Ajay Sugandh secures admission to IIM Ranchi
 For Ajay Sugandh, securing admission to one of the prestigious Indian Institutes of Management (IIM) is a dream come true. Clearing the Common Admission Test (CAT) with a percentile of 90, he has bagged an admission offer at IIM, Ranchi. CAT is a national-level computer-based management entrance examination to reputed IIMs. More than 2 lakh candidates appear for the test and a few with a percentile of 90-99 secure a position on one of the IIM campuses.
For Ajay Sugandh, securing admission to one of the prestigious Indian Institutes of Management (IIM) is a dream come true. Clearing the Common Admission Test (CAT) with a percentile of 90, he has bagged an admission offer at IIM, Ranchi. CAT is a national-level computer-based management entrance examination to reputed IIMs. More than 2 lakh candidates appear for the test and a few with a percentile of 90-99 secure a position on one of the IIM campuses.
IIM Ranchi is a reputed business school established in the year 2009 and is the ninth IIM in the country. It holds the 10th rank in the NIRF ranking. The eligibility of the candidates is evaluated through CAT, followed by the written eligibility test (WAT) and Personal Interview (PI).
Ajay Sugandh is a CSE graduate hailing from Guntur, Andhra Pradesh. After completing an MBA from IIM, Ranchi, he wishes to pursue a career in Marketing. Ajay is trained by the TIME coaching institute that helped him crack the difficult test. He had prepared for a year and worked on soft skills, aptitude etc. His hobbies include watching movies and reading books.
Speaking of the support received from SRM University-AP, Ajay acknowledged, “Firstly, I am grateful to the faculty members of the Department of CSE who have been a constant support in reaching my goals. Secondly, the tremendous support from all my peers and family has encouraged me to manage my course CAT preparation together”.
- Published in CSE NEWS, Departmental News, News, Students Achievements
ECE students accomplish international internship in Canada
 Yoganand B, Parshal Chitrakar, Agniswar Paul, Abirami Ravishankar are four brilliant students from the Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering at SRM University-AP who have successfully completed an international internship with EION Wireless Inc, Canada. The students worked as engineering interns with this reputed wireless solutions firm in Canada for five and a half months (Jan 15- June 30) obtaining an internship salary of 500 CAD per student every month. Through this opportunity, the students could build a system that is able to send data to long distances.
Yoganand B, Parshal Chitrakar, Agniswar Paul, Abirami Ravishankar are four brilliant students from the Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering at SRM University-AP who have successfully completed an international internship with EION Wireless Inc, Canada. The students worked as engineering interns with this reputed wireless solutions firm in Canada for five and a half months (Jan 15- June 30) obtaining an internship salary of 500 CAD per student every month. Through this opportunity, the students could build a system that is able to send data to long distances.
Selection Process:
a. Internal selection: Based on the CV and projects undertaken, the ECE Faculty conducted interviews and shortlisted the students.
b. Personal Interview: The shortlisted students attended the interview with the company in which, the company scrutinised their project, skills, and whether they were relevant to the company’s requirements.
c. Techincal Interview: This round focused on analysing technical skills. A technical problem statement was given to members and was asked to come up with a solution in 10 minutes.
d. Coding test: In this round, coding questions were distributed and students had to submit documents of output and on how the code was processed.
For engineering graduates, technical skills and hands-on experience with industry is inevitable. SRM University-AP ensures that every student grabs opportunities to excel in their respective disciplines.
Student Testimonial- Parshal Chitrakar:
I would like to thank the faculty of the ECE Department at SRM AP for this great opportunity. Being a part of this internship programme by EION wireless has been one of my first and best experiences in the industry. Being a fresher, this opportunity gave me a chance to apply my knowledge and skills in developing real-time applications. This five and a half months internship taught me different ways to look at things, work with people from diverse backgrounds, and helped me develop my technical as well as soft skills. Before this, I was focused only on personal achievements, but when we work for a company it has to be focused on the public demand and common good. I think this is the main difference between academia and industry. There is no such difference between academic-based projects and industry-based projects; it is just how we think, showcase our abilities and how our work reaches the target stakeholders.
- Published in Departmental News, ECE NEWS, News, Students Achievements
Assessing the benefits of irrigation against heat stress in agriculture
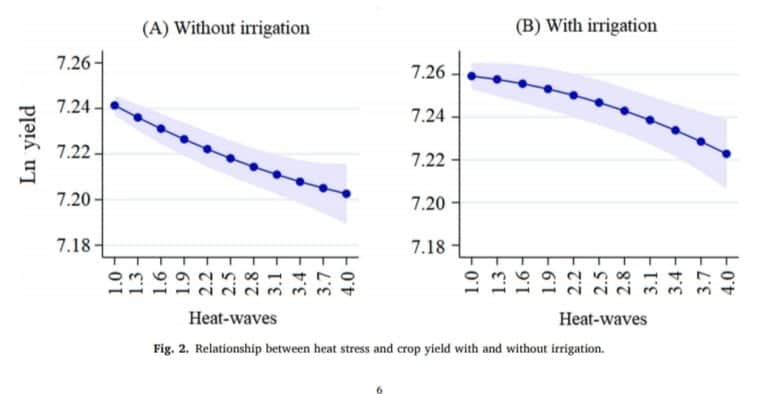 Heat stress negatively affects crop yield and its impact has increased over time. Researchers in India study this situation with utmost priority. Consequently, Dr Ghanshyam Kumar Pandey, Assistant Professor in the Department of Economics at SRM University-AP has co-authored a paper with Pratap S Birthal and et. al titled “Benefits of irrigation against heat stress in agriculture: Evidence from wheat crop in India” in the journal Agricultural Water Management, Vol 255, having an Impact factor 4.02.
Heat stress negatively affects crop yield and its impact has increased over time. Researchers in India study this situation with utmost priority. Consequently, Dr Ghanshyam Kumar Pandey, Assistant Professor in the Department of Economics at SRM University-AP has co-authored a paper with Pratap S Birthal and et. al titled “Benefits of irrigation against heat stress in agriculture: Evidence from wheat crop in India” in the journal Agricultural Water Management, Vol 255, having an Impact factor 4.02.
Applying the fixed effects regression technique to the highly spatially disaggregated district-level data from 1966–67 to 2011–12. This paper has assessed the impact of heat stress on wheat production in India and concurrently evaluated the role of irrigation in offsetting its harmful impact. The study has brought out three key highlights:
(i) Heat stress negatively impacts crop yield, and the impact has increased over time.
(ii) Irrigation, besides its contribution towards improving crop yield, also moderates the harmful impact of heat stress, but over time its effectiveness has declined.
(iii) The measure of heat stress built on multiple aspects of excess temperature (i.e., intensity, persistence, and frequency) explains variation in crop yield better than working on a single aspect of it.
Given the increasing scarcity of irrigation water and rising temperature, these findings suggest the need for exploring technological and policy options for improving irrigation water use, efficiency, and breeding of crops for heat tolerance and low water footprints.
This research paper is written in collaboration with ICAR-National Institute of Agricultural Economics and Policy Research, PUSA, New Delhi. Dr Ghanshyam’s future projects are focused on climate change and agriculture, and the effect of climate change on the livestock sector in India.
Read the full paper here: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2021.106950
- Published in Departmental News, Economics Current Happenings, Economics News, News, Research News
CSE students complete Semester Abroad Programme at UC Davis
 Barukula Snehitha Naga Sai and Kamma Samhitha are two brilliant third-year Computer Science Engineering students selected for the enviable Semester Abroad Programme (SAP) at the University of California, Davis. The students received a partial scholarship from SRM University-AP to complete their final semester abroad with the global study programme at UC Davis. The selection process for the semester abroad programme generally starts at the end of the 3rd and 5th semesters when our university carries out student interviews. A minimum of 8.7 CGPA is required to be eligible for the SAP scholarship and the programme focuses on building engineering design processes along with developing behavioural and communication skills of meritorious students.
Barukula Snehitha Naga Sai and Kamma Samhitha are two brilliant third-year Computer Science Engineering students selected for the enviable Semester Abroad Programme (SAP) at the University of California, Davis. The students received a partial scholarship from SRM University-AP to complete their final semester abroad with the global study programme at UC Davis. The selection process for the semester abroad programme generally starts at the end of the 3rd and 5th semesters when our university carries out student interviews. A minimum of 8.7 CGPA is required to be eligible for the SAP scholarship and the programme focuses on building engineering design processes along with developing behavioural and communication skills of meritorious students.
The Study Abroad Programme provided Snehitha and Samhitha with the opportunity to cooperate with industrial designers. For practical hands-on experiences, Snehitha worked for the UC Davis school of nursing. Besides that, UC Davis promotes a variety of student clubs and technical programmes that bring students from all over the world together. This opportunity also helped students to live in a new culture and travel through different cities abroad. Prof Ragunathan and Dr Priyanka from the Department of Computer Science and Engineering constantly supported the students throughout their semester abroad journey at UC Davis.
For engineering graduates, technical skills and hands-on experience with industry is inevitable. SRM University-AP ensures that every student grabs opportunities to excel in their respective disciplines.
Snehitha extended her gratitude to all her professors at SRM University-AP who guided her to this achievement. “I really appreciate the curriculum structure at SRM AP that offers us practical knowledge rather than forcing us to memorise theories. The concrete understanding of the subject aided me greatly in learning about real-world problems, and accomplish this dream of studying a semester abroad”, she said.
This programme has taught me how to be adaptable, resilient and above all, how to make the best use of resources available. I have been and am fortunate to study from the best professors, both at SRM AP and UC Davis”, said Samhitha.
- Published in CSE NEWS, Departmental News, News, Students Achievements

