Agricultural development is one of the powerful tools to boost the economy of any developing country. The recent advancement of IoT-based smart agriculture systems helps to achieve more productivity with relatively less overhead. The Department of Computer Science and Engineering is glad to announce that their faculty; Dr Sobin CC, Associate Professor; Dr Sonam Maurya, Assistant Professor; and Dr Amit Kumar Singh, Assistant Professor; have published a patent titled “Smart Agriculture System using Delay Tolerant Internet of Things” (Application No. 20224102799), a framework for smart agricultural applications using Delay Tolerant Internet of Things (DT-IoT) which can handle the issues related to disruptions in network connectivity.
The inherent limitations of IoT-based smart agriculture systems majorly in terms of resource constraints, frequent network disconnections and vulnerability to many attacks may affect their advantages over the traditional systems. The application using DT-IoT, with access to greater network connectivity can deliver relevant data in real-time. Furthermore, the stored data can be processed and analysed to help farmers in making critical decisions related to their farm filed. Hence, their innovation focuses on designing and developing a prototype for a smart agricultural application using the Internet of Things (IoT).
One of the simplest outcomes of providing smart agricultural solutions for remote villages in India will be greater support to the farmers to improve their productivity and better decision-making in cultivation. But advanced technologies need Internet connectivity in the field to function, which is still a dream in many of the remote villages in India. The lack of proper communication facilities faces off the application of IoT networks. This fact has motivated them to propose a smart agricultural system to work on agricultural application issues using delay-tolerant characteristics. The use of delay-tolerant features in traditional IoT provides a solution for smart agriculture which can handle issues related to disruptions in connection to improve communications.
Another important aspect is that many of the applications, including IoT/Sensor networks, are either simulation-based or experimental. A very few of the applications are developed and implemented in the real-time field for the benefit of farmers in remote villages. In most of the remote villages in India, most of the farmers are poor, many of them are even without primary school education and they rely mostly on traditional agricultural practices which they received from their previous generations. Therefore, their study proposed to test and implement the smart agricultural system with real-time automated solutions related to irrigation, controlled fertilisation, cultivation, production quality, quantity, crop health etc. using IoT with delay-tolerant support. They are also in the process of collaborating with academia and industry to execute this project.
Social Implications
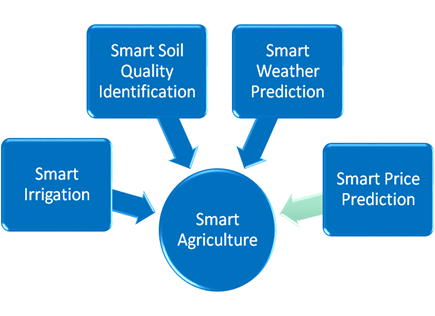
- Proposed smart agriculture system will assist in real-time monitoring of farm field conditions, like irrigation, soil quality, and nutrient deficiency.
- It provides support to farmers to improve their productivity and decision-making in crop cultivation.
- The proposed system will provide optimization in terms of seed selection, resource utilisation, planning cultivation, marketing, harvest quality, etc., using Machine Learning techniques.
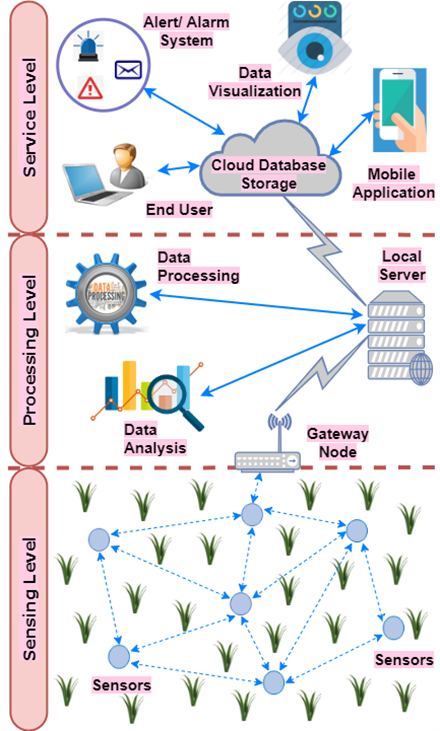
- Agricultural field data analysis (for data collected by the large group of sensors) and its visualisation.
- Weather prediction (for better planning).
- Price prediction (for better marketing strategies).
Fig 1: Main components of the proposed Smart Agriculture System
Fig 2: Illustration of 3-level architecture implementation in the Smart Agriculture System

