Cutting-Edge Research by Dr Chinnadurai Elevates MIMO Wireless Communication Standards

A Survey on Resource Allocation and Energy Efficient Maximization for IRS-Aided MIMO Wireless Communication
In a significant advancement for wireless communication technology, Dr Sunil Chinnadurai, Associate Professor in the Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering, has made a remarkable contribution to the field. His latest paper, titled “A Survey on Resource Allocation and Energy Efficient Maximization for IRS-Aided MIMO Wireless Communication,” has been published in the prestigious journal IEEE Access.
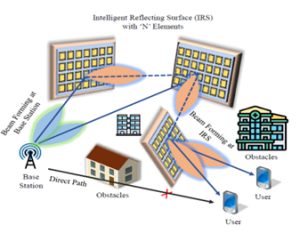
The paper delves into the intricacies of Intelligent Reflecting Surfaces (IRS) and their role in enhancing Multiple Input Multiple Output (MIMO) wireless communication systems. Dr. Chinnadurai’s research focuses on optimizing resource allocation and maximizing energy efficiency, which is a critical aspect of sustainable technological development.
This publication is expected to pave the way for more efficient and environmentally friendly wireless communication solutions, reflecting Dr Chinnadurai’s commitment to innovation and excellence in research.
Abstract of the Research
This paper surveys the integration of Multiple-Input Multiple-Output (MIMO) systems with Intelligent Reflecting Surfaces (IRS) in wireless communications. It explores how IRS technology enhances MIMO performance by manipulating the propagation environment through improved signal manipulation and beamforming. The survey covers resource allocation, energy efficiency techniques, optimization strategies, and practical implementation challenges. Key research areas and future directions are highlighted, emphasizing the potential of MIMO-enabled IRS systems to enhance wireless communication efficiency and coverage significantly.
Explanation of the Research in Layperson’s Terms
This paper explores how two advanced technologies, MIMO and IRS, can improve wireless communications. MIMO uses multiple antennas to enhance data transmission, while IRS involves smart surfaces that direct signal paths to boost strength and coverage. By combining these technologies, the paper examines how to make wireless networks faster, more reliable, and energy-efficient. It discusses practical ways to implement these improvements and identifies challenges and future research areas to make these advancements widely usable. In essence, this combination promises better wireless connectivity for everyone.
Practical Implementation or the Social Implications Associated with the Research
Integrating MIMO and IRS technologies into wireless networks can significantly enhance network performance, especially in urban and rural areas. Telecommunications companies can install IRS panels on structures to boost signal strength and coverage, while smart homes and cities can benefit from improved IoT connectivity and energy management. This combination also promotes energy-efficient networks, reducing operational costs and environmental impact. Socially, this technology can bridge the digital divide, providing better internet access to underserved areas and enhancing education, healthcare, and economic development. It supports new business models and innovations, leading to job creation and economic growth. Improved connectivity enhances quality of life through better access to information, entertainment, and remote work opportunities. Additionally, it strengthens public safety by improving communication during emergencies. Combining MIMO and IRS technologies promises a more connected, efficient, and sustainable world.
Pictures Related to the Research:
Future Research Plans
Future research on MIMO and IRS integration should focus on advanced optimisation for resource allocation and energy efficiency, innovative beamforming strategies, practical deployment challenges, and robust security protocols. Enhancing energy efficiency and contributing to standardization and regulation is also critical. These efforts will unlock the full potential of MIMO and IRS, leading to more efficient, reliable, and secure wireless communication systems.
- Published in Departmental News, ECE NEWS, News, Research News
From Views to Votes: Faculty Duo Unveils Political Activism on YouTube
 In a significant contribution to the field of politics, Dr Vineeth Thomas and Dr Chandana Deka, Assistant Professors in the Department of Political Science, have published an insightful paper titled “Political Influencer in Indian Democracy” in the esteemed Journal Economic and Political Weekly. Their work delves into the burgeoning role of YouTube as a platform for political engagement, highlighting a shift in the digital landscape where entertainment and politics intersect.
In a significant contribution to the field of politics, Dr Vineeth Thomas and Dr Chandana Deka, Assistant Professors in the Department of Political Science, have published an insightful paper titled “Political Influencer in Indian Democracy” in the esteemed Journal Economic and Political Weekly. Their work delves into the burgeoning role of YouTube as a platform for political engagement, highlighting a shift in the digital landscape where entertainment and politics intersect.
The paper explores the emergence of a new breed of political influencers who are leveraging the power of social media activism to shape public discourse. This pioneering study offers a fresh perspective on the dynamics of political communication in the age of digital media.
Abstract
In the YouTube landscape dominated by entertainment, Dhruv Rathee emerges as a prominent voice in political discourse and social media activism. His casual demeanour belies his impactful mission to mobilise Indians against perceived authoritarianism under the Modi government. Rathee’s journey began in 2016, focusing initially on educational content before delving into political commentary. His videos, known for their thorough research and straightforward presentation, address issues like governance, free speech, and electoral fraud. Despite criticisms of superficiality in his economic analyses, Rathee’s engaging style and significant social media influence highlight the transformative power of digital platforms in shaping public discourse. While YouTube journalism thrives on engagement and immediacy, traditional media’s depth and editorial rigor ensure its continued relevance in the media ecosystem.
Explanation of the Research in Layperson’s terms
Dhruv Rathee, a prominent YouTuber, has made a significant impact in the realm of political discourse and social media activism in India. Starting his journey around 2016, Rathee transitioned from creating educational content to addressing political issues, driven by his dissatisfaction with Prime Minister Narendra Modi’s administration. His videos are characterized by meticulous research and straightforward presentation, covering a wide range of topics such as governance, free speech, electoral fraud, and media bias. Rathee’s engaging style, which blends factual rigor with a conversational tone, has enabled him to connect with a broad audience, making complex political issues accessible to the layperson.
Despite criticisms of his sometimes superficial understanding of economic issues, Rathee’s ability to mobilise large audiences and his significant social media presence underscore the transformative potential of digital platforms in shaping public discourse. However, YouTube journalism, which often centers around individual personalities, can lack the depth and breadth of traditional journalism, emphasizing engagement and immediacy over comprehensive coverage.
In Traditional media, with its extensive resources, editorial rigor, and established trust, continues to play a vital role in the media landscape. Although mainstream media has faced criticism for spreading misinformation and manipulating public discourse, its structured approach to news remains indispensable. Both YouTube and traditional media have their strengths and limitations, highlighting the need for a balanced approach to news consumption from multiple sources to ensure a well-rounded understanding of current events.
Practical Implementation or the Social Implications Associated
The practical implementation of this research emphasises the necessity for a balanced approach to news consumption, combining insights from both YouTube influencers and traditional media to foster informed public discourse and preserve democratic values.
Collaborations
Electoral Politics
Future Research Plans
Indian govt and politics
- Published in Departmental News, News, Political Science News, Research News
Founder Chancellor Meets the Honourable CM of Andhra Pradesh

SRM University-AP Founder Chancellor Dr T R Paarivendhar and Pro-Chancellor Dr P Sathyanarayanan met with the Honourable Chief Minister of Andhra Pradesh, Shri Nara Chandrababu Naidu, to extend their congratulations on his fourth tenure as the head of the state government. Upon assuming the office as the Chief Minister after his landslide victory, Shri Chandrababu Naidu generously welcomed the institution leaders with the assurance and support for the university’s development and the provision of necessary facilities.
Founder Chancellor Dr T R Paarivendhar remarked, “Shri Chandrababu Naidu is a visionary leader with an ambitious dream to revitalise the governance, economy, and businesses in the capital city of Amaravati. As the first educational institute to plant roots in Amaravati soil, we confidently look forward to the cordial support in developing SRM University-AP into a world-class university.”
Pro-Chancellor of SRM University-AP, Dr P Sathyanarayanan, congratulated the veteran leader on his political triumph and conveyed his best for his successful tenure. He said, “With Shri Chandrababu Naidu, an exemplary commander at the apex of the state, Andhra Pradesh is set to transcend the frontiers of socio-economic development. SRM University-AP as an academic university will flourish with the development of Andhra Pradesh.”
SRM University-AP was established in the year 2017 when Shri Chandrababu Naidu was presiding as the Chief Minister of the State. Currently housing the School of Engineering and Sciences, Easwari School of Liberal Arts and Paari School of Business, the university has a visionary plan to extend its campus to include a law school, medical school and other emerging schools and programmes. Shri Chandrababu Naidu-led state support will propel the progress of the varsity, helping to provide quality education, employment and academic capital to the ground roots of Andhra Pradesh.
- Published in News
Navigating the Future: Advancements in NLP for Enhanced Healthcare
 In a significant contribution to the intersection of technology and healthcare, Dr V M Manikandan, Assistant Professor in the Department of Computer Science and Engineering along with a team of dedicated undergraduate students, has co-authored a pivotal book chapter. The chapter, titled “Advancements and Challenges of Using Natural Language Processing in the Healthcare Sector,” has been published in the insightful book “Digital Transformation in Healthcare 5.0.”
In a significant contribution to the intersection of technology and healthcare, Dr V M Manikandan, Assistant Professor in the Department of Computer Science and Engineering along with a team of dedicated undergraduate students, has co-authored a pivotal book chapter. The chapter, titled “Advancements and Challenges of Using Natural Language Processing in the Healthcare Sector,” has been published in the insightful book “Digital Transformation in Healthcare 5.0.”
The collaborative effort by Dr Manikandan, Mr Shasank Kamineni, Ms Meghana Tummala, Ms Sai Yasheswini Kandimalla, and Mr Tejodbhav Koduru delves into the innovative applications and potential hurdles of implementing natural language processing (NLP) technologies in healthcare. Their work highlights the transformative power of NLP in analysing vast amounts of unstructured clinical data, thereby enhancing patient care and medical research.
This academic achievement showcases the expertise and commitment of the faculty and students and underscores the institution’s role in driving forward the digital revolution in healthcare. The chapter is expected to serve as a valuable resource for researchers, practitioners, and policymakers interested in developing smarter, more efficient healthcare systems.
Introduction of the Book Chapter
“Digital Transformation in Healthcare 5.0: IoT, AI, and Digital Twin” delves into how advanced technologies like IoT, AI, and digital twins are reshaping healthcare. It provides a comprehensive look at the integration challenges and technological advancements aiming to modernise medical practices. The chapter “Advancements and Challenges of Using Natural Language Processing in the Healthcare Sector” specifically explores how NLP processes vast data in healthcare to transform it into actionable insights, enhancing efficiency and patient care while highlighting the implementation challenges of these technologies. This book is crucial for healthcare and technology professionals interested in the future of digitally enhanced healthcare.
Significance of the Book Chapter
The chapter “Advancements and Challenges of Using Natural Language Processing in the Healthcare Sector” is significant because it encapsulates my interest and expertise in harnessing NLP to enhance healthcare operations. It showcases the potential of technology in transforming healthcare data into valuable, actionable insights, directly aligning with my focus on improving patient outcomes through technological innovation.
- Published in Computer Science News, CSE NEWS, Departmental News, News, Research News