The focus of the network keeps changing with every generation of communication technology. The 5G era is waiting for the next generation to bring a remarkable revolution in communication technologies. Applying various changes and modifying the drawbacks of 5G technology can help us to improve the features of the upcoming 6G. The Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering is delighted to inform you that the paper, “Network Resource Allocation for Emergency Management based on Closed Loop Analysis” has been published by Dr Udaya Sankar, Assistant Professor, and BTech students; Sai Jnaneswar J and VMVS Aditya, in “ ITU Journal on Future and Evolving Technologies – 2nd special issue on AI and machine learning solutions in 5G and future networks”.
Abstract of the research
 Telecommunication systems being a critical pillar of emergency management, intelligent deployment, and management of slices in an affected area, will help emergency responders. Techniques such as automated management of ML (machine learning) pipelines across the edge and emergency responder devices, usage of hierarchical closed-loops, and offloading inference tasks closer to the edge, can reduce latencies for first responders in case of emergencies. This paper describes the major findings of building a Proof of Concept (PoC) for network resource allocation for emergency management using a hierarchical autonomous artificial intelligence (AI)/ML-based closed-loops in the mobile network, which was organized by the Internal Telecommunication Union Focus Group on Autonomous Network (ITU FGAN). The background scenario for this PoC included the interaction between a higher closed-loop in the Operations Support System (OSS) and a lower closed-loop in RAN (Radio Access Network) to intelligently share RAN resources between the public and emergency responder slice. Representation of closed-loop “controllers” in a declarative fashion (Intent), triggering “imperative actions” in the “underlay” based on the intent, setup of a data pipeline between various components, and methods of “influencing” lower layer loops using specific logic/models, were some of the important aspects investigated by various teams. The main conclusions are summarised in this work, along with the significant observations and limitations from the PoC as well as future directions.
Telecommunication systems being a critical pillar of emergency management, intelligent deployment, and management of slices in an affected area, will help emergency responders. Techniques such as automated management of ML (machine learning) pipelines across the edge and emergency responder devices, usage of hierarchical closed-loops, and offloading inference tasks closer to the edge, can reduce latencies for first responders in case of emergencies. This paper describes the major findings of building a Proof of Concept (PoC) for network resource allocation for emergency management using a hierarchical autonomous artificial intelligence (AI)/ML-based closed-loops in the mobile network, which was organized by the Internal Telecommunication Union Focus Group on Autonomous Network (ITU FGAN). The background scenario for this PoC included the interaction between a higher closed-loop in the Operations Support System (OSS) and a lower closed-loop in RAN (Radio Access Network) to intelligently share RAN resources between the public and emergency responder slice. Representation of closed-loop “controllers” in a declarative fashion (Intent), triggering “imperative actions” in the “underlay” based on the intent, setup of a data pipeline between various components, and methods of “influencing” lower layer loops using specific logic/models, were some of the important aspects investigated by various teams. The main conclusions are summarised in this work, along with the significant observations and limitations from the PoC as well as future directions.
Explanation of the research
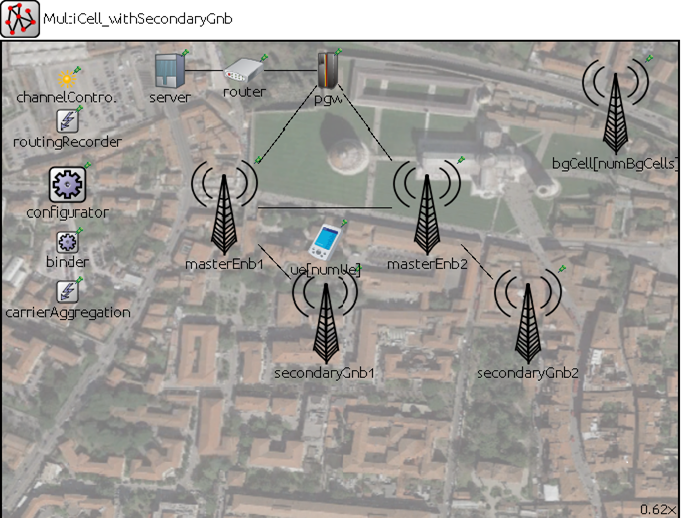
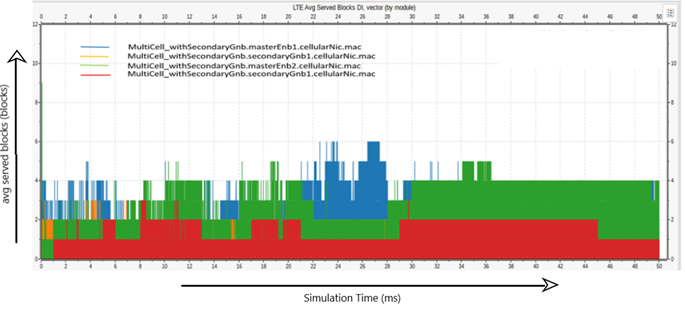 This is a collaborative study where the researchers have developed and implemented a hierarchical closed-loop that autonomously handles an emergency case. This project contains several groups working on separate functions such as monitoring, computing, ML selection, and resource allocation. Some presented how the AI agents and the network can be adapted to assist mobile network users in Search, Diagnostic, and Rescue (SDAR) missions. Some integrated the implementation of the closed loops in O-RAN based software. The researcher’s role in this project is to generate the data which will be used for analysis and this gets integrated with another team. Rather than putting dummy data and analysing or creating and training a machine learning model, we use the Simu5g simulator which is library-based on OMNET++ framework to generate data, mainly resource allocation data. In Simu5g they configure the required network, set all the input parameters such as and simulate it for a specific duration of time. After simulation, the various results are obtained like SINR, throughput, resource block allocation, and many more. This data of the selected parameter results is converted into CSV files and handed over to the required for ML. This project blends all the chunks of work like monitoring, computing, ML selection, and resource combination, to facilitate network resource allocation for emergency management.
This is a collaborative study where the researchers have developed and implemented a hierarchical closed-loop that autonomously handles an emergency case. This project contains several groups working on separate functions such as monitoring, computing, ML selection, and resource allocation. Some presented how the AI agents and the network can be adapted to assist mobile network users in Search, Diagnostic, and Rescue (SDAR) missions. Some integrated the implementation of the closed loops in O-RAN based software. The researcher’s role in this project is to generate the data which will be used for analysis and this gets integrated with another team. Rather than putting dummy data and analysing or creating and training a machine learning model, we use the Simu5g simulator which is library-based on OMNET++ framework to generate data, mainly resource allocation data. In Simu5g they configure the required network, set all the input parameters such as and simulate it for a specific duration of time. After simulation, the various results are obtained like SINR, throughput, resource block allocation, and many more. This data of the selected parameter results is converted into CSV files and handed over to the required for ML. This project blends all the chunks of work like monitoring, computing, ML selection, and resource combination, to facilitate network resource allocation for emergency management.
Practical implementations of the research
In this project, the researchers have gathered the simulated data and want to analyse it and apply machine learning algorithms to improve the condition of existing 5G networks. AI/ML model will help to analyse the data which helps in optimizing resource allocation. Optimization algorithms for resource allocation like Interference minimization, Throughput maximization, and many more. Optimising such parameters would be really helpful for the development of new generation networks.
Collaborations
The paper was developed as part of a build-a-thon track, “ITU AI/ML in 5G Challenge: applying machine learning in communication networks” challenge. The researchers worked under the problem statement “ITU-ML5G-PS-014: Build-a-thon (PoC) Network resource allocation for emergency management based on closed-loop analysis”. This project is guided by Dr. V Udaya Sankar under AI-Designed Wireless (AIDW) Project Simulated network scenarios using simu5g for measuring resource allocation. This build-a-thon challenge was started on June 7, 2021 and ended on November 5, 2021. The research team was placed fifth among 12 teams who participated across the world in the “build a thon” track of the global challenge. While the overall challenge saw over 600 participants across more than 80 countries, the “build a thon” track was a unique coding challenge from ITU FG AN. The team worked on the simulation of the 5G system and corresponding analysis using Simu5G from ITU global partners. After the build-a-thon, the teams that have participated in the build-a-thon under the problem statement “ITU-ML5G-PS-014: Build-a-thon (PoC) Network resource allocation for emergency management based on closed-loop analysis” were collaboratively developed the journal from the observations and results that were made during this build-a-thon.
The current research work focuses on the Implementation of a simulation environment to generate data for model training and testing purposes, and serve as a simulation underlay for testing. The simulations allow us to study various configurations and analyse them to optimize the allocations. For the later stages, various machine learning techniques can be applied for the data that was generated through simulation, and further, the comparison can be done for various machine learning techniques.


Good research piece. More follow up research or required implementation of full use case