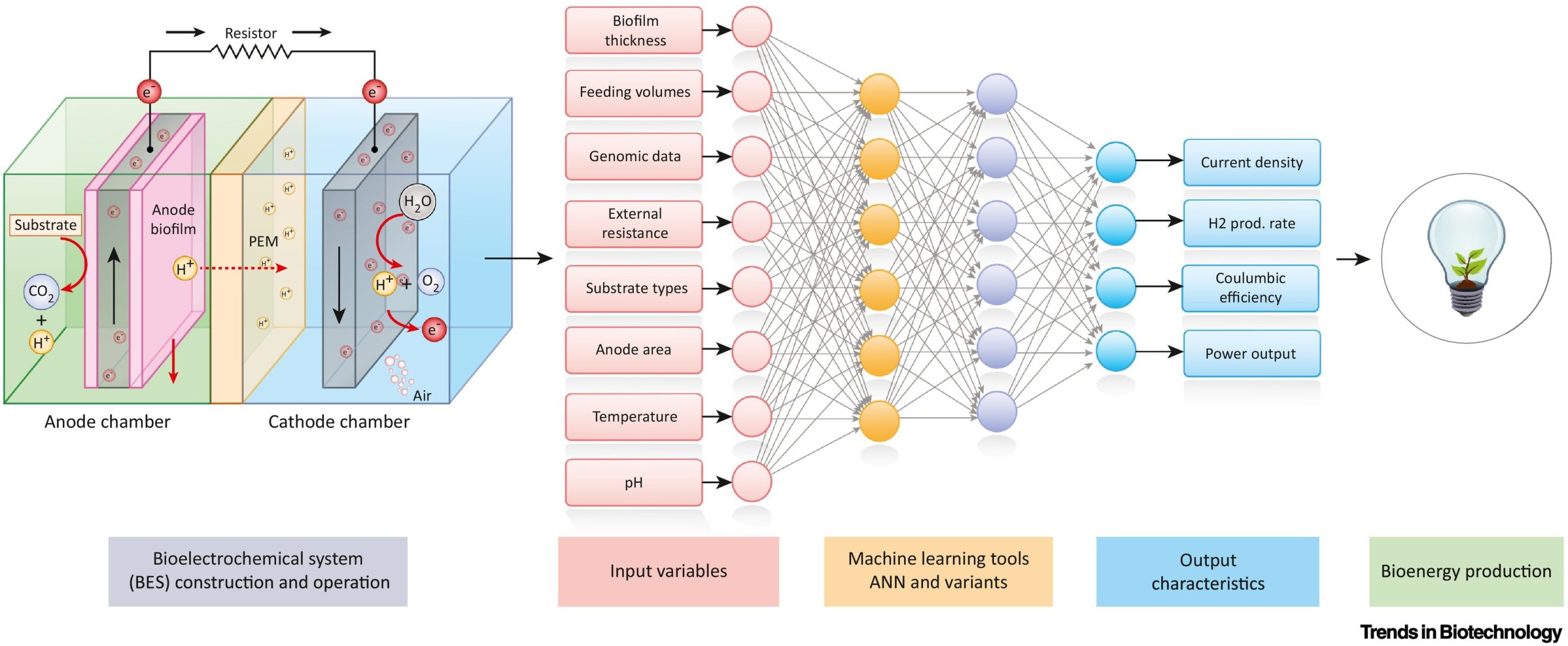
Bioelectrochemical systems (BESs) are highly evolved and sophisticated systems that produce bioenergy via exoelectrogenic microbes. Artificial intelligence (AI) helps to understand, relate, model, and predict both process parameters and microbial diversity, resulting in higher performance. This approach has revolutionised BESs through highly advanced computational algorithms that best suit the systems’ architecture for suitable fuel production.
About the Research
The performance of the microbial reactors primarily depends on the activity of the biocatalysts, indirectly governed by the microbial community structure and function. In this context, microbial dynamics are crucial for performance consistency and are sensitive to both biotic and abiotic stress in the reactor. To address this, a comprehensive, mechanistic understanding of the community dynamics is essential. Understanding the metabolic and electrochemical potentials would provide a basis for the selection and control of efficient communities with ramped metabolic flux and boosted electrogenic activity. The research will help in the development of an improved system for green fuel production.
According to Dr Lakhveer Singh and his collaborators, Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs) and Adaptive Neuro-fuzzy Systems (ANFISs), backed with iterative and backpropagation abilities, can be applied to Microbial Fuel Cells (MFCs) with improved computational models. This will eventually provide a breakthrough in operational and translational research predicting newer parameters, such as predictions of the emergence of substrate-specific microbial communities in biosensors or bioreactors. They intend to work on this in future.

