Dr Debajyoti Kundu, from the Department of Environmental Science and Engineering, has conducted pioneering research on the composition of bio-earth recovered from landfill mining at the Bhandewadi landfill in Nagpur, India. His study, Unveiling the Composition of Bio-Earth from Landfill Mining and Microplastic Pollution, reveals the presence of microplastics in bio-earth, raising concerns about its safety for agricultural use. The research underscores the importance of addressing microplastic contamination to ensure the sustainable application of landfill-mined materials in agriculture.
Dr Debajyoti Kundu, from the Department of Environmental Science and Engineering, has conducted pioneering research on the composition of bio-earth recovered from landfill mining at the Bhandewadi landfill in Nagpur, India. His study, Unveiling the Composition of Bio-Earth from Landfill Mining and Microplastic Pollution, reveals the presence of microplastics in bio-earth, raising concerns about its safety for agricultural use. The research underscores the importance of addressing microplastic contamination to ensure the sustainable application of landfill-mined materials in agriculture.
A Brief Abstract:
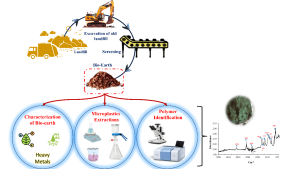
This study explores the composition of bio-earth derived from landfill mining at the Bhandewadi landfill, Nagpur, India, and investigates the presence of microplastics within it. The bio-earth was characterized by key parameters such as moisture content, organic carbon, nutrient levels, and heavy metal concentrations. Microplastic contamination was also assessed using ATR-FTIR spectroscopy, revealing a significant presence of microplastics in the bio-earth. The findings highlight the need for further research and strategies to mitigate microplastic pollution to ensure the safe use of bio-earth in agricultural applications.
Explanation in layperson’s terms:
In this study, we looked at bio-earth, which is a material recovered from old landfill sites, and examined its quality and the presence of harmful microplastics. Landfill mining is an emerging technique that helps recover valuable resources from old waste. Bio-earth is often used as a natural fertilizer, but the problem is that it can contain tiny plastic particles (microplastics) which can harm the environment. Our research found that the bio-earth from a landfill in Nagpur, India, had both useful nutrients for plants and significant levels of microplastics. This is concerning because it could affect the safety of using such material in farming or gardening. Our work suggests that more research is needed to figure out how to remove these plastics and make the bio-earth safer for agricultural use.
Practical Implementation:
The findings of this research have significant implications for environmental management and waste recycling. The presence of microplastics in bio-earth poses risks to soil health, plant growth, and potentially to human health when used in agriculture. The research highlights the need for proper waste management techniques to reduce microplastic contamination and improve the safety of recycled materials like bio-earth. This study also calls for developing strategies to remove or reduce microplastics from landfill mining processes, ensuring that bio-earth can be used safely as a fertilizer or soil conditioner without further environmental harm.
Collaborations:
This research was conducted through collaboration between several esteemed institutions:
CSIR – National Environmental Engineering Research Institute (CSIR-NEERI), Nagpur, India
Banaras Hindu University (BHU), Varanasi, India
Future Research Plans:
We plan to develop methods for removing microplastics from bio-earth, assess their impact on soil and plant health, and explore sustainable waste processing techniques to reduce plastic contamination. Our goal is to enhance the safety and sustainability of landfill-mined materials in agriculture.
The link to the article:
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10661-024-13229-2