Dr Divya Chaturvedi, Assistant Professor, Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, has come up with an exciting proposal for enhanced connectivity and high-speed data transmission across the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) devices. Her research paper titled “Design of Antenna-Multiplexer for Seamless On-Body Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) Connectivity” has been published in the journal ‘IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs’, having an impact factor of 3.71. It was published in collaboration with Dr Arvind Kumar from Vellore Institute of Technology and Dr Imaculate Rosaline from Ramaiah Institute of Technology, Bangalore.
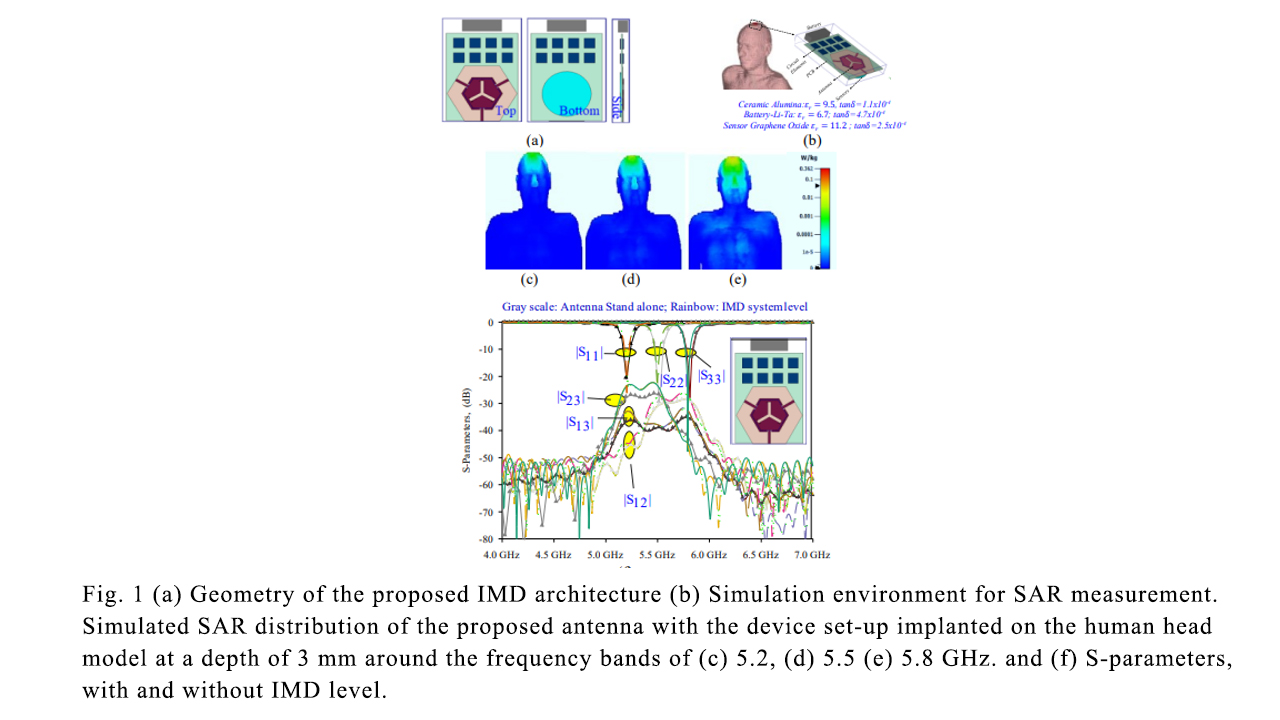
The research looks into the design and development of a multi-band self-triplexing antenna for Medical Things (IoMT) applications. The antenna is designed to operate at 5.2, 5.5 and 5.8 GHz and self-isolation is achieved below -23.9 dB. It also offers seamless communication links to other devices operating at the same frequencies. The designed antenna is cost-effective and compact in size, that can easily fit into any implantable medical device. To avoid the harmful effect of radiation, the SAR value should be <1.6 W/kg. The SAR for this antenna is achieved at 0.362 W/kg in a very simple profile. Due to its compact size, the antenna can be easily mounted in a wireless portable device. The self- triplexing property of the device also enables full-duplex communication between different devices in a single antenna. This design suggestively simplifies the density of the RF front-end subsystem and leads to a simple and efficient communication system.
Abstract of the Research
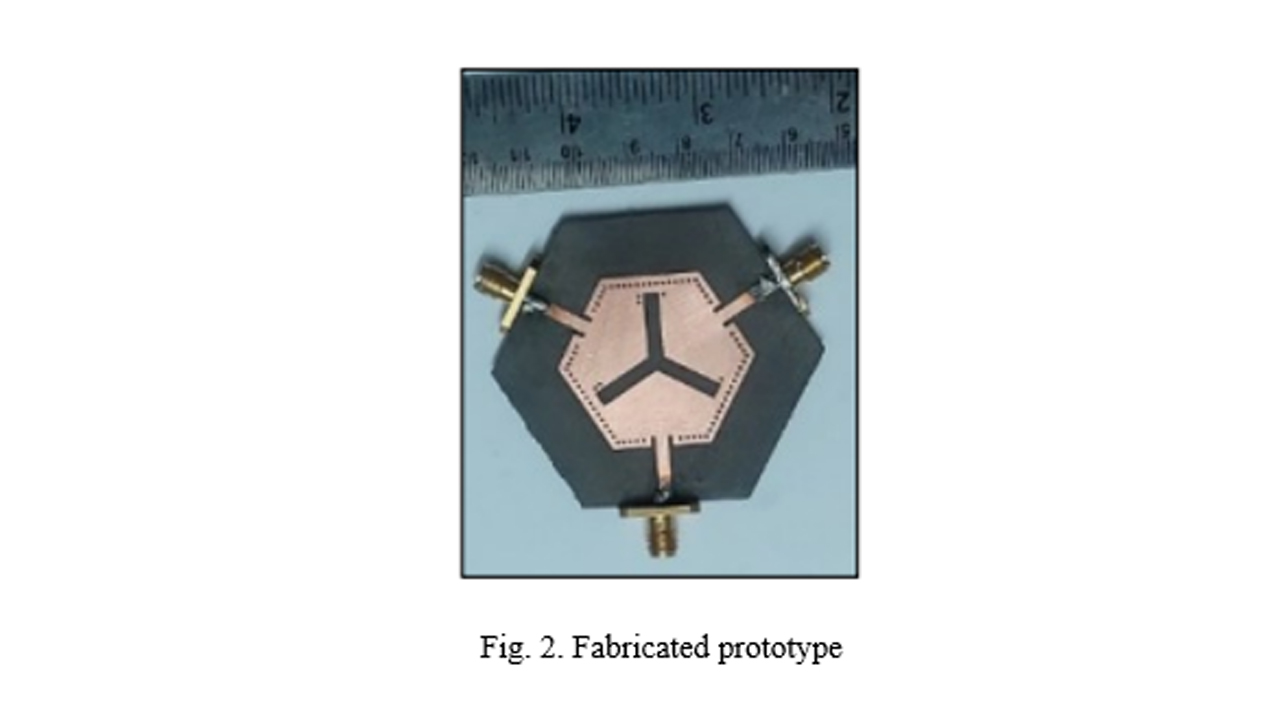
Here, a compact design of antenna-multiplexer is engineered specifically to meet the stringent requirement imposed by intricate subsystems operating at 5.2, 5.5, and 5.8 GHz frequency bands for Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) applications. The proposed design includes a hexagonal-shaped substrate integrated waveguide (HSIW) cavity, tripole-shaped radiating slot, tuning vias, and three inset microstrip feedlines. A tripole-shaped slot is imprinted on the top of the SIW. This slot subdivides the cavity into trio-radiating segments and each segment offers a single frequency band. Further, the frequency bands are tuned at 5.2/5.5/5.8 GHz. The design maintains mutual port isolation better than 23.9 dB. Compared with the conventional tri-frequency antennas, the proposed design is highly compact and doesn’t need any additional circuitry to improve the port isolations. The measured results confirm the expected performance of the design. Furthermore, the proposed antenna is optimized within an implantable medical device (IMD) and simulated inside a realistic Human Head model at a depth of 3 mm and the Specific Absorption Rate (SAR) value is estimated. The SAR values are well below 0.362 W/Kg at the functioning bands due to the unidirectional radiation pattern from the antenna.
Her future research plan includes designing and developing a cost-effective bra-like prototype of Antenna-Array Sensors for breast cancer detection.