Dr Vimal Babu, Associate Professor in the Department of Management along with his PhD scholar Ms Rukma R, have co-authored a research paper titled “Enhancement of New Random Forest Algorithm to Predict the Employee Attrition Rate.” Published in the International Journal of Enterprise Network Management (ABDC-B), the paper also includes contributions from Dr Vijaya Prabhagar M, Assistant Professor at IIM Jammu.
Their work focuses on improving machine learning techniques to better predict employee attrition, that is, the employees who are likely to leave the organisation. The study focuses on the impact of HR analytics adoption by applying algorithms to predict employee attrition. It uses the Random Forest algorithm to identify reasons for attrition. However, this algorithm can be slow due to the large number of decision trees it uses. To improve it, the study proposes a new method that selects the best decision trees using a technique called fractional factorial design, which outperforms all others in predicting employee attrition.
Abstract
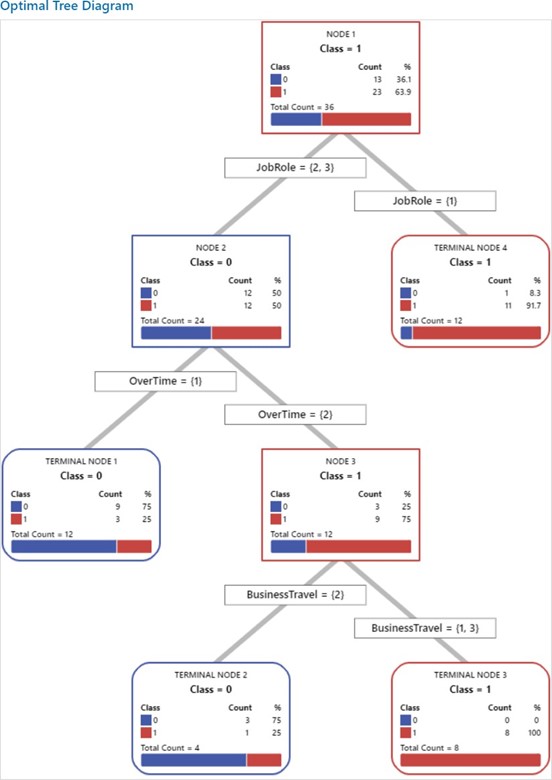
The problem of employee attrition in every organisation concerns the employee turnover ratio, thereby increasing the cost of investment in human resources. Various factors are reasonable for the rapid attritions at different phases. The purpose of the current study is to predict the employees who are likely to leave the organization. The factors that lead to attrition are identified using the Random Forest algorithm. The Random Forest algorithm is a widely used supervised machine-learning technique for classification and prediction. However, the random forest algorithm has certain issue like it is too slow and ineffective for real time predictions. i.e., the large number of trees can make the algorithm, which results in a slower model. Therefore, the study proposes, a new alternative for choosing the appropriate decision trees based on the concept of fractional factorial design of experiments. The different performance criteria were compared across the modified random forest algorithm, existing random forest algorithm, Support Vector Machine (SVM), Logistic Regression (LR), Navie Bayes (NB), K – Nearest Neighbour (K-NN), Decision Tree, XG Boost tree and Neural Network (NN). It was found that the modified random forest algorithm excelled in all criteria and performed better than the existing ones.
Practical Implementation/Social Implications of the Research
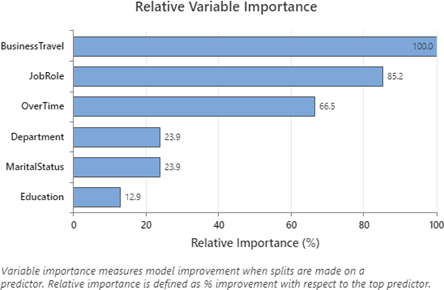
Practical implication: It emphasises the importance of focusing on factors like Business Travel, Job Role, Over Time, Department, Marital Status, and Education to reduce employee attrition. Organisations should design retention programs that support frequent travellers, manage overtime effectively, and address specific departmental needs. Tailoring job roles, promoting work-life balance through flexible hours, and providing educational opportunities are key strategies for enhancing employee satisfaction and retention.
Social Implication: The measures of this study can transform work culture into a more supportive and inclusive environment, promote gender equality by supporting employees with family responsibilities, and contribute to economic stability through reduced attrition. By investing in employee well-being, organizations can also strengthen their community engagement and corporate social responsibility initiatives for both employees and the broader society.
Future Research Plans
Future research could explore other factors influencing employee attrition, such as organizational culture, leadership style, and employee engagement. Longitudinal studies could track changes over time to understand the long-term effects on attrition rates. Additionally, investigating the interplay between identified factors, such as how Job Role and Over Time influence attrition, could provide deeper insights. Expanding the study across different industries and locations may reveal specific trends, allowing for tailored retention strategies. Lastly, incorporating qualitative methods like interviews and focus groups could offer a richer understanding of employees’ experiences and perceptions, complementing the quantitative findings.