The Department of Environmental Science is glad to announce that Assistant Professor Dr Pankaj Pathak and her PhD Scholar Mr Gopa Nandikesh have published an article titled “Occurrence, environmental risks and biological remediation mechanisms of Triclosan in wastewaters: Challenges and perspectives” in the Journal of Water Process Engineering having an Impact Factor 7.34. The paper was published in collaboration with Dr Lakhveer Singh, Sardar Patel University, Himachal Pradesh.
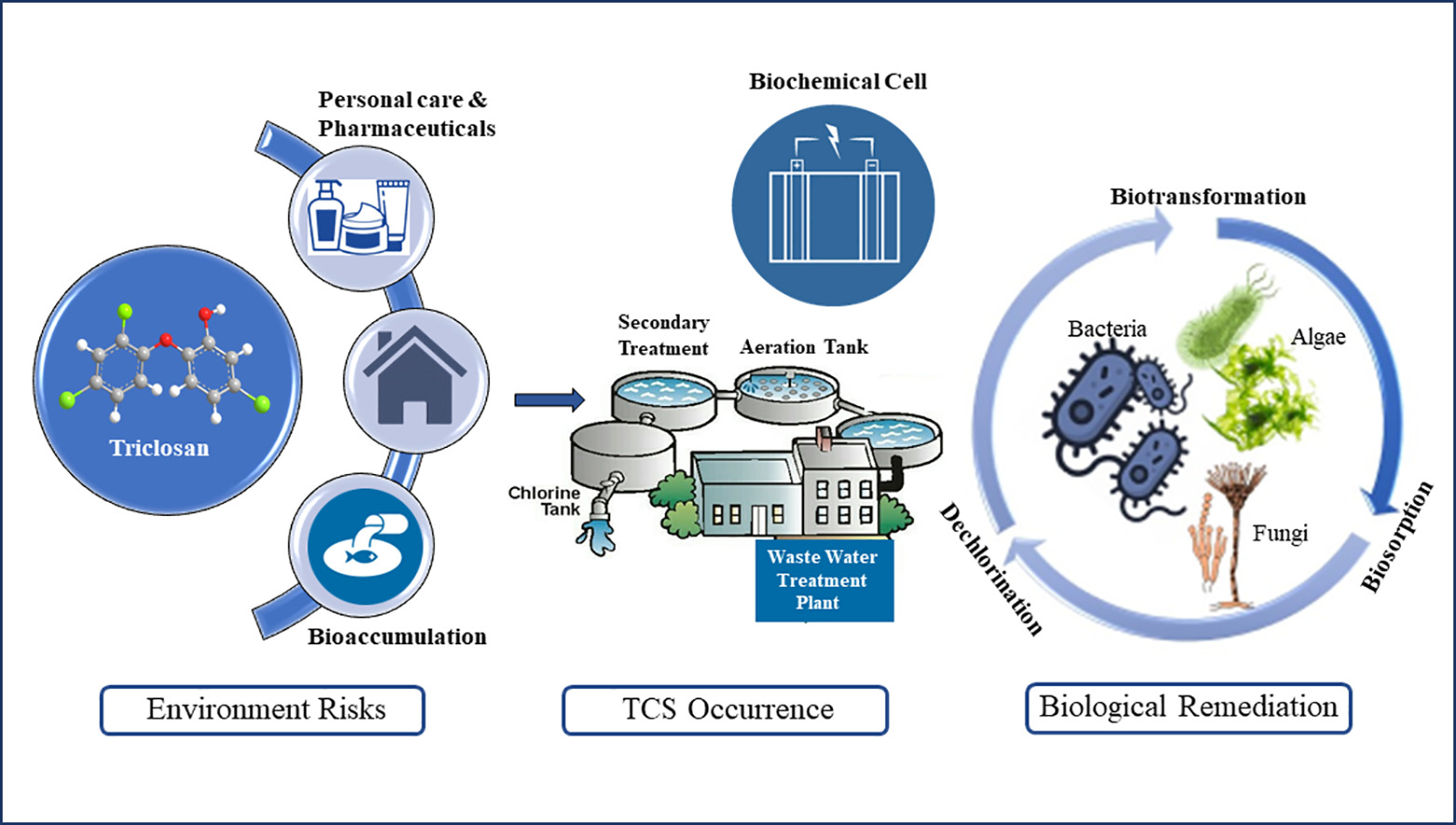
The paper makes a comprehensive understanding of the disadvantages and consequences associated with the excessive use of Triclosan (TCS), an anti-microbial agent widely used in pharmaceutical and personal care products (PPCPs). The article also suggests various ways to achieve the bioremediation of Triclosan using microbial degraders and the different challenges associated with such practices.
The extensive use of TCS in PPCPs has increased over the past few decades, and its sizeable production and consumption are causing adverse effects on the environment and humans. TCS has been made into the list of emerging micropollutants (EMPs) due to its omnipresence in water resources and even in biological samples such as urine and breast milk. Therefore, it is imperative not only to understand the current status of TCS pollution but their occurrence, exposure routes, and environmental risks to identify remediation technologies for mitigating TCS.
Their research targets to provide cumulative data on the abundance of emerging TCS in water resources and its associated health burdens simultaneously. It is identified that TCS remediation can be achieved through advanced physical and chemical methods such as enzyme oxidation and ozonation. However, there are drawbacks such as high energy consumption and the formation of toxic by-products.
The article endeavours to provide an in-depth understanding of the biological remediation of TCS by microbial degraders as well as its superiority over other remediation techniques. Insights into the various microbial communities such as bacteria, algae, and fungi and their unique bioremediation mechanisms are comprehensively summarised. Moreover, challenges associated with existing bioremediation methods and future perspectives are also discussed in the present work.

