
Socially relevant and community-centric research is of primal focus at SRM University-AP leading to innovations that transpire into transforming society. Dr Vimal Babu and his research scholar Ms Rukma R, Paari School of Business, have undertaken creative research to understand employee attrition in organisations critically. The research cohort employed a modified Random Forest Algorithm for assessing employee attrition and analysing its findings and benefits to Human Resource departments of corporate houses. Their groundbreaking invention and research titled “A System to generate a Model Predicting an Employee Attrition Rate and a Method Thereof” with Application No: 202341031320 has recently been filed and published under the Patent Office Journal.
Abstract
The problem of employee attrition in every organization concerns the employee turnover ratio, thereby increasing the cost of investment in human resources. Various factors are reasonable for the rapid attritions at different phases. The purpose of the current study is to predict the employees who are likely to leave the organization. The factors that lead to attrition are identified using the Random Forest algorithm. Random Forest algorithm is one of the widely used supervised machine learning technique for both classification and prediction. However, the random forest algorithm has specific issues, such as it is too slow and ineffective for real-time predictions. i.e., the large number of trees can make the algorithm, which results in a slower model. Therefore, the study proposes a new alternative for choosing the appropriate decision trees based on the concept of fractional factorial design of experiments. The different performance criteria were compared across the modified random forest algorithm, existing random forest algorithm, Support Vector Machine (SVM), Logistic Regression (LR), Navie Bayes (NB), K – Nearest Neighbour (K-NN), Decision Tree, XG Boost tree and Neural Network (NN). It was found that the modified random forest algorithm excelled in all criteria and performed better than the existing ones.
The findings of this study offer valuable assistance to human resources departments by providing necessary insights into potential employees’ decisions to leave the company. By analysing the identified factors or reasons for leaving the organisation, HR professionals can better understand attrition patterns and make informed decisions to improve employee retention. The proposed method not only assists in identifying the factors contributing to employee attrition but also predicts the likelihood of attrition based on employee signals. This predictive capability enables organisations to proactively address potential attrition cases and take preventive measures to retain valuable employees.
Practical implications of the research
Overall, the practical applications include designing retention strategies, predicting attrition cases, tailoring employee engagement initiatives, developing HR policies, optimising recruitment and selection processes, benchmarking attrition rates, and implementing continuous improvement measures. These applications can collectively contribute to reducing employee attrition and enhancing overall employee retention in organizations.
Collaborations and Future research plans
The applicants, viz. Ms Rukma, R.; Dr Vimal Babu and Dr Vijaya Prabhagar, M. plan to collaborate in the intersecting area of HR and analytics to arrest employee attrition by employing sophisticated analytics models and explore the future scope of our research to come up with impactful research outputs benefitting the industry.
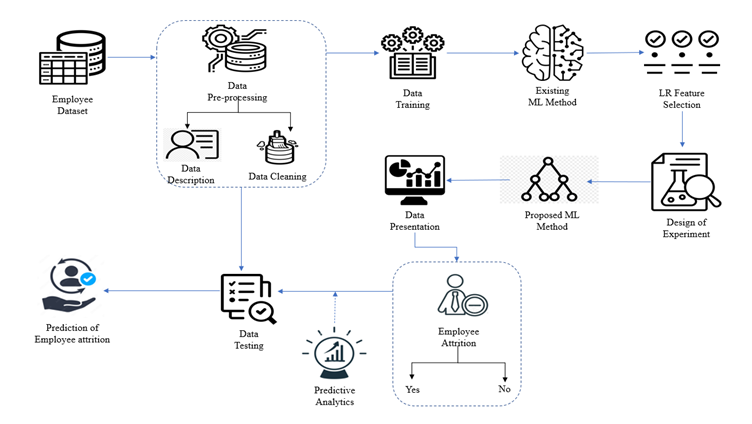
Phases of prediction of employee attrition

