
Dr Debajyoti Kundu, Assistant Professor, Department of Environmental Science and Engineering, has conducted an impactful study on developing polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA), an eco-friendly solution that can help reduce plastic waste and make food packaging more sustainable. His recent paper “Advancements in microbial production of polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA) from wastes for sustainable active food packaging: An eclectic review”, published in the Q1 journal Biocatalysis and Agricultural Biotechnology, Dr Debajyoti investigates how microorganisms can convert waste into a special type of plastic called PHA, which can be used for food packaging.
Unlike regular plastics, PHA is biodegradable and safe for both the environment and human health. The study reviews recent innovations in making PHA stronger and more effective for packaging, including its ability to prevent food spoilage and improve food safety.
Abstract
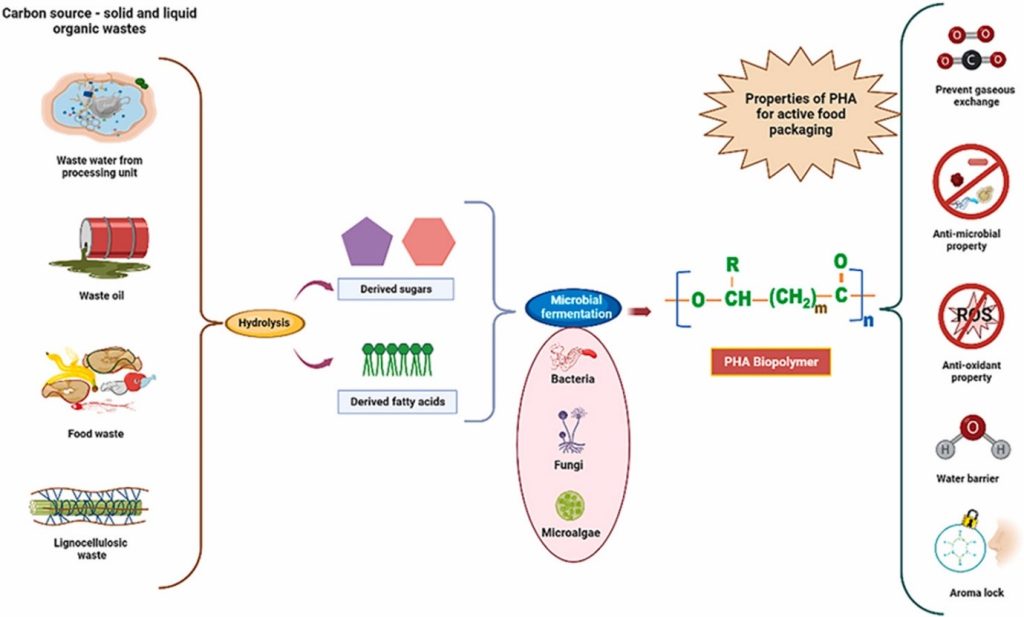
This study explores advancements in microbial production of polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA) from waste resources for sustainable active food packaging. It highlights the eco-friendly nature of PHAs as bioplastics and their potential to replace synthetic plastics in food packaging. The paper discusses recent technological improvements in PHA production and formulations, focusing on enhancing material properties to make PHA a viable alternative. It also examines trends in active packaging, including antimicrobial, antioxidant properties, and spoilage indicators, which can significantly improve food safety and quality.
Practical Implementation/ Social Implications of the Research
The practical implementation of this research involves using PHA-based materials for food packaging to replace conventional plastics. This can lead to reduced environmental pollution due to PHA’s biodegradability and lower reliance on fossil fuels. Social implications include improved food safety through active packaging features like antimicrobial and antioxidant properties, potentially reducing foodborne illnesses and extending shelf life. Additionally, using waste to produce PHA promotes waste recycling and resource efficiency.
Collaborations
This research is a collaborative effort among various prestigious institutions including St. Joseph’s University, SRM Institute of Science and Technology, Gurudas College, and SRM University-AP.
Moving forward, Dr Debajyoti will continue to work on improving the production processes and formulations of PHA to enhance its mechanical properties and cost-effectiveness. Additionally, he will explore new waste sources for PHA production and develop advanced active packaging technologies, such as smart packaging with sensors for real-time monitoring of food quality. Collaborations with industry partners to scale up production and test real-world applications of PHA-based packaging are another key focus.

