 In an impressive achievement, Dr Ashok Kumar Pradhan, Associate Professor of the Department of Computer Science and Engineering, along with PhD Scholar Ms Ghanta Swetha and BTech CSE students Mr Bandi Sai Harshith, Mr Estamsetty Srikanth, Mr Guduri Venkata Sai Kumar, and Mr Atmakuri Pavan Kumar, has successfully published a patent titled “A SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR AUTOMATED PLANT DISEASE DETECTION.” The application has been officially recognised with Application Number: 202441052706, as recorded in the Patent Office Journal.
In an impressive achievement, Dr Ashok Kumar Pradhan, Associate Professor of the Department of Computer Science and Engineering, along with PhD Scholar Ms Ghanta Swetha and BTech CSE students Mr Bandi Sai Harshith, Mr Estamsetty Srikanth, Mr Guduri Venkata Sai Kumar, and Mr Atmakuri Pavan Kumar, has successfully published a patent titled “A SYSTEM AND METHOD FOR AUTOMATED PLANT DISEASE DETECTION.” The application has been officially recognised with Application Number: 202441052706, as recorded in the Patent Office Journal.
This innovative system aims to revolutionise the agricultural sector by providing an automated mechanism for detecting diseases in plants. Thus, it enhances crop management and ensures healthier yields. The team’s dedication to advancing technology and improving agricultural practices showcases the potential of computer science in solving real-world problems.
The patent not only reflects the hard work and collaboration among the faculty and students but also signifies a step forward in the integration of technology with agriculture. As the world faces challenges related to food security, such innovations play a critical role in safeguarding plant health and agricultural productivity.
Congratulations to Dr Pradhan, Ms Swetha, and the student inventors on this significant milestone in their academic and professional endeavours!
Abstract of the Research:
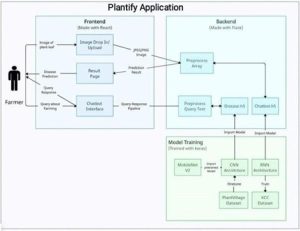
The innovation that is being presented in this project is a software-based system that is intended to help farmers by offering an automated way to identify plant diseases. This innovation combines a number of technological elements:
Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs): These networks are used to recognise and categorise plant diseases from images of both healthy and sick plants with high accuracy. This is leveraging transfer learning with pre-trained CNN architectures to improve performance even with sparsely annotated data.
MobileNetV2 Architecture: Designed with the specific purpose of classifying agricultural diseases in mind, this model is effective and lightweight, making it ideal for use in resource- constrained settings such as farms.
Weather API Integration: This helps farmers make decisions about crop management and disease prevention by giving them access to real-time weather data.
AI-Powered Website: Acts as a user interface for farmers to communicate with the system, submit plant photos, post queries, and get weather and diagnostic updates.
Chatbot: Utilizes Recurrent Neural Networks (RNN) and Natural Language Processing (NLP) to respond to user inquiries and provide guidance on crop management and disease prevention.
All things considered, this innovation is a system that integrates various software components, artificial intelligence, and data integration to produce a complete tool for raising agricultural productivity and managing diseases.
Research in Layperson’s Terms
1. Automated Plant Disease Prediction: Current approaches frequently use traditional diagnostic procedures and manual inspection, which can be laborious and prone to human mistakes. The suggested method uses CNNs to automatically and precisely recognise images, increasing the efficacy and precision of plant disease diagnosis.
2. This project assists farmers in making decisions on crop management and disease prevention by providing them with access to current weather information.
3. Farmers can query various farming issues and receive responses. This is done by leveraging RNNs and NLP.
4. Use of Transfer Learning: The system uses transfer learning to use pre-trained CNN architectures, which enables it to function well even with a small amount of annotated data. Compared to typical machine learning models, which frequently need big datasets and intensive training, this is a major improvement.
Integration with Smart Agriculture Systems: – This method combines disease prediction with smart agriculture systems, allowing for real-time monitoring and decision-making, in contrast to independent diagnostic instruments.
Practical Implementation or the Social Implications Associated
1. Field Diagnosis by Farmers: – Farmers can snap photos of their crops in the fields and instantly receive a disease diagnosis and treatment suggestions by using the platform.
2. Agricultural Extension Services: Using the system, agricultural extension agents may help farmers more effectively by offering guidance and support.
3. Agricultural Research: – Researchers can investigate plant diseases and create novel remedies and management techniques by utilizing the extensive annotated picture library and diagnostic tools.
4. Commercial Farming Operations: – By incorporating the system into their precision agriculture techniques, large-scale farming operations can maximize crop health management and operational effectiveness.
5. Policy Formation and Governance: – Governmental organizations can monitor plant disease outbreaks and create regional or national plans for disease control and prevention using aggregated data from the platform.
Future research plans
We may use privacy and security enhancement tools and techniques to make the data more secure

